Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Petrolla A, Gonzalez RS. Cowden syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colontumorcowden.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cowden syndrome is one component of the PTEN hamartomatous tumor syndrome, which also includes Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, PTEN related Proteus syndrome and Proteus-like syndrome
Essential features
- Syndrome with autosomal dominant inheritance caused by mutations in PTEN and sometimes other genes
- Causes benign hamartomatous overgrowths of skin, GI tract and thyroid
- Also increases risk of malignancy of breast, thyroid, endometrium and colorectum
Sites
- Affected organs include skin, breast, endometrium and thyroid
- Gastrointestinal manifestations:
- Esophagus: glycogenic acanthosis
- Stomach, duodenum and small bowel: multiple hamartomatous polyp, hyperplastic polyp, ganglioneuroma, adenoma and inflammatory polyp
- Possible association with gastric cancer (Am J Gastroenterol 2005;100:476)
- Colon: multiple polyps, usually hamartomas (resemble juvenile polyps); also ganglioneuroma, adenoma, inflammatory polyp, others (J Natl Cancer Inst 2013;105:1607)
- Lifetime colorectal cancer risk ~9 - 16% (Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:400, Gastroenterology 2010;139:1927)
Clinical features
- Gastrointestinal hamartoma found in 35 - 80% of patients; increased risk for colorectal cancer
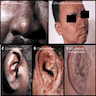
- Mucocutaneous lesions include trichilemmoma, acral keratosis and oral papilloma
- Macrocephaly; dysplastic gangliocytoma of cerebellum (Lhermitte-Duclos disease)
- Breast fibroadenoma, fibrocysttic disease and carcinoma
- Thyroid goiter, adenoma and carcinoma
- Increased risk for endometrial carcinoma
Diagnosis
Case reports
- 29 year old woman with Cowden syndrome diagnosed from multiple gastric polyposis (World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:861)
- 73 year old man with Cowden syndrome presenting with gastric carcinoma and GI polyposis (Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;6:184)
Treatment
Microscopic (histologic) description
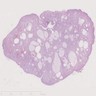
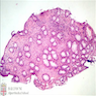
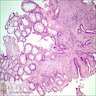
- Colon polyps: nondysplastic epithelium, dilated glands, expanded stroma; histologically similar to juvenile polyps; may also show intramucosal lipomas (Mod Pathol 2018;31:643)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Germline PTEN (phosphate and tensin homologue, 10q23) mutation in 70 - 80% of patients (J Clin Oncol 2004;22:2954)
- Other mutations: SDH (succinate dehydrogenase) B and C mutations, KLLN, PIK3CA, others (OMIM: Cowden Syndrome [Accessed 21 April 2021])
Board review style question #1
Cowden syndrome is caused by a germline mutation in what gene?
- BMPR1A
- KRAS
- PTEN
- STK11
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2