Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Patel P, Yeaney G. Xanthelasma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/eyeeyelidxanthelasma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
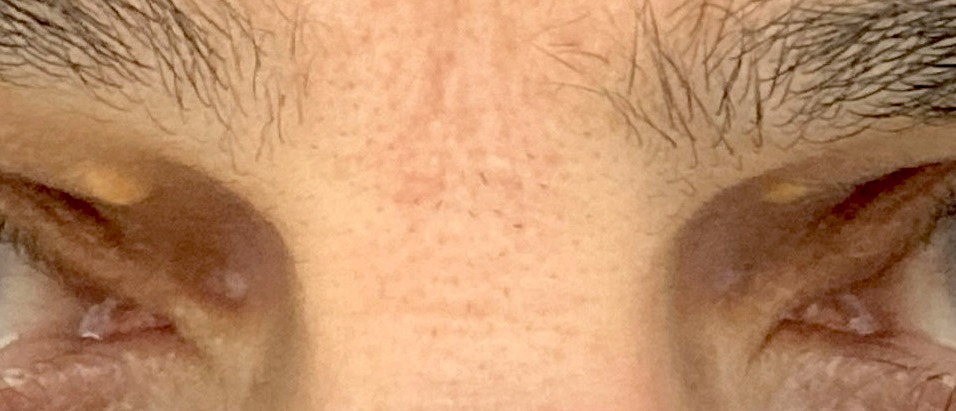
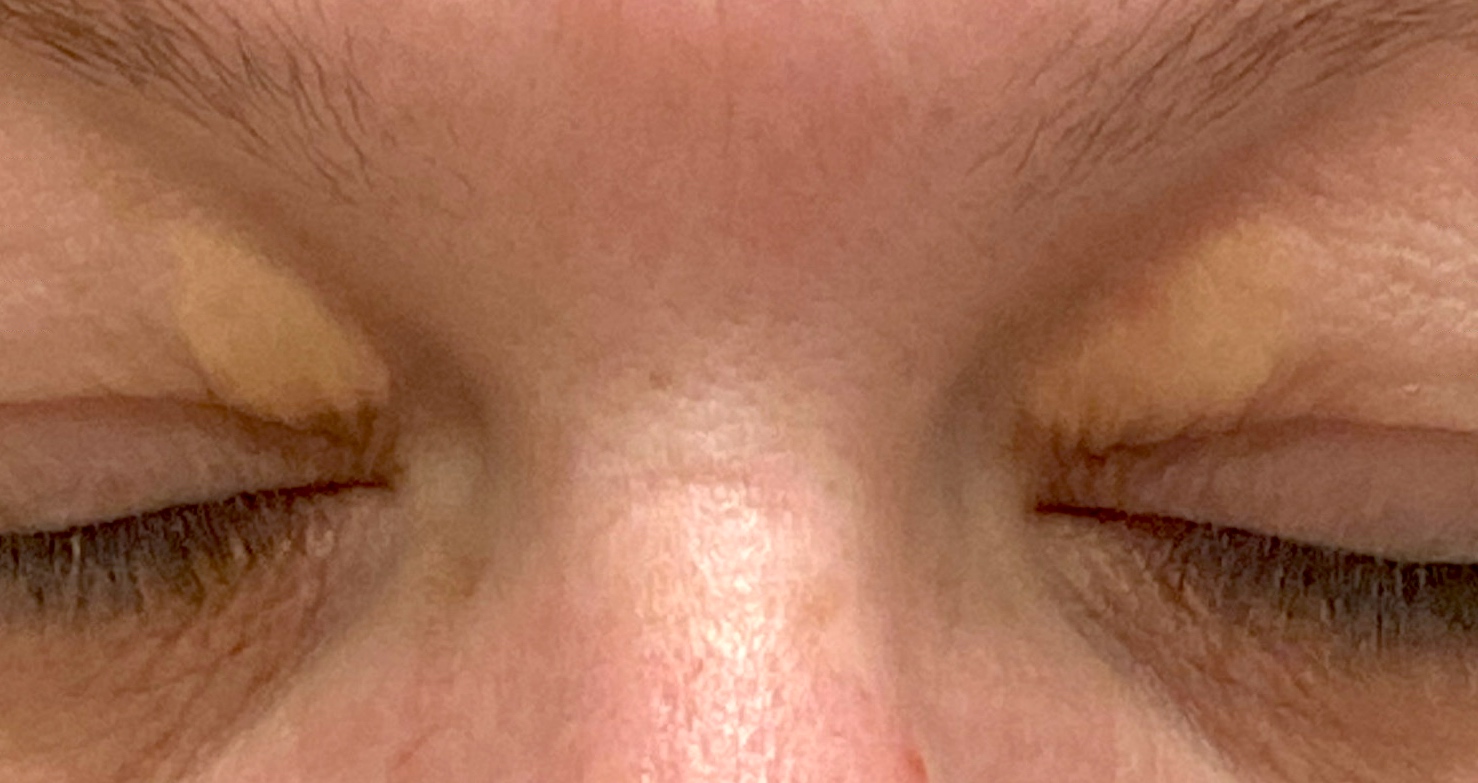
- Xanthelasma is a soft yellow, lipid laden plaque occurring bilaterally on the medial aspect of eyelid skin
- It may occur in association with primary hypercholesterolemia
Essential features
- Yellow, lipid laden plaques occur symmetrically on bilateral medial upper and lower eyelids
- Typically occurs in middle aged to elderly patients; occurs in women more than men (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- About half of patients have hyperlipidemia (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
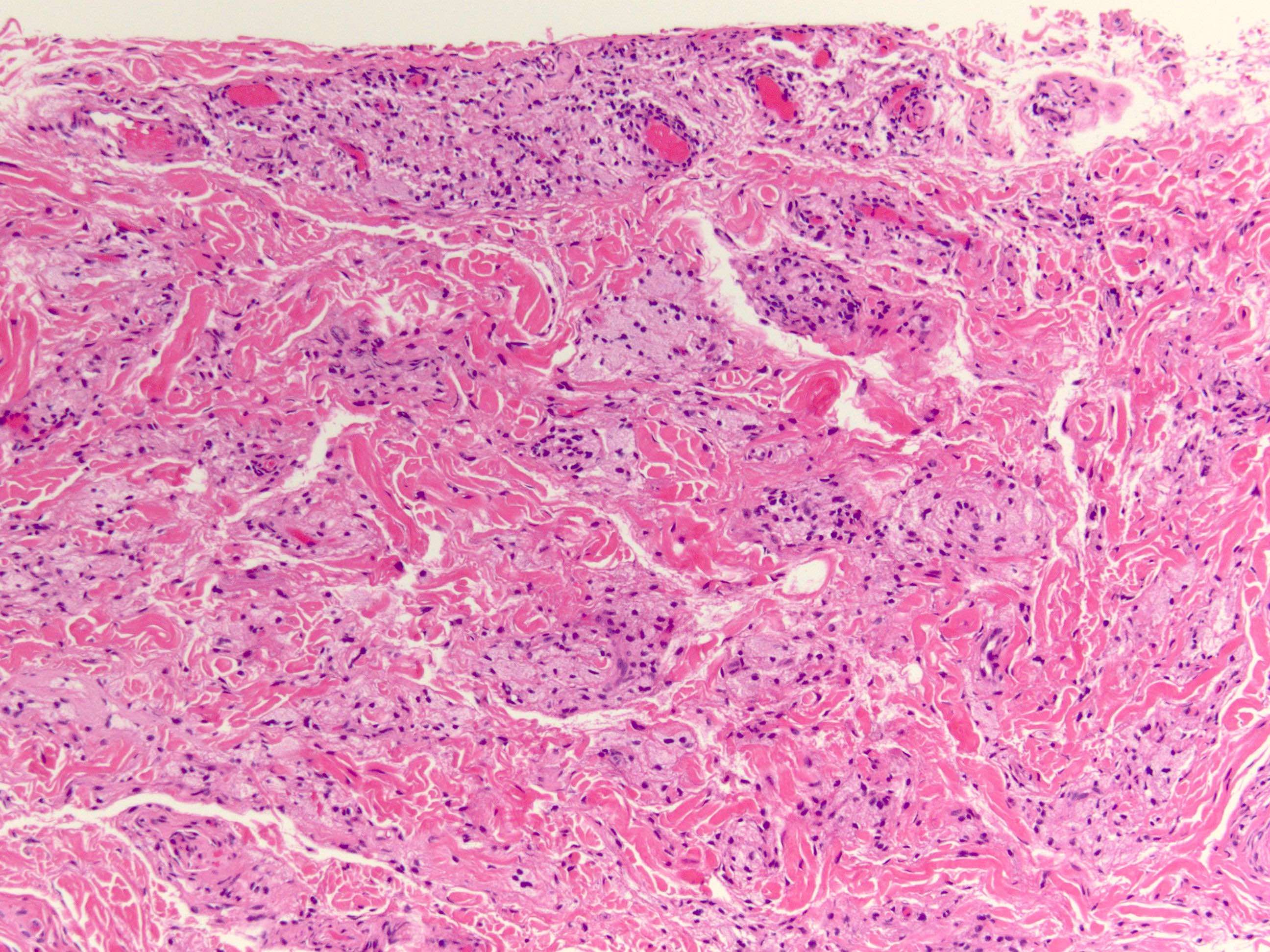
- Histopathology reveals foamy histiocytes in the superficial dermis
Terminology
- Xanthelasma palpebrarum
- Cutaneous xanthoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- F > M (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- Age of onset: 15 - 73 years; peak: 30 - 50 years (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2017;11:1)
- ~Half of patients with hyperlipidemia (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- Increased likelihood of familial hyperlipidemia if presentation occurs at < 40 years of age (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- May be associated with atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2023;11:e4982)
Sites
- Symmetric on eyelids
Pathophysiology
- Intracellular cholesterol rich deposition (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2017;11:1)
Etiology
- Primary hyperlipidemias (especially type 2a) (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- Low high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2017;11:1)
- Secondary hyperlipidemias, such as hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, drugs (glucocorticoids, estrogens, etc.) (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- Diet rich in saturated fats, cholesterol and alcohol (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2017;11:1)
Clinical features
- Thin, yellow papules and plaques symmetrically distributed on the medial upper or lower eyelids
