Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Kamal M, Hassell LA. Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasm. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumormxdnrndcrnnonnrndocrnnplsm.html. Accessed December 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Extremely rare and aggressive with a high grade neuroendocrine component (in the majority of cases)
- Composed of neuroendocrine cells, nonneuroendocrine cells or amphicrine cells that show both neuroendocrine and nonneuroendocrine cell differentiation (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;76:125)
Essential features
- Mix of neuroendocrine and nonneuroendocrine components, each constituting at least 30% of the tumor; both components should be histologically and immunohistochemically proven
- Biological behavior is predominantly driven by the endocrine component, which is mostly poorly differentiated (World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
- Prognosis of mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasm (MiNEN) is intermediate between that of pure adenocarcinoma and pure poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (Neuroendocrinology 2017;105:412)
- When considering treatment, the more aggressive component of MiNEN should be considered first; MiNEN containing a well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor (NET) (grades 1 or 2) component and an adenocarcinoma component should be treated as adenocarcinoma (J Chin Med Assoc 2015;78:454)
Terminology
- Mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinomas, glandular neuroendocrine mixed tumor, mixed epithelial endocrine neoplasms, mixed adenoneuroendocrine tumors (J Clin Med 2020;9:273, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Age range of 32 - 96 years (Mol Clin Oncol 2018;9:219)
- M > F
- < 2% of all colorectal malignancies (Mol Clin Oncol 2018;9:219)
Sites
- Colonic MiNEN represents 11.2% of all gastroenteropancreatic tract MiNEN (World J Gastroenterol 2019;25:5991)
- In the colon, the rectosigmoid / sigmoid colon is more frequent than the ascending / transverse colon, cecum or ileocecal valve (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2020;2020:5927610)
Pathophysiology
- 3 main hypotheses:
- First hypothesis: 2 components (endocrine and nonendocrine) arise independently from distinct precursor cells and unite
- Second hypothesis: 2 components originate from a common pluripotent stem cell that undergoes biphenotypic differentiation during tumorigenesis
- Third hypothesis: 2 components arise from a common precursor but postulates that the neuroendocrine component develops from an originally nonneuroendocrine cell, via progressive accumulation of genetic aberrations (World J Gastroenterol 2019;25:5991)
Etiology
- Association with longstanding intestinal inflammatory disease (BMC Cancer 2005;5:157, J Clin Gastroenterol 1998;26:353)
Clinical features
- Mass lesion, gastrointestinal bleeding, bowel obstruction, intussusception or paraneoplastic syndromes, rarely carcinoid syndrome
Diagnosis
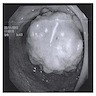
- Discovered during colonoscopy, some are diagnosed on evaluation of distant metastasis
- Imaging features are nonspecific and necessitate histopathologic confirmation
