Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Frozen section images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Lai J. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophagusbasaloidSCC.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Variant of squamous cell carcinoma with distinct basaloid morphology
Essential features
- Esophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) is a rare variant of SCC
- Morphological differential diagnoses could include adenoid cystic carcinoma, neuroendocrine carcinoma (particularly small cell type), carcinosarcoma and epithelioid sarcoma
- BSCC is not human papillomavirus (HPV) related and has a relatively poor prognosis as compared to morphologically similar HPV related SCC
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C15.9 - malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Generally older males
- Reported incidence: 1 - 11% of squamous cell carcinomas; true incidence likely ~2%
Sites
- More common in mid to distal esophagus
Pathophysiology
- Similar molecular pathology and etiology as squamous cell carcinoma (see Molecular / cytogenetics description below)
- No association with HPV (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1608)
Etiology
- Genetic and environment
Clinical features
- Patients present with dysphagia and weight loss
- Usually widespread metastases at presentation
Diagnosis
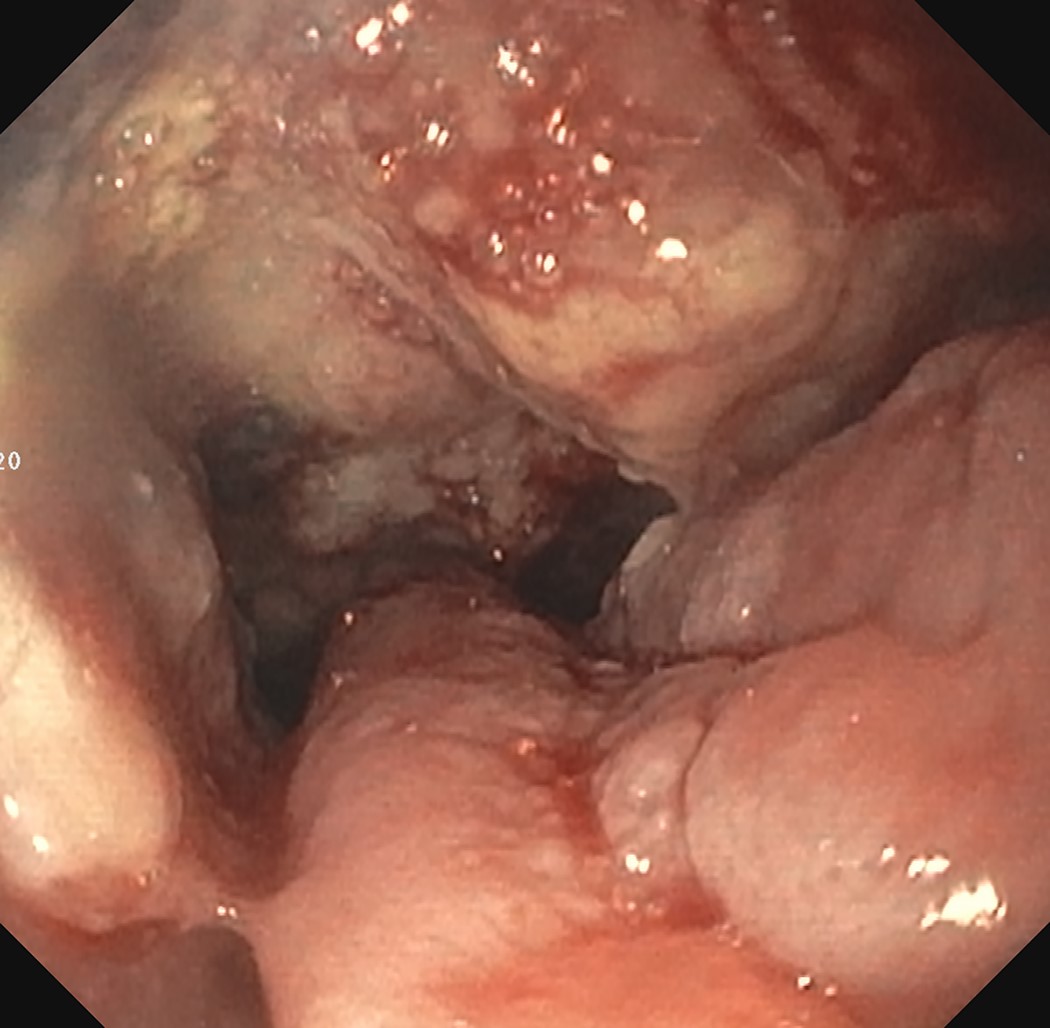
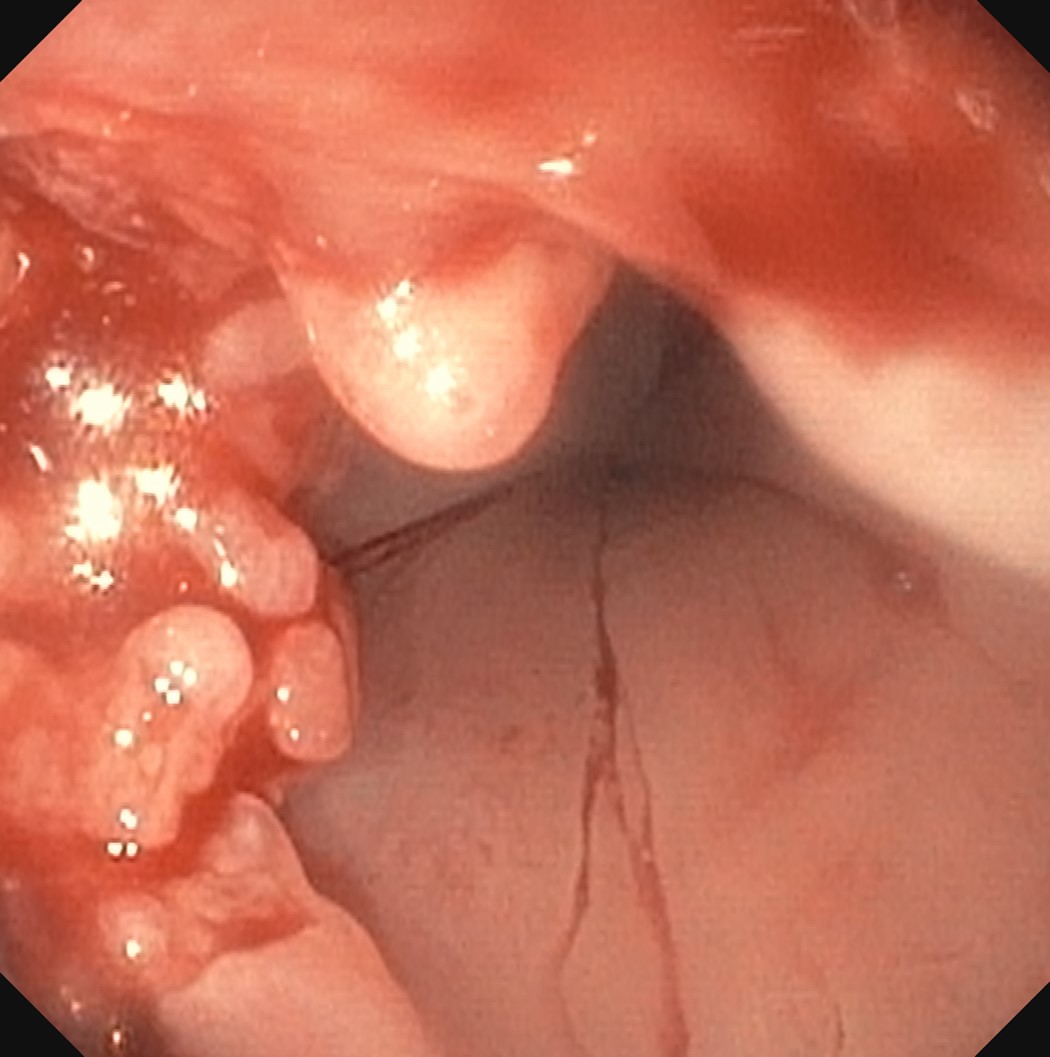
- Endoscopic biopsy
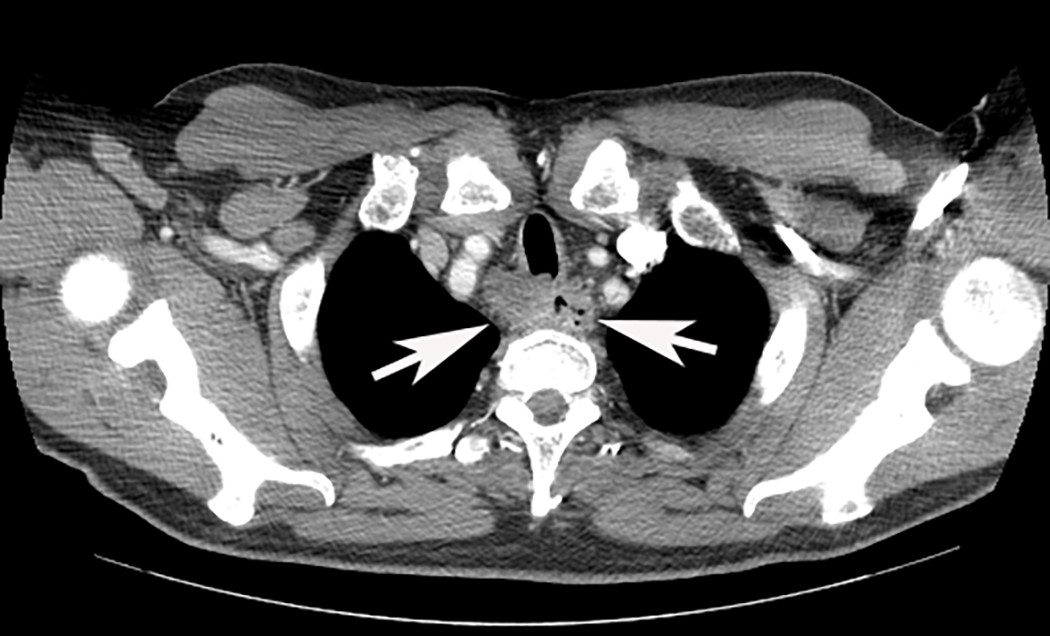
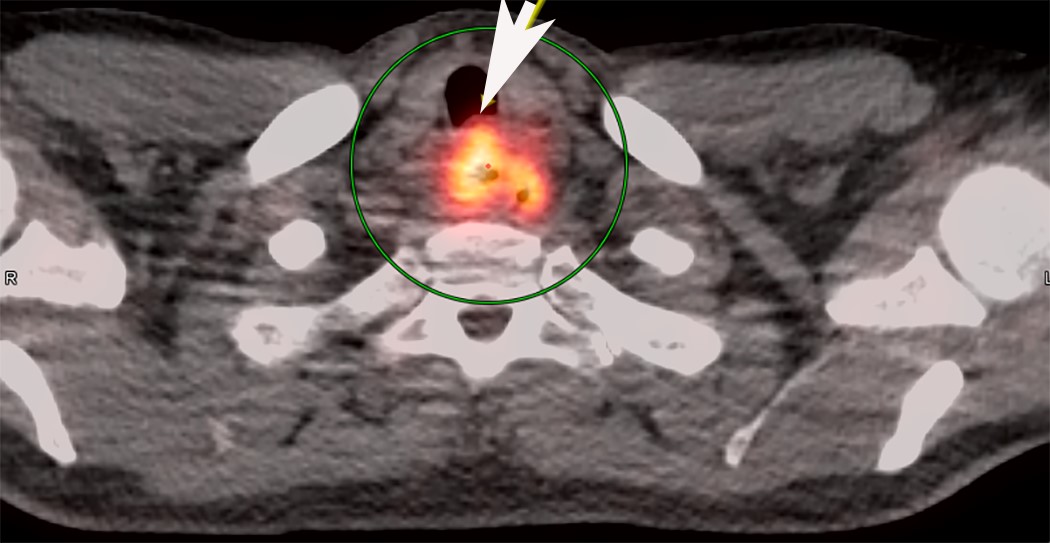
Radiology description
- Positive for esophageal wall thickening or mass on CT scans
- Positive for high metabolism in PET / CT
Prognostic factors
- Very poor prognosis in some cases (J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2012;138:1165)
- Even though more likely to be poorly differentiated at presentation, BSCC of the esophagus could have similar clinical features and survival outcomes when compared with SCC (J Am Coll Surg 2018;226:1086, Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:3659)
