Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Laboratory | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorirf.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nonneoplastic fibrosis that develops in retroperitoneum and may encroach upon colon
Essential features
- Benign fibrosing process of the retroperitoneum that can rarely involve the gastrointestinal tract secondarily
- Some cases belong to the spectrum of IgG4 related disease
Terminology
- Also called Ormond disease, idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis
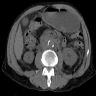
Sites
- Arises in retroperitoneum, often at aortic bifurcation
- Gastrointestinal tract involvement is rare
Etiology
- IgG4 positive plasma cells implicated as a causative factor (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1833)
- Can also be caused by methysergide or lymphoma or may be idiopathic
Clinical features
- Patients present with lower back or abdominal pain; bowel obstruction is rare
- IgG4 related cases usually seen in males
- Associated with other IgG4 related diseases, such as sclerosing cholangitis, Riedel thyroiditis, inflammatory pseudotumor of orbit (World J Gastroenterol 2013;19:7661)
- Can cause obstructive uropathy
Laboratory
- Increased serum IgG and IgG4 in patients with IgG4 related disease
Case reports
- 39 year old woman with bowel obstruction (Ann Surg 1972;176:199)
Treatment
- Options include steroids, azathioprine, tamoxifen and surgery (Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21:2485)
Gross description
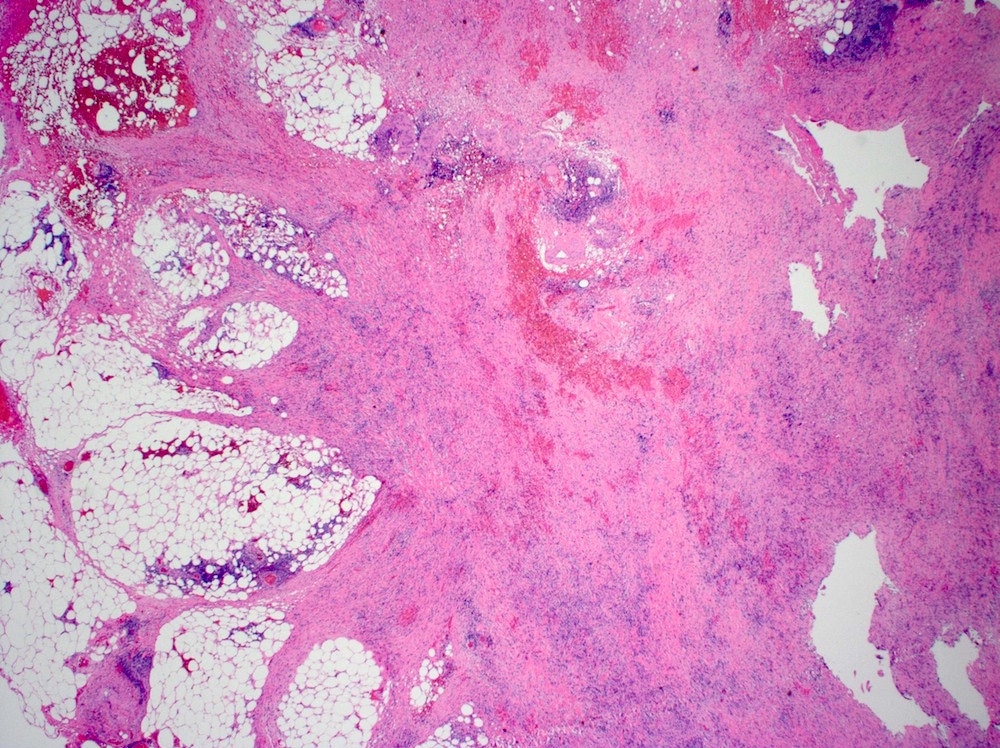
- Poorly circumscribed fibrotic mass
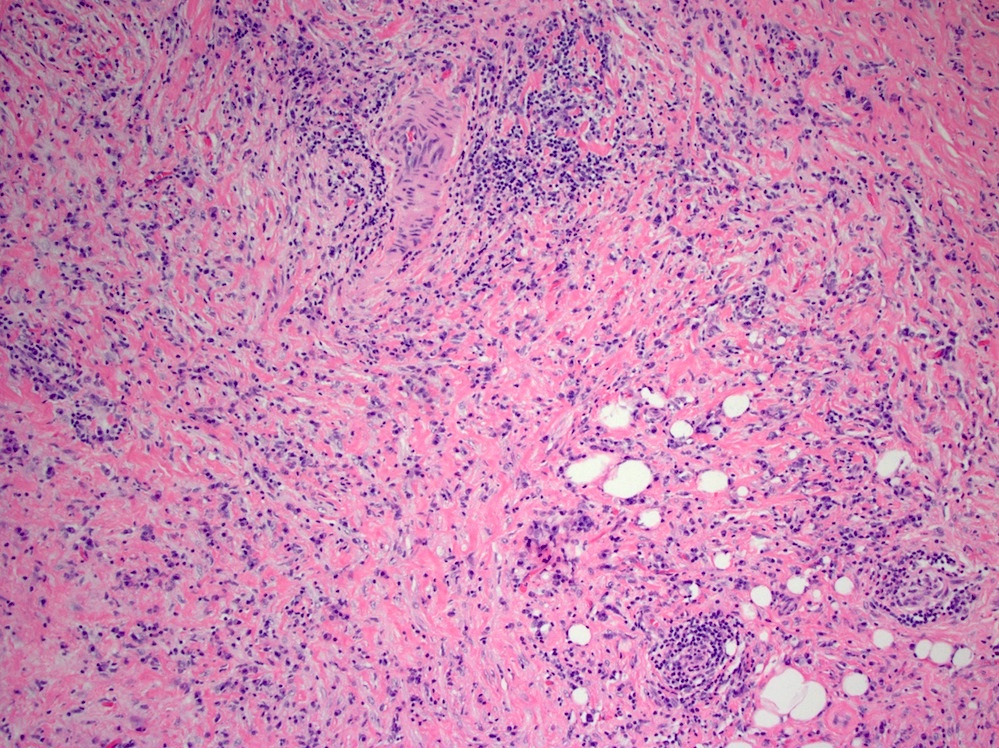
