Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Lee M, Kulbiski A, Asadbeigi SN. Accessory tragi. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/earaccessorytragi.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Accessory tragus is a benign congenital anomaly of the external ear that often appears as a skin colored papule located in the preauricular region (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519)
Essential features
- Accessory tragi are usually located near the tragus
- May have associated renal (hydronephrosis, horseshoe kidney) and cardiac abnormalities and associations with some congenital syndromes
- Important distinguishing feature of accessory tragi is the presence of a cartilaginous core but this may not always be present
Terminology
- Heterotrophic tragi, supernumerary tragi (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Often inaccurately labeled as preauricular skin tags, accessory auricle, polyotia, rudimentary ear or supernumerary pinna (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Cervical tragus (if it is located on the neck) (Arch Surg 1982;117:968)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Congenital malformation (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- No sex predilection
- Most cases are sporadic but familial cases have been documented (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Estimated prevalence is 1.7:1,000 (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
Sites
- Accessory tragi are usually located near the tragus (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- May less commonly present on the cheek from tragus to angle of mouth, along the anterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, in the nasal vestibule, on the glabella or the suprasternal area (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
Pathophysiology
- Auricle is formed from fusions between the first and second branchial arches; accessory tragus results from incomplete fusion between the arches
- As the mandible grows, the auricle ascends from the lower lateral neck to the side of the head; therefore, accessory tragi may occur along this migratory line due to their origin from the mandibular branchial arch (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- During development, the auricle ascends from the lower lateral neck to the side of the head; accessory tragi may occur anywhere along this migratory line (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
Clinical features
- Usually unilateral but can be bilateral (6% of cases) or multiple (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519)
- May be pedunculated or sessile and soft or firm depending on presence of cartilage (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519, Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- Papule is typically 3 - 5 mm in size (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- May be covered in vellus hair (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- Can be associated with hearing impairments (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772, BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- May have associated renal (hydronephrosis, horseshoe kidney) and cardiac abnormalities (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Usually isolated; few reports on familial accessory tragi and cases with other associated anomalies of the first and second branchial arches
- Has associations with Delleman syndrome, Goldenhar syndrome, Haberland syndrome and Townes-Brocks syndrome, Treacher-Collins syndrome, VACTERL syndrome, Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome and Down syndrome (Int J Dermatol 2014;53:1442, BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- These associations are more common when there are multiple lesions
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is based off clinical presentation and patient history (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Histological evaluation can confirm clinical diagnosis (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
Prognostic factors
- Benign defect; excellent prognosis (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
Case reports
- 1 day old girl with accessory tragus located on nasal vestibule (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- 21 month old girl with accessory tragus in the middle ear (Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2010;74:1338)
- 3 year old boy with postauricular mass (Cureus 2021;13:e13645)
