Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | CPT coding | Sites | Laboratory | Case reports | Cytology description | Cytology images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Talibi S, Sayeed S. Liquid based cytology. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cytopathologyliquidbased.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Liquid based preparation (LBP): samples from various sources are collected or rinsed in a preservative solution; the cell suspension is then evenly distributed as a monolayer on a glass slide for examination
- The 2 most popular methods used today are ThinPrep (Hologic, Marlborough, Massachusetts) and SurePath (Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey)
Essential features
- LBP allows for easier processing, potential for automation (for cervical pap tests), fewer slides required per case and less screening time compared with conventional / direct smears
- Improvements in identification of morphologic features with less air drying artifact, improved nuclear and cytoplasmic details, reduction in background blood and inflammation and increased cellularity
- Familiarity with known pitfalls is needed: i.e., cell clusters / papillae are broken up, smaller cell size, more prominent nucleoli in benign conditions, lack of background mucin, necrosis or change in quality of background elements
CPT coding
- Gynecological:
- Nongynecological:
- 88112 - enriched / concentrated preparation (e.g., liquid based slide preparation: ThinPrep, SurePath)
- FNA:
- No specific separate charge
Sites
- Gynecological: cervix, vagina (Pap test)
- Body cavity fluids (pleural, peritoneal, pericardial)
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Gastrointestinal (GI): anal (Pap test), pancreas, bile duct, liver
- Genitourinary (GU): urethra, bladder, ileal conduit, renal pelvis, ureter
- Respiratory: bronchus, lung
- Hematologic: lymph nodes
- Head and neck: thyroid, salivary gland
- Breast
Laboratory
- Specimen collection:
- Collection medium: methanol based PreservCyt (for ThinPrep Hologic, Marlborough, Massachusetts) and CytoRich Red preservative fluid (SurePath Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey)
- Cervical or vaginal sample:
- ThinPrep: collection using Rovers Cervex-Brush Combi device (a green broom-like device with an integrated endocervical sampler), endocervical brush or spatula
- Following collection, the device is rinsed in the PreservCyt vial, then vigorously swirled before discarding