- CT is helpful in identifying and staging the disease
Laboratory
Radiology description
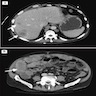
- Contrast enhanced CT may reveal intraluminal heterogeneous enhancing mass, irregular wall thickening and mesenteric haziness (J Clin Imaging Sci 2013;3:10)
- CT may additionally show pneumoperitoneum, free intraperitoneal fluid, particularly around the cecum and in the pelvis (Chirurgia (Bucur) 2017;112:152)
- PET / CT using 68Ga-Dotatate may provide localization of neuroendocrine components (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2018;211:267)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- High tumor grade
- Increased number of genetic / chromosomal alterations (J Clin Med 2020;9:273)
- Prognosis of MiNEN is intermediate between that of pure adenocarcinoma and pure poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (Neuroendocrinology 2017;105:412)
- Disease stage and tumor type
- Vascular invasion and CD117 expression (worse prognosis) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:601)
- Large cell type, peritumoral lymphoid reaction tumor and microsatellite instability (better prognosis) (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:601)
- Higher volume of high grade neuroendocrine component (> 50%) has worse survival rate (J Chin Med Assoc 2015;78:454)
- Low grade MiNEN composed of adenoma with well differentiated low grade neuroendocrine tumors; behaves as an indolent disease (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1503)
Case reports
- 36 year old woman with ascending colonic polyposis (Int Cancer Conf J 2017;6:175)