- 21 year old man with pedunculated cervical mass (Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 2022;34:121)
- 48 year old woman with trichofolliculoma mimicking accessory tragus (J Audiol Otol 2020;24:99)
Treatment
- Clinically insignificant; reassurance is reasonable (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Surgical excision can be performed for cosmesis or if local irritation occurs (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Incomplete surgical excision may leave an exposed cartilaginous fragment, potentially leading to chondrodermatitis (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Unclear guidelines on screening for hearing, renal and cardiac abnormalities (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
Gross description
- Sessile or pedunculated papule, often covered with fine hair
- 3 - 5 mm in size
- Smooth surface
- Soft or firm depending on amount of cartilage
- Skin colored
- Reference: Int J Dermatol 2014;53:1442
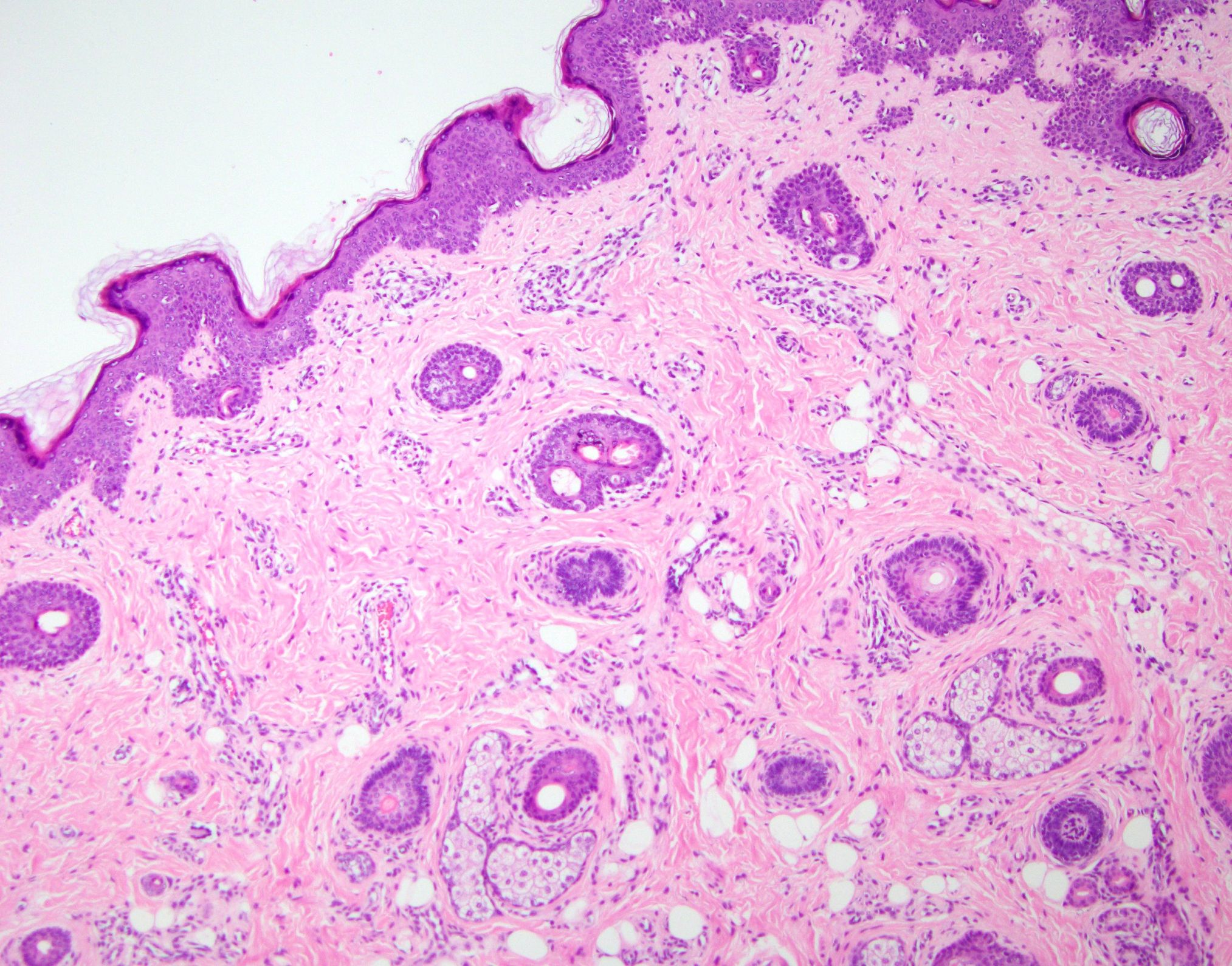
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mild orthokeratosis over the epidermis (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Prominent connective tissue structure in subcutaneous fat (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645, Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- Numerous vellus hair follicles and sebaceous glands present in the papillary dermis (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013008645)
- Fibrovascular tissue with fat lobules (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- May be sessile or pedunculated polyp (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
- With or without central cartilage surrounded by adipose tissue (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:61)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Sepideh Nikki Asadbeigi, M.D.
Videos
Dr. Michael Lee explains the major histological features of an accessory tragus
Sample pathology report
- Skin, left ear, excision:
- Accessory tragus (see comment)
- Microscopic description: The sections reveal a pedunculated lesion covered by slightly acanthotic epidermis. At the core of the lesion, there is fibroadipose mature tissue with some adnexal structures and a fragment of cartilage. Atypia was not identified.
Differential diagnosis
- Hair follicle nevus (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519)
- Connective tissue framework in subcutaneous fat and numerous hair follicles are found in both entities
- Accessory tragus is differentiated by the presence of more abundant subcutaneous adipose
- Potential presence of a cartilaginous component in accessory tragus will also help distinguish between them
- Location on the anterior ear is more suggestive of accessory tragus
- Trichofolliculoma (An Bras Dermatol 2015;90:519)
- Connective tissue framework in subcutaneous fat and numerous hair follicles are found in both entities
- Will contain a central cyst and radiating hair follicles
- Potential presence of a cartilaginous component in accessory tragus will also help distinguish between them
- Auricular fistulas (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Both may be present at birth
- These will usually present as depression or pits around the helix of ear, not a nodule anterior to the ear
- Congenital branchial cysts (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Both may be congenital
- These are located more commonly on upper lateral aspect of neck
- Congenital branchial cysts often grow slowly over time
- When excised, may drain clear or mucinous fluid mixed with granular cellular debris
- Epidermoid cysts (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Usually not congenital
- Can become inflamed or infected
- May express keratinized substance with cheesy consistency when excised
- True preauricular skin tag (Can Fam Physician 2012;58:772)
- Not present at birth
- Will never contain cartilage
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Presence of a cartilaginous core. An accessory tragus is characterized by the presence of a cartilaginous core, which is a remnant of the normal auricular cartilage. In contrast, a hair follicle nevus lacks a cartilaginous component. This histological distinction helps differentiate between the 2 entities but may not always be present in an accessory tragus. Answers B, C and D are incorrect because a dense connective tissue framework, sebaceous glands and well developed hair follicles can all be found in both entities.
Comment Here
Reference: Accessory tragi
Comment Here
Reference: Accessory tragi