- SurePath: collection using broom-like devices (Rovers Cervex-Brush Device and Rovers Cervex-Brush Combi Device), endocervical brush or spatula
- Following collection, the device is placed in the vial; the device head is pulled or snapped off and remains in the vial
- ThinPrep: collection using Rovers Cervex-Brush Combi device (a green broom-like device with an integrated endocervical sampler), endocervical brush or spatula
- Anal sample:
- ThinPrep: using moistened Dacron swab or cytobrush to collect sample, rotate in collection medium, then vigorously swirl device before discarding
- SurePath: using moistened swab collect sample, place in SurePath vial; the device head remains in the vial
- Brushing (bronchial, bile duct): rinse device into collection medium
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) sample: collect needle rinse / aspiration material directly into collection medium
- Specimen processing:
- SurePath:
- Sample is vortexed then passed through a small opening using a syringe device (causing disaggregation)
- Sample is poured into a centrifuge tube with a density gradient reagent
- Specimen is centrifuged and the pellet is resuspended; this step is repeated 5 times
- Tubes are then transferred to the PrepStain instrument
- Robotic arm transfers the fluid into a cylinder, the cells settle into a cationic polyelectrolyte coated slide, a 13 mm diameter deposit is made
- Staining is performed in the same instrument using the robotic arm
- ThinPrep:
- Vial is placed on a stage and a plastic cylinder with a 20 mm diameter; a polycarbonate filter is bonded to the surface and is inserted on top of the vial
- Rotor spins the cylinder, dispersing the cells, then a vacuum is applied to the cylinder to trap the cells onto the filter
- Instrument monitors the cell density on the filter; once a threshold is reached, the cylinder with the attached filter is inverted 180 degrees
- Filter is pressed on to a glass slide, creating a 20 mm diameter deposit
- Slide is immediately dropped into an alcohol bath
- Staining is performed in a separate device
- SurePath:
- Advantages (compared with conventional smear technique):
- General (Diagn Cytopathol 2013;41:257):
- Standardization of processing
- Minimal air drying artifact from immediate fixation
- Compatible with automated screening devices
- Allows batch processing
- Residual sample can be used for additional testing (human papillomavirus [HPV], Neisseria gonorrhoeae [GC], chlamydia, cell block, florescent in situ hybridization [FISH], molecular testing)
- Uniform distribution of cells in a monolayer with less overlap
