Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Elastofibromatous change. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colonelastofibromatous.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Increase in elastin fibers in colonic submucosa
Essential features
- Uncommon collection of amorphous elastotic material in colon
- Seemingly no clinical significance but can mimic amyloid
Terminology
- Also called elastosis
- Called elastofibroma if forms a polyp
Sites
- Occurs throughout gastrointestinal tract
- In colon, favors left side; can present in rectum
Clinical features
- Patients typically older than 45
- No sex predilection
- May cause nonspecific gastrointestinal symptoms or be asymptomatic
Case reports
- 58 year old woman (Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:793)
- Elastofibromatous polyp of sigmoid colon (Can J Gastroenterol 2003;17:275)
Gross description
- May appear as a polyp or as a linear white lesion
Microscopic (histologic) description
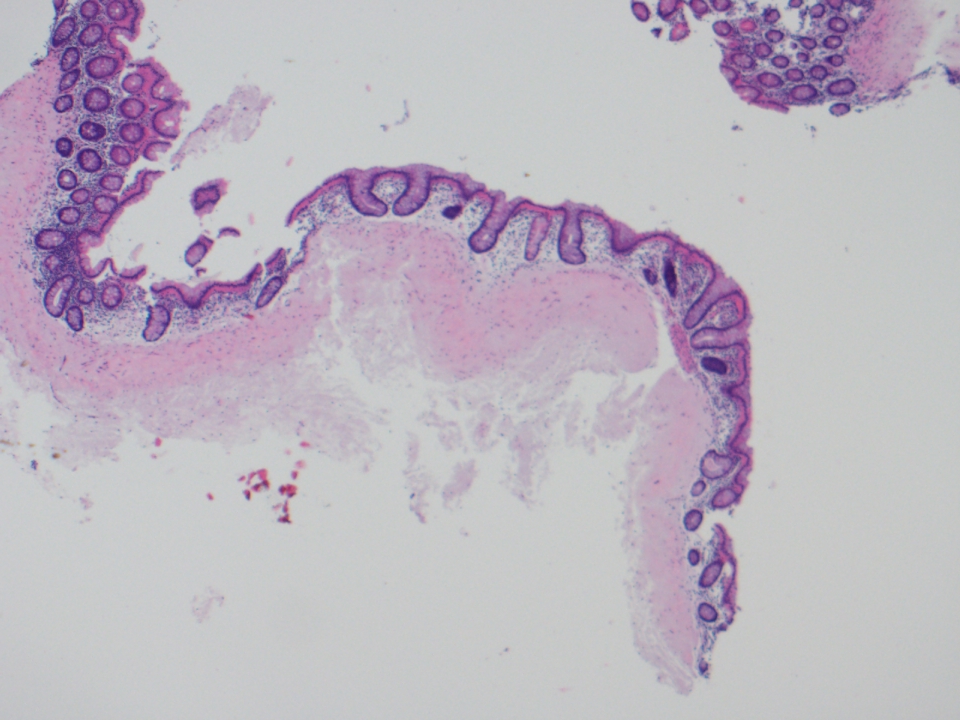
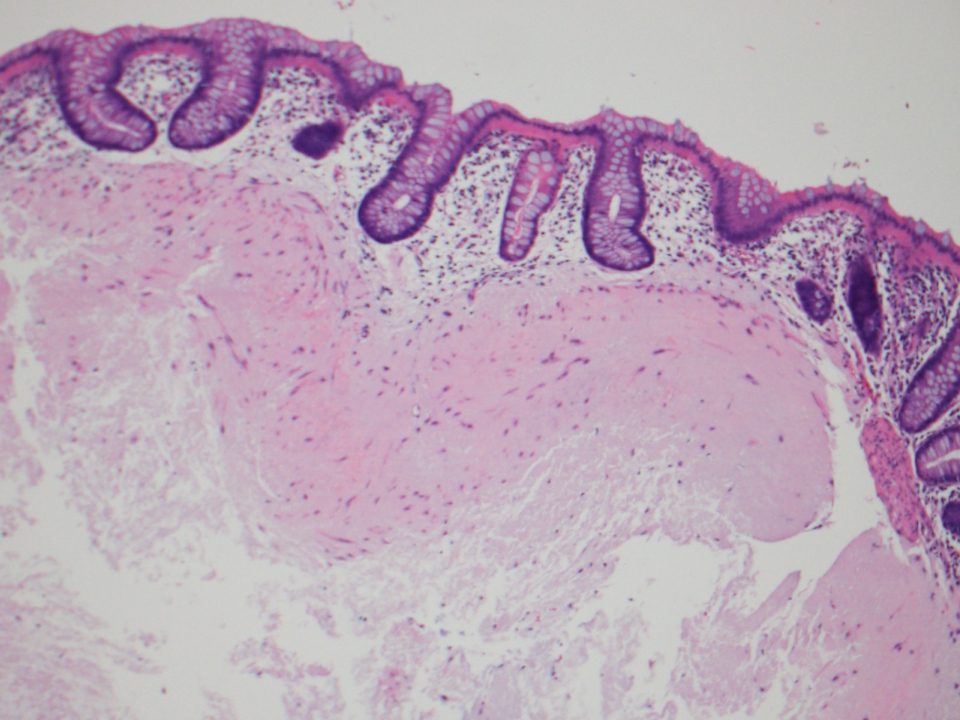
- Eosinophilic to gray amorphous material, sometimes with fibrous tissue, involving submocusa or muscularis mucosae
- May be centered around blood vessels (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;122:232)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
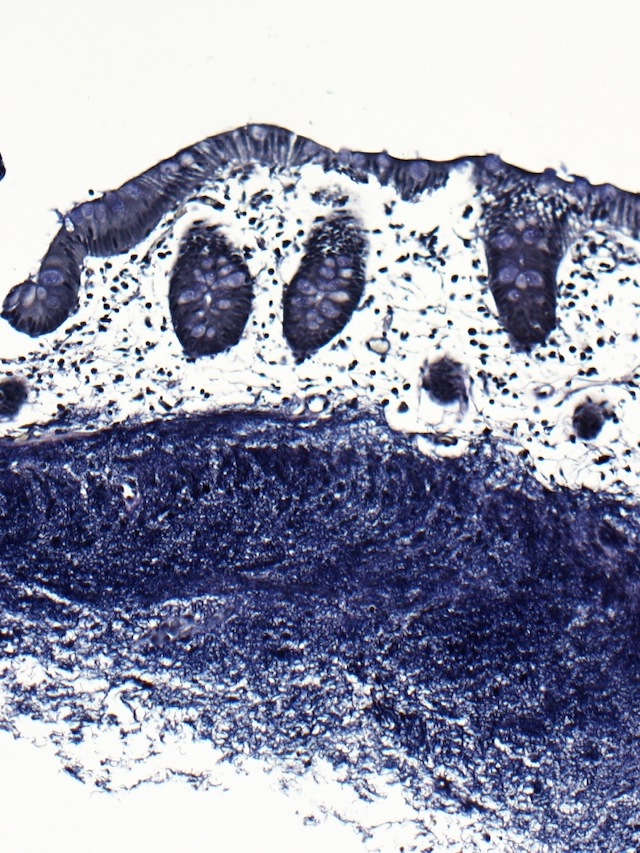
- Elastin stain highlights elastic fibers
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Descending colon, polypectomy:
- Colon with elastofibromatous change (see comment)
- Comment: The polyp consists of submucosal amorphous material that is negative on a Congo red special stain and positive on an elastin special stain.
Differential diagnosis
- Amyloidosis:
- Shows birefringence with Congo red stain
- Lifting agent granuloma:
- Can contain inflammatory component
- History of polypectomy at site
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1