Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Electron microscopy images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Weisenberg E. Esophageal manifestations of collagen vascular disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophagusscleroderma.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Characterized by fibrosis, inflammation, increased collagen and vasculitis
- Can be part of CREST syndrome (Calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon, Esophageal involvement, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasia)
- Involves esophagus in 75%+ patients, usually distal 2/3, with aperistalsis and reduced tone of lower esophageal sphincter
- Commonly causes reflux esophagitis (Semin Arthritis Rheum 2006;36:173), strictures, Candida esophagitis, Barrett esophagus (J Clin Gastroenterol 2006;40:769 but similar prevalence of Barrett as other reflux esophagitis patients, Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:2882)
Case reports
- 38 year old man with achalasia (Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2006;131:1799)
- 51 year old woman with CMV esophagitis (J Clin Rheumatol 2001;7:384)
Treatment
- No treatment for underlying disease; proton pump inhibitors for reflux esophagitis, dilation for strictures
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Resection specimens: atrophy and replacement fibrosis of inner circular layer of muscularis propria and resulting stenosis; longitudinal layer is usually involved; also submucosal fibrosis, mild inflammation, intimal proliferation of arterioles (Gut 2006;55:1697)
- Biopsies: ulcers or erosions resembling reflux esophagitis, Candida or Barrett
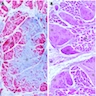
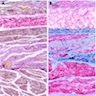
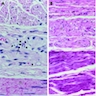
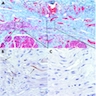
Microscopic (histologic) images
Electron microscopy images
Differential diagnosis
- Cricopharyngeal dysphagia
- Primary visceral myopathy
- Sjögren syndrome
- Systemic lupus erythematosus