- May be associated with cirrhosis, thyroid disorder, nephrotic syndrome
- Periorbital hyperpigmentation noted in > 80% of women with xanthelasma (J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2016;9:52)
Diagnosis
- Clinical diagnosis based on characteristic appearance
- Biopsy not usually required
Laboratory
- Lipid panel to evaluate for hypercholesterolemia
Prognostic factors
- Increased risk of recurrence with the following (Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;110:1310)
- All 4 eyelids are involved
- Underlying hyperlipidemia
- Prior recurrence
Case reports
- 29 and 40 year old women with xanthelasma palpebrarum arising as a side effect of nilotinib (BMJ Case Rep 2016;2016:bcr2015213511)
- 45 year old White man with a several year history of xanthelasma of the bilateral medial canthal area (Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2023;11:e4982)
- 46 year old Japanese woman with a 1 year history of asymptomatic yellowish papules on the neck and elbow (J Dermatol 2019;46:e362)
- 66 year old man presented with longstanding lesions on the 4 eyelids for several years, recently becoming larger and heavily pigmented (Am J Dermatopathol 2023;45:646)
- 70 year old man with bilateral extensive nodular xanthelasma palpebrarum (Int Ophthalmol 2018;38:803)
Treatment
- Conservative, as nodules often recur
- Excision, laser ablation or topical treatment for cosmesis
- Lipid lowering agent (Ann Intern Med 2020;172:701)
- References: Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2023;11:e4982, Dermatol Surg 2020;46:847
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Lipid laden foamy histiocytes in superficial dermis, clustering around blood vessel walls
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Additional stains are not required
- Oil red O
- CD68
- CD163
- Reference: Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1994
Negative stains
- BRAF V600E (wild type)
- CD1a
- Langerin
- Reference: Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1994
Videos
Xanthelasma (xanthoma of eyelid)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, eyelid, shave biopsy:
- Xanthelasma
Differential diagnosis
- Periorbital Erdheim-Chester disease:
- Similar but more abundant sheets of foamy histiocytes forming mass lesion