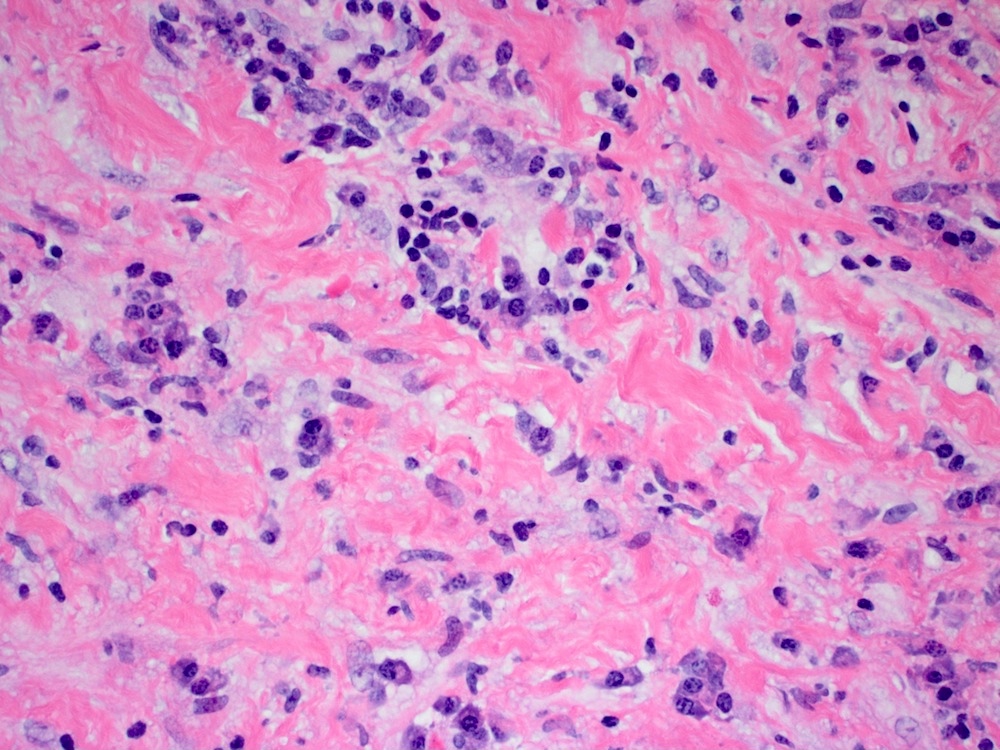
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Storiform fibrotic process infiltrated by eosinophils and IgG4 positive plasma cells (which may be sparse)
- May show obliterative phlebitis, fat necrosis
- Similar findings may be observed in lymph nodes (Am J Clin Pathol 1996;105:430)
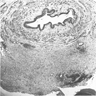
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- IgG4 (in plasma cells)
Sample pathology report
- Transverse colon and adjacent soft tissue mass, excision:
- Prominent bland fibrotic process involving soft tissue and focally extending into colon wall (see comment)
- Negative for malignancy.
- Margins of resection unremarkable.
- Comment: The soft tissue fibrosis shows a storiform pattern and contains abundant chronic inflammation. An immunostain for IgG4 highlights numerous plasma cells. The overall findings are most consistent with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis.
Differential diagnosis
- Sclerosing mesenteritis:
- Involves mesentery rather than retroperitoneum; can also be IgG4 related
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
- Spindle cells more prominent; may be positive for ALK1
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis?
- Colon is often secondarily involved
- Most patients present with lower gastrointestinal bleeding
- Numerous IgG4 positive plasma cells are seen histologically
- Obliterative arteritis can be seen
Board review style answer #1
C. Numerous IgG4 positive plasma cells are seen histologically
Comment Here
Reference: Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis
Comment Here
Reference: Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis