Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology / etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Weisenberg E. Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophagusverrucousscc.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Highly differentiated variant of squamous cell carcinoma that is locally invasive with a pushing, as opposed to an infiltrative border, that is identical to lesions of the same name in the upper aerodigestive tract
- Metastases are uncommon
Epidemiology
- Extremely rare
- Male predominance
- Ages 36 - 76 years
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Cases related to chronic mucosal irritation, lye ingestion, diverticular disease, reflux esophagitis (Gastroenterology 1996;110:904)
- Reported case with positive HPV stain (Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;36:311)
Clinical features
- Slow growing, nodal metastases are uncommon and distant metastases are not reported but still has high mortality because of advanced local disease with the development of fistulas (J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1993;8:107, J Clin Gastroenterol 1991;13:102, Minerva Chir 2005;60:61)
Diagnosis
- Tissue biopsy, knowledge of clinical and endoscopic findings may be essential to prevent misdiagnosis
Case reports
- 51 year old man with dysphagia
- 58 year old woman (Case Rep Gastroenterol 2013;7:498)
Treatment
- Resection, possible endoscopic resection (Dis Esophagus 2014;27:452)
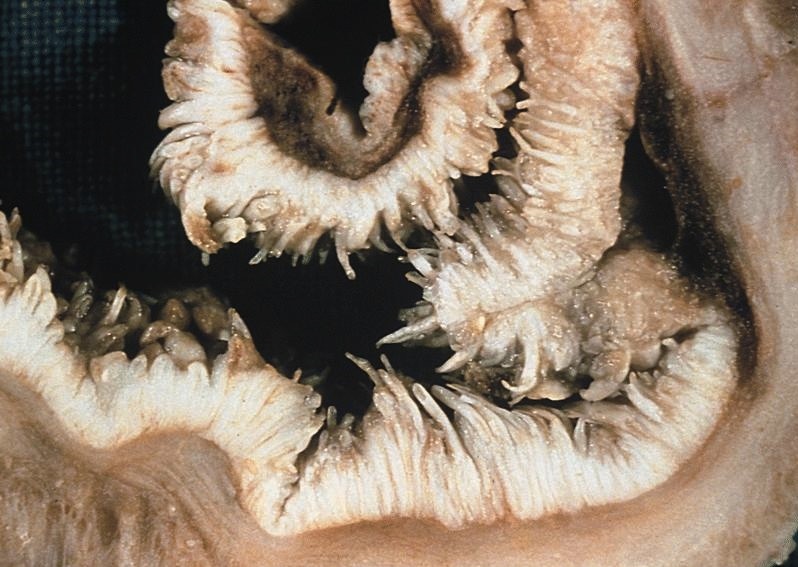
Gross description
- Large, exophytic, polypoid, generally circumferential mass
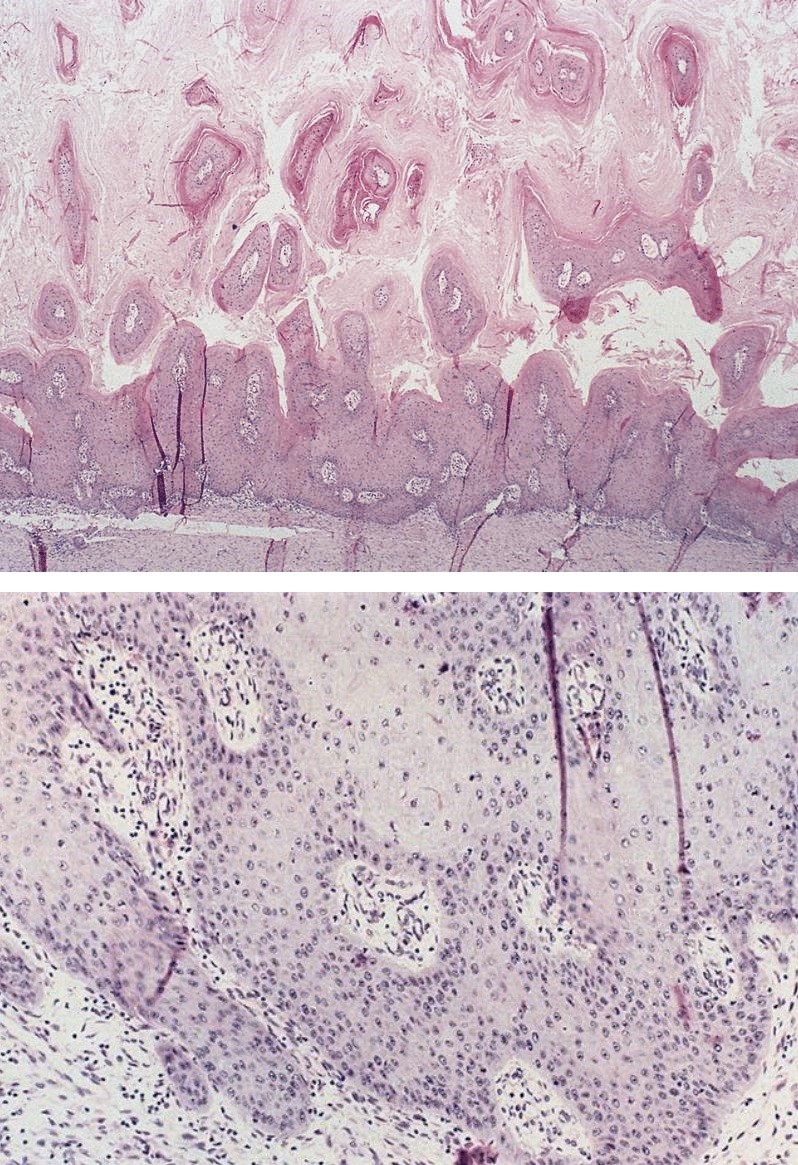
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Similar to oral cavity counterpart
- Well differentiated with papillary fronds covered by squamous epithelium
- Bland cytologic features with mild atypia
- Variable parakeratosis and hyperkeratosis
- Pushing type of invasion with blunt epithelial projections
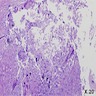
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Carcinoma cuniculatum: deeply penetrating and burrowing growth pattern (Ann Diagn Pathol 2005;9:134)
- Superficial biopsies may be diagnosed as squamous papillomas or other benign lesions
- Papillomas are generally under 3 cm in dimension, generally do not demonstrate circumferential growth, lack ulceration, do not cause stricture and do not invade submucosa or muscularis, which are common findings in verrucous carcinoma (Can J Gastroenterol 2004;18:459, Am J Gastroenterol 1996;91:1031)