- 45 year old man with colon tumor demonstrating thyroid and liver metastasis (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2020;2020:5927610)
- 64 year old man with chronic anemia and right colonic intussusception due to a giant pedunculated lesion (Case Rep Surg 2016;2016:7684364)
- 66 year old man with abdominal pain, loss of weight, anemia, irregular circumferential mass in the left half of transverse colon (Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2015;4:399)
- 68 year old woman with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting with rising carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and alpha fetoprotein (AFP) (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:6395)
- 85 year old woman with anemia and laterally spreading tumor in the transverse colon (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;76:125)
Treatment
- First consideration is the more aggressive component of MiNEN
- MiNEN containing a well differentiated NET (grades 1 or 2) component and an adenocarcinoma component, should be treated as adenocarcinoma (J Chin Med Assoc 2015;78:454)
- Surgery preferred for nearly all potentially curable cases
- Chemotherapy and radiotherapy considered on case by case basis (World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
- Antiprogrammed death 1 receptor monoclonal antibody (pembrolizumab) therapy is effective where 5 - 10% of tumor cells express the programmed cell death receptor ligand 1 (J Immunother 2019;42:274)
Gross description
- Polypoid or ulcerated tumor with raised edges or large fungating mass (World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
- Cut surface of the tumor often shows white tan, poorly circumscribed lesions with an infiltrating border
- Focal necrosis and foci of hemorrhage may be seen
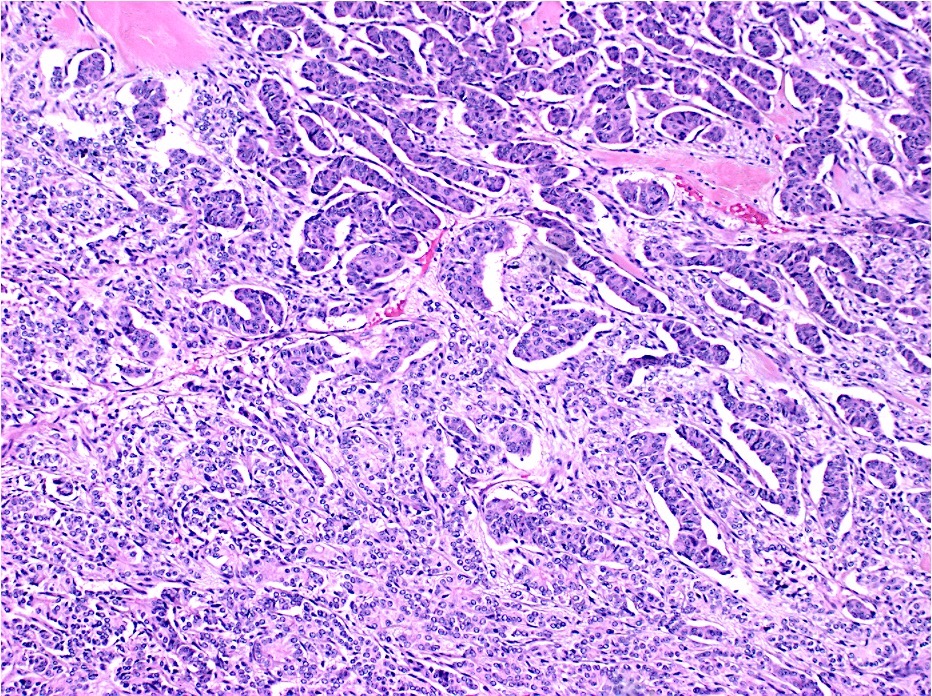
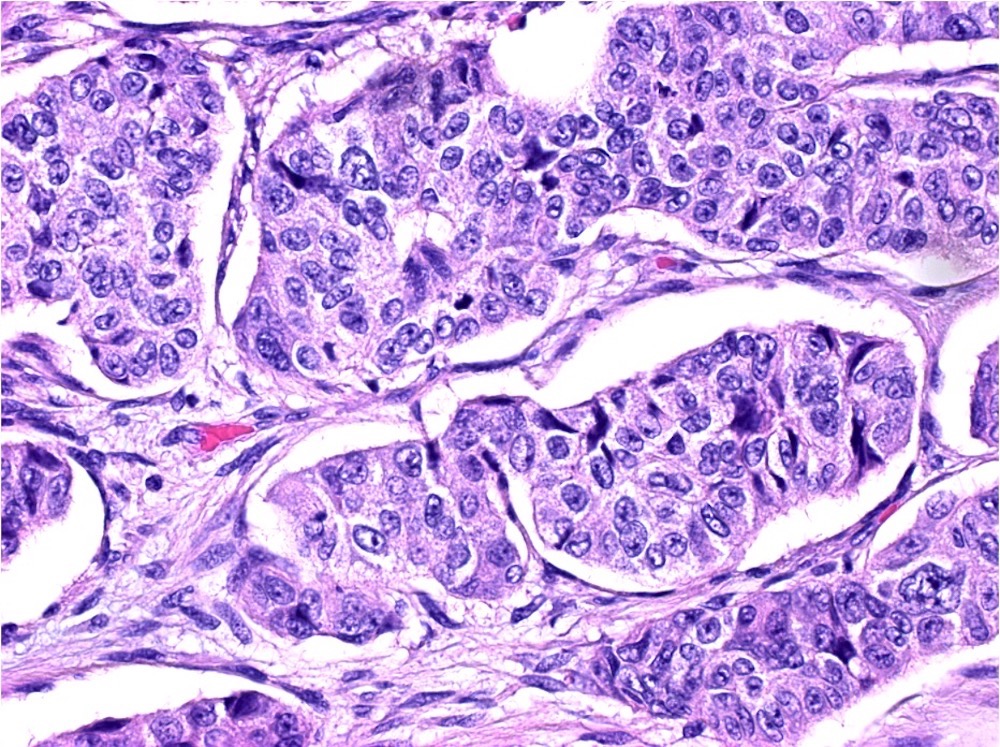
Microscopic (histologic) description
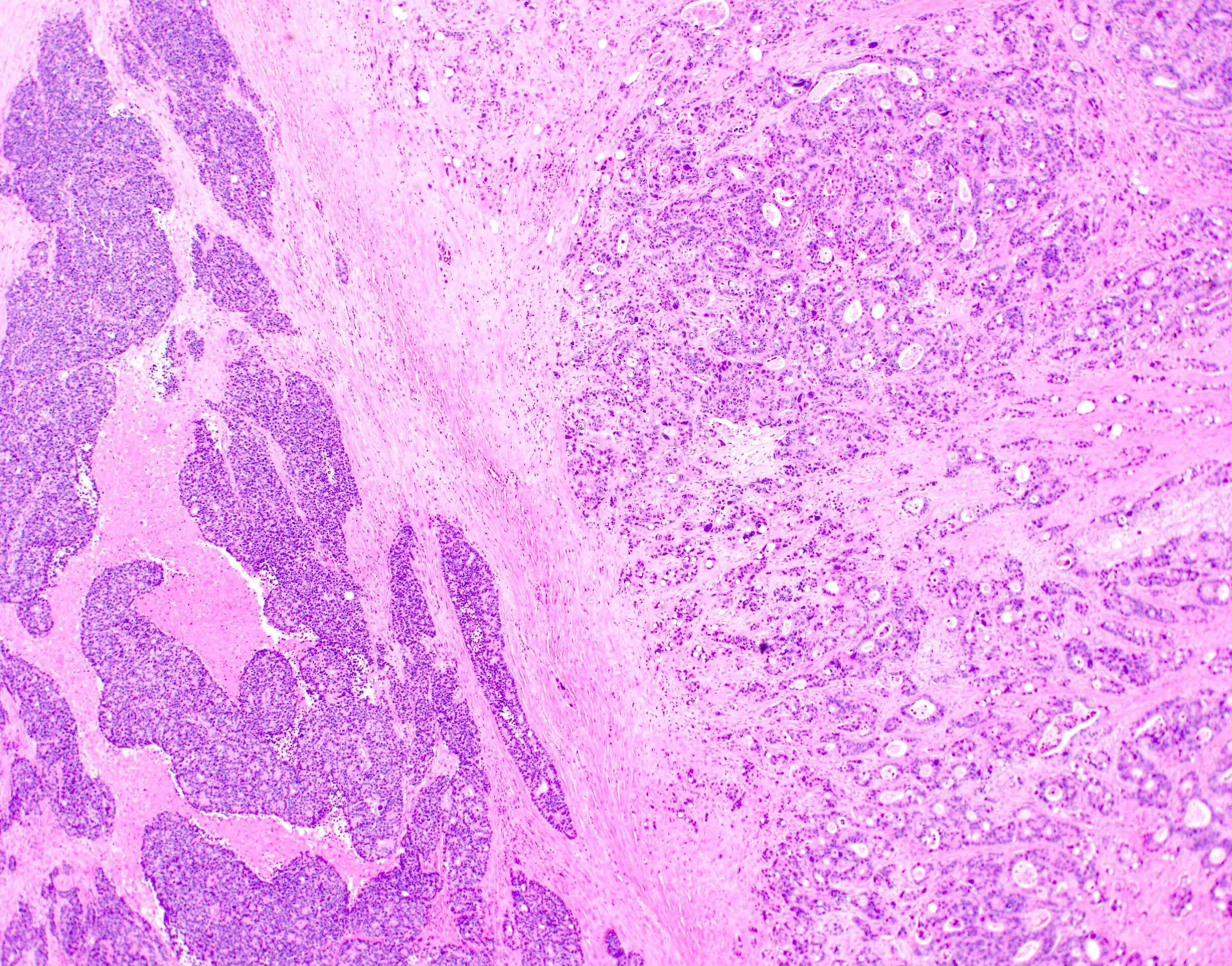
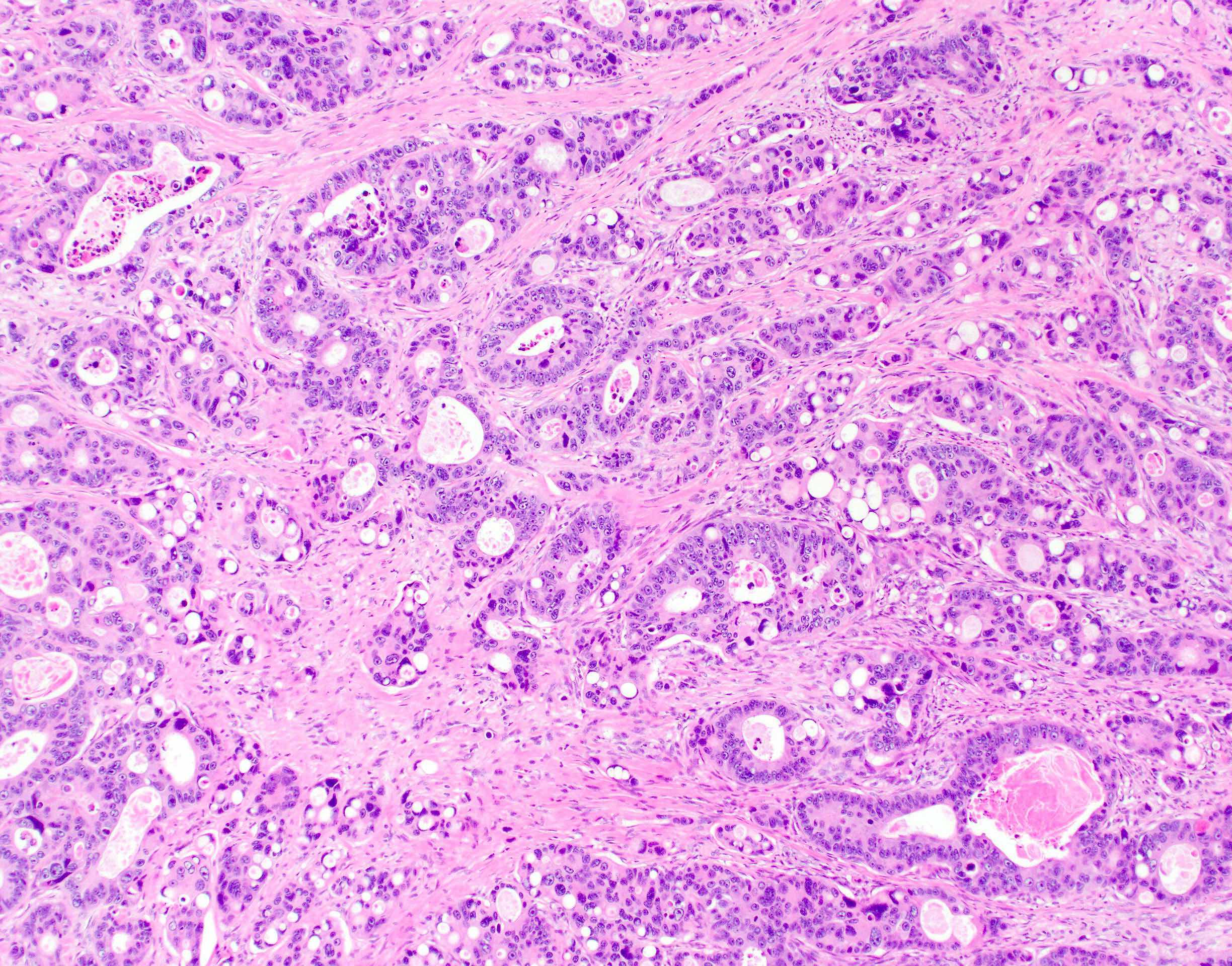
- 2 components include epithelial / nonneuroendocrine component (mostly adenocarcinoma; less commonly, squamous cell carcinoma, acinar cell carcinoma, adenoma and other tumors) and neuroendocrine component, each constituting at least 30% of the tumor
- This cut off value only applies to resected specimens after histological examination of the entire neoplasm within the specimen
- Previously, these mixed neoplasms were classified under the category of mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma; however, it is now recognized that the nonneuroendocrine component is not necessarily adenocarcinoma and either one or both components may not be carcinomas
- Both components should be histologically and immunohistochemically proven
- Per WHO, evaluate and grade each histologic component separately
- All neuroendocrine components are classified according to the WHO criteria based on mitotic and Ki67 index, into well differentiated neuroendocrine tumors (G1, G2 and G3) and poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas (small or large cell neuroendocrine tumors)
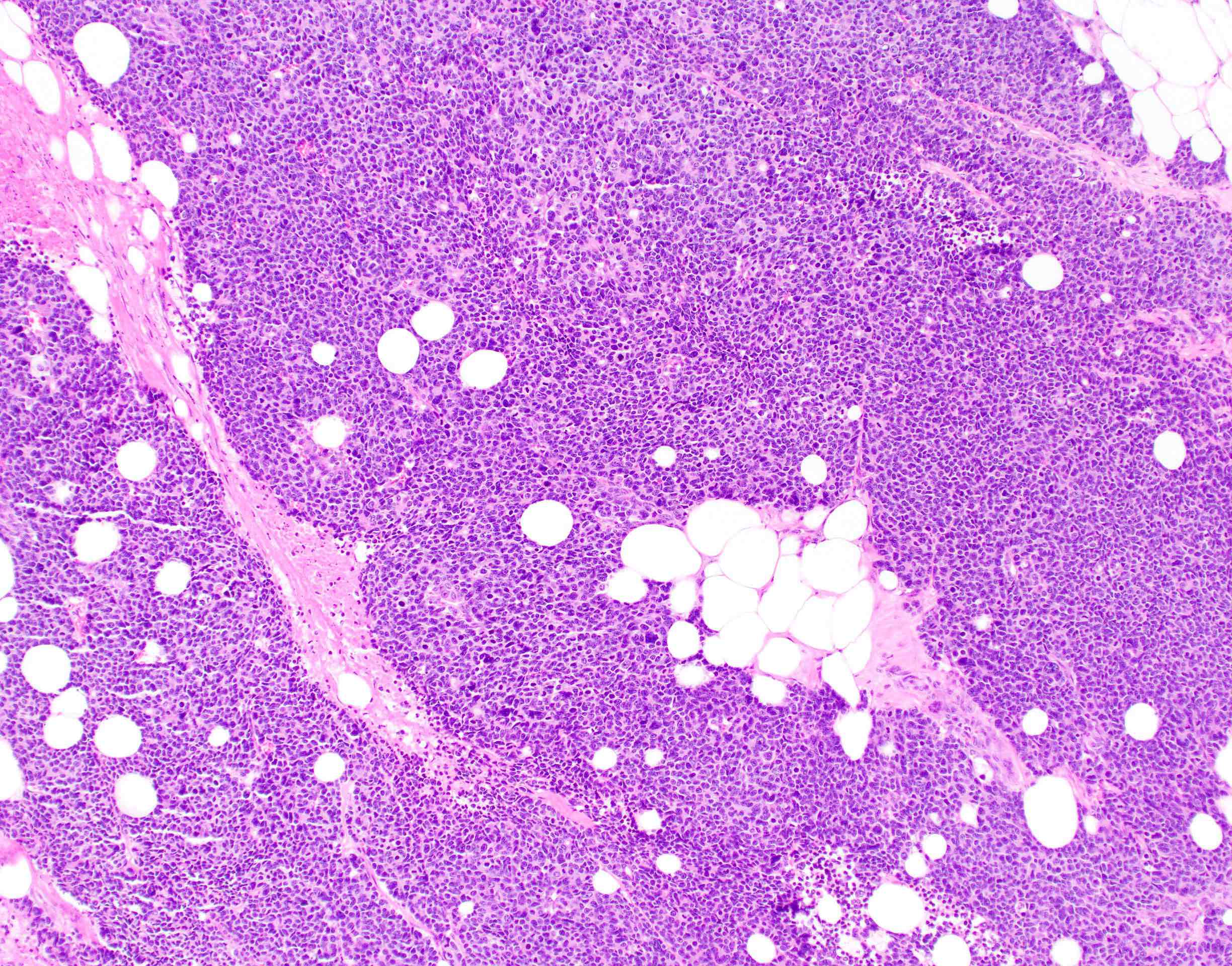
- Neuroendocrine component is mostly high grade and demonstrate a high mitotic index
