Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Clinical features | Clinical images | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumormetastases.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Secondary involvement of colon by a neoplasm of extracolonic origin
- Uncommon (for example, occurs in 2% of breast and lung carcinomas)
Essential features
- Metastases more common in small intestine than in colon
- Primary lesion is often but not always identifiable
- Most common primaries are stomach, lung, prostate, breast and ovarian carcinomas and melanoma
Clinical features
- Endometrioid adenocarcinoma: if associated with colonic endometriosis, then represents an enigmatic primary rather than a metastasis
- Leukemia: usually involves right colon and terminal ileum, as polypoid or transmural infiltrates
- Melanoma: may have long interval between primary lesion and metastases (Dis Colon Rectum 2003;46:441)
- Prostate: more common to be direct spread / invasion than a metastasis
- Resections for rectal cancer may rarely contain lymph nodes with metastatic prostate carcinoma
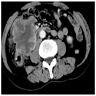
Clinical images
Case reports
- 41 year old man with gastric metastasis to colon (Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2004;20:552)
- 55 and 57 year old women with breast metastases to colon (Tech Coloproctol 2004;8:s135)
- 60 year old man with bladder metastasis to colon (Dig Liver Dis 2006;38:609)
- 64 year old man with lung metastasis to colon (World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:5930)
Gross description
- Central ulceration extending toward mucosa but often sparing it
Microscopic (histologic) description
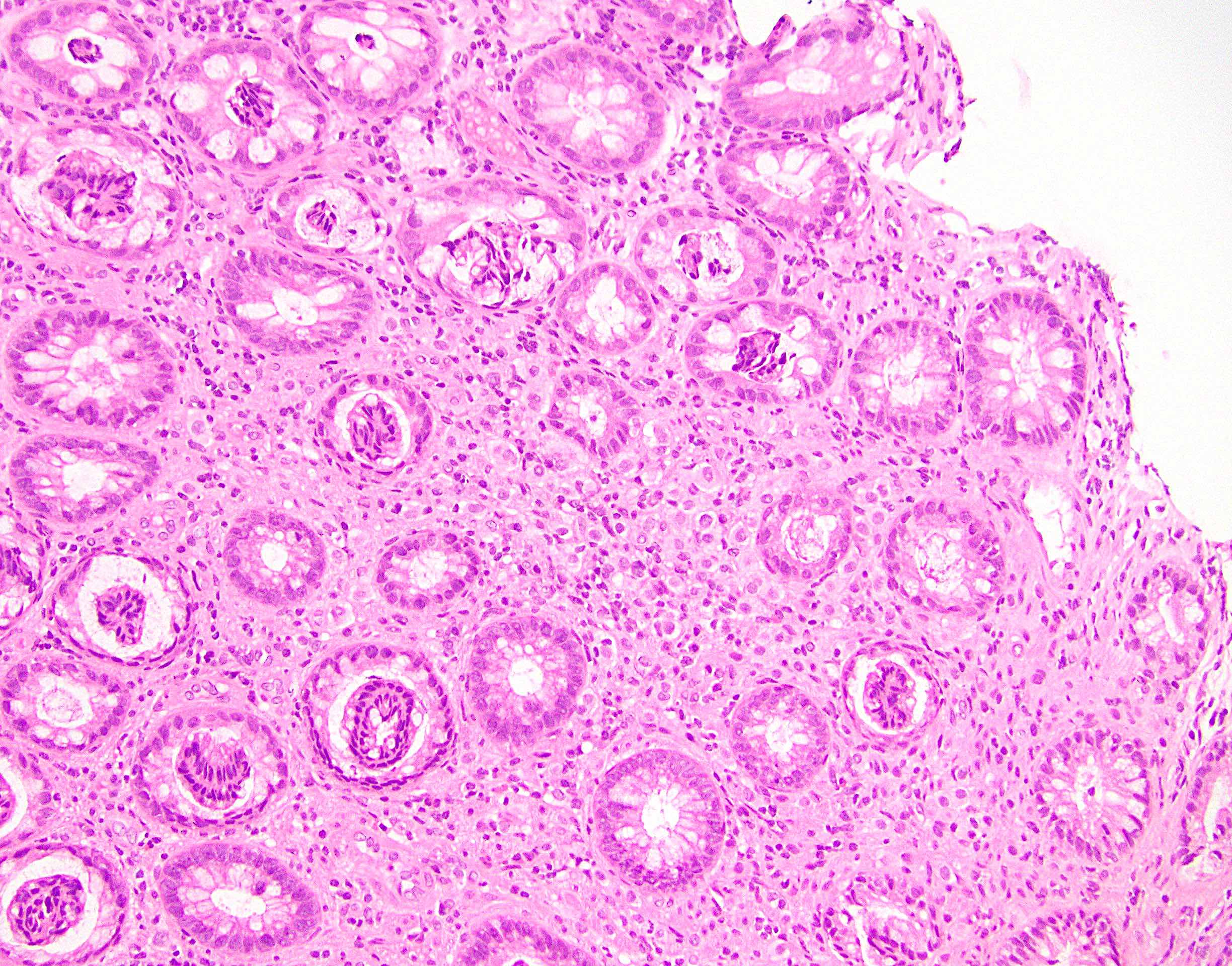
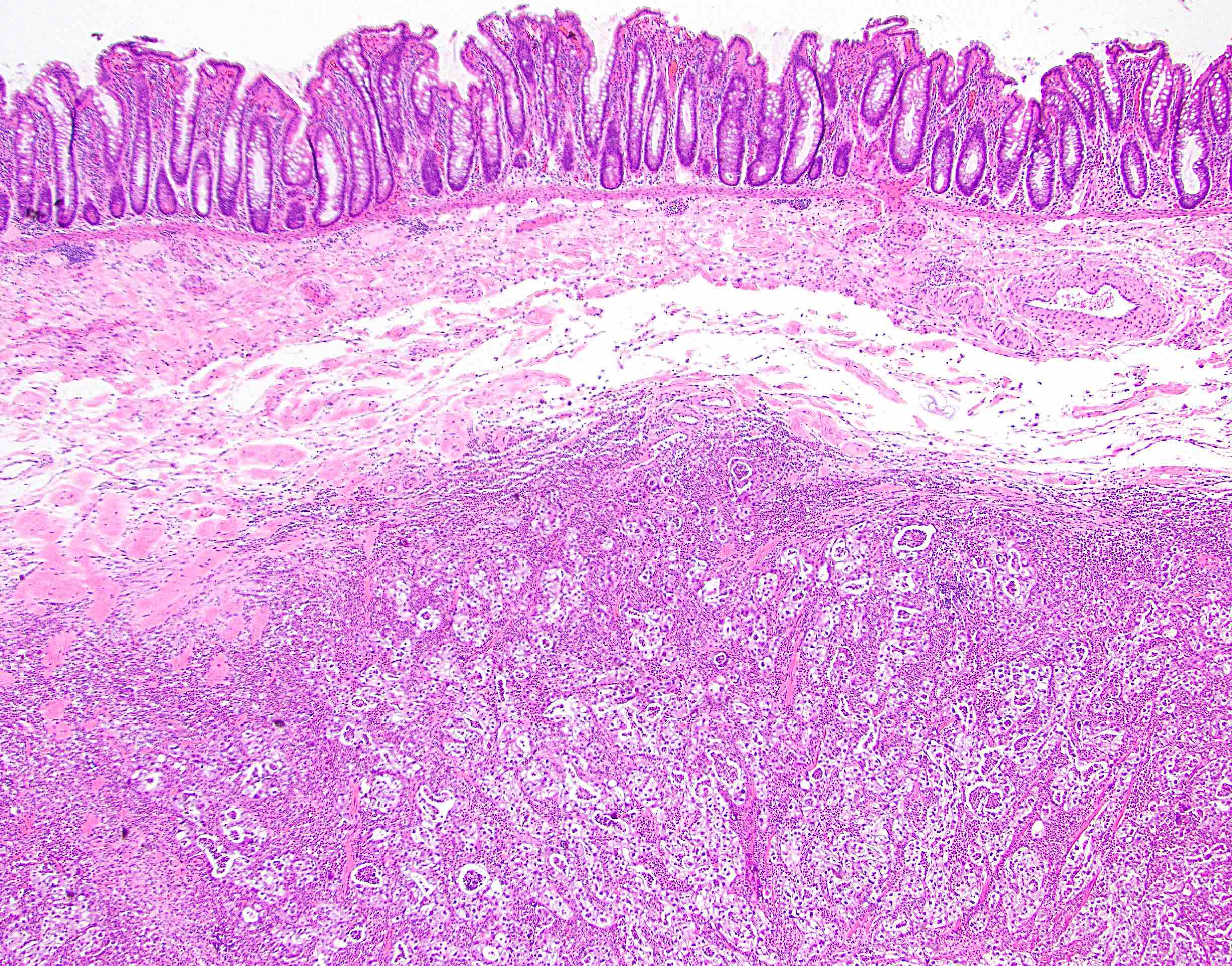
- Disease usually resembles primary tumor microscopically
- Metastases may be present along serosal surface or within the wall but mucosal involvement is uncommon
- Adjacent / overlying colonic epithelium is not dysplastic
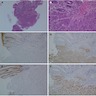
Microscopic (histologic) images
Sample pathology report
- Descending colon, resection:
- Segment of colon with multiple serosal foci of metastatic high grade serous carcinoma, consistent with known ovarian primary
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Eight lymph nodes, negative for malignancy (0/8).
Differential diagnosis
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor:
- Primary colorectal carcinoma:
- Precursor lesion may be present; colonic adenocarcinomas are usually CK20+, CDX2+, CK7-
Board review style question #1
While metastases to the colon are rare, some diseases metastasize there more often than others. Which of the following malignancies metastasizes to the colon relatively frequently?
- Melanoma
- Salivary gland carcinoma
- Synovial sarcoma
- Urothelial carcinoma
Board review style answer #1