Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Grading | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Cai C. Meningioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumormeningiomageneral.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Most common primary CNS tumor, arising from arachnoid cap cells associated with dura mater or choroid plexus, accounting for 36% all CNS tumors (Neuro Oncol 2015;17:iv1)
- Growing along external surface of brain, spinal cord or rarely, within the ventricular system
Essential features
- 3 grades exist based on WHO criteria:
- Most are slow growing WHO grade 1 (benign)
- 20 - 25% are WHO grade 2 (increased likelihood of recurrence)
- 1 - 6% are WHO grade 3 (malignant with metastatic potential)
- While there are 15 WHO recognized morphological meningioma variants, this topic focuses more on WHO grade 1 variants
- WHO grade 1 meningiomas have low mitotic index (< 4/10 high power field), no brain invasion and < 3 atypical features (necrosis, small cell change, sheeted architecture, macronuclei and hypercellularity)
ICD coding
- ICD-10:
- D32.9 - benign neoplasm of meninges, unspecified
- D32.0 - benign neoplasm of cerebral meninges
- D32.1 - benign neoplasm of spinal meninges
- C70 - malignant neoplasm of meninges
- C70.0 - malignant neoplasm of cerebral meninges
- C70.1 - malignant neoplasm of spinal meninges
- C70.9 - malignant neoplasm of meninges, unspecified
- D42 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of meninges
- D42.0 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of cerebral meninges
- D42.1 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of spinal meninges
