Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Mucosal Schwann cell hamartoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumormucosalschwann.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign mucosal proliferation composed of Schwann cells
Essential features
- Benign, incidental spindle cell lesion
- Not associated with any clinical syndrome
- Positive for S100, negative for EMA
Terminology
- Has been called neuroma or neurofibroma in past
Sites
- Can arise anywhere in the colorectum but more common distally
Clinical features
- Average patient age is 62 years, with a female predominance (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:781)
- Not associated with any particular syndrome
- Lesions do not recur
Diagnosis
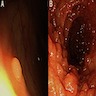
- Discovered incidentally during colonoscopy
Case reports
- 20 year old man with multiple colonic lesions (BMC Gastroenterol 2015;15:128)
- 59 year old man with ulcerative colitis (Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2013;9:183)
Gross description
- Small (6 mm or less) sessile polyp
Microscopic (histologic) description
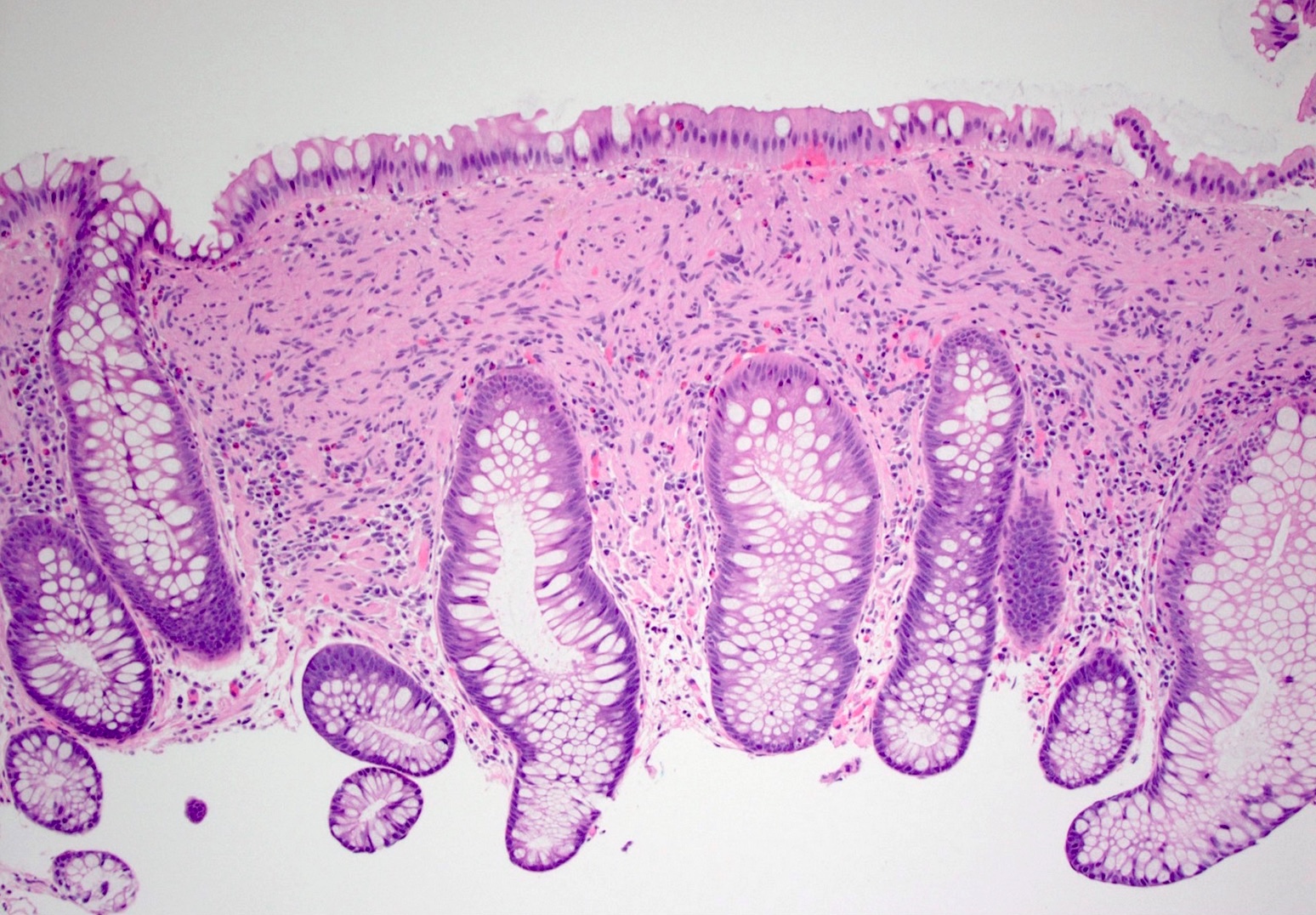
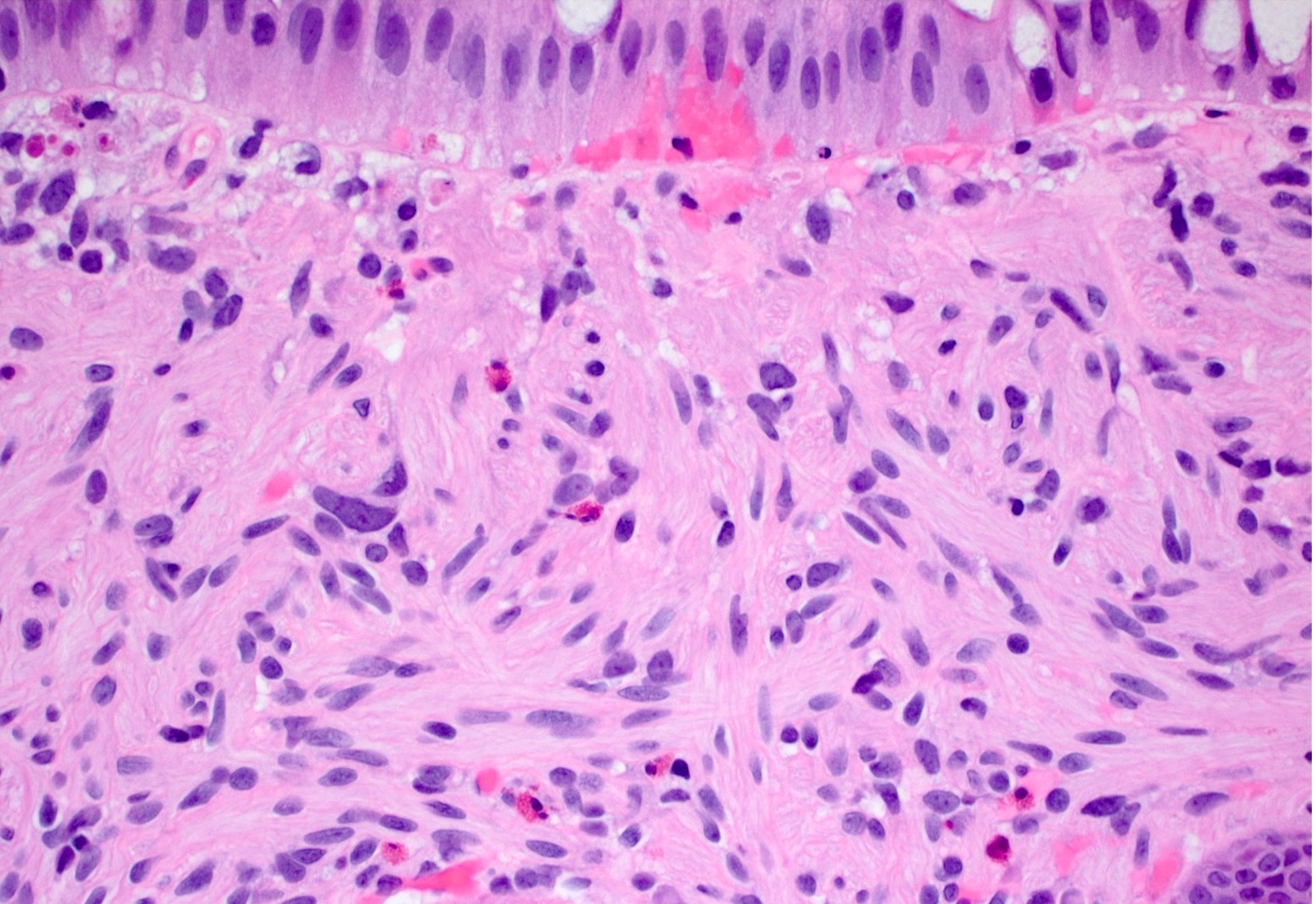
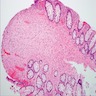
- Poorly circumscribed mucosal proliferation of spindle cells, with no whorling, no palisading, no fasciculation
- Nuclei are generally small, bland and elongated
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
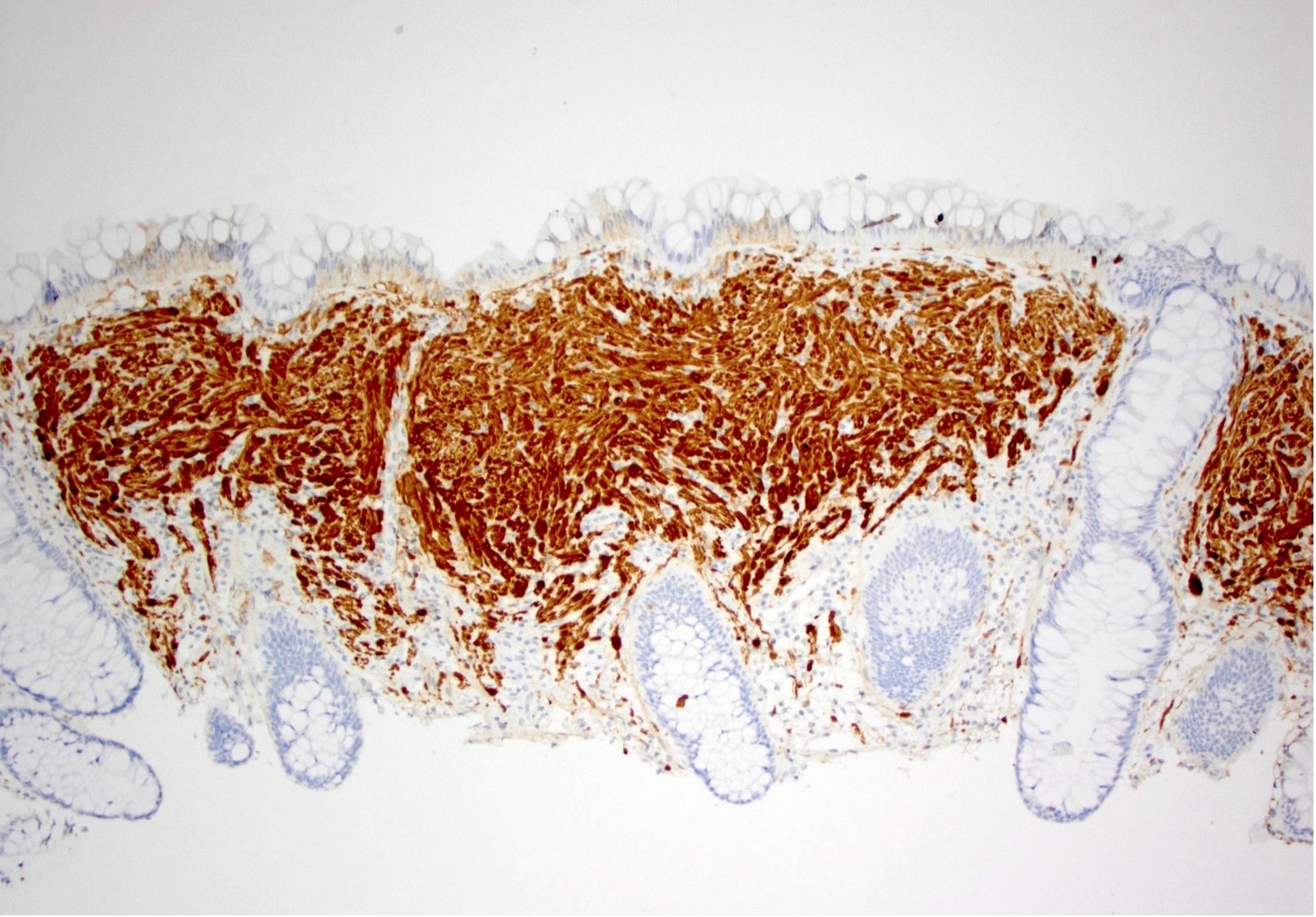
- S100 (lesional cells)
- Neurofilament / NFP (rare intralesional axons)
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Transverse colon, polypectomy:
- Mucosal Schwann cell hamartoma (see comment)
- Comment: An immunohistochemical stain for S100 is positive.
Differential diagnosis
- Perineurioma:
- Ganglioneuroma:
- Ganglion cells present
- Neurofibroma:
- Unlikely to involve mucosa
- Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumor:
- Cells are epithelioid; lesion extends into superficial submucosa (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1310)
- Tactile corpuscle-like body:
- Usually small, incidental finding in mucosal biopsy (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1668)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1