- Lower rate of unsatisfactory samples
- Minimal cell loss
- Less screening time
- Reduction in inflammation or blood in background
- Useful when onsite evaluation is unavailable
- SurePath:
- Staining step included in processing
- Better reduction in background blood
- ThinPrep:
- T5000 processor allows for 20 samples to be processed at once
- Fully automated, hands free process
- Less operator training required
- General (Diagn Cytopathol 2013;41:257):
- Disadvantages:
- General:
- Does not allow for real time adequacy assessment
- Some ancillary tests cannot be performed: microbial culture, flow cytometry
- SurePath:
- More manual steps (centrifugation steps)
- More operator training required
- Cells have a more 3 dimensional distribution
- ThinPrep:
- Staining performed separately
- More collection training required to prevent unsatisfactory sample collection (cervical, vaginal and anal samples)
- Excess blood may be present
- Loss of background material needed for diagnosis
- General:
Case reports
- 32 year old woman with placental site nodule misinterpreted as a low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (Case Rep Oncol 2020;13:1415)
- 57 year old woman with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix (Cytojournal 2017;14:28)
- 58 year old man with pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma arising in the anterior mediastinal tumor (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:333)
- 65 year old man with a history of Merkle cell carcinoma presents with pleural effusions post COVID-19 pneumonia (Diagn Cytopathol 2022;50:E37)
- 73 year old man with diffuse large B cell lymphoma with cryptococcal meningitis, ThinPrep of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (J Pathol Transl Med 2018;52:61)
Cytology description
- General features of LBP compared with conventional / direct smears (Diagn Cytopathol 2007;35:621, Diagn Cytopathol 2013;41:257):
- Fragmentation of cell groups (clusters, papillary structures)
- Smaller cells and nuclei
- More discohesive cells
- Loss of background material (necrosis, blood, inflammation, mucin, colloid)
- Retention of blood (in ThinPrep)
- Artifactual aggregation of lymphoid cells
- Prominent nucleoli in benign / reactive conditions
- Site specific features:
- Gynecological (cervix, vagina)
- Compared with conventional pap smears:
- Cells and their nuclei are smaller
- Potentially less hyperchromatic
- Nucleoli may be more visible
- Background elements may appear different or cling to cells (DeMay: The Art and Science of Cytopathology, 2nd Edition, 2011)
- Improved detection of LSIL (CIN 1) but no significant difference in detection of HSIL (CIN 2 / CIN 3) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:200, JAMA 2009;302:1757, Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:167)
- Equivalent for detection of endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ and endometrial pathology (Cancer 2007;111:482, Diagn Cytopathol 2000;23:260)
- Decreased number of unsatisfactory specimens (Acta Cytol 1998;42:189)
- In 2020, FDA approval of primary HPV testing using Cobas 6800 / 8800 systems manufactured by Roche (Basel, Switzerland)
- Standardized reporting system and adequacy assessment: The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology (Nayar: The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology - Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes, 3rd Edition, 2015)
- Compared with conventional pap smears:
- Body cavity fluids (pleural, peritoneal, pericardial)
- In effusions, cells "round up"
- Blood is less likely to obscure cells
- High cellularity and discohesive pattern
- ThinPrep for pleural effusions: similar to cytospin Diff-Quik stained for distinguishing mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma (key features seen in both) (Diagn Cytopathol 2005;32:137)
- College of American Pathologist (CAP) interlaboratory comparison program: highest diagnostic concordance rate was seen with ThinPrep slides and the lowest was with conventional smears (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:53)
- Exception: pericardial fluids, which had the highest concordance rates with SurePath (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:53)
- Standardized reporting system: The International System for Serous Fluid Cytopathology (Chandra: The International System for Serous Fluid Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2020)
- CSF
- General features of liquid based preparation compared with cytospin method (Cytopathology 2019;30:236)
- Clear background
- Enhanced cell enhancement
- Better nuclear details
- Higher cellularity per slide
- General features of liquid based preparation compared with cytospin method (Cytopathology 2019;30:236)
- GI (anal, bile duct, pancreas, liver)
- Anal pap test
- Liquid based preparation and conventional smears yield comparable results (Diagn Cytopathol 2014;42:840)
- Standardized reporting system: The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology (Nayar: The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology - Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes, 3rd Edition, 2015)
- Bile duct brushing
- Nuclear atypia-like conventional smear but with enhanced preservation of the nuclear features and greater 3 dimensional architecture (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:1116)
- Pancreatic FNA
- General features of liquid based preparation compared with conventional smears (Diagn Cytopathol 2004;30:71):
- Smaller cell clusters, more single cells
- Lack of background mucin - potential to under call mucinous neoplasms
- Nucleoli more conspicuous in benign cells - potential to overcall as atypical
- SurePath showed superior accuracy and sensitivity for malignant pancreatic lesions compared with conventional smears in the absence of rapid onsite evaluation (Endosc Int Open 2020;8:E1611)
- ThinPrep has a higher sensitivity in detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma for samples obtained by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), with better preservation and cytological detail (Diagn Cytopathol 2005;32:70)
- Standardized reporting system: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Pancreaticobiliary Cytology (Pitman: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology System for Reporting Pancreaticobiliary Cytology - Definitions, Criteria and Explanatory Notes, 2015 Edition, 2015)
- General features of liquid based preparation compared with conventional smears (Diagn Cytopathol 2004;30:71):
- Anal pap test
- GU (urine, bladder washing, ileal conduit)
- Morphologic features of high grade urothelial carcinoma (HGUC) cells appear to be similar in samples prepared using ThinPrep and cytospin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts) methods (Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:119)
- N/C ratio is preserved between both methods for HGUC; slightly more hyperchromasia in ThinPrep (Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:119)
- The Paris System appears valid for ThinPrep (Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:119)
- Standardized reporting system: The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology (Rosenthal: The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology, 1st Edition, 2016)
- Respiratory (bronchial wash, bronchial brush, bronchoalveolar lavage [BAL], sputum, FNA)
- Reduction of mucus, inflammation and blood
- Nuclear details are more preserved (Diagn Cytopathol 2008;36:167)
- Background may be clumped
- Morphology of microorganisms may be similar to conventional smears
- More uniform, dispersed cells
- Small cell carcinoma (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;29:8)
- Decreased, more subtle nuclear molding
- Less prominent nuclear smearing
- More noticeable amount of cytoplasm
- Diagnosis of lung tumors using ThinPrep may be improved compared with direct smears when evaluating small cell carcinoma (Surg Oncol 2006;15:173, Diagn Cytopathol 2003;29:8)
- Hematologic (lymph nodes)
- Compared with conventional smears liquid based cytology features:
- Lack of background material including necrosis, may be a disadvantage
- Comparison of SurePath and conventional smears showed no difference in cellularity or presence of monolayer sheets; better nuclear and cytoplasmic details were seen (J Cytol 2016;33:187)
- In thyroid lymphoma specimens, larger nuclei in > 10% lymphoid cells, elongated nuclei and swollen, naked nuclei helped to distinguish thyroid primary lymph from benign lymphoid cells (Acta Cytol 2018;62:93)
- Increased sensitivity for metastatic malignancy in cervical lymphadenopathy (Diagn Cytopathol 2016;44:169)
- Use of ThinPrep slides for grading of follicular lymphoma in FNA samples - counting centroblasts improved due to better fixation, improved nuclear morphology, clean background, random distribution of cells allowing of nonbiased counting (Cancer 2006;108:319)
- Compared with conventional smears liquid based cytology features:
- Head and neck (thyroid, salivary gland)
- Thyroid
- Compared with conventional smears:
- Similar accuracy for thyroid neoplasms (Am J Clin Pathol 1995;104:150, Cancer 1998;84:17)
- Superior nuclear features
- Follicles and papillary fragments may be more fragmented; follicular cells usually present in groups, single cells and sheets
- ThinPrep may have lower accuracy for detecting chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (62% compared with 92% on direct smear) (Cancer 1998;84:17)
- Less detection of diffuse or watery colloid (Am J Clin Pathol 1995;104:150, Cancer 2001;93:179)
- Watery colloid may be present as tissue paper-like material (Diagn Cytopathol 2004;30:7)
- Standardized reporting system: The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (Ali: The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology - Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes, 2nd Edition, 2018)
- Compared with conventional smears:
- Salivary gland
- ThinPrep compared with conventional smears (Acta Cytol 2014;58:552):
- Normal acinar groups: intact cytoplasm, no bare nuclei
- Minimal to no cellular debris (extracellular mucin)
- Difficult to evaluate nuclear detail of different lymphocytes due to smaller cell size
- Smaller, less complex groups of epithelial cells
- More background cells (epithelial and myoepithelial)
- Decrease quantity and quality of matrix / stroma - loose stroma appears as porous, moth eaten leaves
- ThinPrep compared with conventional smears (Acta Cytol 2014;58:552):
- Standardized reporting system: The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology (Faquin: The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology, 1st Edition, 2018)
- Thyroid
- Breast
- Conventional smears limited by drying artifact while ThinPrep aspirates of carcinomas show better nuclear detail and greater cellularity (Diagn Cytopathol 1999;21:137)
- ThinPrep of benign masses show greater epithelial cellularity, better nuclear detail and more specimens with myoepithelial cells (Diagn Cytopathol 1999;21:137)
- Pitfalls reported in ThinPrep compared with conventional smears (Diagn Cytopathol 2017;45:655):
- Fibroadenoma: bipolar cells can appear singly dispersed with preserved cytoplasm, resembling carcinoma
- Solid papillary carcinoma: singly dispersed cells with plasmacytoid features that mimic lobular carcinoma
- More prominent nucleoli and cytological atypia - potential for overcall
- Clumping of epithelioid histiocytes that may be interpreted as atypical
- Gynecological (cervix, vagina)
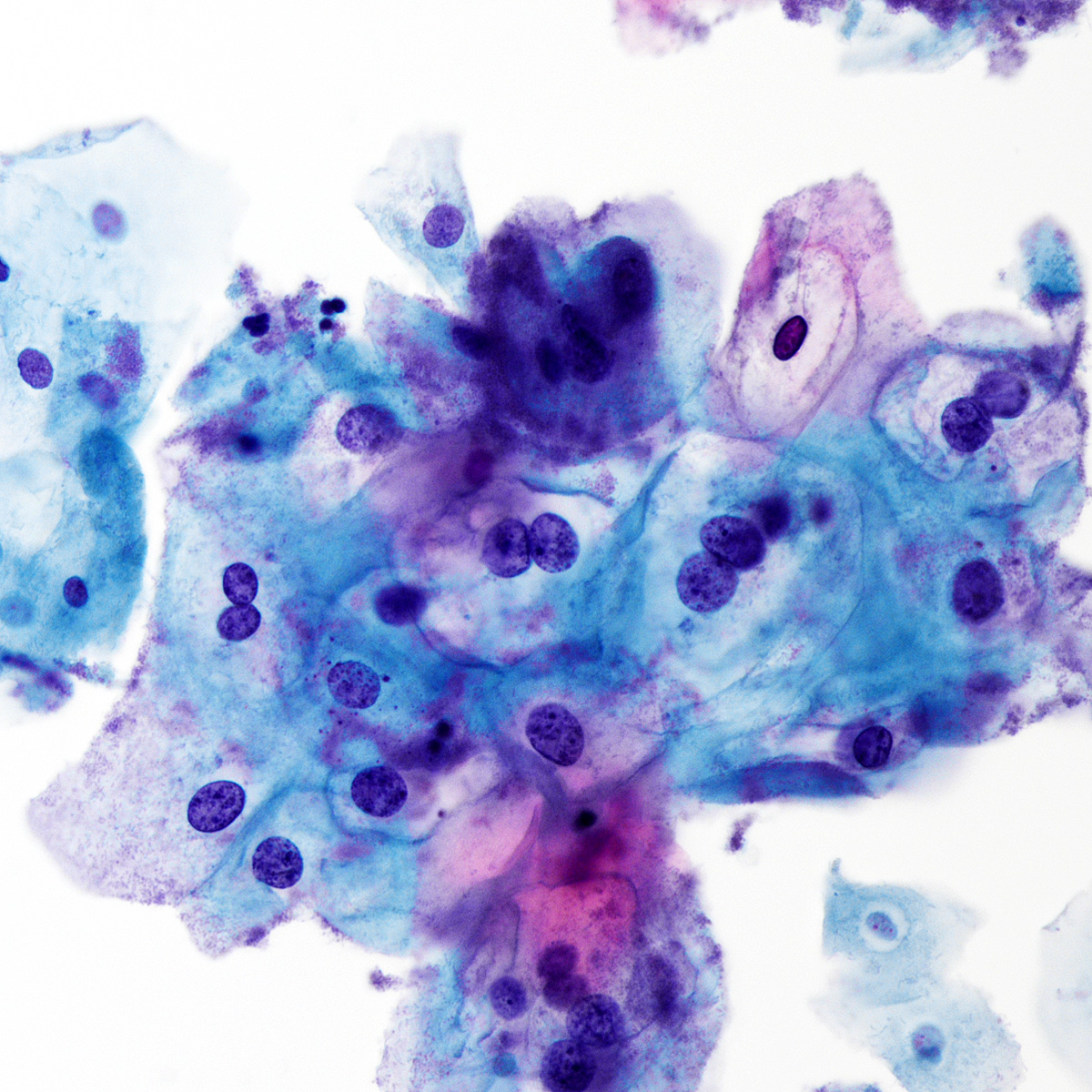
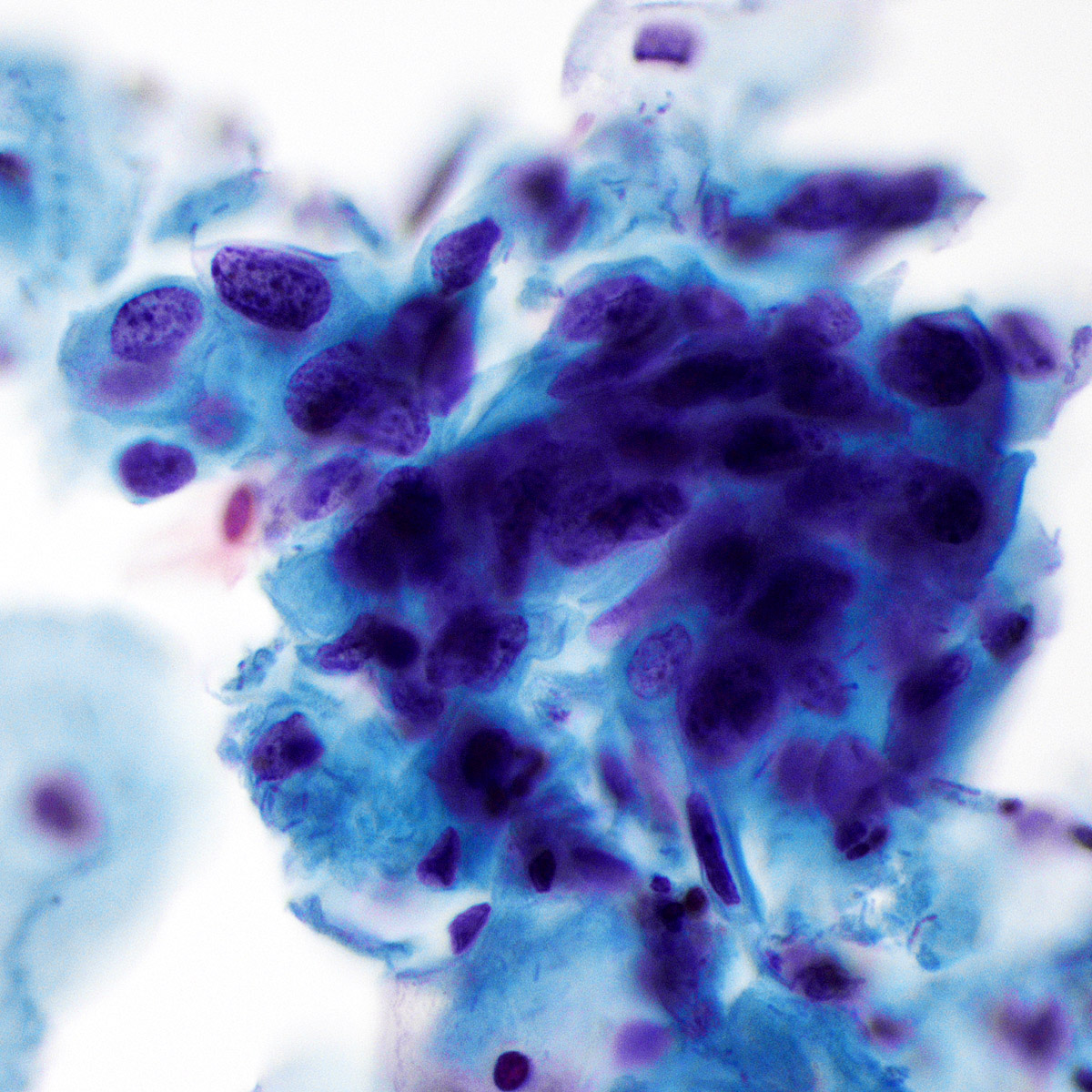
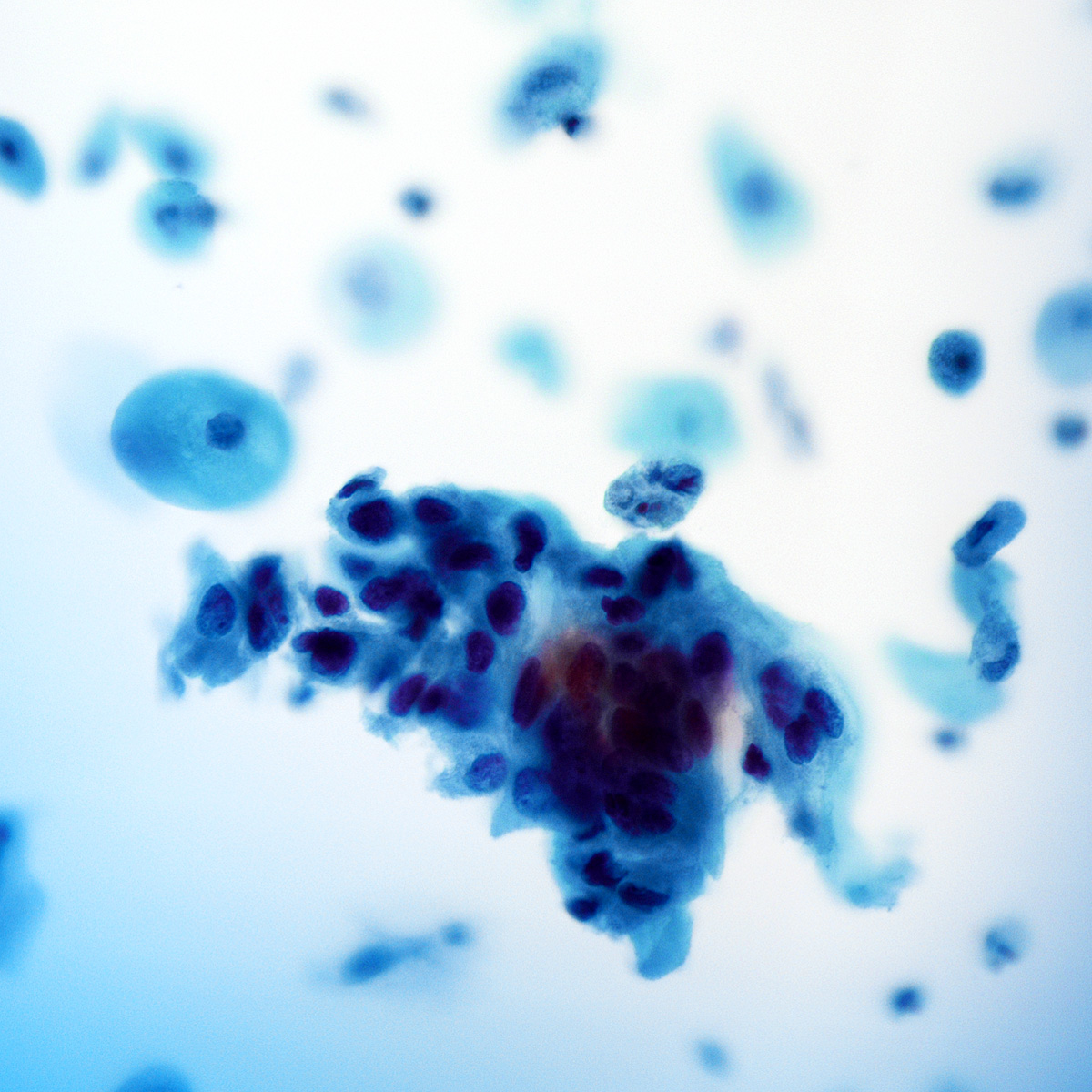
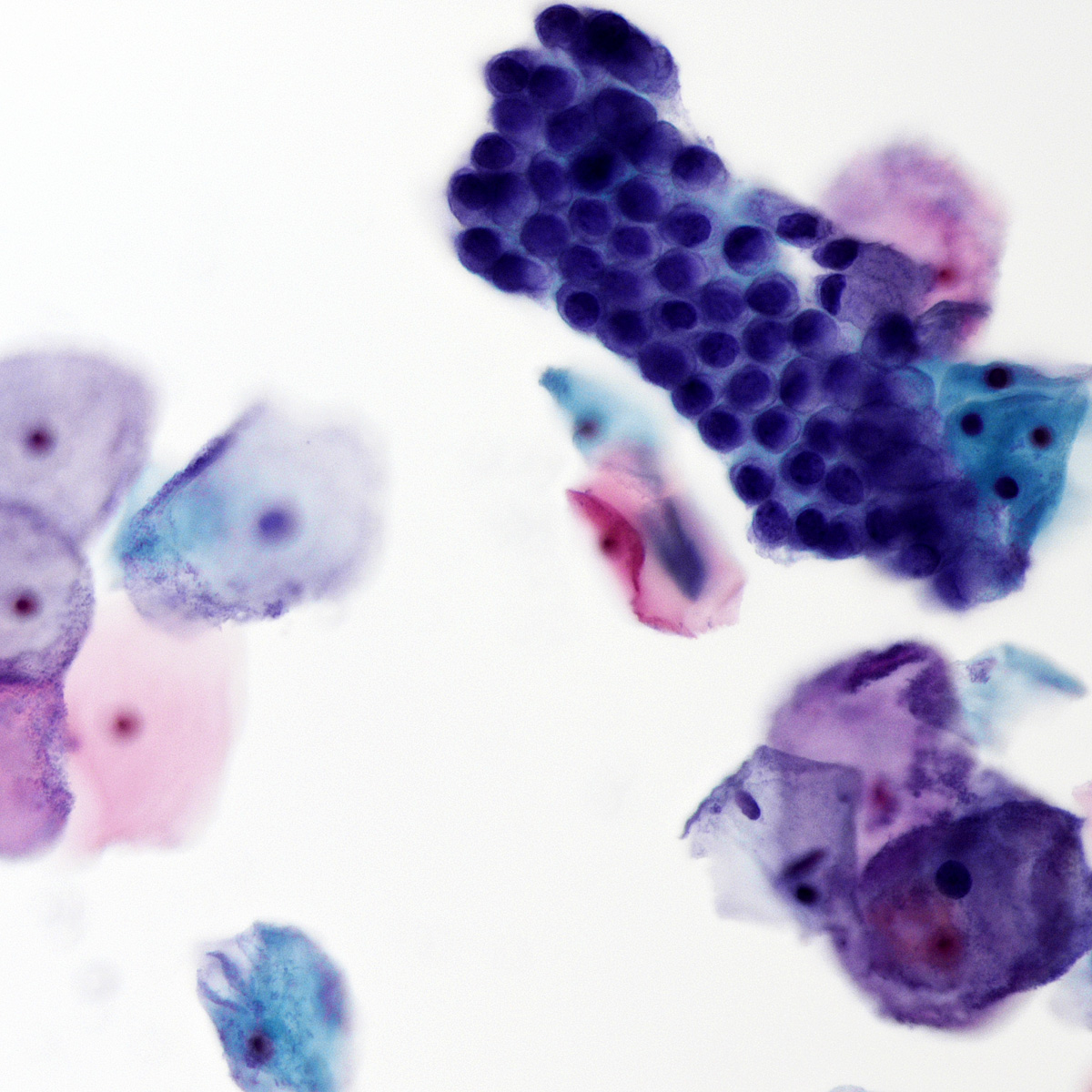
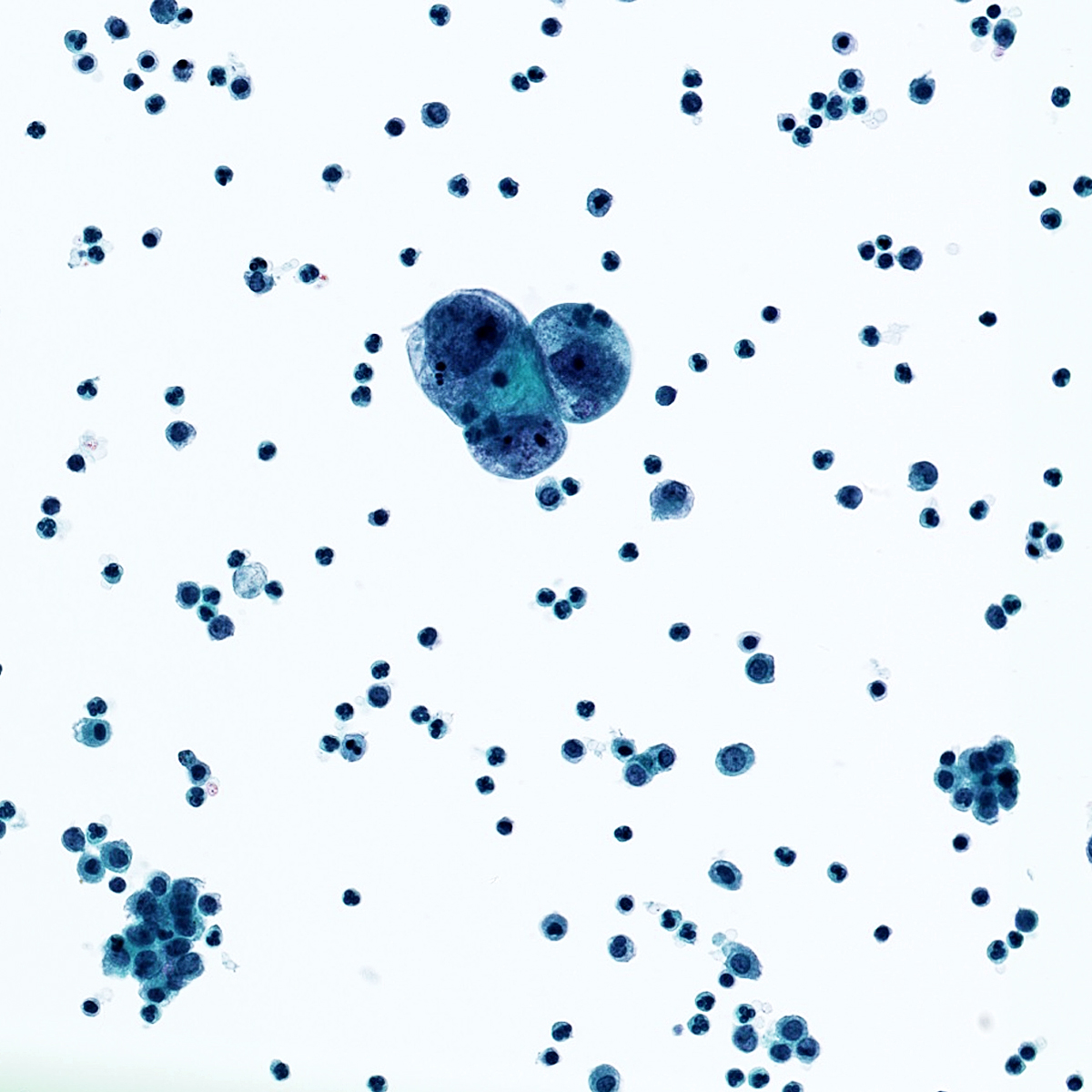
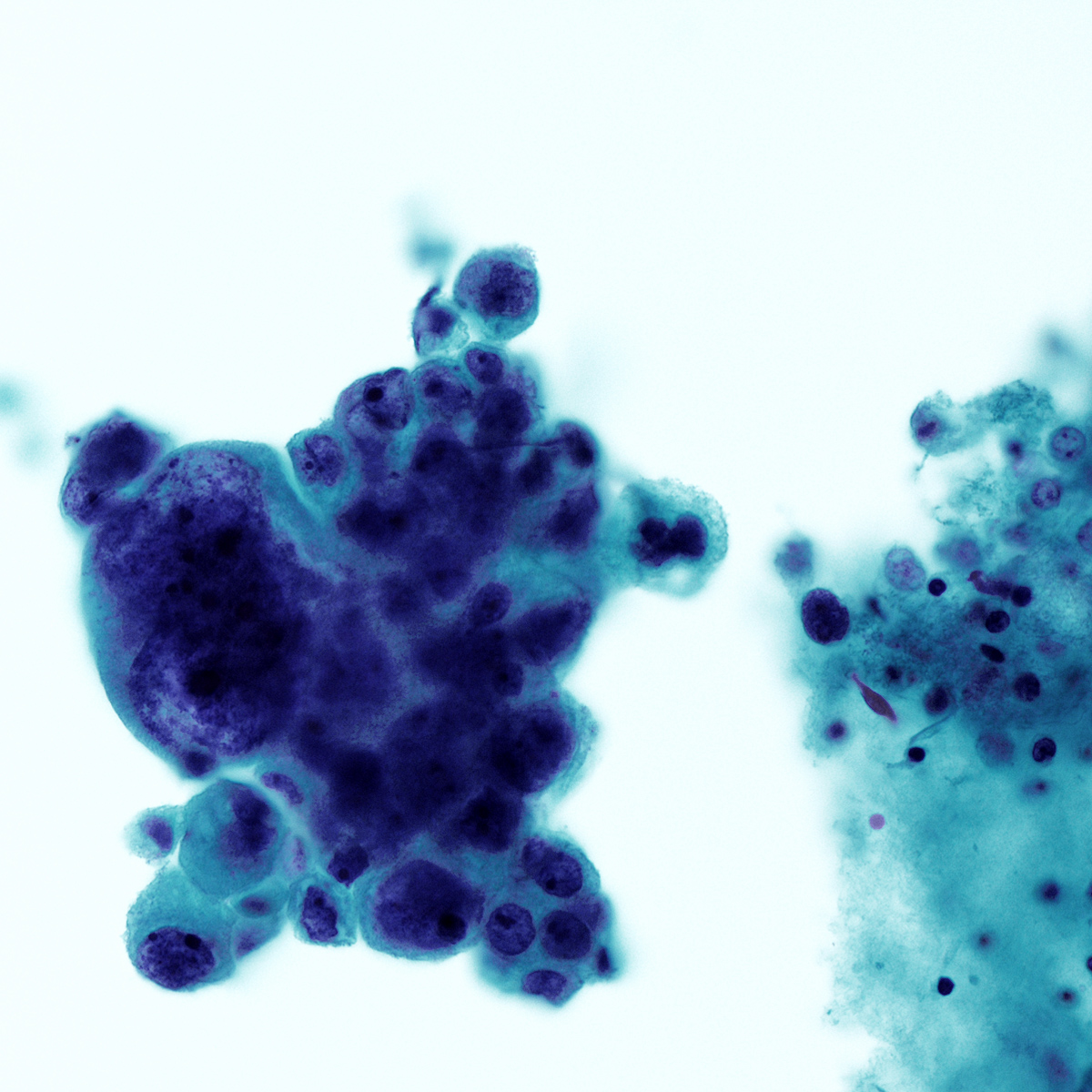
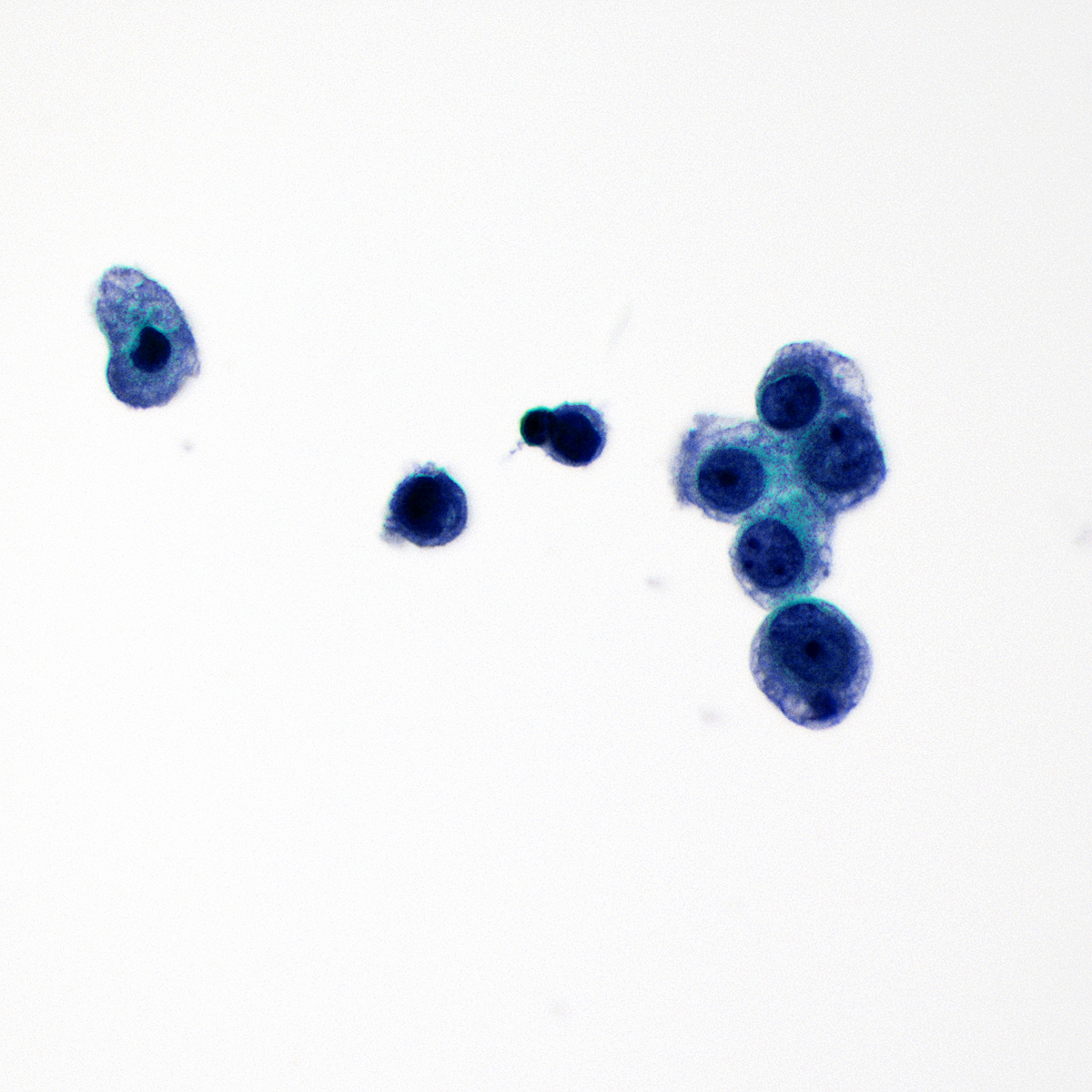
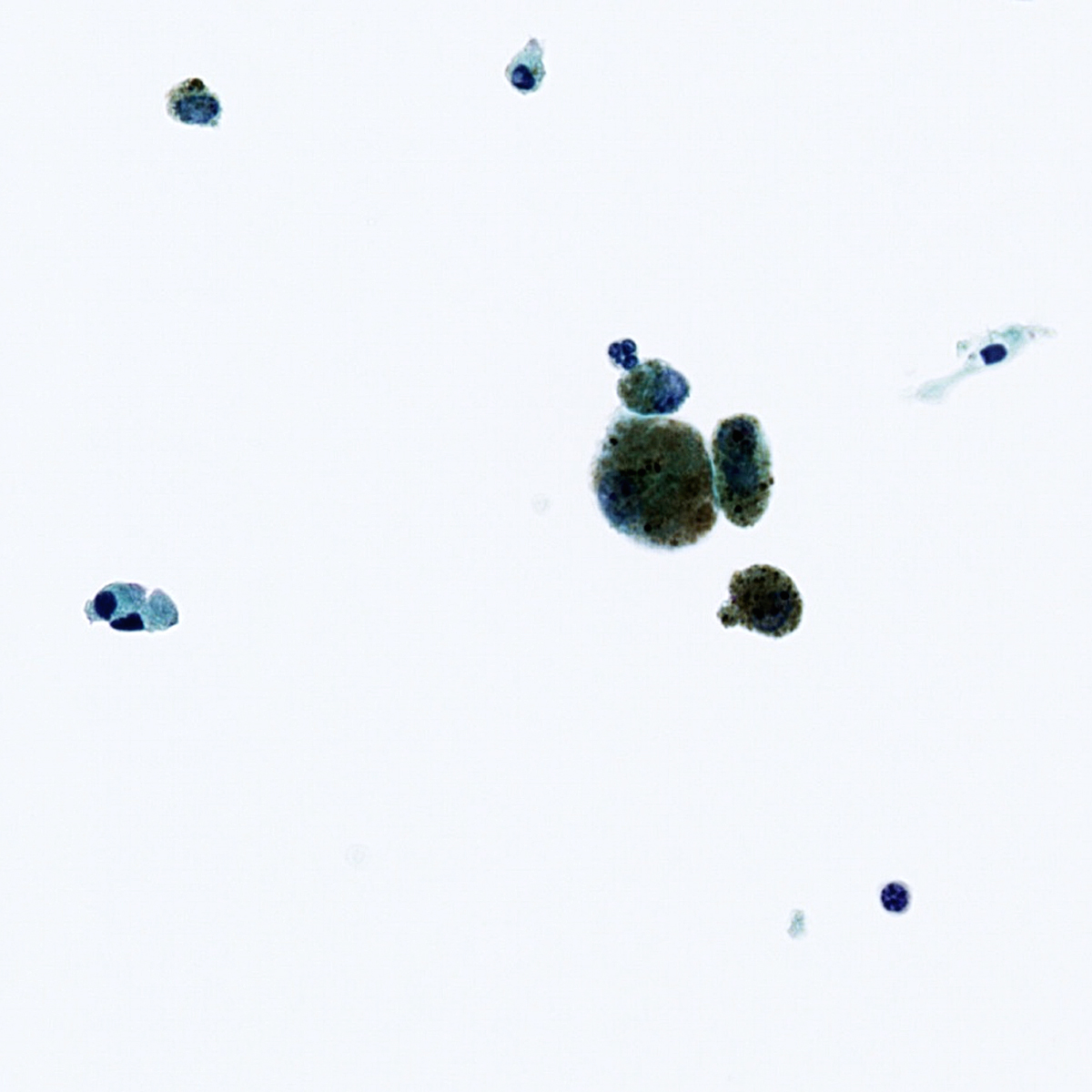
Cytology images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Urine cytology:
- See Cytology-general, normal findings & biomarker testing
- Residual sample from ThinPrep utilized for 69 gene, urothelial carcinoma specific next generation sequencing panel (Cancer Cytopathol 2021;129:537)
- Almost every mutation detected in the cytology specimen was present in the formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) bladder tumor sample (Cancer Cytopathol 2021;129:537)
- Biliary duct brushing:
- Combination of FISH probes 1q21, 7p12, 8q24 and 9p21 useful for the identification of biliary tract malignancy, with a significantly higher level of sensitivity (64.7%) than UroVysion probes (Gastroenterology 2015;149:1813)
- Samples collected in PreservCyt or CytoLyt
- Combination of FISH probes 1q21, 7p12, 8q24 and 9p21 useful for the identification of biliary tract malignancy, with a significantly higher level of sensitivity (64.7%) than UroVysion probes (Gastroenterology 2015;149:1813)
- Thyroid FNA:
- See Molecular testing in FNA
- Using 6 groups of 10+ follicular cells as a cutoff, nearly 97% of thyroid FNA samples collected in ThinPrep vial contained enough DNA for BRAF mutational assay (200 ng of DNA used as minimum criteria) (Cancer Cytopathol 2014;122:114)
- 18 gene next generation sequencing panel successfully performed from residual ThinPrep sample (J Cancer 2020;11:7276)
- Lower negative predictive value but a higher positive predictive value, compared to ThyroSeq v2 testing (J Cancer 2020;11:7276)
- Cellularity and storage time may affect the quantity and quality of nucleic acid extracted from thyroid FNA specimens collected in CytoLyt (Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:656)
Sample pathology report
- Pleural fluid, thoracentesis:
- Specimen adequacy:
- Satisfactory for evaluation
- Microscopic interpretation:
- Malignant cells present
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma
- Cell block shows similar features
- Specimen adequacy:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
E. Reduction in background blood and inflammation (Demay: The Art & Science of Cytopathology, 2nd Edition, 2011)
Comment Here
Reference: Liquid based cytology
Comment Here
Reference: Liquid based cytology
Board review style question #2
A pleural effusion sample has been entirely placed in a ThinPrep vial and processed. A single ThinPrep slide and cell block has been created. The clinical information received with the specimen is "rule out lymphoma". Which known limitation of liquid based preparation applies in this scenario?
- FISH studies cannot be performed
- Flow cytometry cannot be performed
- Immunohistochemistry cannot be performed
- Microbial culture cannot be performed
- Molecular testing cannot be performed
Board review style answer #2
B. Flow cytometry cannot be performed. Since the specimen was entirely placed in the methanol based ThinPrep vial, flow cytometry and microbial culture tests cannot be performed. Flow cytometry may be required for diagnosis when the clinical suspicion includes lymphoma. Immunohistochemistry, molecular testing and FISH studies can all be potentially performed on the cell block. In some instances, molecular and FISH testing can be performed on residual sample collected in ThinPrep vials.
Comment Here
Reference: Liquid based cytology
Comment Here
Reference: Liquid based cytology