- D42.9 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of meninges, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Mainly adults, mean age of 65
- F > M
- 66% of cerebral meningiomas occur in women; 90% of spinal cord meningiomas occur in women (Neuro Oncol 2012;14:v1)
- Rare cases may occur in pediatric population, which are typically associated with genetic syndromes or childhood radiation (Acta Neuropathol 2021;142:873)
Sites
- Extra-axial mass growing along external surface of brain, spinal cord, rarely within the ventricular system or outside of the CNS (ectopic)
- Common CNS sites:
- Convexity
- Skull base
- Falx and tentorium
- Spinal cord
- Common CNS sites:
- Ectopic:
- Head and neck region is the most common ectopic site, including scalp skin, intraosseous, orbit, paranasal sinuses, ear and temporal bone (Head Neck Pathol 2009;3:116)
- Rare cases in lung, salivary glands and mediastinum have also been reported (Cancer 1996;78:2328, J Med Case Rep 2011;5:271, World J Surg Oncol 2012;10:17)
Pathophysiology
- Meningiomas driven by chromosome 22q alterations (e.g. NF2, SMARCB1) arise in neural crest cell derived meninges, including convexities, falx, tentorium and spinal cord
- Meningiomas driven by hedgehog signaling pathway, PI3K signaling, TRAF7, KLF4 and POLR2A arise in the mesodermal derived meninges of the midline and paramedian anterior, central and ventral posterior skull base (Oncogene 2021;40:875)
Etiology
- Risk factors:
- Radiation, either high dose or low dose (Nat Commun 2017;8:186, Acta Neuropathol 2017;134:155)
- Hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives (J Clin Oncol 2008;26:279, J Neurosurg 2013;118:649)
- Germline mutations in NF2 or SMARCB1 and SMARCE1 predispose to familial and multiple meningiomas (Neurogenetics 2012;13:1, J Med Genet 2011;48:93, Nat Genet 2013;45:295)
Clinical features
- Common symptoms include headaches, seizures and focal neurological deficit due to tumor compression (Neurosurg Clin N Am 2016;27:239)
Grading
- Grade 1 variants
- Angiomatous:
- Vascular component should exceed 50% of total tumor area
- Can further divide into microvascular and macrovascular variants
- Mean Ki67 index is ~2%
- Does not recur if entirely resected
- Differential diagnosis includes hemangioblastoma for the microvascular variant and vascular malformations for the macrovascular variant (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:390)
- Genetically characterized by polysomy of chromosome 5, 13 and 20 (Oncotarget 2014;5:10596)
- Fibroblastic:
- Spindle cell neoplasm with few or no meningothelial nests or whorls; often has thick bundles of collagen
- Resembles schwannoma or solitary fibrous tumor but is positive for meningothelial markers SSTR2A and EMA and negative for STAT6
- NF2 mutated meningiomas are predominantly fibroblastic or transitional and more commonly located in convexity, falx or tentorium (Nat Genet 2013;45:285, Oncogene 2021;40:875)
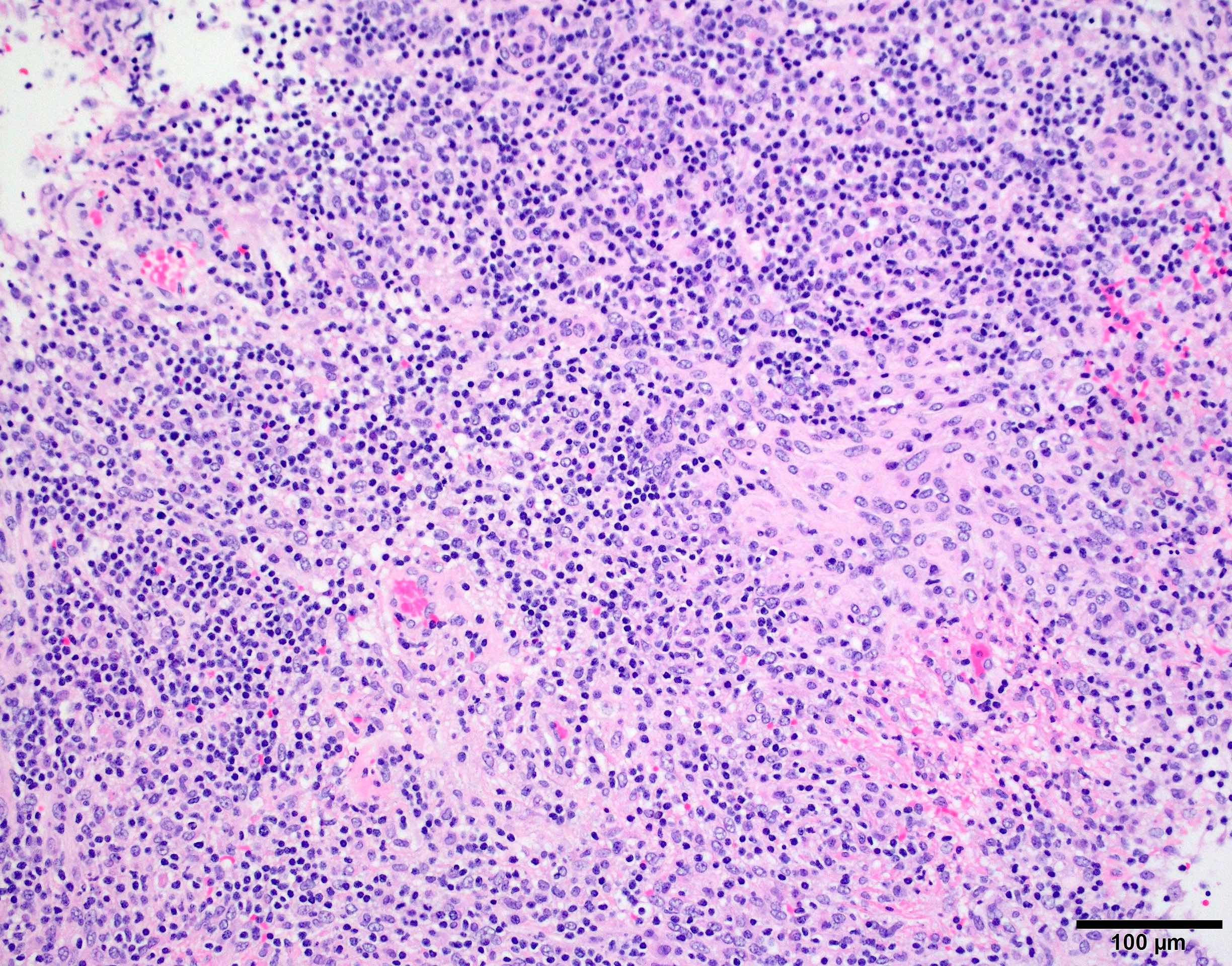
- Lymphoplasmacyte rich:
- Rare, comprising < 1% of meningiomas
- Extensive lymophoplasmacyte infiltrates that overshadow an inconspicuous meningothelial component
- May be associated with Castleman disease or other hematopoietic neoplasm (Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6:504, World Neurosurg 2017;106:152)
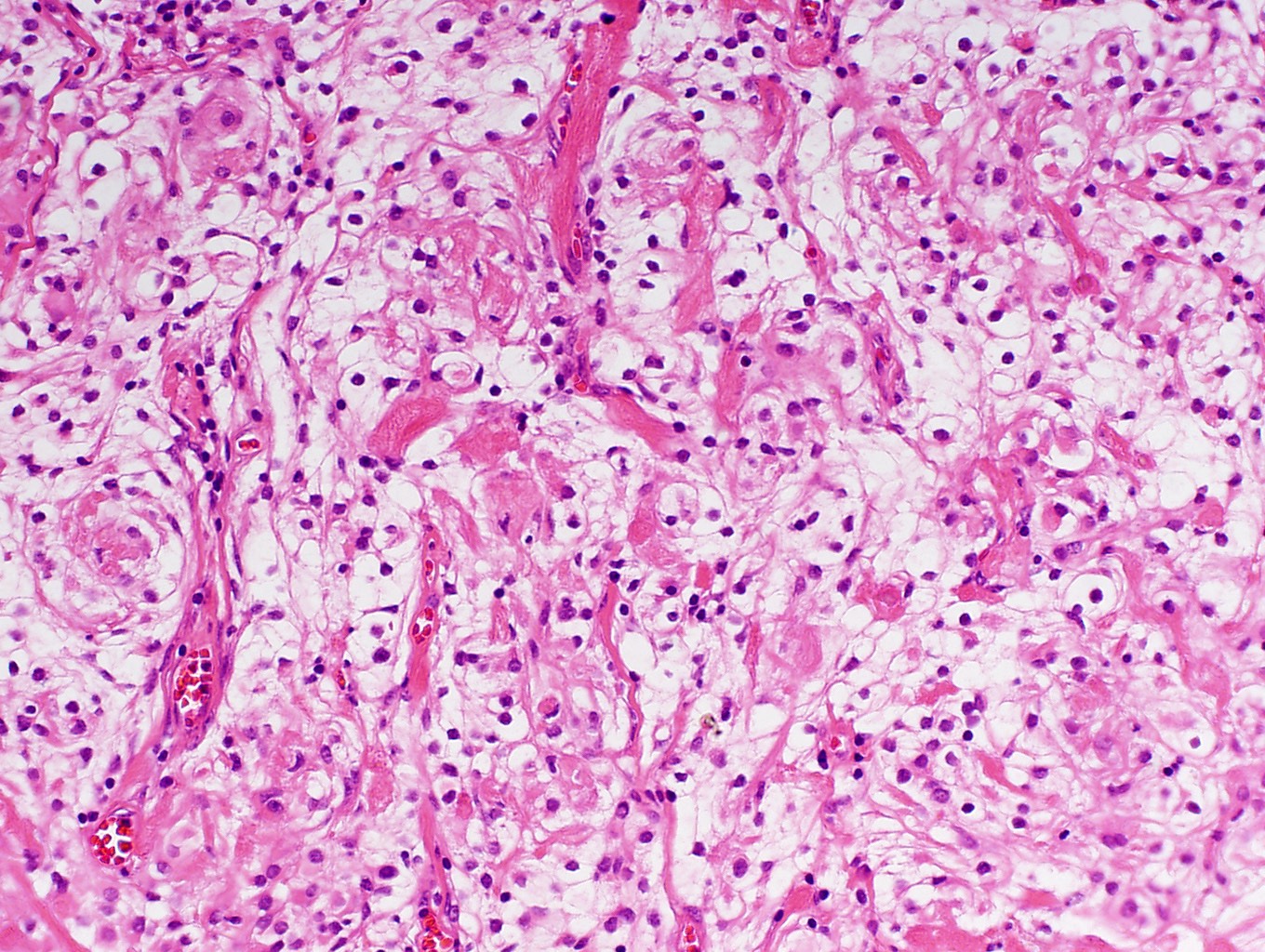
- Meningothelial:
- Most common variant
- Lobulated architecture, often contains meningothelial whorls
- Syncytial cells with indistinct cell membranes, eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Round uniform nuclei, intranuclear pseudoinclusions common
- May have sparse psammoma bodies
- Meningiomas with SMO or AKT1 mutations are predominantly meningothelial and more commonly located in the midline or paramedian skull base (Nat Genet 2013;45:285, Oncogene 2021;40:875)
- Metaplastic:
- Rare, < 1% of all meningiomas
- May contain foci of bone, cartilage, fat or xanthomatous morphology (J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2020;63:657, Chin J Cancer Res 2013;25:112)
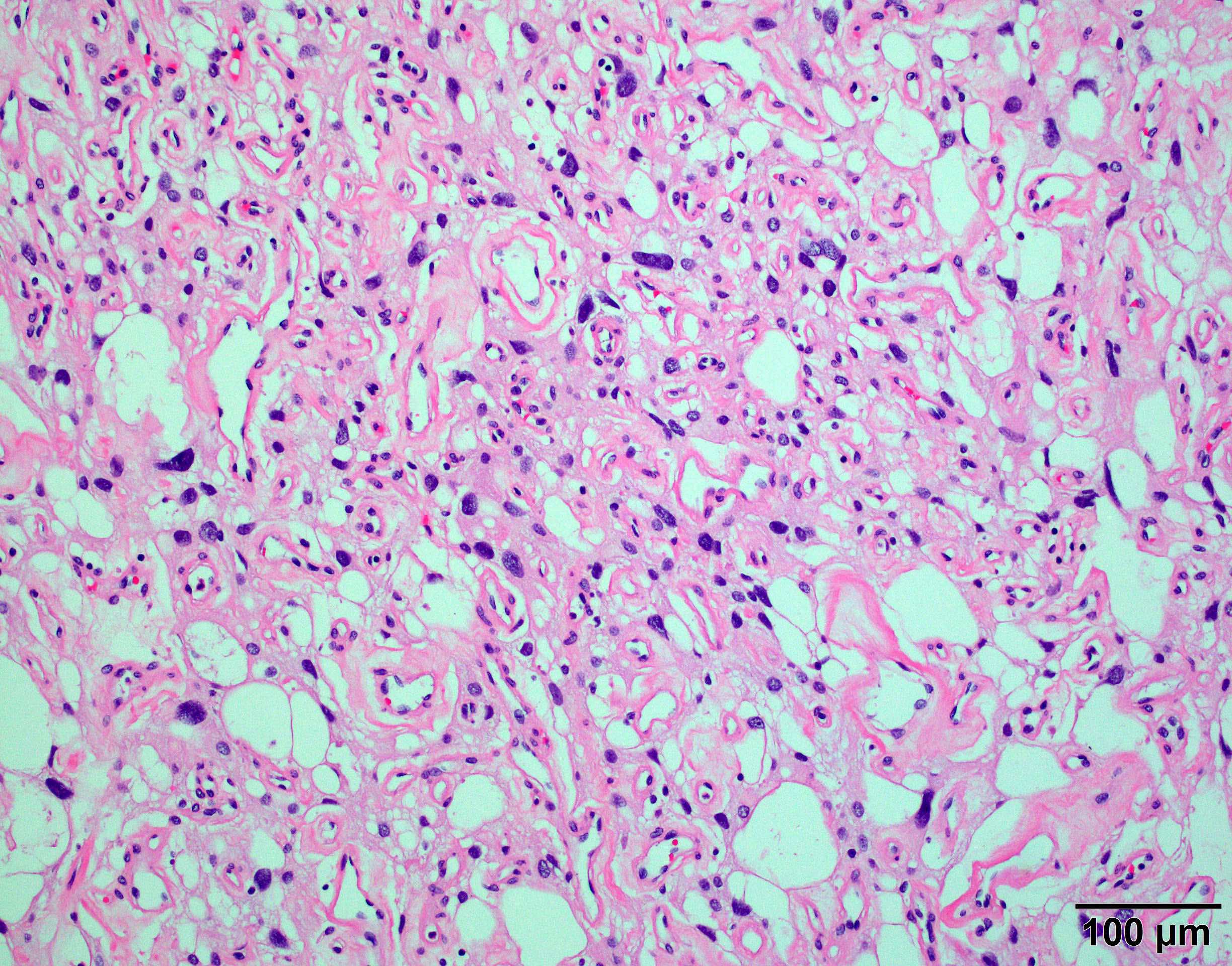
- Microcystic:
- Cells have elongated processes and vacuolated cytoplasm that resembles microcysts
- May have prominent nuclear pleomorphism but usually low mitotic index
- Often rich in vasculature and overlaps with angiomatous meningioma
- Small areas of classic meningothelial nests may be present
- Microcystic areas are weakly but diffusely positive for hypoxic marker carbonic anhydrase IX (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2019;78:1081)
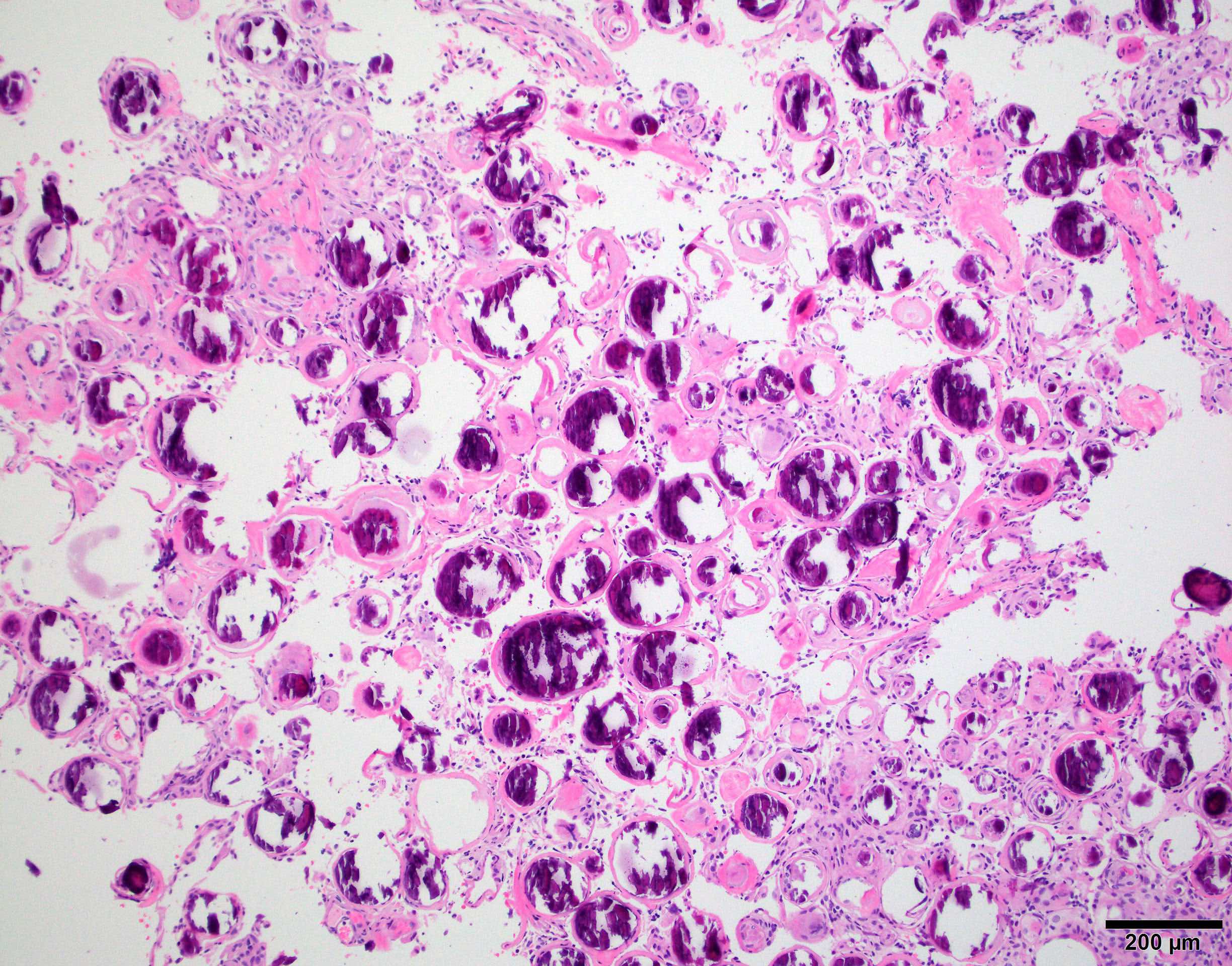
- Psammomatous:
- Found in spinal region
- Numerous psammoma bodies, intervening meningothelial cells hard to find
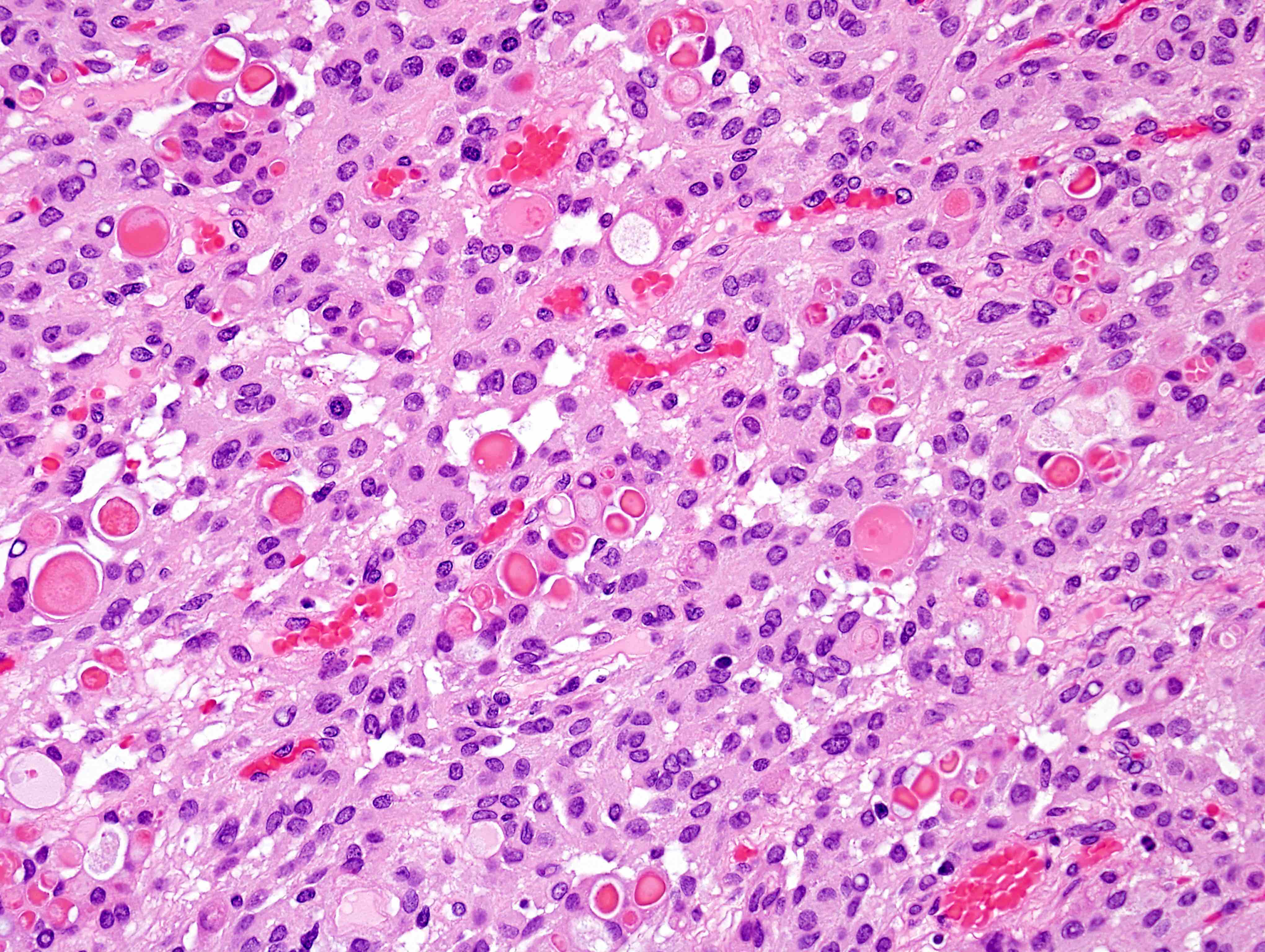
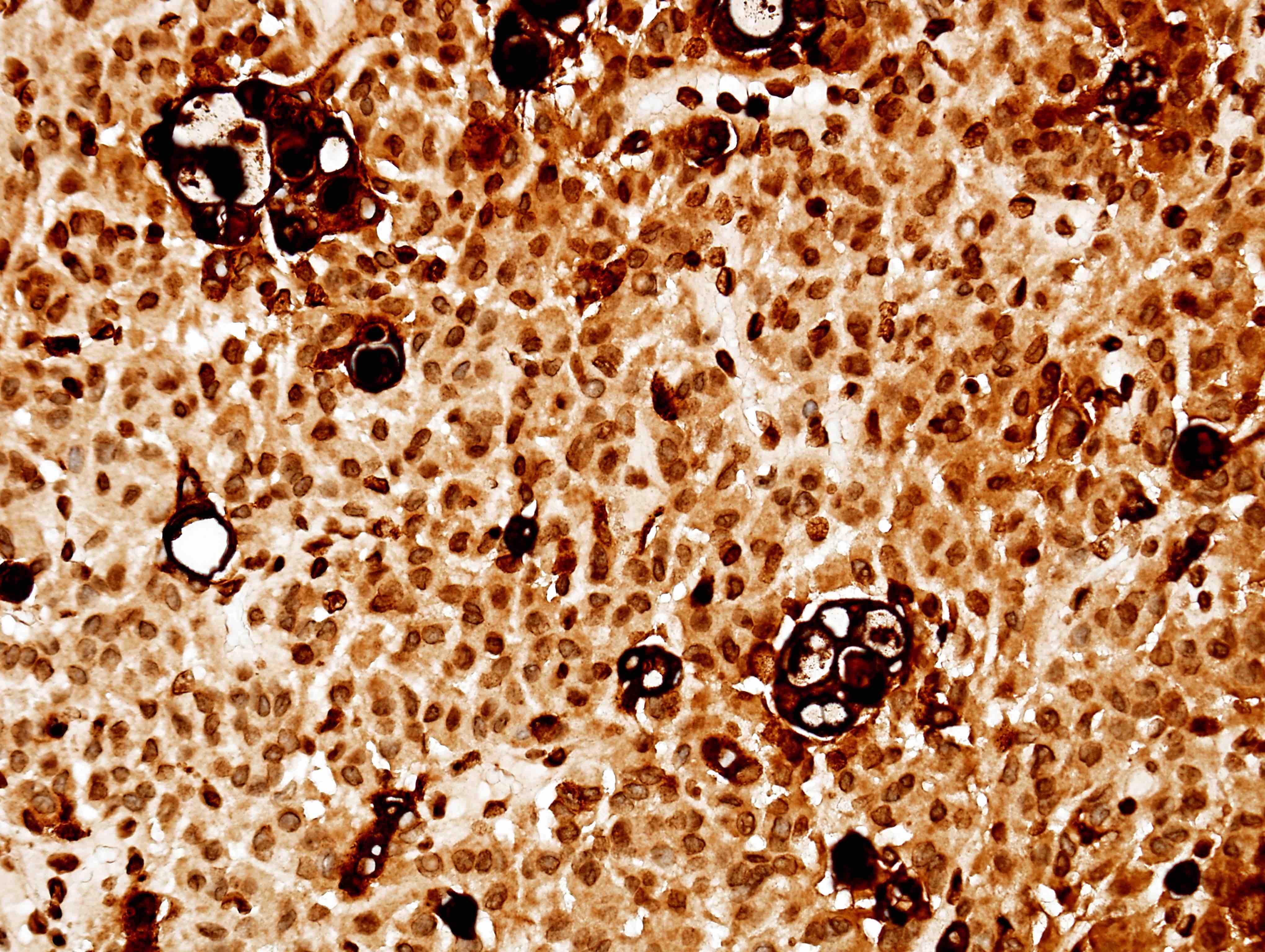
- Secretory:
- Eosinophilic round secretions (pseudopsammoma bodies) positive for CEA and PAS
- Genetically characterized by combined KLF4 and TRAF7 mutations (Acta Neuropathol 2013;125:351)
- Transitional:
- Mixed meningothelial and fibroblastic features
- Usually prominent whorls, psammoma bodies and clusters of syncytial cells
- NF2 mutated meningiomas are predominantly fibroblastic or transitional (Nat Genet 2013;45:285)
- Angiomatous:
- Grade 2 variants