- Patients with BSCC and SCC should undergo stage specific treatment to achieve optimal outcomes (J Am Coll Surg 2018;226:1086)
- Better prognosis that occurs with HPV associated BSCC of upper aerodigestive tract is different from BSCC of esophagus
Case reports
- 64 year old man with neuroendocrine and glandular differentiation (Clin J Gastroenterol 2021;14:32)
- 68 year old woman with lung metastasis of esophageal BSCC (Surg Case Rep 2020;6:199)
- 87 year old man with an esophageal subepithelial lesion (Clin J Gastroenterol 2021;14:1324)
Treatment
- Same as conventional squamous cell carcinoma
- Often unresectable due to advanced stage
Gross description
- Generally deeply invasive, large bulky ulcerated fungating masses
Frozen section description
- Tumor cells show nests, trabeculae, cords and cribriform pattern infiltrating the myxoid stroma
- Morphologically it could mimic adenoid cystic carcinoma
Frozen section images
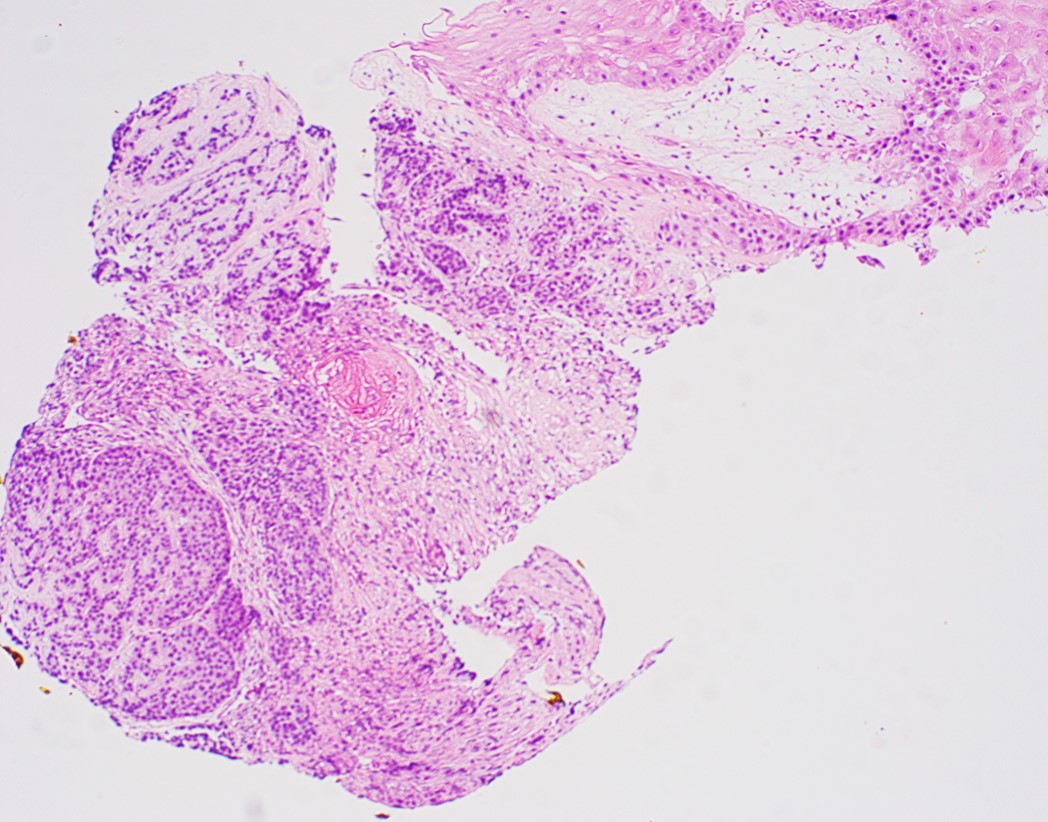
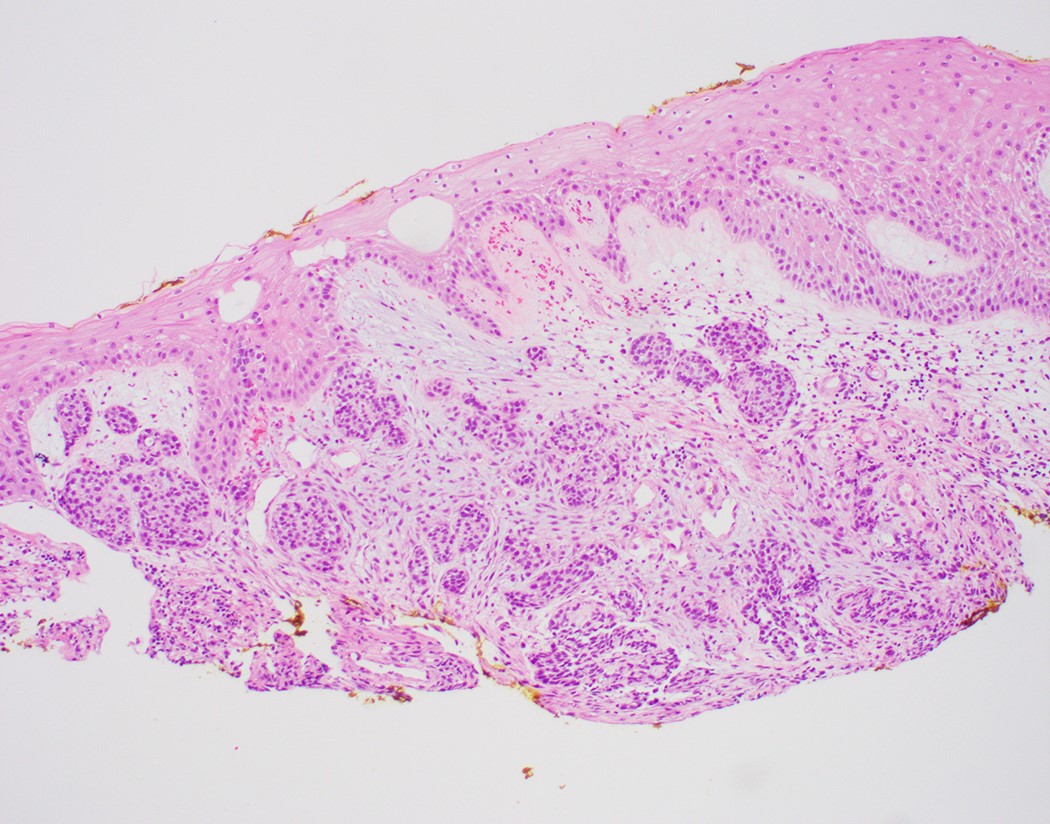