- Small cell type: nested or diffuse proliferation of tumor cells with round to oval nuclei, finely dispersed chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli and scant cytoplasm
- Large cell type: cells with abundant cytoplasm, vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (Endocr Pathol 2016;27:284)
- Prominent oncocytic differentiation represented by large cells with marked eosinophilia, has also been reported in a mixed tumor of the transverse colon (Endocr Pathol 2013;24:54)
- Amphicrine tumors are distinguished by a divergent immunophenotype in which both exocrine and neuroendocrine traits are expressed in the same cell (Cancer Cell Int 2019;19:310)
- About 5% of colorectal MiNEN show low grade neoplasms, combining adenomas with G1 / G2 NET (Neuroendocrinology 2017;105:412)
- Because of possible response to platinum based treatments, the presence of even a minor component of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (SCNEC) should be mentioned in the diagnosis
- Presence of a focal (< 30%) neuroendocrine component does not change the diagnostic categorization but it may be mentioned in the report
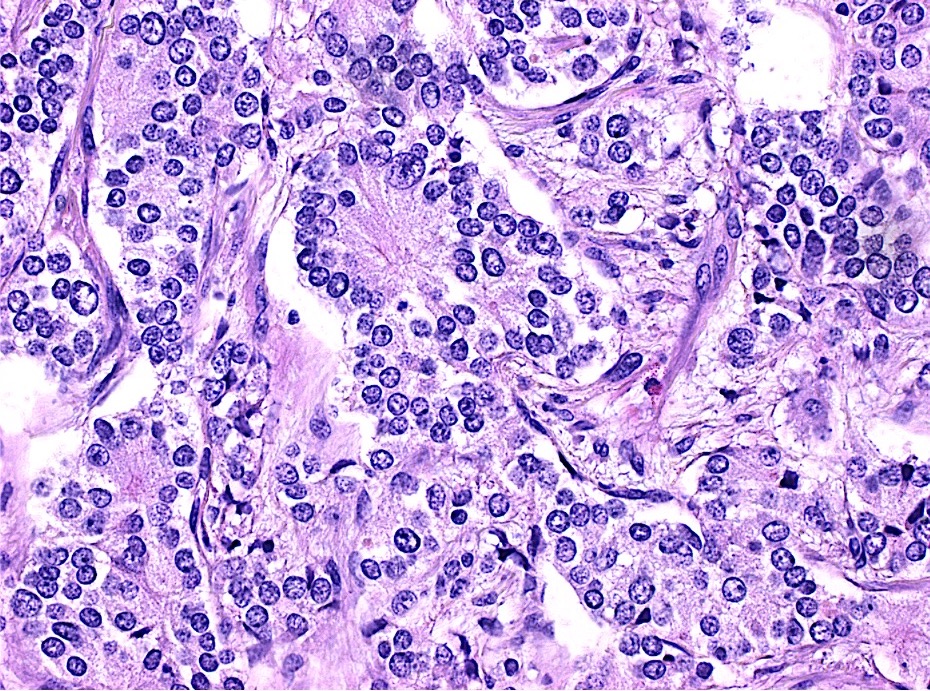
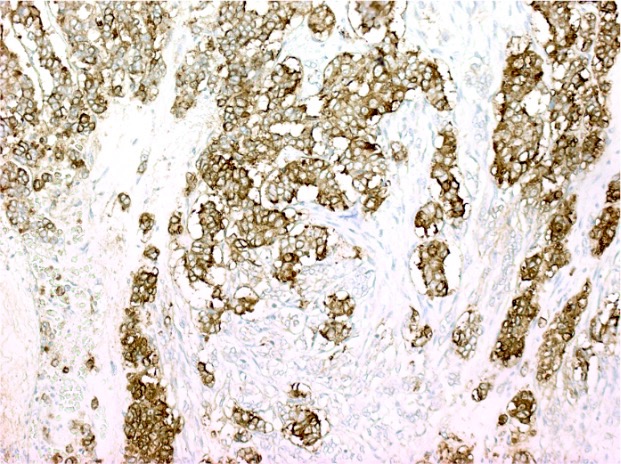
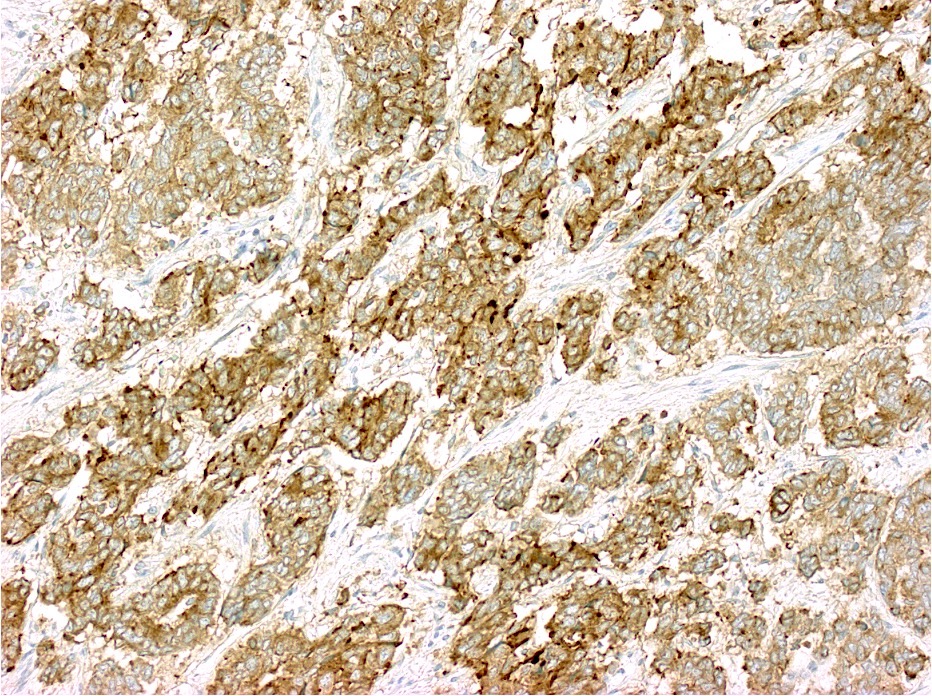
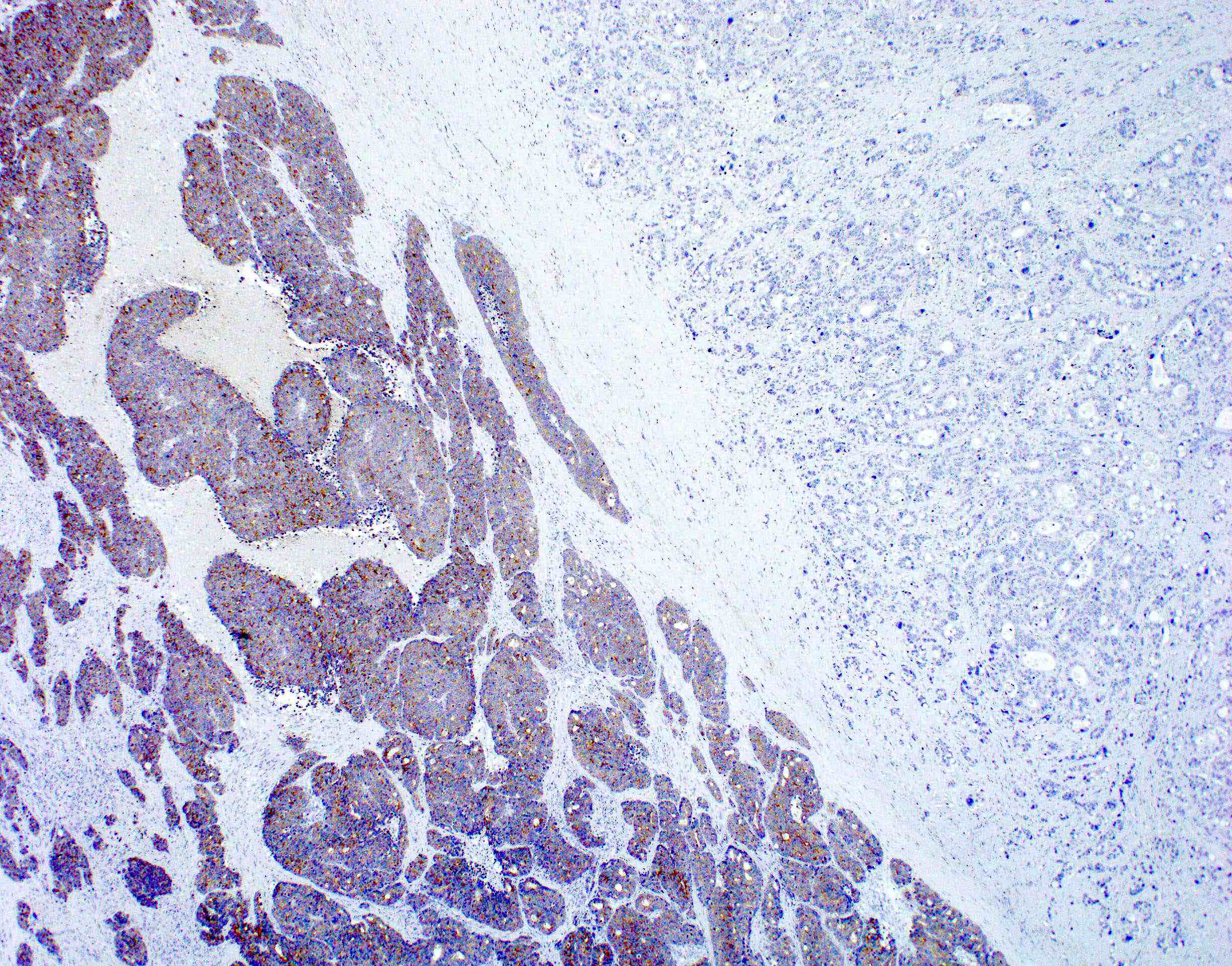
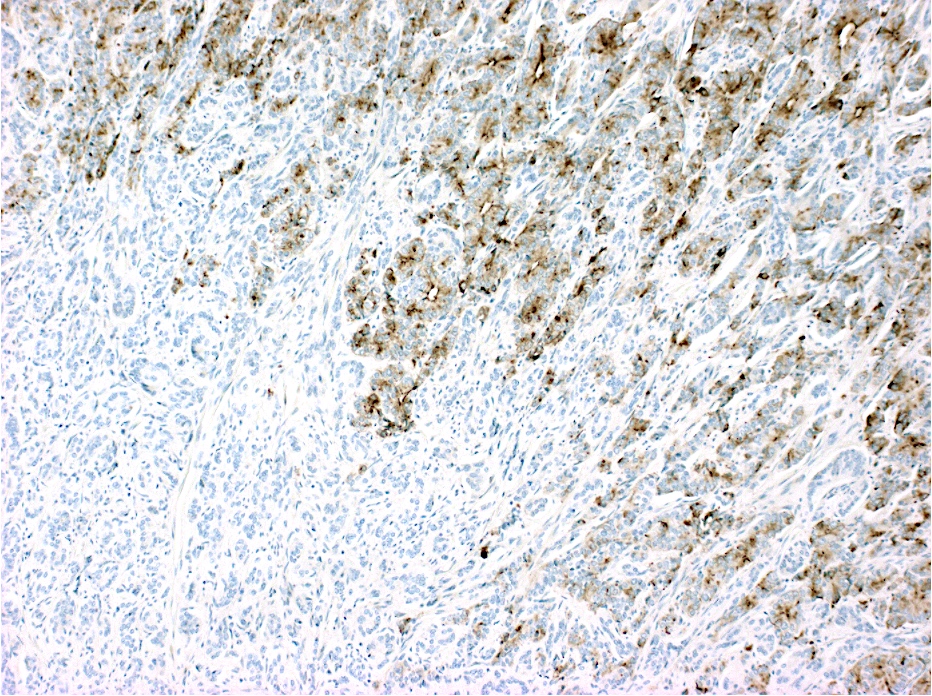
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Lewis A. Hassell, M.D. and Catherine E. Hagen, M.D.
Positive stains
- Adenocarcinoma component: Alcian blue, pancytokeratin AE1 / AE3, cytokeratins and CDX2
- Acinar cell carcinoma component: BCL10, trypsin