- Grade 3 variants
- Upcoming 2021 WHO CNS tumor classification emphasizes that the criteria defining atypical or anaplastic (i.e. grade 2 and 3) meningioma should be applied regardless of the underlying subtype (Neuro Oncol 2021;23:1231)
Diagnosis
- Diagnose by imaging and pathology of biopsy / resection specimen
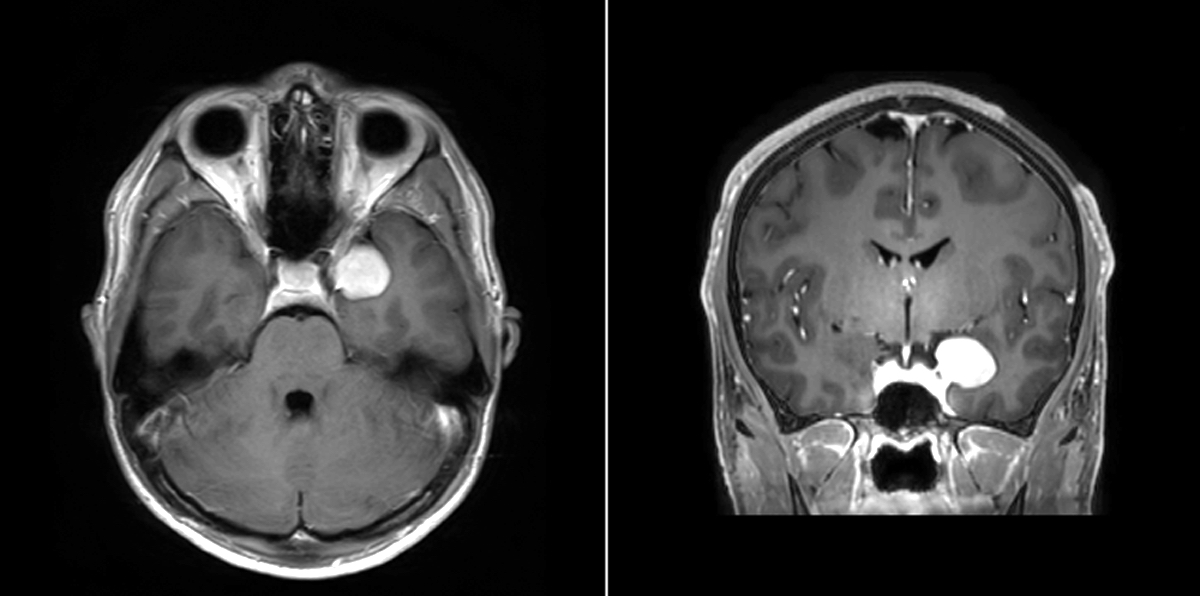
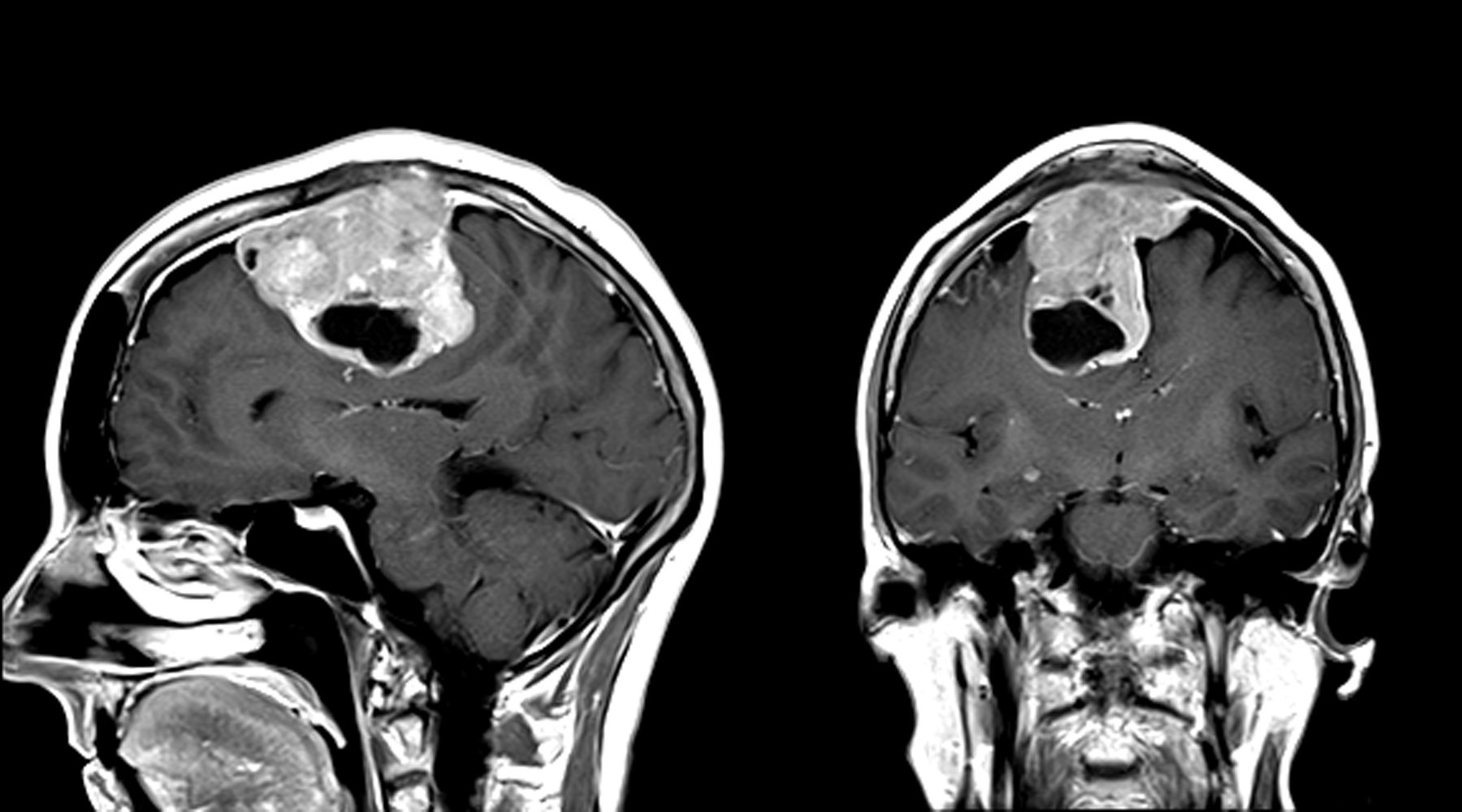
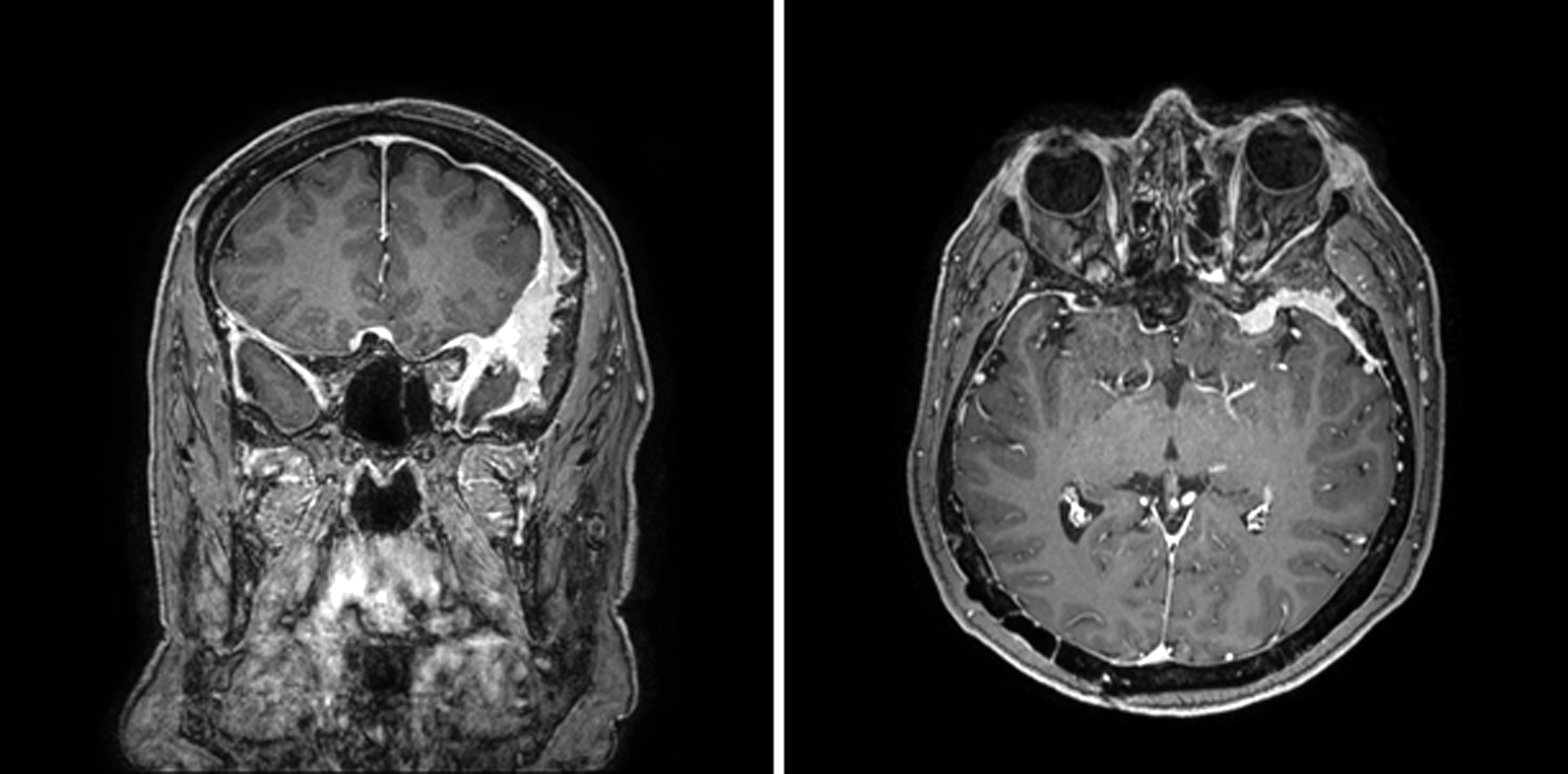
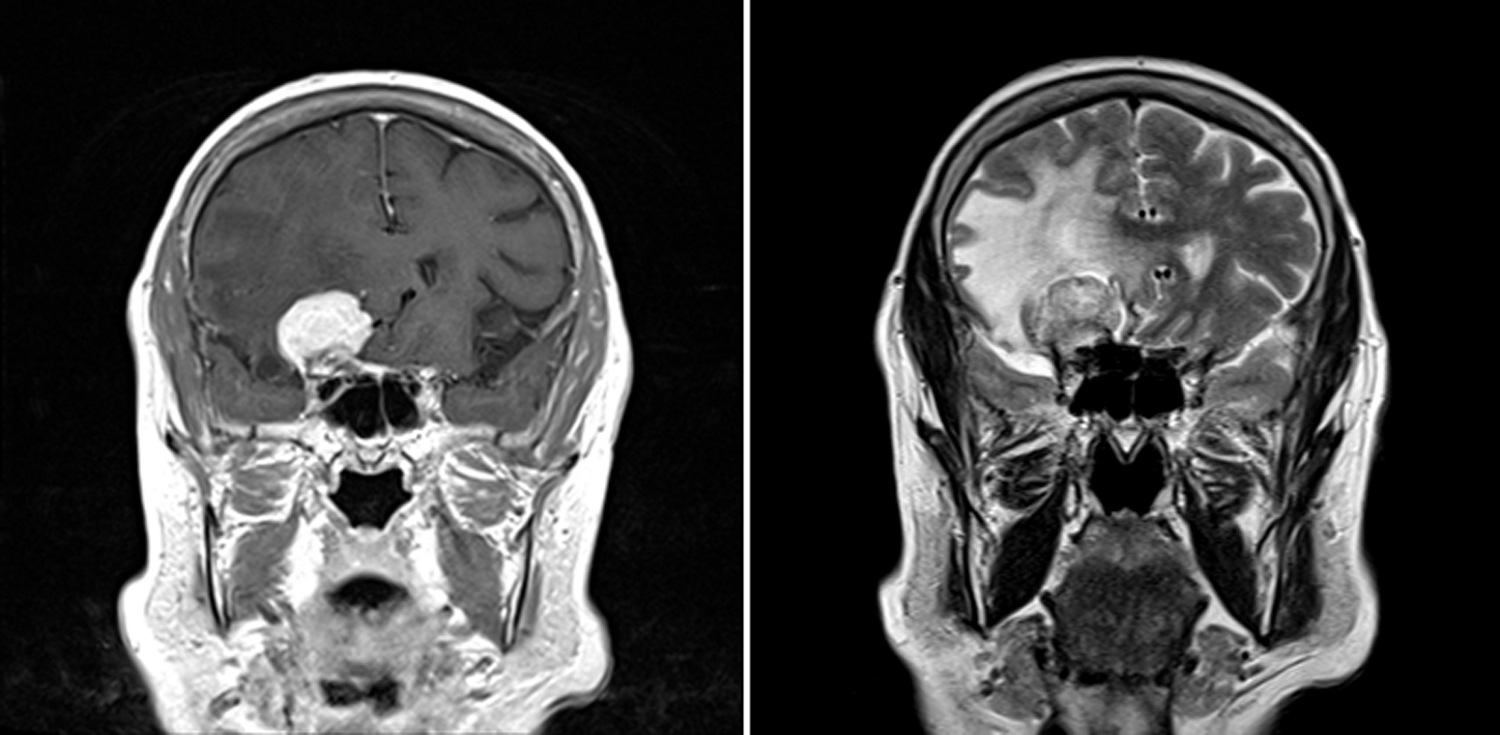
Radiology description
- Extra-axial mass with dural tail
- Uniformly contrast enhancing
- Extensive peritumoral edema is usually associated with brain invasion (Neuro Oncol 2021;23:324)
- With the caveat that several special grade I variants (angiomatous, microcystic, secretory and lymphoplasmacyte rich) can have prominent peritumoral edema (J Neurooncol 2013;111:49)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Extent of surgery and WHO grading (J Neurosurg 2015;122:4, Neuro Oncol 2016;18:863)
- Most recently, DNA methylation profiling is reported to better predict tumor recurrence and prognosis than the WHO histological classification (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:682)
- Recurrent losses of chromosome 1p, 6q, 14q, 18q and gain of 1q are indicators of poor prognosis (Acta Neuropathol 2017;133:431)
- Loss of H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) by IHC predicts poor prognosis in grade 1 and 2 meningiomas but not grade 3 (Acta Neuropathol 2018;135:955)
- TERT promoter mutation is seen in high grade meningioma progressed from low grade, not in primary atypical meningioma (Brain Pathol 2014;24:184)
Case reports
- 22 year old man with microcystic meningioma, WHO grade I (Case #104)
- 32 year old man with xanthomatous meningioma (Turk Neurosurg 2019;29:141)
- 36 year old man with lymphoplasmacyte rich meningioma (World J Clin Cases 2020;8:4272)
- 49 year old woman with dumbbell meningioma of the upper cervical spinal cord (J Orthop Sci 2013;18:1042)
- 52 year old woman with thoracic psammomatous meningioma with osseous metaplasia (World J Surg Oncol 2019;17:150)
- 56 year old man with angiomatous meningioma of orbit mimicking as malignant neoplasm (Orbit 2011;30:183)
- 61 year old man with left brain mass (Case #373)
Treatment
- Observation, if asymptomatic
- Gross total resection is usually curative
- Postoperative radiation if incompletely excised or WHO grade 2 or 3 (Neurosurg Focus 2015;38:E3)
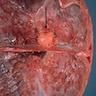
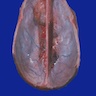
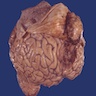
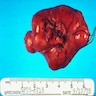
Gross description
- Rounded and well circumscribed
- Attached to dura
- Tumor separates readily from brain
- May grow en plaque (along dural surface) and cause reactive (hyperostotic) bone changes
- Reference: Perry: Practical Surgical Neuropathology - A Diagnostic Approach, 1st Edition, 2010
Gross images
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Arachnoid plane exists between meningioma and CNS parenchyma
- Histology varies by variant (see Grading)
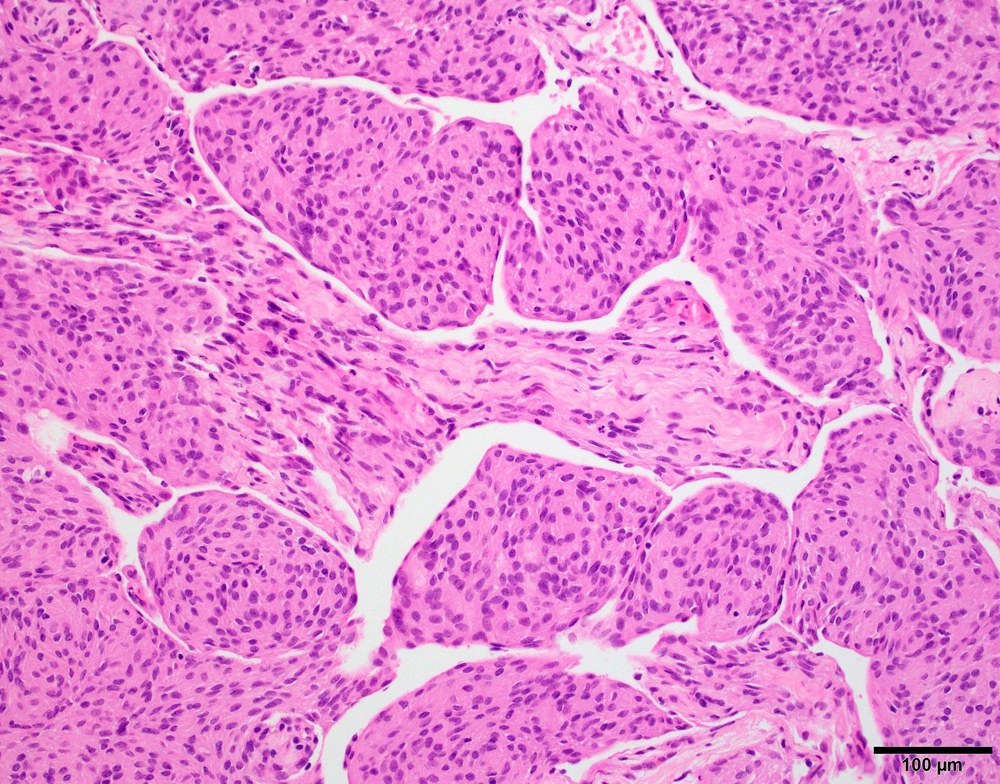
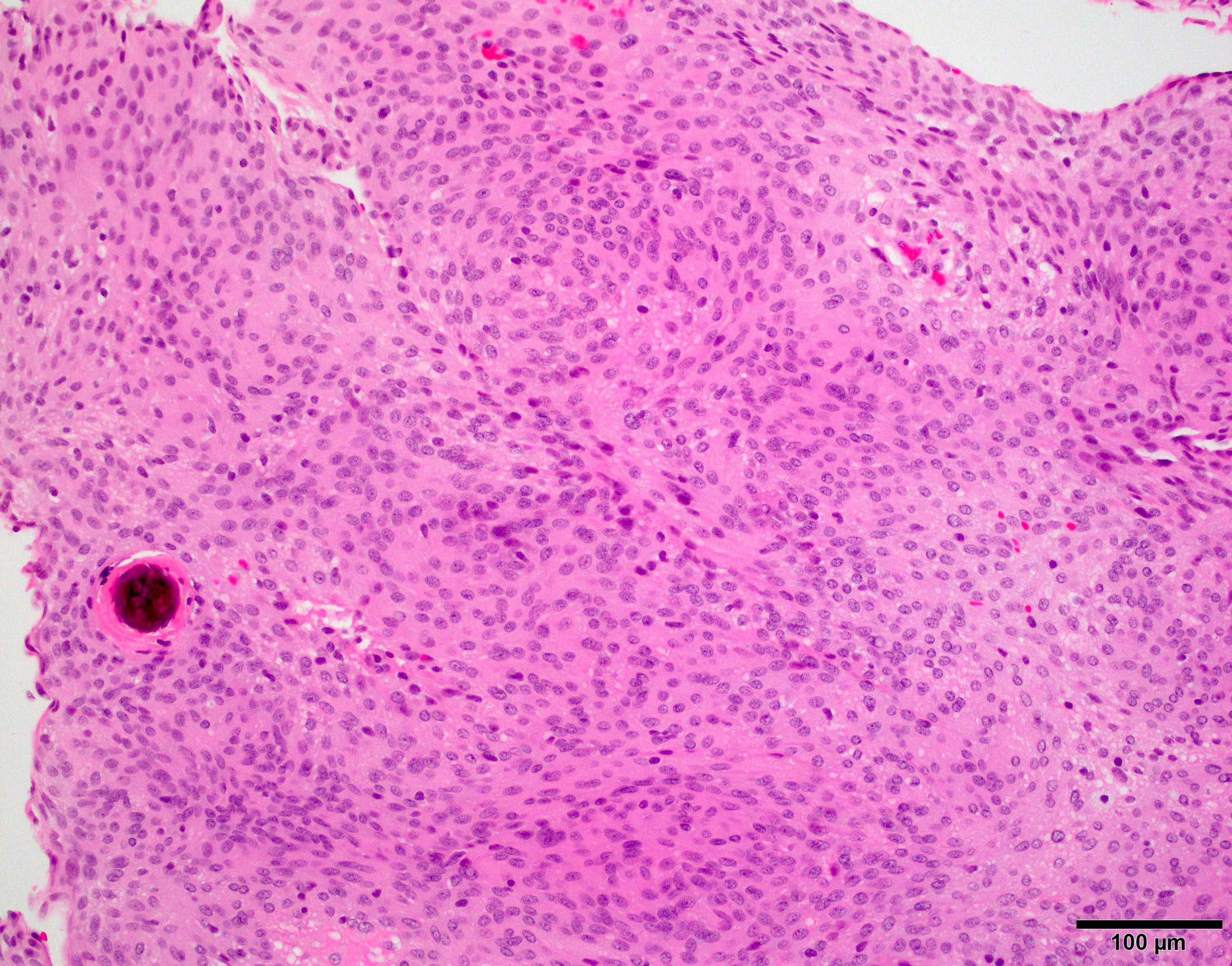
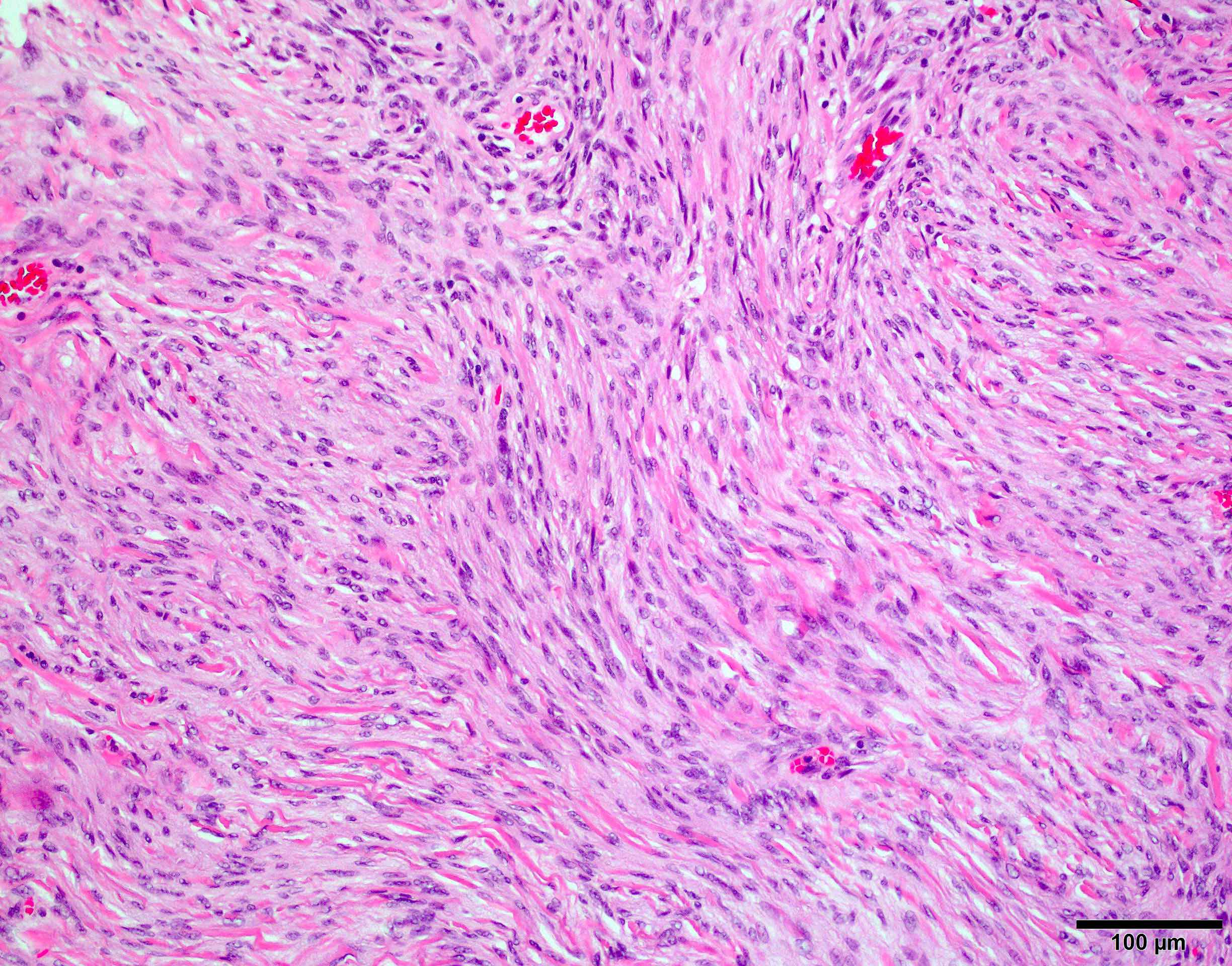
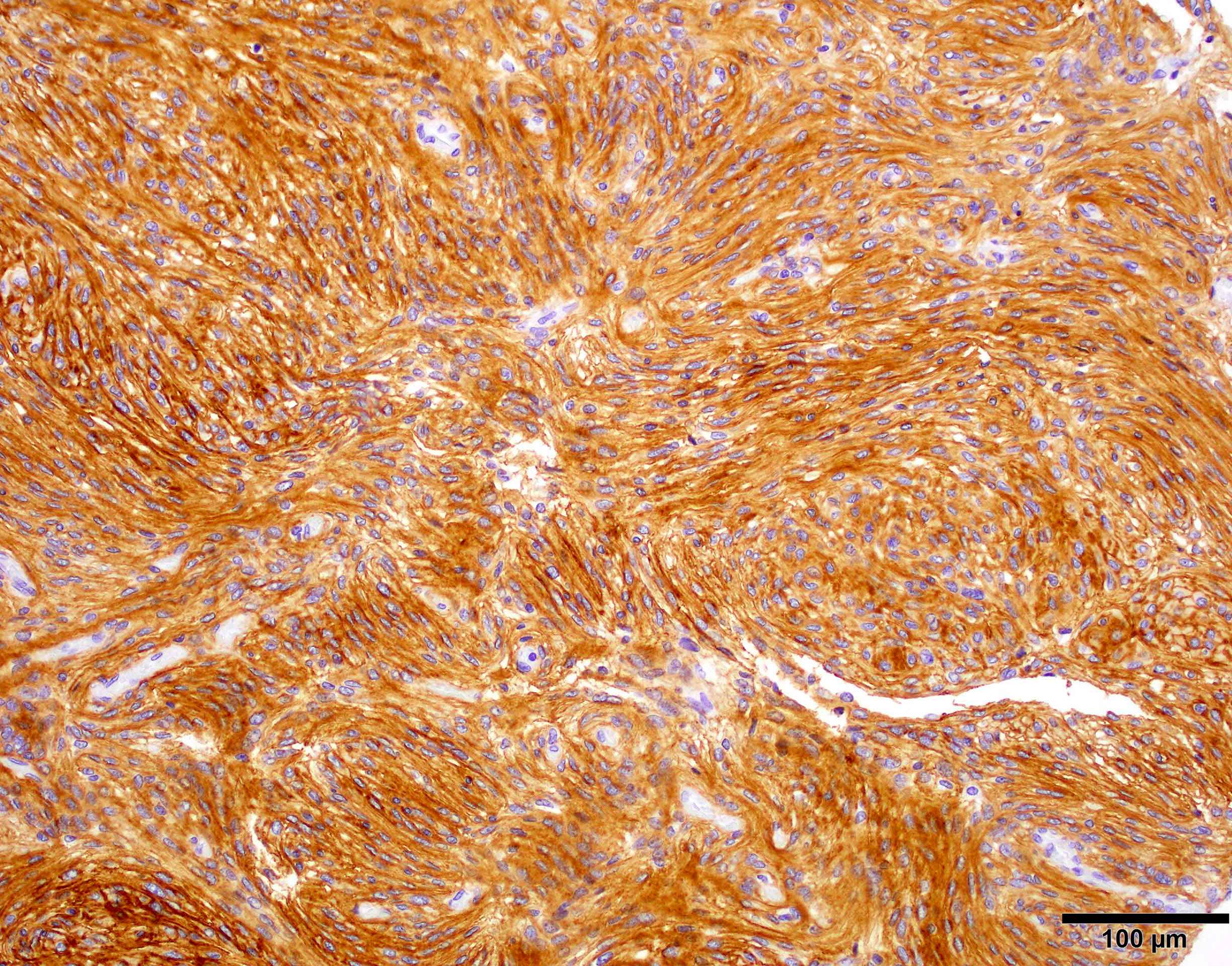
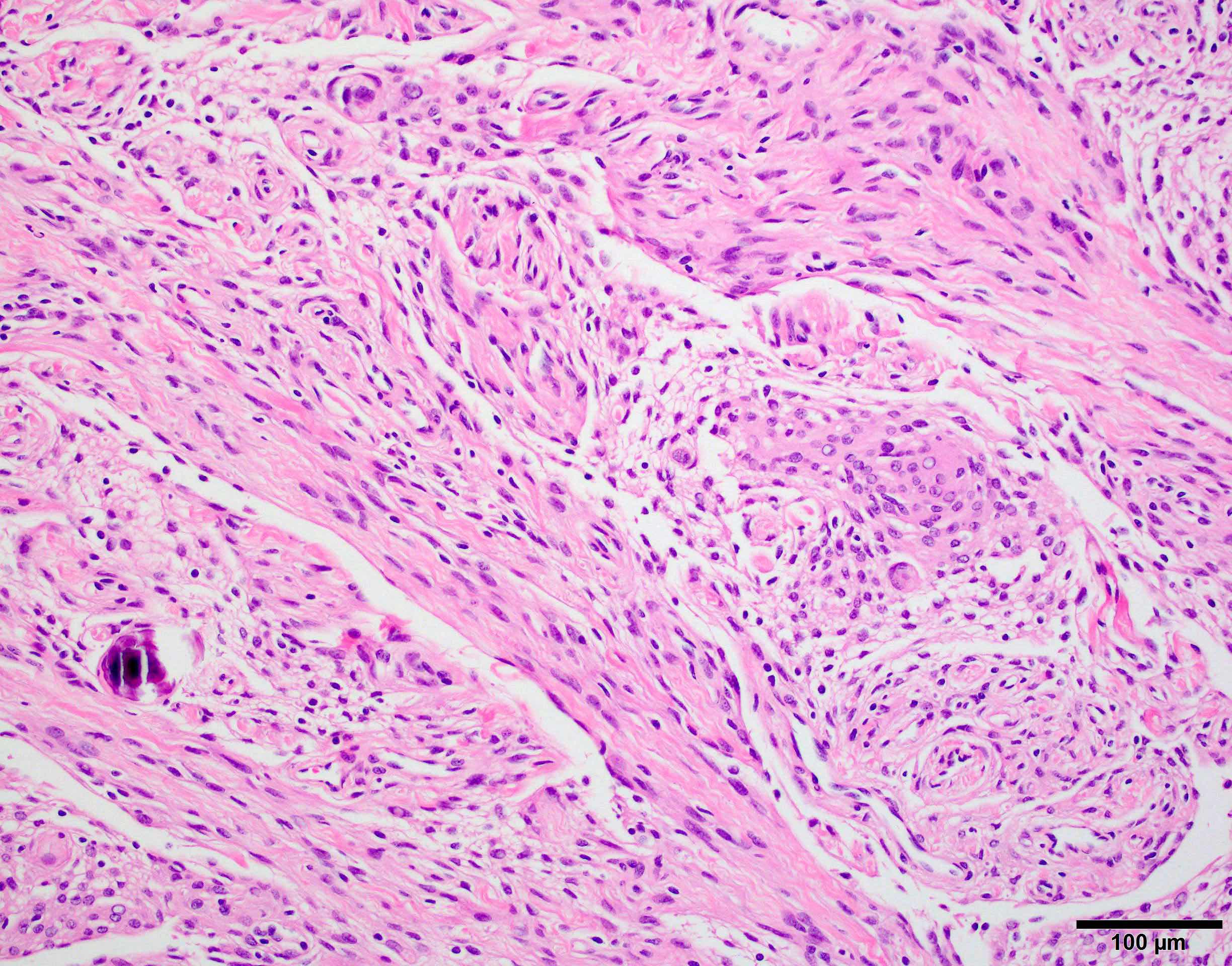
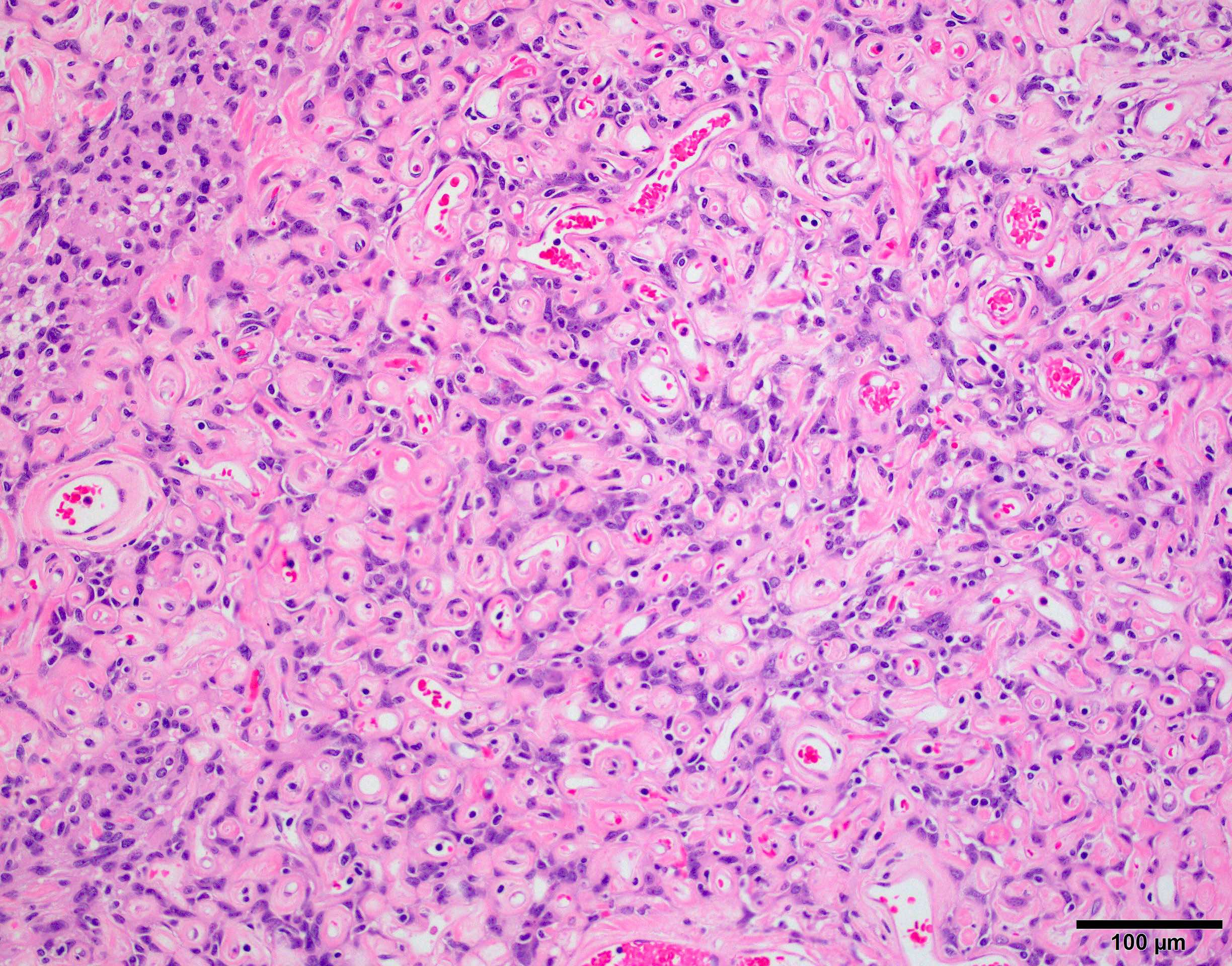
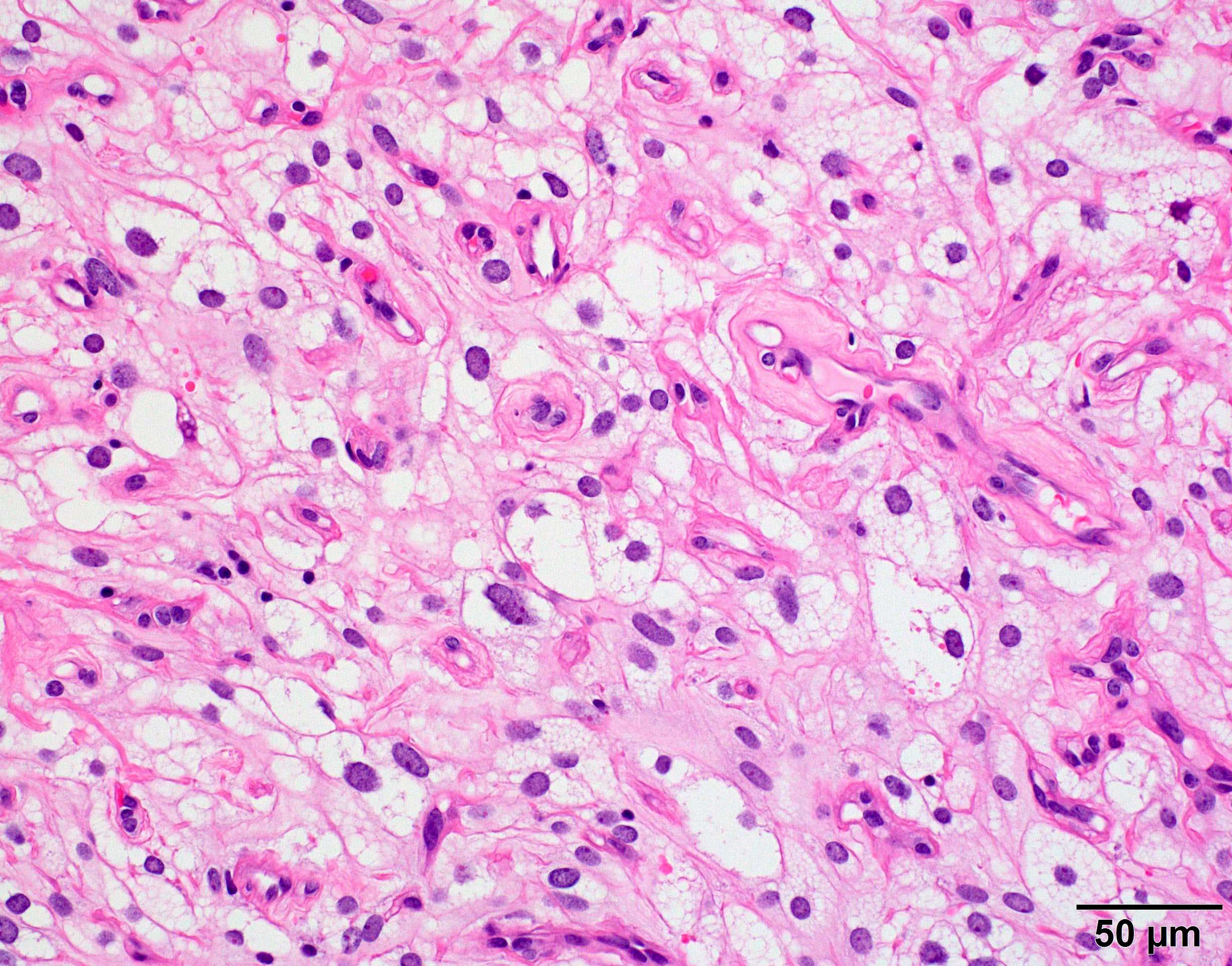
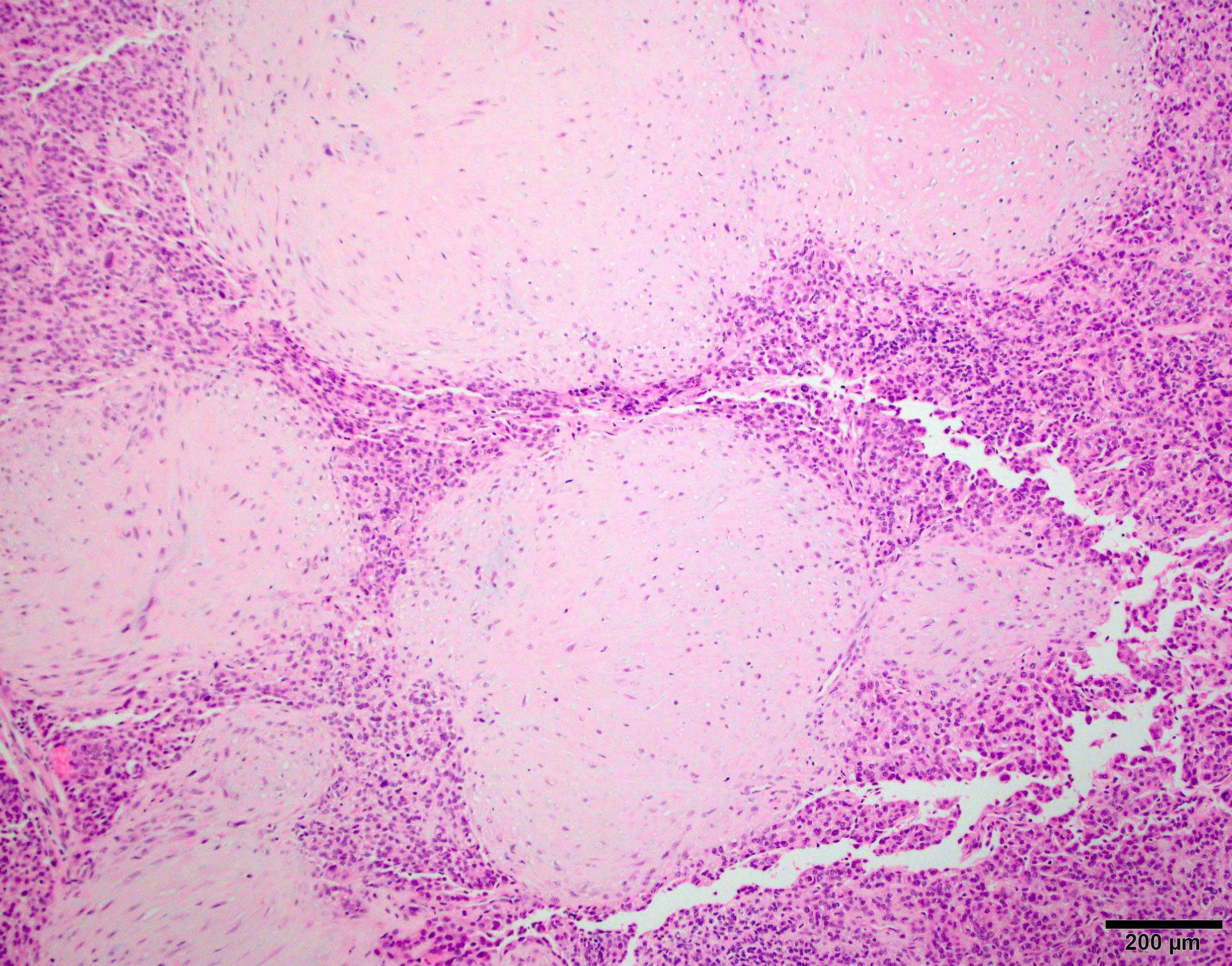
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Chunyu Cai, M.D., Ph.D.
Meningothelial meningioma:
Microcystic meningioma:
Lymphoplasmacyte rich meningioma:
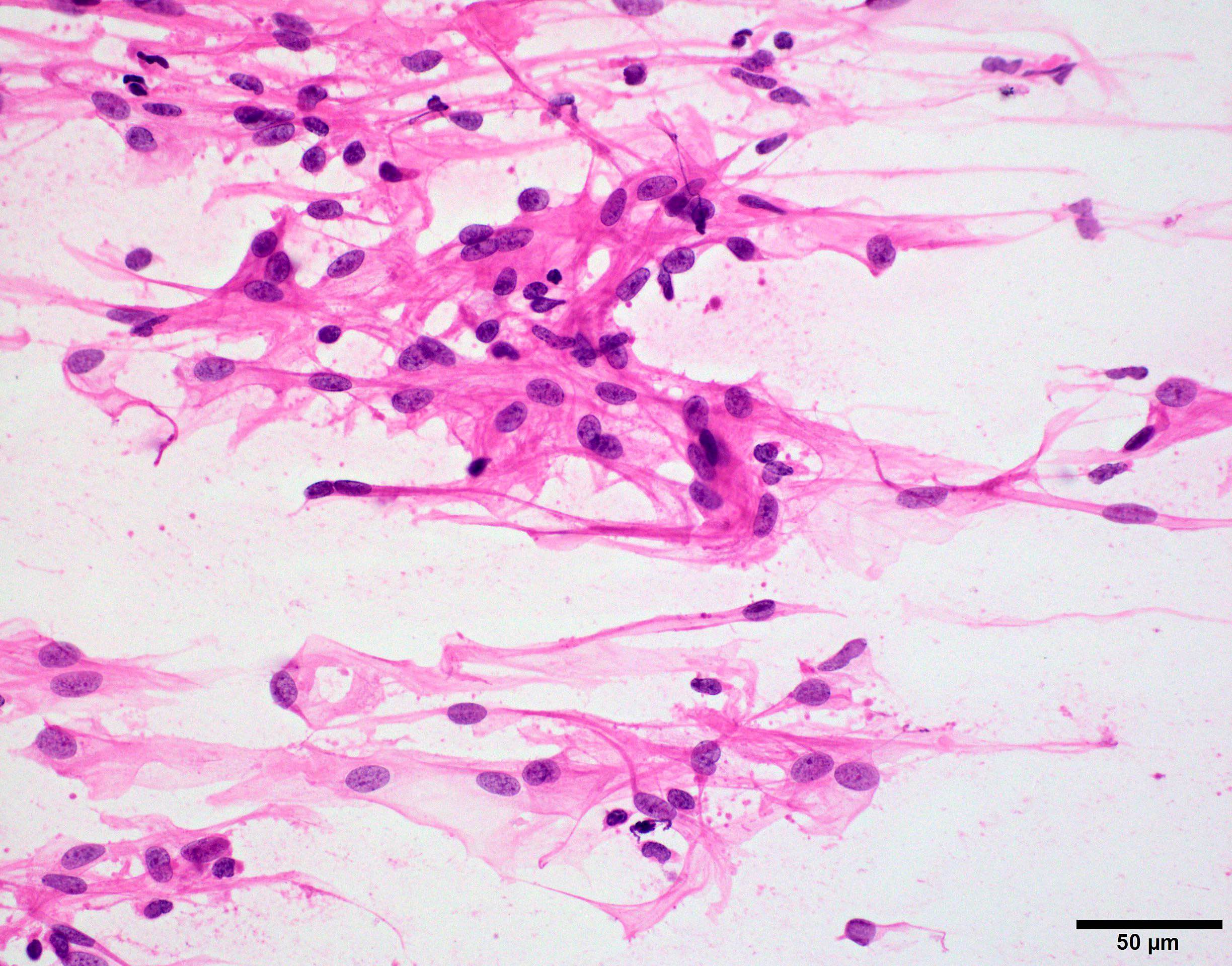
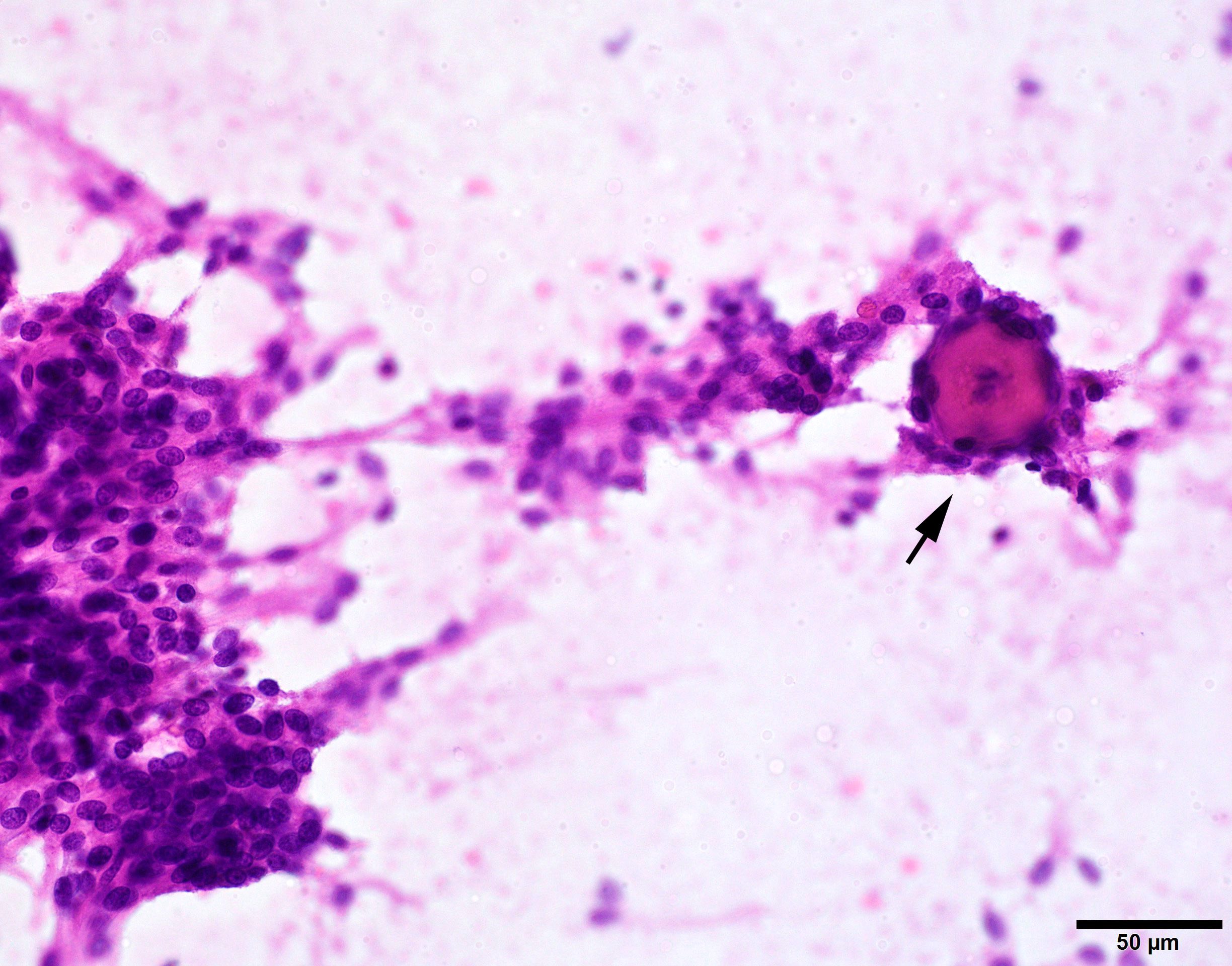
Cytology description
- Epithelioid cells with round to oval nuclei and streaked cytoplasm; may contain intranuclear pseudoinclusions
- Meningothelial nests or whorls and psammoma bodies are highly characteristic for meningioma on brain tumor crush preps (Burger: Smears and Frozen Sections in Surgical Neuropathology 1st Edition, 2009)
Cytology images
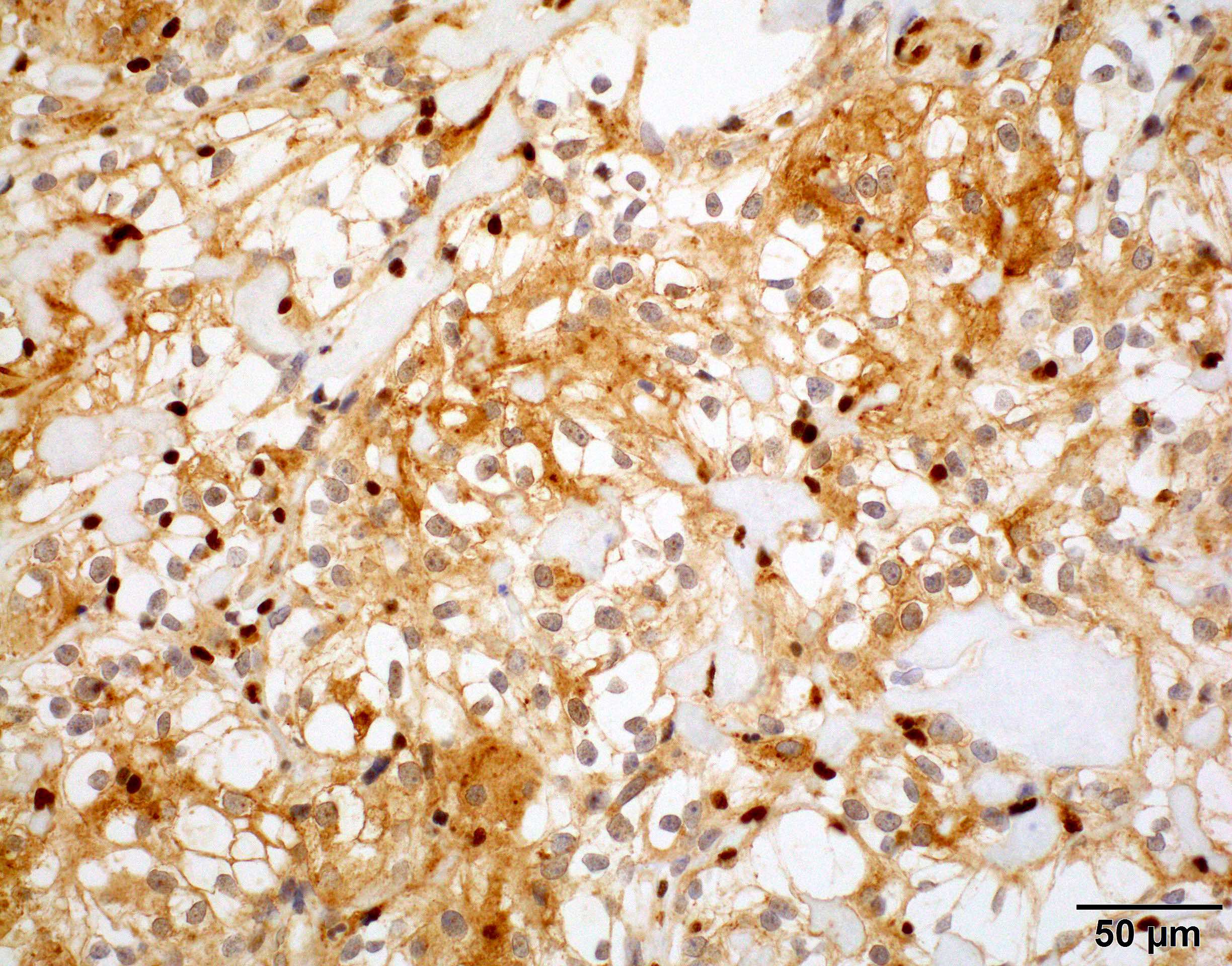
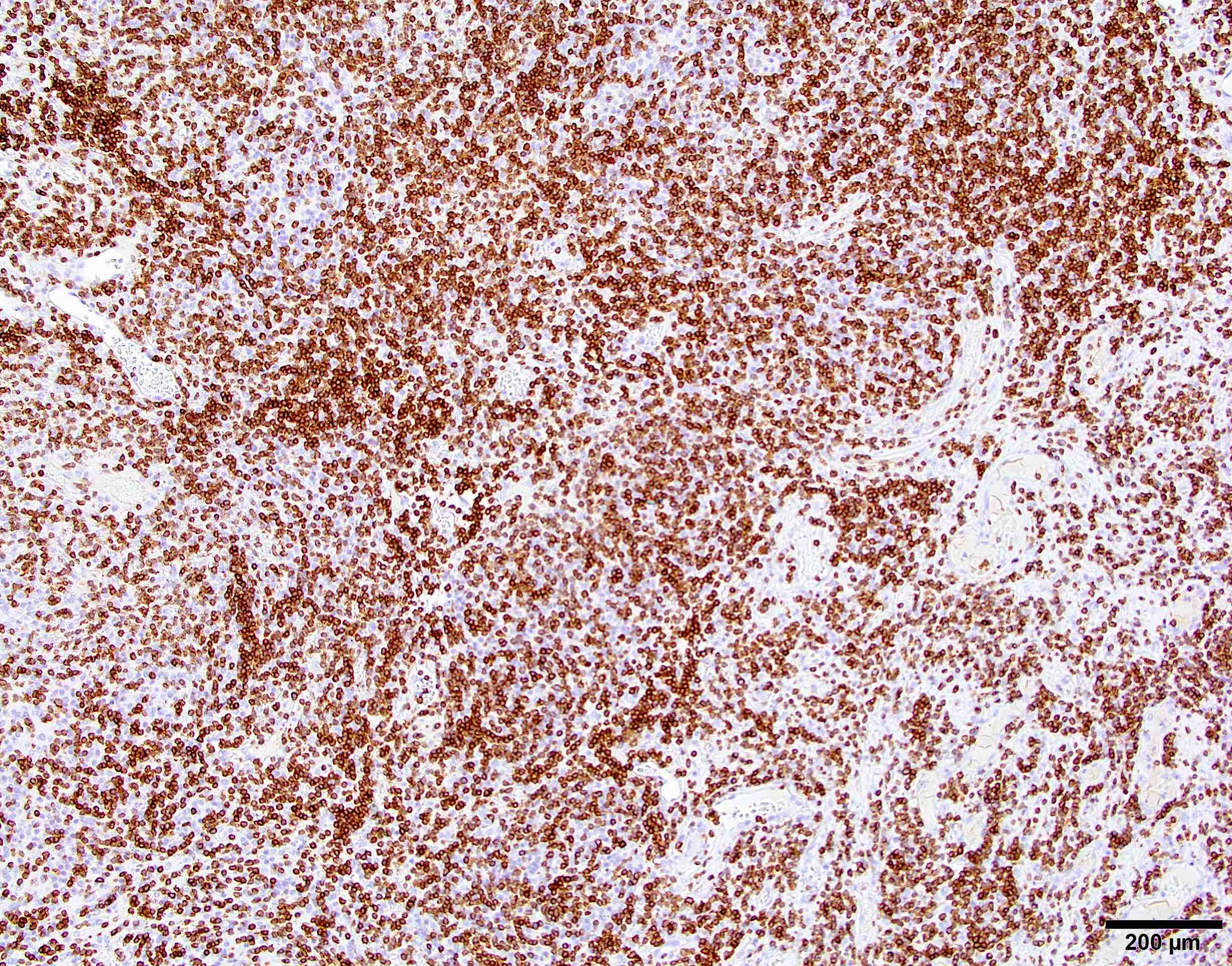
Positive stains
- Somatostatin receptor 2a (SSTR2a) is a specific meningioma marker in CNS tumors (Acta Neuropathol 2015;130:441, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- EMA: usually patchy, not diffuse
- Progesterone receptor: diffuse strong nuclear in low grade meningiomas and diminished in high grade meningiomas (J Clin Neurosci 2014;21:421)
Negative stains
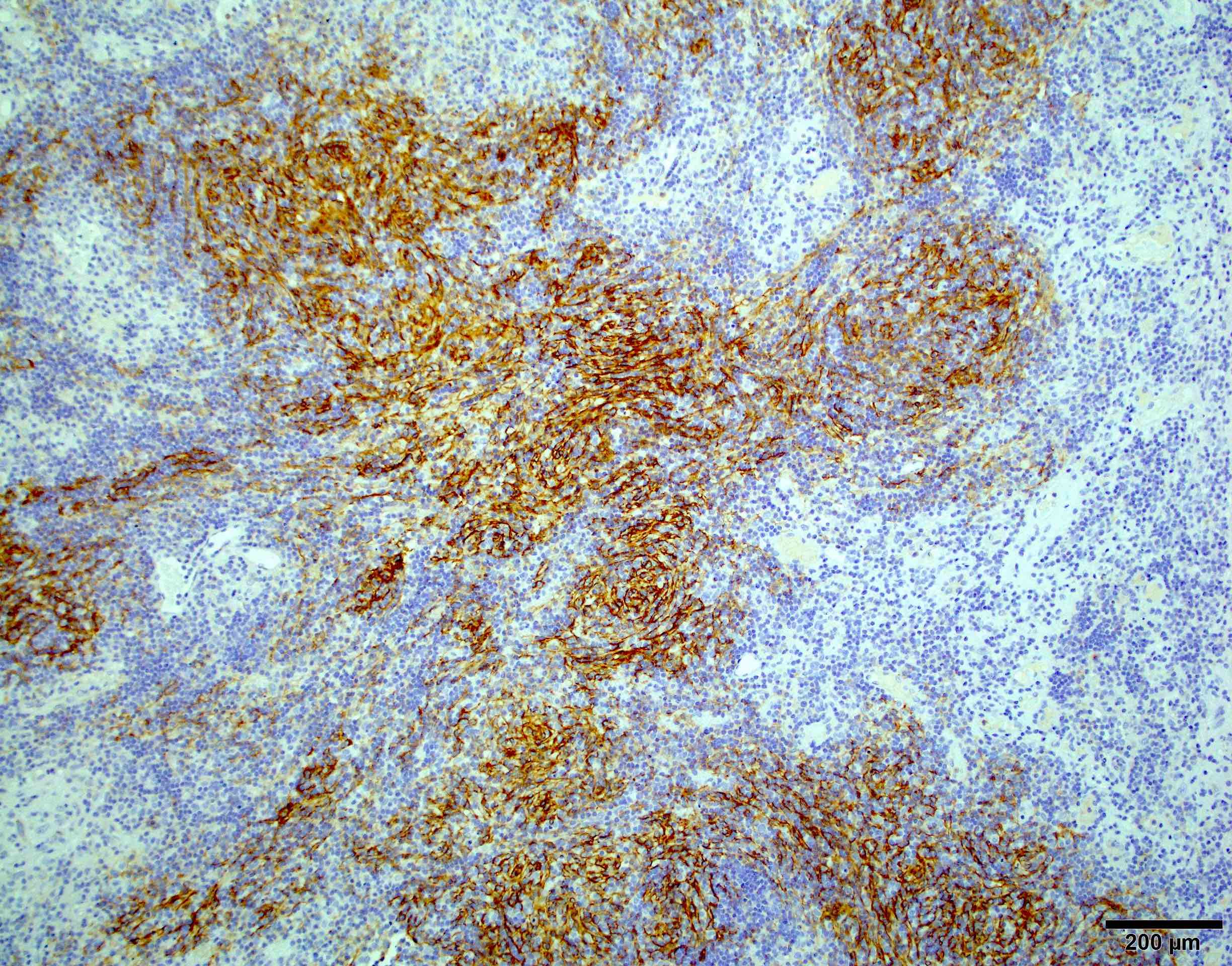
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP):
- Useful in highlighting entrapped brain in cases with brain invasion
- Differentiates chordoid meningioma (negative) from chordoid glioma (positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- Brachyury: differentiates chordoid meningioma (negative) from chordoma (positive) (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669)
- STAT6: useful to distinguish meningioma (negative) from solitary fibrous tumor / hemangiopericytoma (positive) (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1989;98:291)
- Inhibin: differentiates angiomatous or microcystic meningiomas (negative) from hemangioblastoma (positive) (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
- SOX10: differentiates fibrous meningioma (negative) from schwannomas (positive)
- S100 expression can be seen in ~33% of all meningiomas, particularly fibrous meningiomas (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2017;76:289)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Fibrous, transitional and psammomatous morphologies are associated with NF2 mutation, while meningothelial, secretory and microcystic variants are non-NF2 (Oncogene 2021;40:875)
- Majority of atypical meningiomas have loss of NF2 combined with either genome instability (large scale chromosomal alterations) or loss of SMARCB1 (Nat Commun 2017;8:14433)
- Non-NF2 meningiomas are enriched in mutations in TRAF2, KLF4, AKT1 and SMO, most of which are benign and preferentially located in the skull base (Science 2013;339:1077)
- Clear cell meningioma has been linked to SMARCE1 mutation (J Pathol 2014;234:436)
- Nearly 100% of secretory meningioma contain TRAF7 / KLF4 comutations, mutually exclusive to NF2 (Science 2013;339:1077)
- Angiomatous meningiomas contain multiple chromosome alterations, particularly gains of 5 and 20 (100% and 89%); blood vessels are nonneoplastic in origin (Oncotarget 2014;5:10596)
- DNA methylation profiling of meningioma distinguished 6 methylation classes (MCs) in adults, benign (ben) 1 - 3, intermediate (int) A and B and malignant (mal)
- DNA methylation based meningioma classification is reported to better predict tumor recurrence and prognosis than the WHO histological classification (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:682)
- Pediatric meningiomas are mostly associated with genetic syndromes or childhood radiation
- Global DNA methylation profile grouped separately from adult meningiomas and forms 3 groups: group 1 (clear cell and papillary meningiomas), 2A (enriched in NF2 driven high grade meningiomas) and 2B (enriched for rhabdoid, chordoid and other non-NF2 driven high grade meningiomas)
Videos
Molecular classification of meningioma
Sample pathology report
- Brain, inferior skull base mass (resection):
- Meningioma, transitional (WHO grade 1) (see comment)
- Comment: The tumor is a transitional meningioma. There is no evidence of necrosis, brain invasion, sheet-like growth or increased cellularity. There are no prominent nucleoli or small cells with a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio. Mitotic figures are not identified (0/10 high power fields). No brain is present for evaluation of brain invasion.
Differential diagnosis
- Meningothelial meningioma versus meningothelial hyperplasia:
- Meningothelial hyperplasia can be up to 100 cell layers thick and several millimeters in greatest dimension but has a discontinuous growth pattern and never invades dura (Brain Pathol 2005;15:109)
- Meningothelial meningioma is usually a single mass
- Fibrous meningioma versus solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) / hemangiopericytoma:
- Fibrous meningioma versus schwannoma:
- Intracranial myxoid neoplasms (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:669, Brain Pathol 2021;31:e12918):
- Chordoid meningioma: SSTR2a+, EMA+, S100-, GFAP-, brachyury-
- Chordoma: brachyury+, EMA+, S100-, SSTR2a-, GFAP-
- Chordoid glioma: intra-axial, near third ventricle, GFAP+, S100+, EMA+, SSTR2a-
- Chondrosarcoma: S100+, EMA-, brachyury-, GFAP-, SSTR2a-
- Intracranial myxoid mesenchymal tumors: EWS or FUS fusions+, S100+, EMA variable, GFAP-, SSTR2a-, brachyury-
- Clear cell meningioma versus microcystic meningioma / metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
- Clear cell meningioma: SSTR2a+, SMARCE1 loss, CA9-
- Microcystic meningioma: nuclear pleomorphism, SSTR2a+, CA9+, SMARCE1 retained (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2019;78:1081)
- Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: SSTR2a-, PAX8+, RCC+, CA9+ (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:422)
- Angiomatous meningioma and microcystic meningioma versus hemangioblastoma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. SSTR2a and STAT6. The image shows a low grade spindle cell neoplasm. Within the CNS, the main differential considerations are fibrous meningioma, solitary fibrous tumor / hemangiopericytoma and schwannoma. Schwannomas are more common in the cerebellopontine angle and spinal cord but not convexity, so the main differential diagnosis in this case is meningioma versus solitary fibrous tumor. Among the choices, SSTR2a is the most sensitive and specific marker for meningioma and STAT6 is the most sensitive and specific marker for solitary fibrous tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Meningioma
Comment Here
Reference: Meningioma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following typically low grade meningioma variants can have prominent peritumoral edema?
- Angiomatous, microcystic, meningothelial
- Psammomatous, secretory, fibrous
- Secretory, angiomatous, metaplastic
- Secretory, microcystic, lymphoplasmacyte rich
- Transitional, microcystic, meningothelial
Board review style answer #2
D. Secretory, microcystic, lymphoplasmacyte rich. The low grade meningioma variants that may have prominent peritumoral edema are secretory, angiomatous, microcystic and lymphoplasmacyte rich.
Comment Here
Reference: Meningioma
Comment Here
Reference: Meningioma