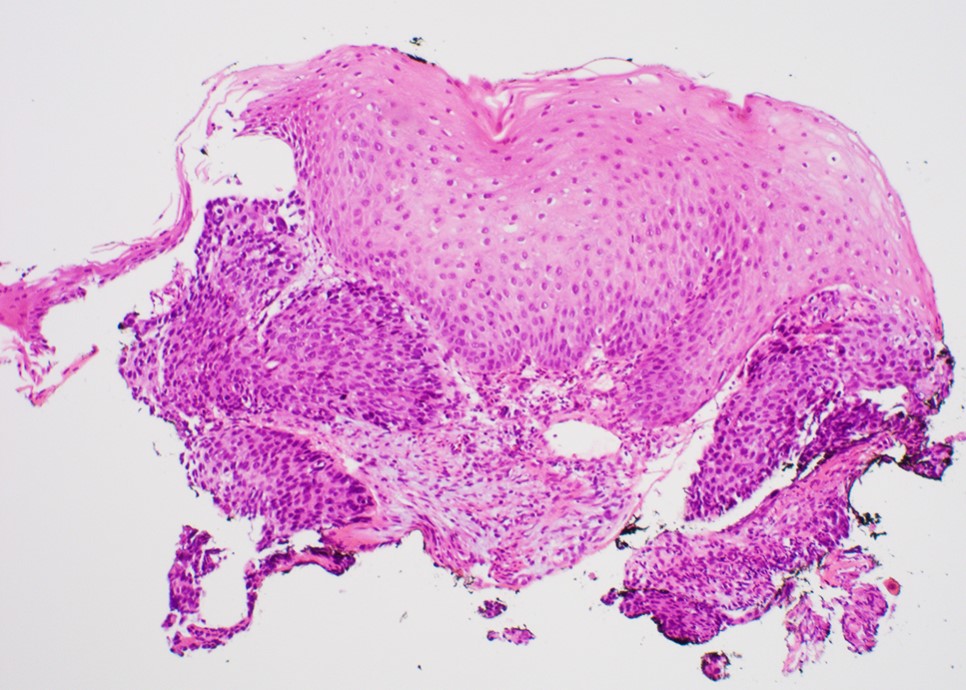
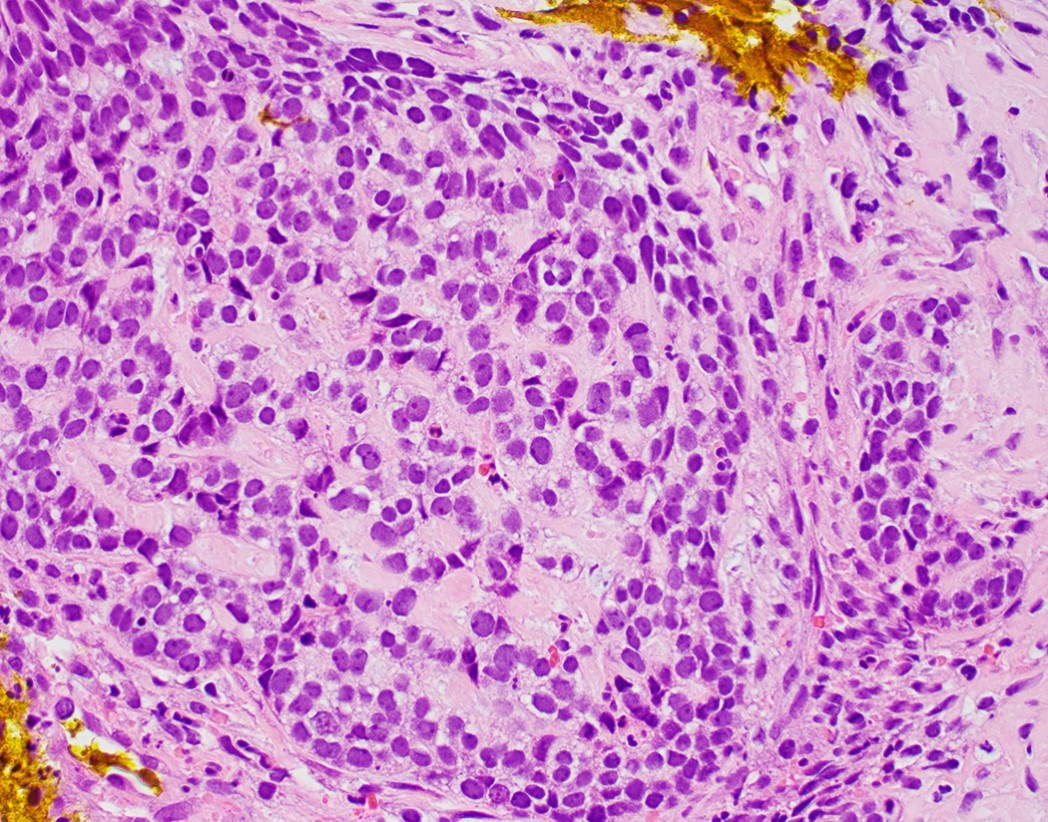
Microscopic (histologic) description
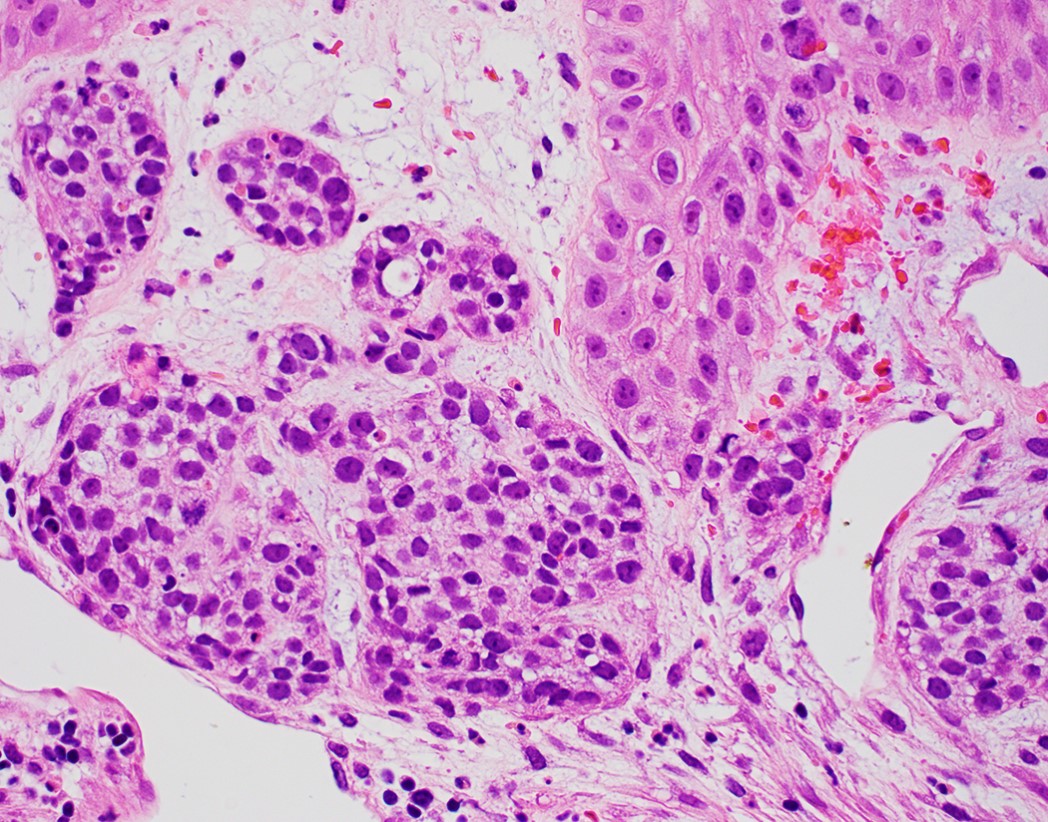
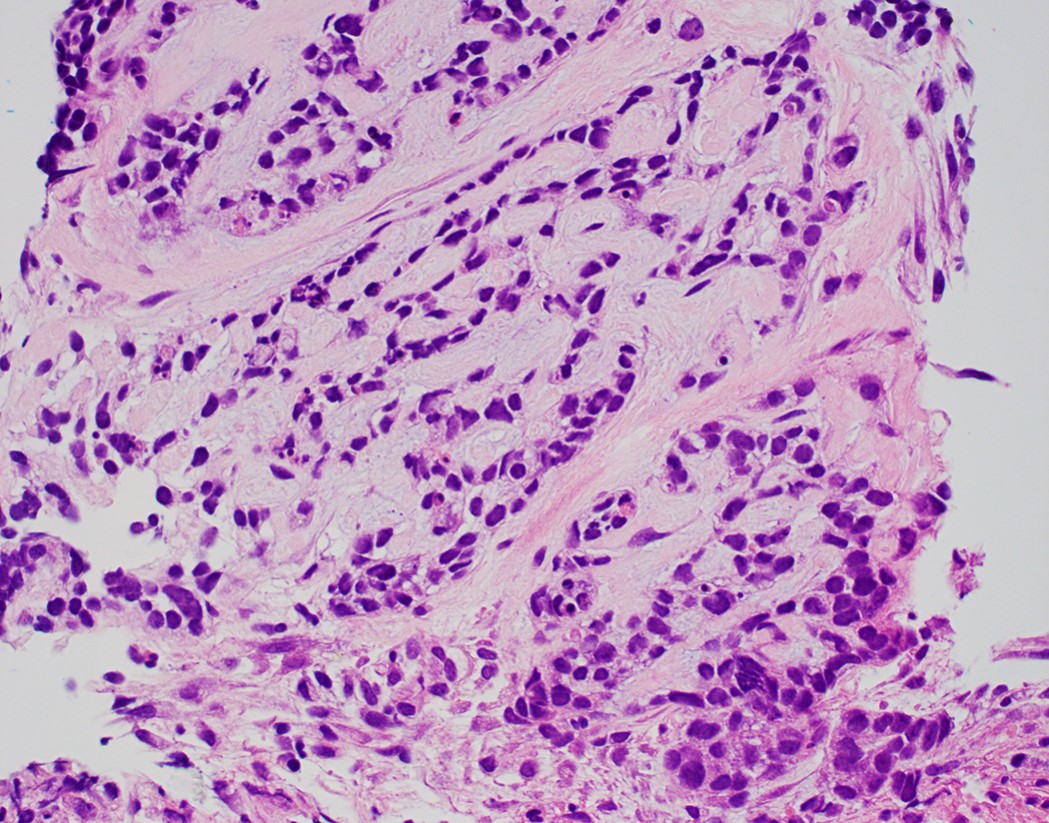
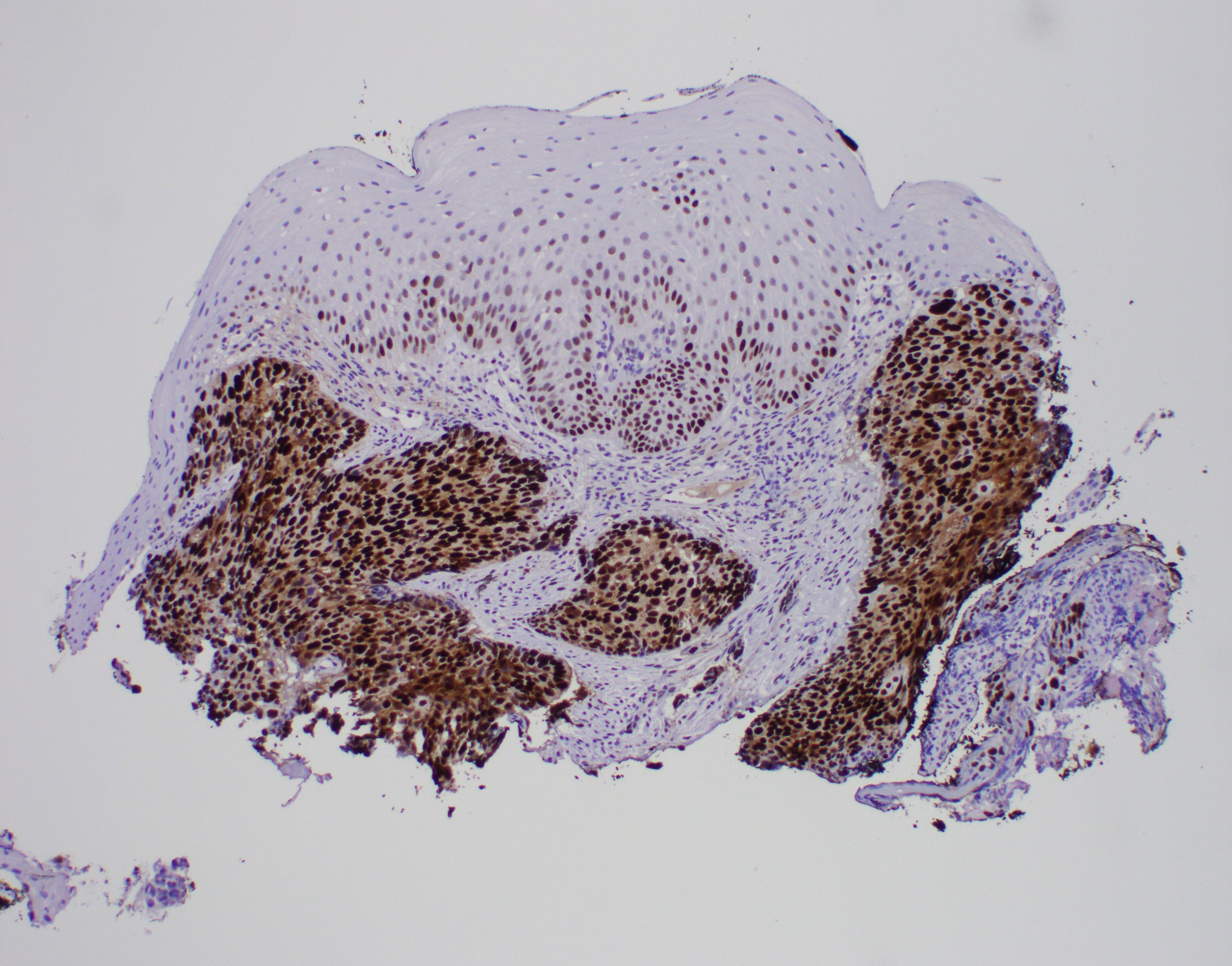
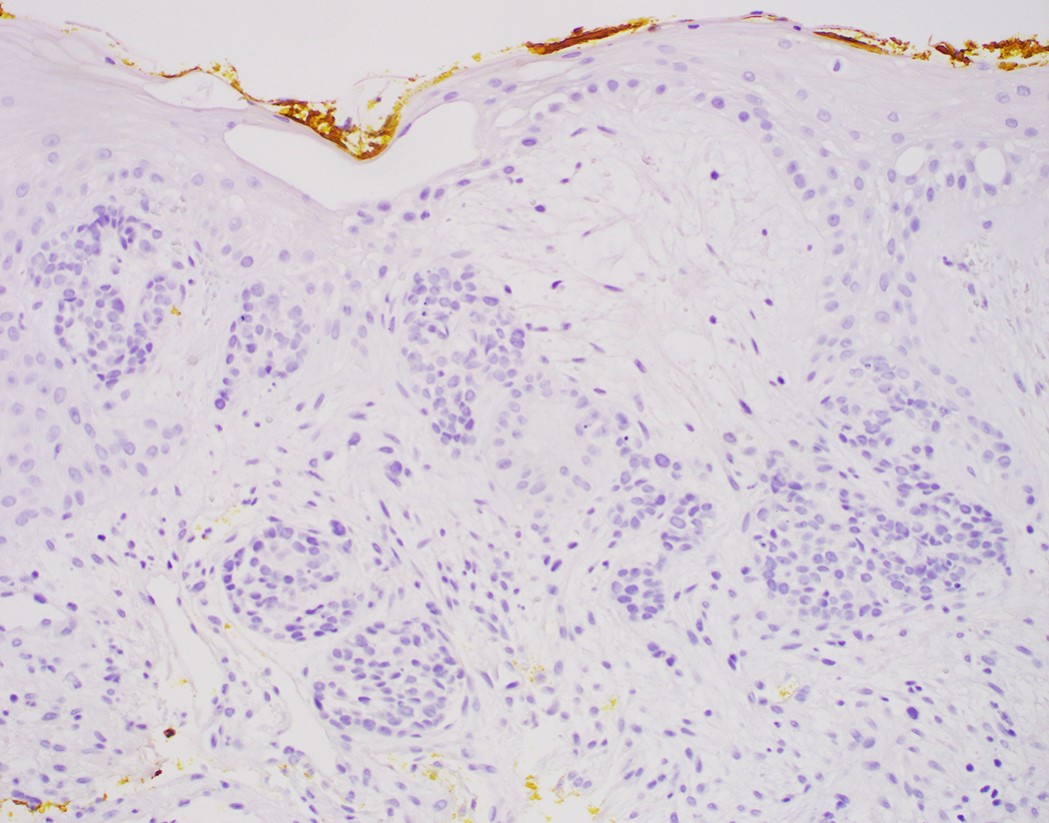
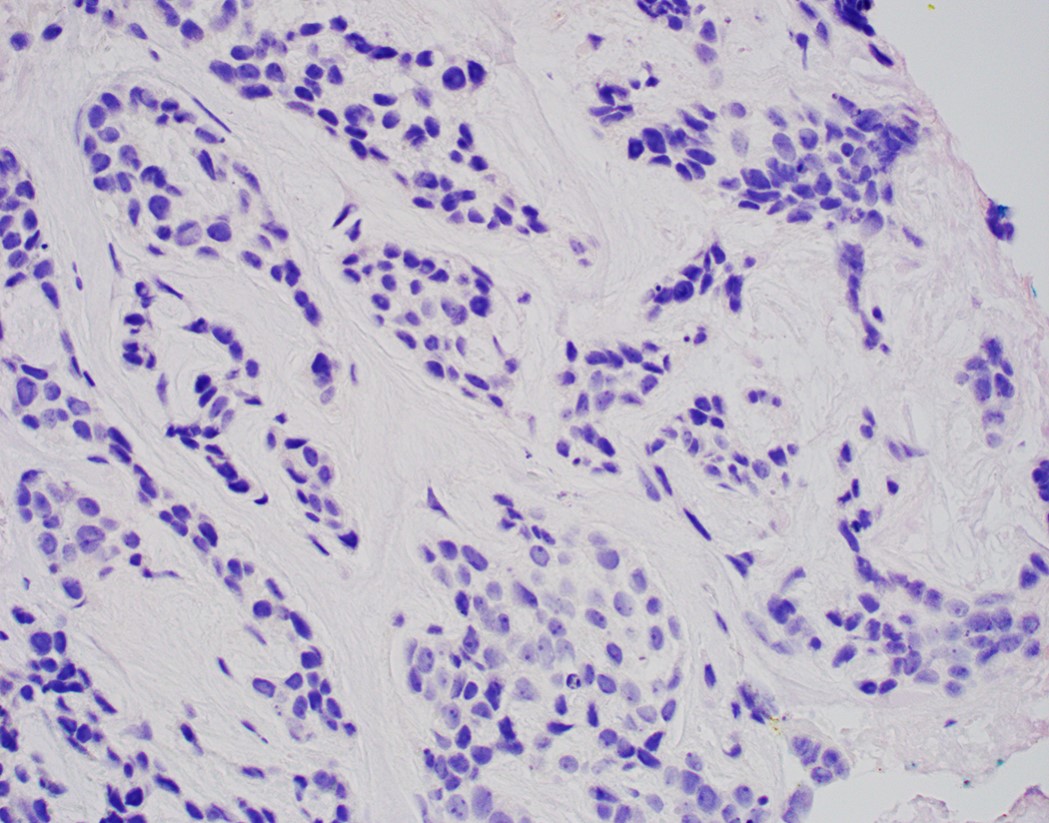
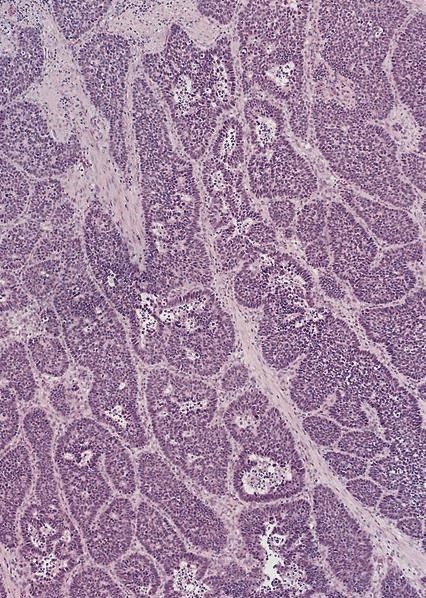
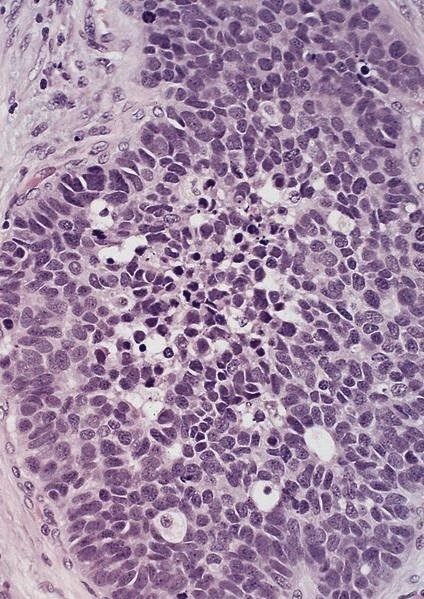
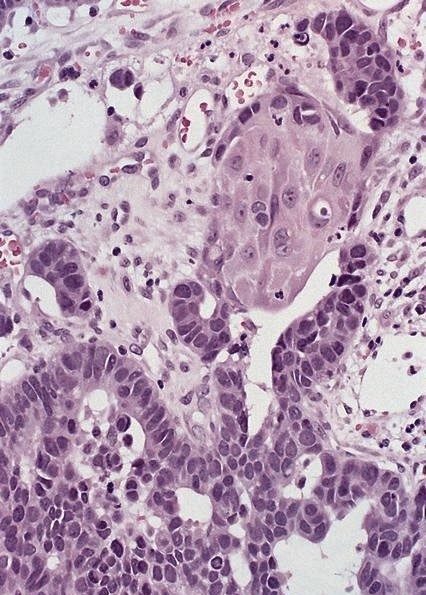
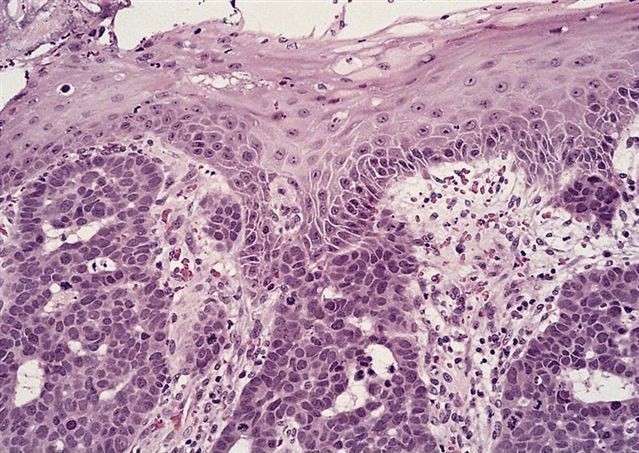
- Solid, cribriform or microcystic nests, strands, trabeculae or lobules of tumor cells (Histopathology 2000;36:331, Methods Mol Biol 2020;2129:7)
- Strands of tumor cells often connected to overlying squamous epithelium
- Nuclei are round to oval, hyperchromatic and peripheral palisading, often with central comedo type necrosis
- Many mitotic figures
- Microcystic pattern contains basophilic material
- While microcysts or necrosis may cause a resemblance to lumina, true lumens are lacking
- Many have areas of stromal hyalinization
