Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Weisenberg E. Adenoid cystic carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/esophagusadenoidcystic.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Primary tumor of esophagus morphologically and immunohistochemically identical to adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary glands
- Believed to arise from esophageal glands
Epidemiology
- Very rare, generally middle age, more common in females
Prognostic factors
- Generally favorable prognosis with excellent survival
- Superior to squamous cell carcinoma and usual adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
Case reports
- 59 year old woman (Int J Clin Pract 2005;59:1101)
- 70 year old woman (Surg Today 1997;27:238)
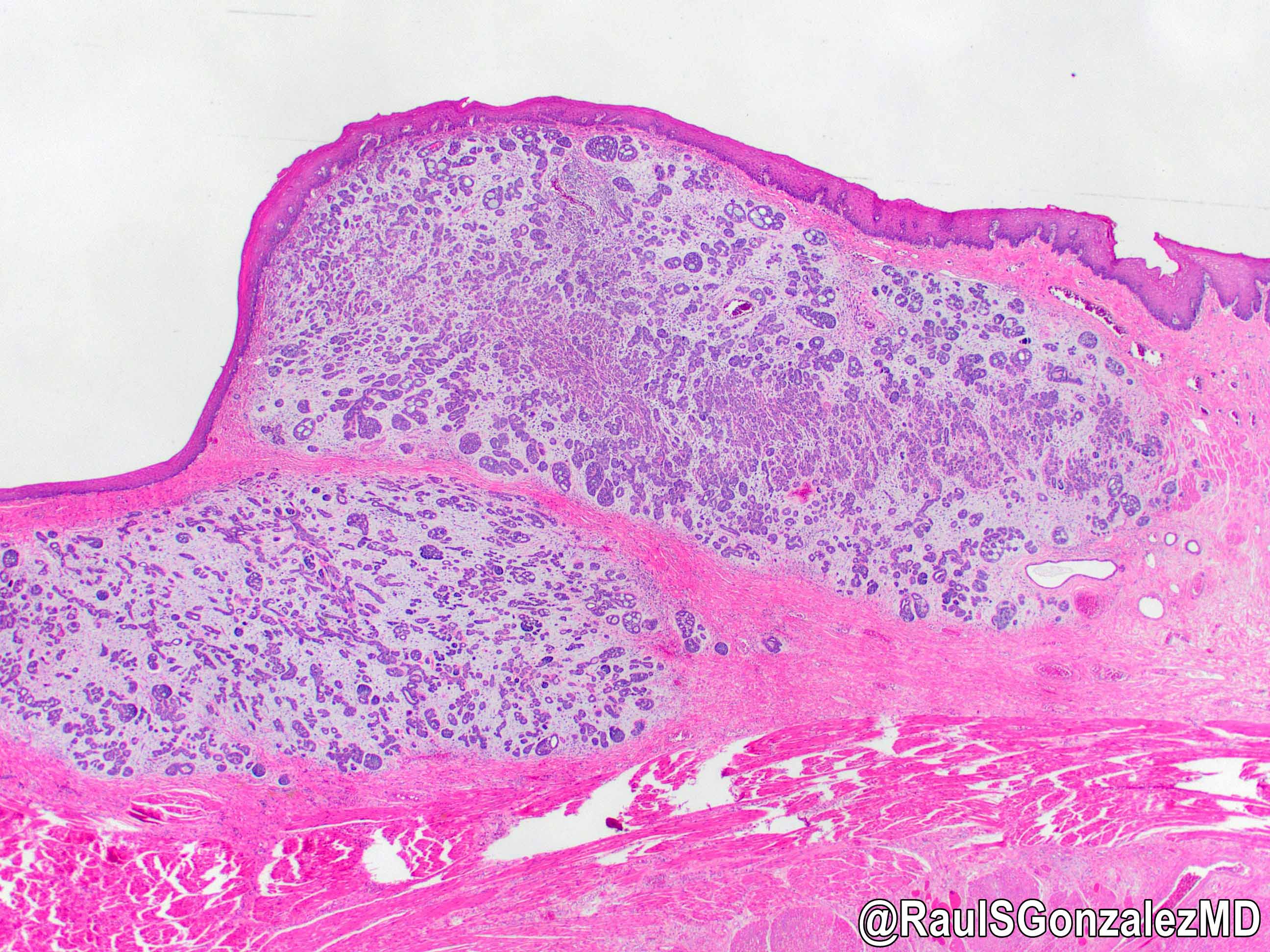
Gross description
- Generally well circumscribed nodule in submucosa
Microscopic (histologic) description
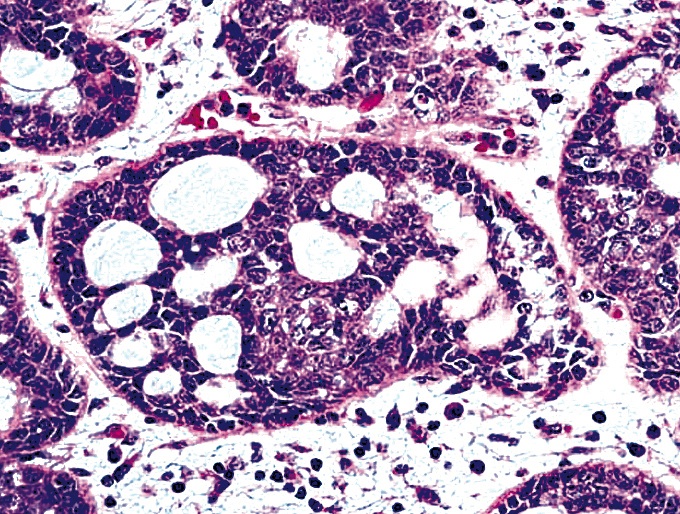
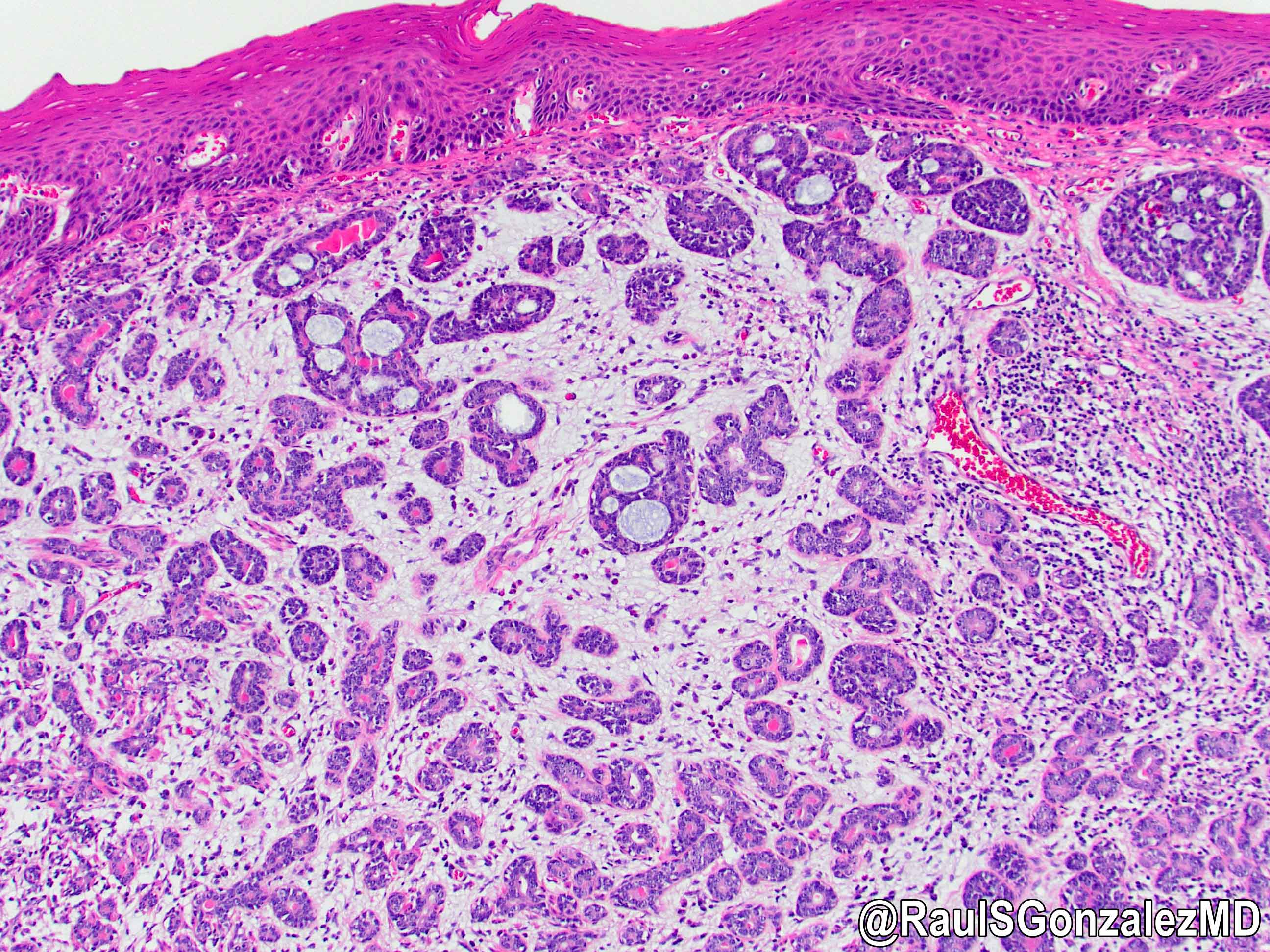
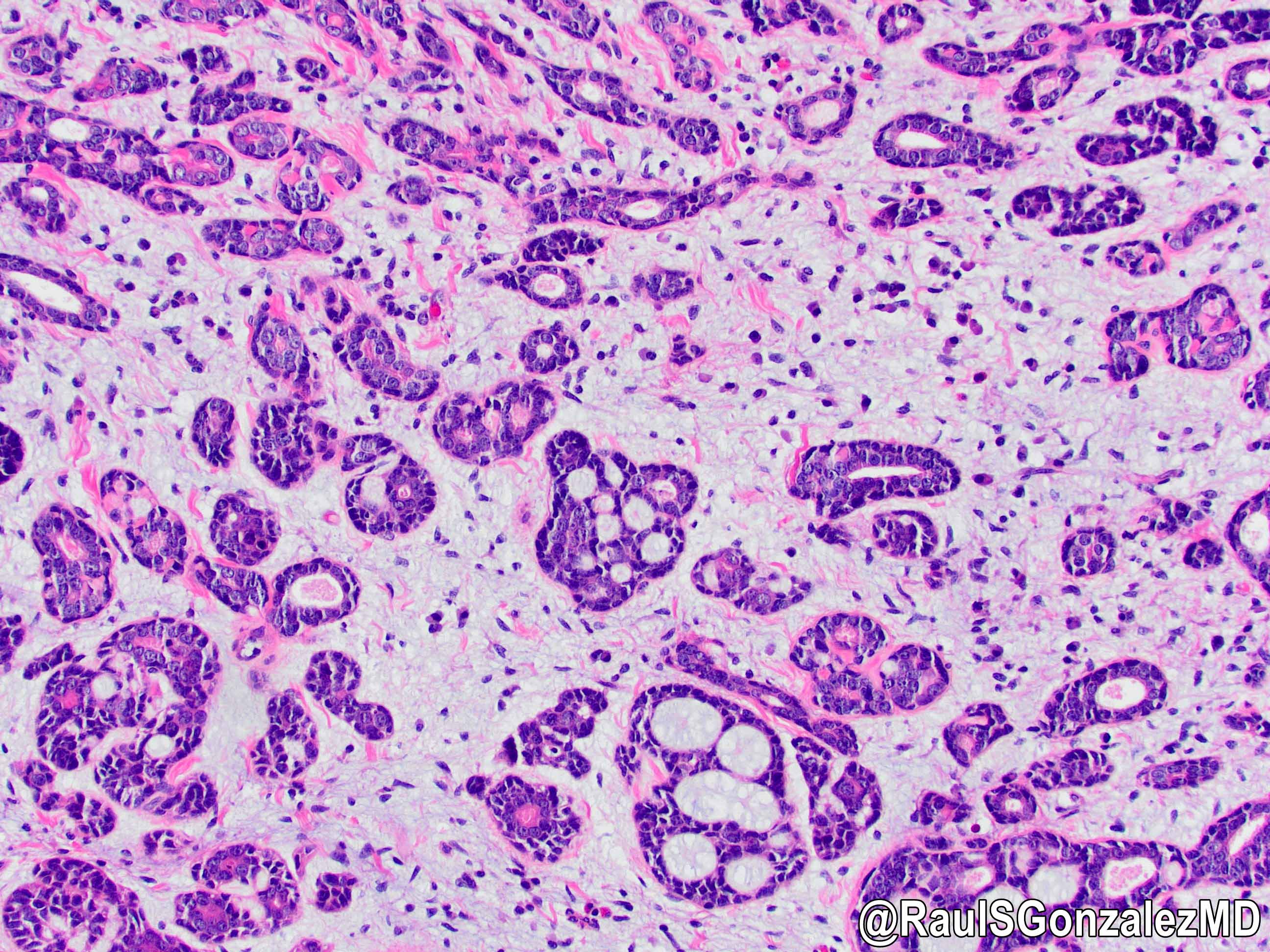
- Identical to tumor in salivary gland
- Inner ductal type epithelium and outer modified myoepithlial cells form solid nests or cribriform spaces containing balls of glyocosaminoglycans and basement membrane material
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Ductal epithelium is strongly cytokeratin and CEA+, while modified myoepithelial cells are weakly cytokeratin positive with strong S100, actin and vimentin positivity in modified myoepithelial cells
Differential diagnosis
- Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma
- More pleomorphic with greater mitotic activity
- Does not form true lumina and lacks CEA staining
- Generally CK19+, not seen in adenoid cystic carcinoma