Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Additional referencesCite this page: Gulwani H. Ehlers Danlos syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/colonehlers.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Inherited heterogenous group of connective tissue disorders characterized by abnormal collagen synthesis (eMedicine, Wikipedia)
- Six variants of EDS have been described, based on clinical and molecular features (Am J Med Genet 1998;77:31)
Clinical features
- Clinical symptoms vary by clinical variant, and include skin hyperextensibility and fragility / poor healing; joint hyperextensibility with a propensity to dislocation; eye symptoms with corneal rupture and retinal detachment; kyphoscoliosis and rupture of the colon and large arteries
Vascular type (type IV):
- Autosomal dominant; caused by a mutation in COL3A1 gene (J Nippon Med Sch 2008;75:254)
- Three distinct types of mutations, which affect either the rate of synthesis, the secretion of type III procollagen or result in structurally abnormal type III collagen
- Associated with a reduced median survival of only 48 years
- Neonates have increased incidence of clubfoot and hip dislocation, and rarely have subarachnoid hemorrhage (Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93;579)
- In children, inguinal hernia, pneumothorax and recurrent joint dislocation or subluxation are common; skin is translucent with visible veins and is easily bruised; distinctive facial features are often present, including protruding eyes, a thin nose and lips, sunken cheeks and a small chin
- Blood vessels and intestines are typically rich in type III collagen, and adult patients often present with vascular rupture/dissection or gastrointestinal perforation
- Uterine rupture may occur during pregnancy, particularly at delivery
Case reports
- 9 year old boy with type IV disease (Case #163)
- 17 year old boy with recurrent spontaneous pneumothoraces and cavitary lesion on chest X-ray (Intern Med 2009;48:717)
- Neuromuscular manifestations (J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2009;11:81)
Treatment
- No specific treatment
- Preventative measures are recommended; some patients may improve with high dose Vitamin C
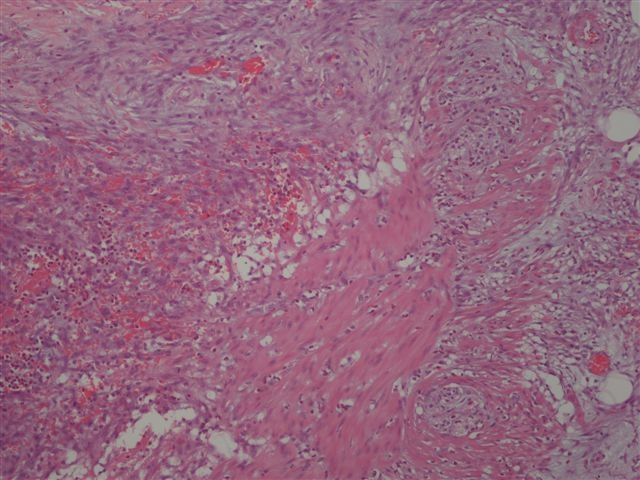
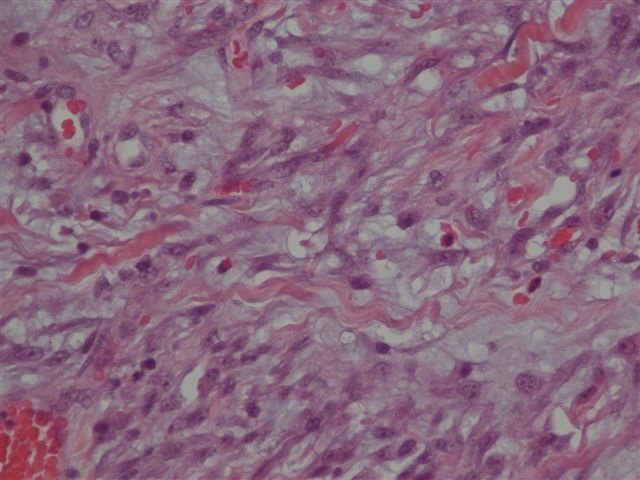
Microscopic (histologic) description
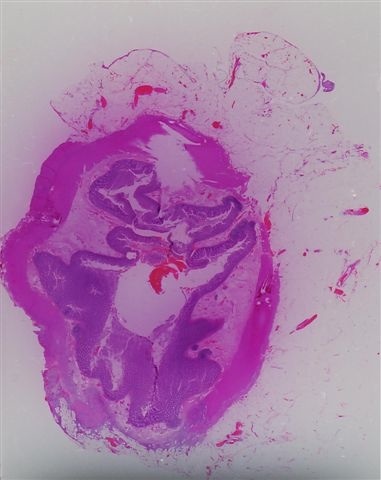
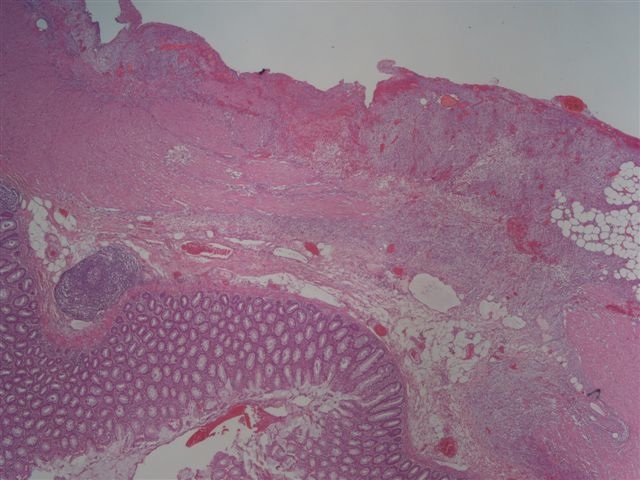
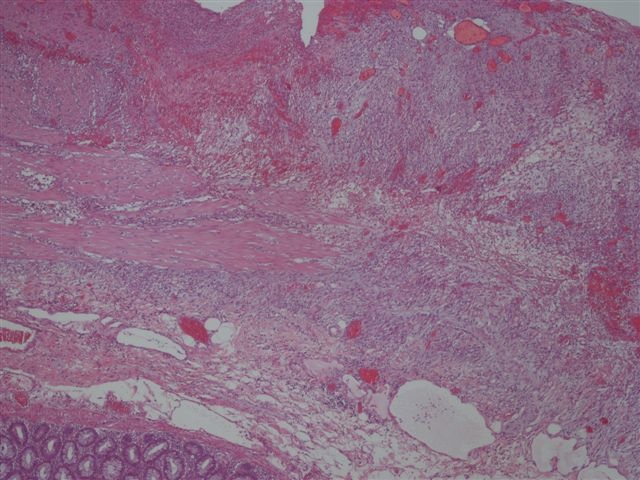
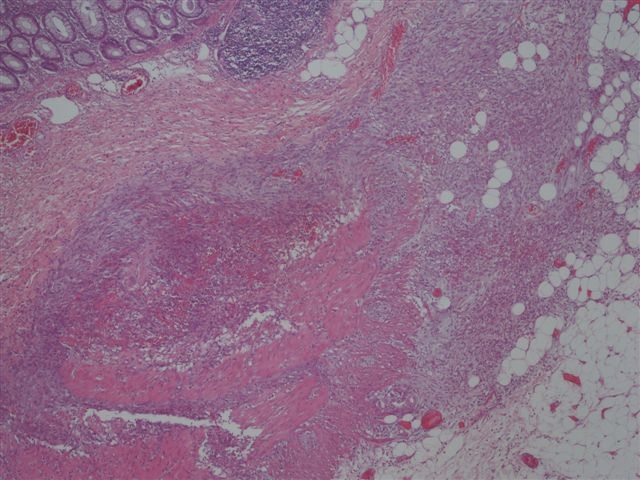
- Often colonic perforation, with mucosal ulceration and thin bowel wall
- May have segmental absence of muscularis propria, with replacement by cellular, reactive fibroblastic proliferation
Additional references