- Often admixed with conventional invasive or in situ squamous cell carcinoma and may see admixed adenocarcinoma, small cell carcinoma and spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Jinping Lai, M.D., Ph.D. and AFIP images
Cytology description
- Basaloid cells
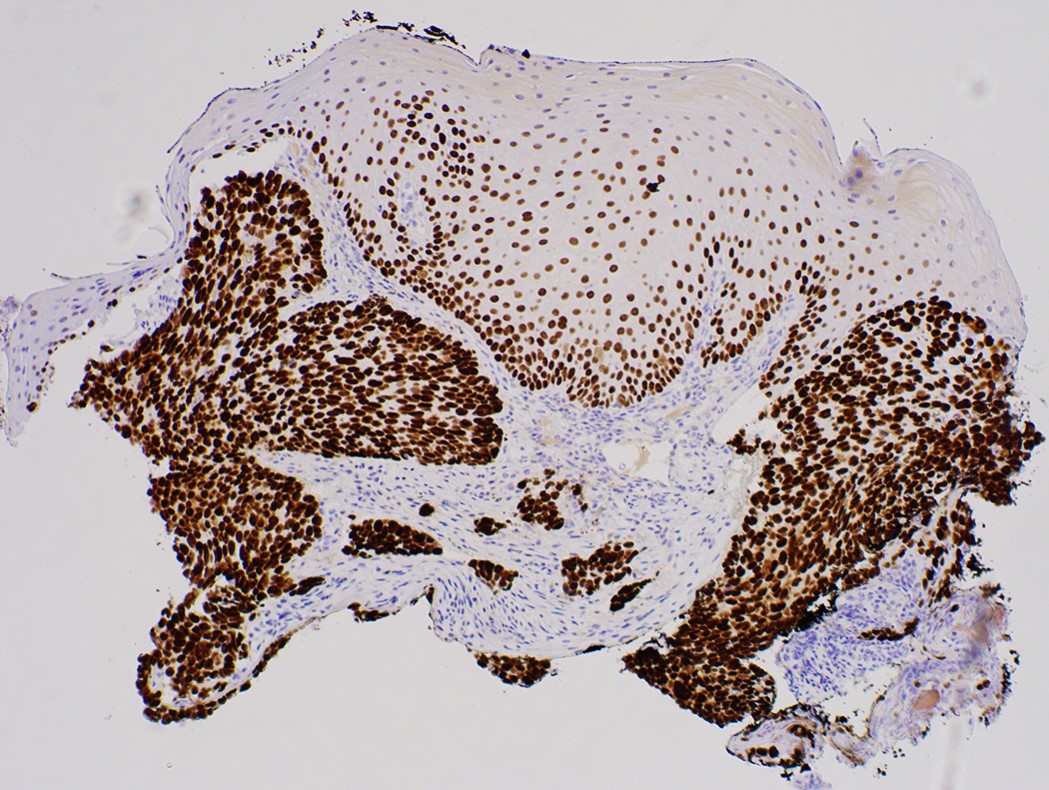
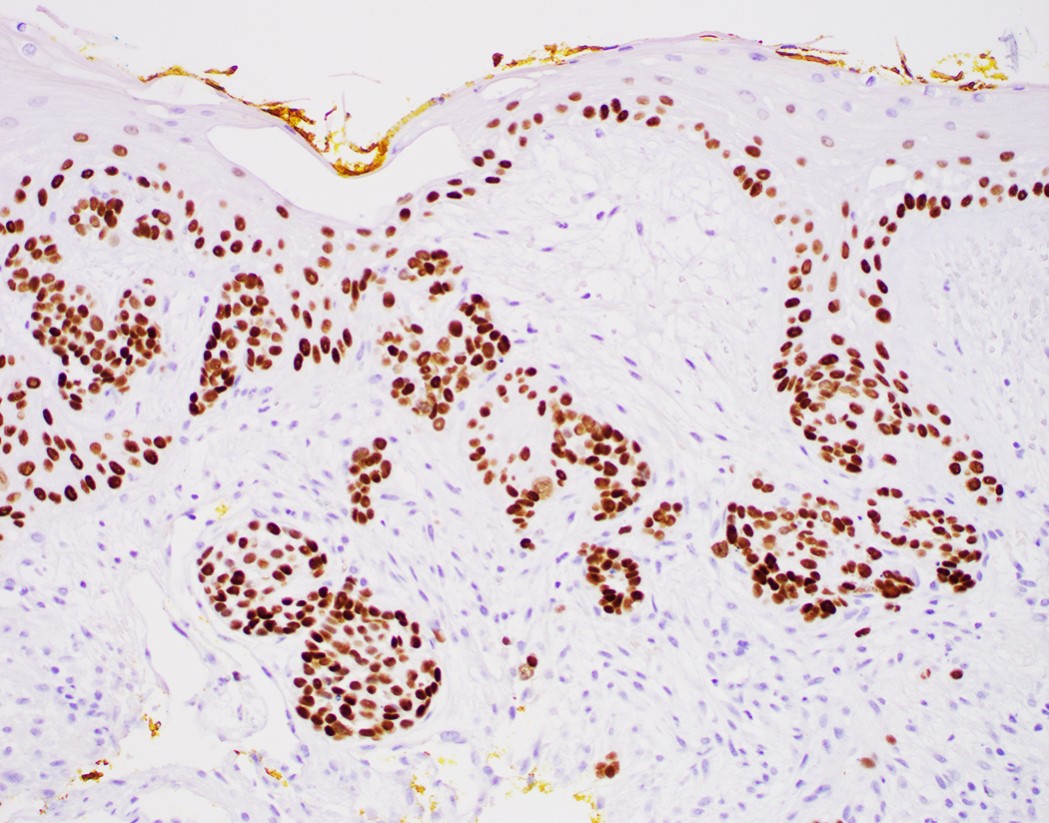
Positive stains
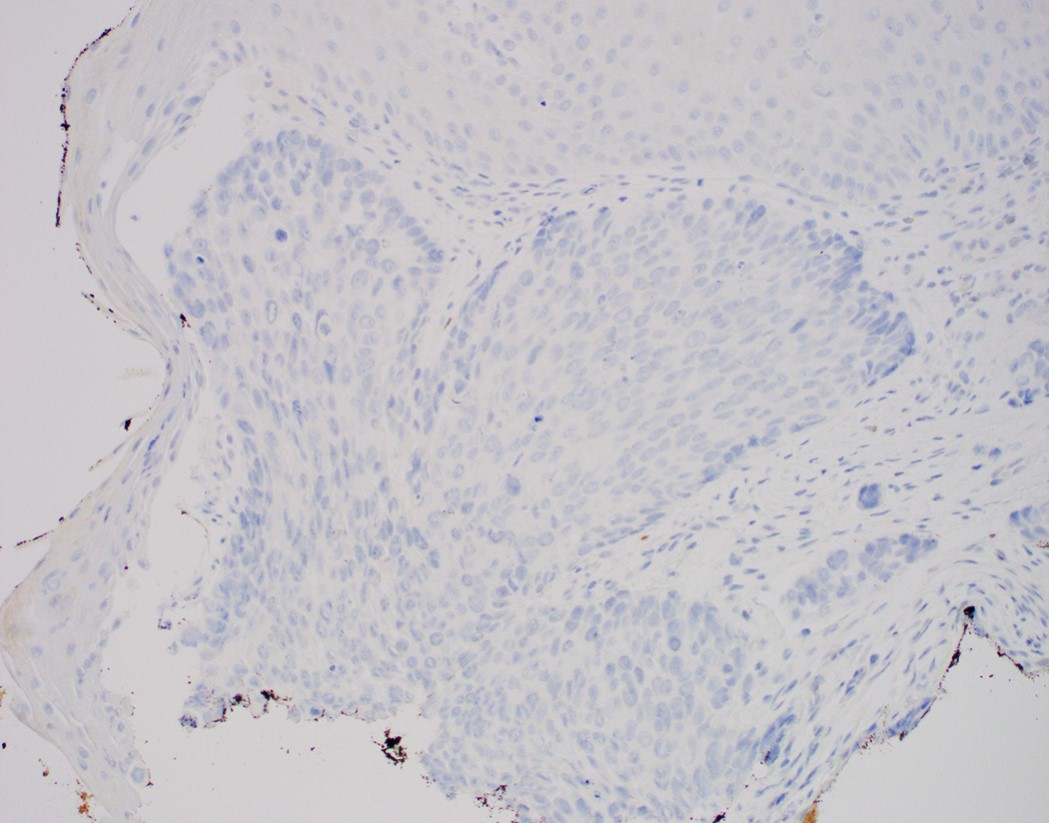
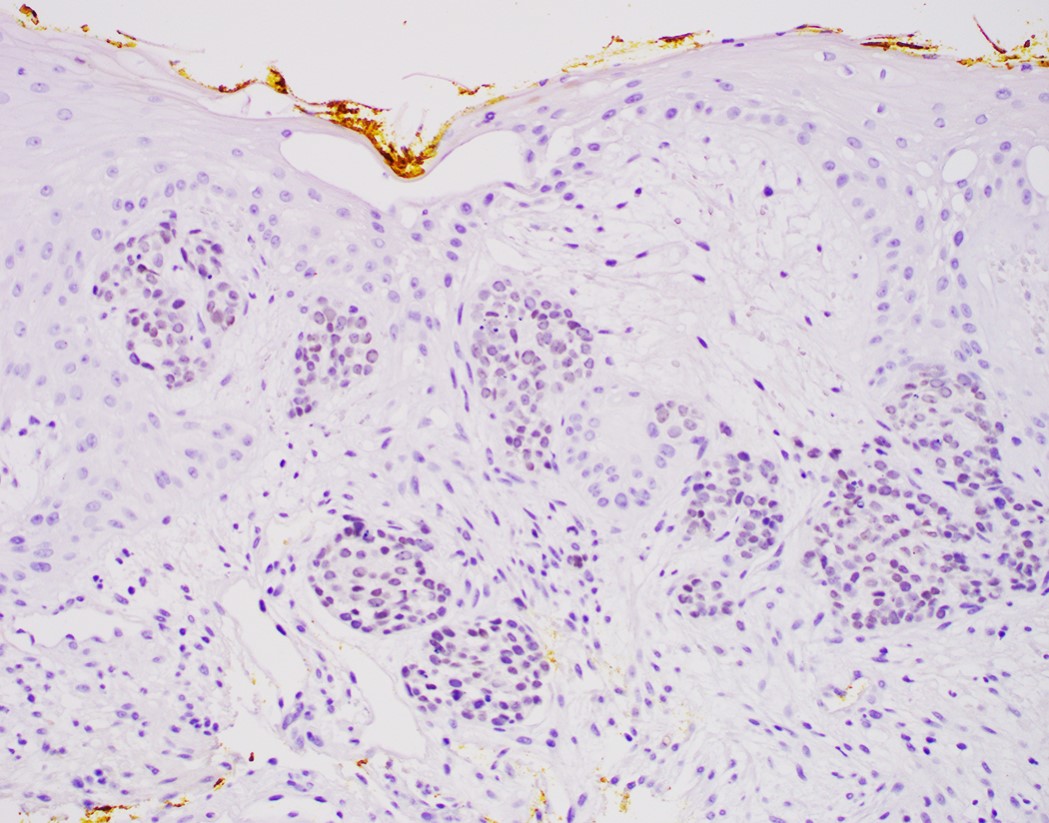
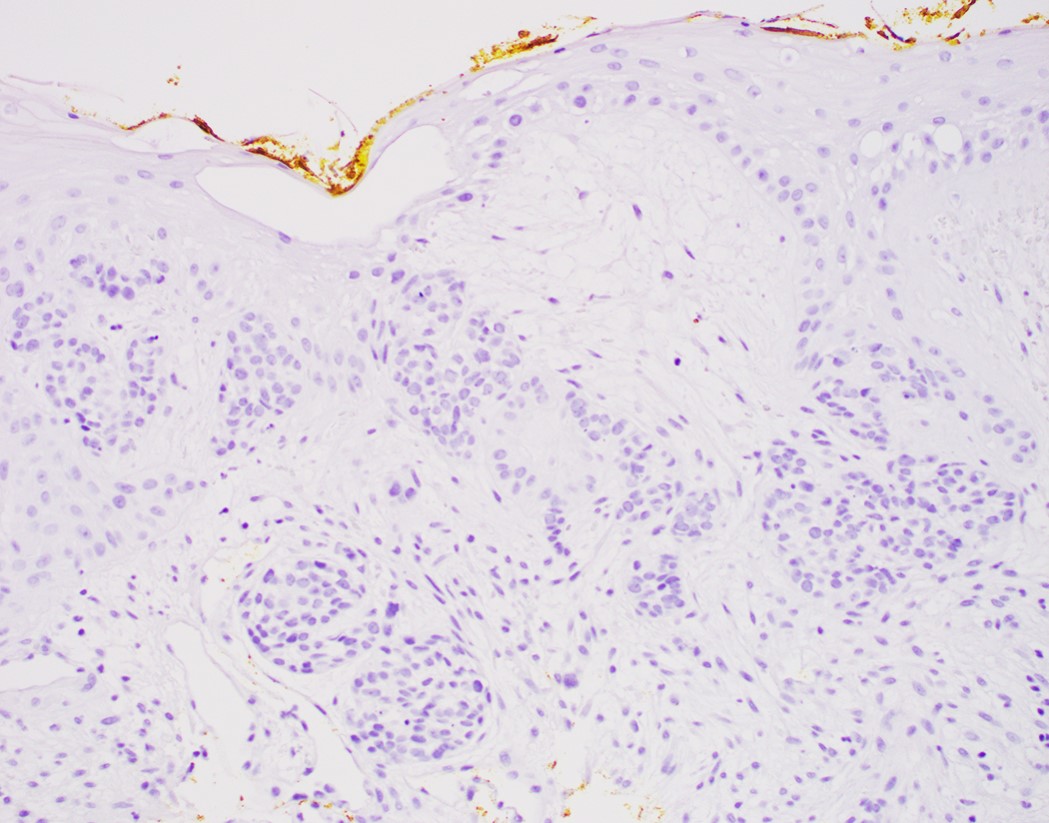
Negative stains
- Neuroendocrine markers
- Smooth muscle actin
- S100 (rarely weakly positive)
Electron microscopy description
- Relatively undifferentiated cellular characteristics
- Undeveloped cell organelles
- Markedly replicated basement membrane
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- p53 and Rb gene mutations similar to conventional squamous cell carcinoma (Hum Pathol 2012;43:2012)
- Up to half of esophageal BSCC cases harbor either an EGFR mutation or amplification and partial activation of the Wnt and hedgehog (HH) signaling pathways (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:2267)
- No KRAS, BRAF or PI3K mutations observed in BSCCs, while 23% of conventional SCC harbored a PIK3CA mutation (Ann Surg Oncol 2015;22:3659)
Sample pathology report
- Esophagus, mid, mass, biopsy:
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Clinical photos are noted. Sections of the biopsy show subepithelial basaloid neoplasm with microcystic nests, strands, trabeculae of tumor cells infiltrating a myxoid stroma. The tumor cells are positive for p40, p63, p53 and intact INI1, while negative for p16, CK7, CK20, CDX2 and synaptophysin. The histologic features and immunoprofile support the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Much better prognosis; female predominance
- No association with in situ or invasive conventional squamous cell carcinoma
- Has myoepithelial differentiation (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e16999)
- Sarcomatoid carcinoma / carcinosarcoma:
- With spindle cell differentiation (Tohoku J Exp Med 2019;249:255, Am J Gastroenterol 2018;113:642)
- Small cell carcinoma:
- Has different morphology with finely granular chromatin, scant cytoplasm and nuclear molding, expresses neuroendocrine markers (Thorac Cancer 2020;11:1119, Am J Clin Oncol 2019;42:534)
Board review style question #1
Compared with conventional squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus, basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus has
- Fewer PI3KCA mutations
- More p53 mutations
- More Rb mutations
- More BRAF mutations
- More KRAS mutations
Board review style answer #1
A. No PI3KCA mutation has been observed in esophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma, while 23% of conventional SCCs of the esophagus harbored a PI3KCA mutation.
Comment Here
Reference: Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style question #2
56 year old man with a smoking history for 20 years and dysphagia for 6 months. A biopsy is made of a lesion at his mid esophagus, shown in the photo above. The cells are diffusely nuclear positive for p40, p63, p53 and INI1, while negative for p16, CK7, CK20, CDX2 and synaptophysin. What is your diagnosis?
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
- Metastatic oropharyngeal HPV related squamous cell carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma, small cell type
- SMARCB1 deficient carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
B. The most likely diagnosis is basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. The tumor cells only show 1 component and are diffusely positive for p40 and p63, making adenoid cystic carcinoma less likely. The tumor cells show eosinophilic cytoplasm with negative synaptophysin, making small cell carcinoma less likely. The tumor cells have an intact INI1, making SMARCB1 deficient carcinoma less likely. p16 is negative, making HPV related metastatic oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma less likely.
Comment Here
Reference: Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma