Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Signet ring cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorsignetring.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare subtype of colorectal carcinoma (< 1%) officially recognized by the WHO (Ann Surg 2013;258:775)
- > 50% of the tumor must have signet ring cell morphology to be classified as signet ring cell carcinoma
Essential features
- May form a diffuse lesion rather than a discrete mass
- Usually high stage with poor prognosis (Dis Colon Rectum 2005;48:1161, Dis Colon Rectum 1999;42:1176)
- Often metastasizes to lymph nodes, peritoneal surface and ovary (less commonly to liver) (ANZ J Surg 2001;71:703)
Terminology
- Sometimes called linitis plastica but this typically refers to signet ring cell carcinoma of stomach
Epidemiology
- May affect younger patients more than classic colorectal carcinoma (Am J Gastroenterol 1996;91:2195)
- Proximal signet ring cell cancers are a distinct subpopulation with a favorable oncologic outcome, possibly due to link with microsatellite instability (Int J Colorectal Dis 2012;27:371)
Sites
- Can occur anywhere in colon, though rectum is a less common location
Etiology
- Can be seen in carcinomas that arise through the microsatellite instability pathway (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1407)
Clinical features
- Presents at earlier age and higher stage than conventional colorectal carcinoma (J Gastrointest Oncol 2014;5:18)
Diagnosis
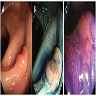
- Diagnosis usually by biopsy, although magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging can also be used (BMC Gastroenterol 2015;15:86)
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognostic indicators include high tumor stage, bowel obstruction, "inefficient" surgery (Int Surg 2014;99:691)
- Prognosis poor even if signet ring cell component is < 50% (PLoS One 2015;10:e0121944)
Case reports
- 30 year old woman with primary signet ring cell carcinoma mimicking segmental Crohn's colitis (Dig Liver Dis 2005;37:537)
- 59 year old man with signet ring cell carcinoma in adenoma of sigmoid colon (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:957)
- 67 year old man with primary signet ring cell carcinoma of colon at an early stage (World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:3446)
- 72 year old woman with signet ring cell carcinoma of colon with peritonitis carcinomatosa (J Gastroenterol 2002;37:550)
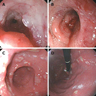
Clinical images
Gross description
- May diffusely infiltrate colon wall, rather than forming an exophytic mass
- Can rarely arise within a polyp
Gross images
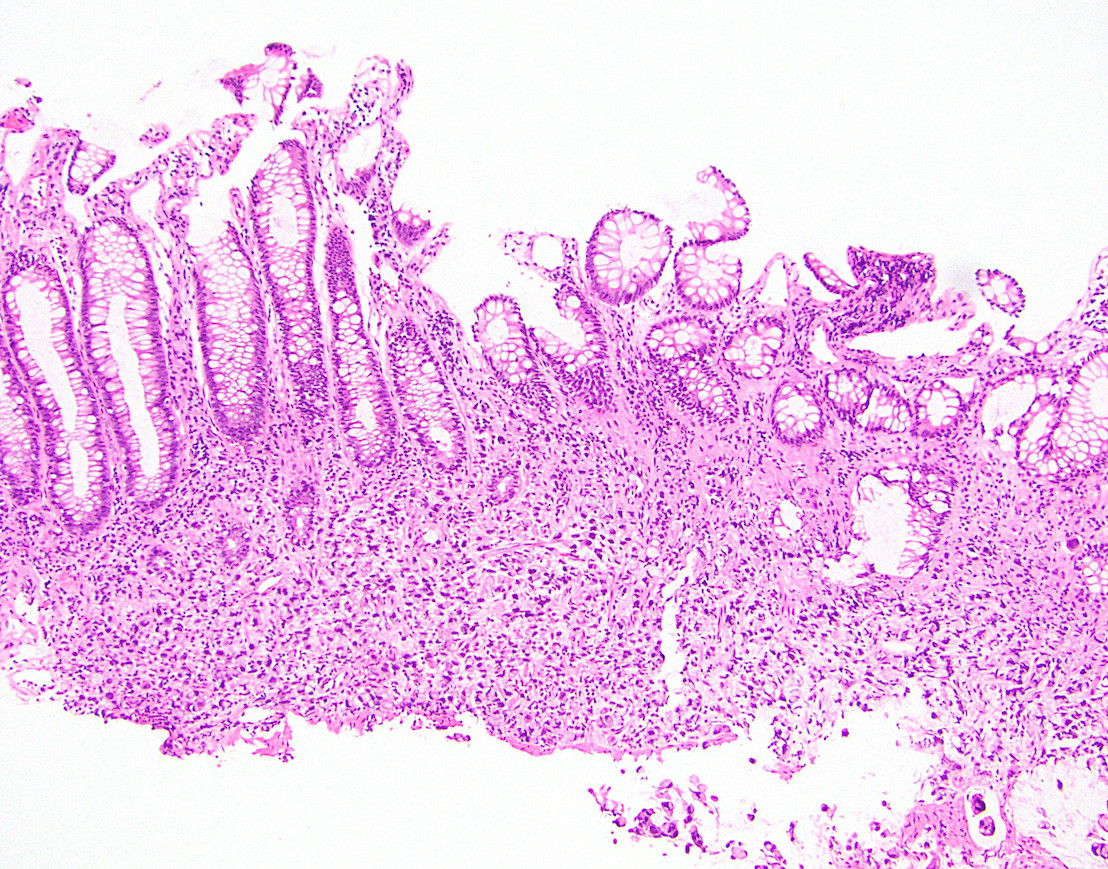
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Proliferation of signet ring cells with intracellular mucin that displaces nucleus to side
- Pools of extracellular mucin often present as well
- Diffuse tissue infiltration less common than in gastric signet ring cell carcinoma
- May rarely be in situ or confined to a polyp (J Surg Res 2010;163:250)
- No gland formation in signet ring cell component, although it may be present elsewhere in the same lesion
Positive stains
- CK20, CDX2, MUC2, MUC5AC; variable MUC1 and HepPar1 (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;121:884, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:183)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Slightly lower rate of KRAS mutation than conventional colorectal carcinoma (Jpn J Clin Oncol 1998;28:202)
- May show microsatellite instability (Mod Pathol 2008;21:1533)
Sample pathology report
- Ascending colon, resection:
- Signet ring cell carcinoma, poorly differentiated (see synoptic report)
Differential diagnosis
- Benign processes with signet ring cell change (most commonly pseudomembranous colitis) (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1429)
- Metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma of stomach, breast or bladder:
- Different staining patterns by immunohistochemistry (Dig Liver Dis 2006;38:609)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1