- Widespread, mulitfocal disorder involving viscera and bones, BRAF V600E
- Periorbital Langerhans cell histiocytosis:
- Injected foreign material, poly-L lactic acid (tissue filler) paraffinoma (J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:536):
- Paraffinoma features: look for empty pseudocystic spaces
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
E. Xanthelasma is correct because there are abundant foamy histiocytes in the superficial dermis. Answer A is incorrect because chalazion typically shows mixed acute and chronic inflammation with extracellular lipid deposits; it is sometimes granulomatous. Answer B is incorrect because Erdheim-Chester is a non-Langerhans histiocytosis with intermixed lymphocytes, which may involve the orbit but also has involvement of other organ systems: bone, CNS, pituitary. Answer C is incorrect because there is not an abundant mixed inflammatory infiltrate with histiocytes showing grooved nuclei. Answer D is incorrect because ruptured epidermal inclusion cyst would show portions of epithelial lines cyst with a surrounding mixed inflammatory infiltrate, often with keratin debris and foreign body giant cells, many of which may contain keratin fragments.
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthelasma
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthelasma
Board review style question #2
A 50 year old woman presents with bilateral medial upper eyelid yellow plaques. Which systemic medical condition is most likely associated with this pathology?
- Acromegaly
- Atherosclerosis
- Breast cancer
- Colon cancer
Board review style answer #2
B. Atherosclerosis. Xanthelasma characteristically presents with symmetric medial upper eyelid yellow plaques. It may be associated with cirrhosis, atherosclerosis, thyroid disorders, nephrotic syndrome, primary hyperlipidemias (especially type 2a) and diabetes mellitus. Answer A is incorrect because acromegaly is growth hormone overproduction and is not associated with xanthelasma. Answer C is incorrect because breast cancer is not associated with xanthelasma. Metastatic breast cancer can cause enophthalmos but not yellow plaques. Answer D is incorrect because colon cancer is not associated with xanthelasma.
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthelasma
Comment Here
Reference: Xanthelasma