- Neuroendocrine component: commonly used immunohistochemical neuroendocrine markers (chromogranin A, synaptophysin, CD56 and neuron specific enolase)
- Synaptophysin and chromogranin A are reported as the most reliable neuroendocrine markers
- Neuroendocrine cells may be positive for peptide hormones (somatostatin, ACTH adrenocorticotropic hormone, VIP vasoactive peptide)
- Both epithelial and endocrine components may show cyclin D1, p53 and beta catenin positivity (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:413)
- E-cadherin, CEA, villin and chromogranin A (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:6395)
- CD133, a marker of cancer stem cells (reported in 64% of MiNEN of digestive tract), has been associated with tumor aggressiveness (Tohoku J Exp Med 2013;229:301)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Mutations in TP53, RB1, PTEN, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), P13KCA, BRAF, KRAS, MYC, BCL9 and FOXP1, SMARC4 gene (Anticancer Res 2014;34:5517, World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
- Abnormalities of chromosome 5q, 11q, 17q and 18q have also been identified (World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:5181)
- MSI instability (Endocr Relat Cancer 2018;25:583)
Videos
Mixed neuroendocrine and nonneuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus
Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasms
Sample pathology report
- Sigmoid colon, resection:
- Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasm with well differentiated adenocarcinoma (G1, 30%) and poorly differentiated small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (70%)
- See synoptic report for more details
Brief synoptic reportTumor site Sigmoid colon Histologic type Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine carcinoma Size 4.5 x 2.0 x 1.2 cm Depth of invasion Subserosal adipose tissue Lymphovascular invasion Present Perineural invasion Not identified Margins Uninvolved by invasive carcinoma, intramucosal
adenocarcinoma, high grade dysplasia and adenomaLymph nodes with metastatic tumor 2 Lymph nodes examined 15 Tumor deposits Not identified Distant metastasis Not applicable AJCC staging pT3 N1
Differential diagnosis
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma:
- No epithelial nonneuroendocrine component is identified
- Adenocarcinoma with scattered neuroendocrine cells:
- Adenocarcinoma with a minor neuroendocrine component that is < 30% of the entire tumor
Additional references
Board review style question #1
An 8 mm polypoid mass located in the sigmoid colon was resected. The microscopic examination revealed a biphasic tumor that was positive for epithelial and neuroendocrine markers, each component accounting for > 30% of the tumor (see images above: chromogranin, trypsin). Which statement is true regarding this lesion?
- It is a common colorectal neoplasm
- It is mostly an aggressive tumor
- More common in females
- Recognized as part of the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 group of tumors
- Treatment is determined by the predominant (volume wise) component
Board review style answer #1
B. It is mostly an aggressive tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasm
Comment Here
Reference: Mixed neuroendocrine nonneuroendocrine neoplasm