Cite this page: Parsons JC. Other anticoagulants & thrombolytic therapy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/coagulationotheranticoagulants.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Danaparoid (Orgaran)
Definition / general
- Approved to prevent deep venous thromboses
- Also an alternative to heparin for patients with heparin induced thrombocytopenia (Crit Care 2007;11:R102)
- Use is decreasing due to newer anticoagulants
- Composed of low molecular weight glycosaminoglycans (mixture of heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate) that primarily inhibit factor Xa, factor IIa to a much lesser extent
Clinical features
- Similar to low molecular weight heparin in having a more predictable anticoagulant effect, with less need for laboratory monitoring
- Monitor, if desired, by measuring inhibitor of factor Xa using standard curve; draw 6 hours after subcutaneous injection; PT and PTT are unaffected
- Therapeutic levels to treat DVT are 0.5 - 0.8 anti-factor Xa units/ml, lower for DVT prophylaxis
- Long half-life, is prolonged with renal failure
- No reversal agent is known but incomplete reversal is shown with protamine sulfate
- Not marketed in the US since 2004, still available in some countries.
Hirudin
Definition / general
- Anticoagulant approved by FDA to treat thrombosis in patients with heparin induced thrombocytopenia (does not itself cause this type of syndrome)
- Derivatives include lepirudin, refludan
- Recombinant protein, cloned from a leech, which directly inhibits factor IIa (thrombin) (Wikipedia: Hirudin [Accessed 19 April 2021])
- Also has fibrinolytic properties
- More predictable anticoagulant effect than standard heparin, less need for laboratory monitoring, although close monitoring is still advised with PTT, though this assay has limitations (ecarin clotting time is preferable)
- Prolongs PT, PTT, thrombin time, ACT and interferes with most clotting based assays
- Therapeutic range to treat DVT is PTT that is 1.5 - 2.5 x normal but more specific assays are also used to monitor, such as ecarin clotting time
- Half-life ~1 hour, may be prolonged if antibodies develop, dramatically prolonged in renal failure
- No reversal agent
- Reference: Thromb Haemost 2008;99:819
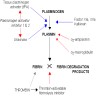
Thrombolytic therapy
Definition / general
- Used to treat myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, arterial or venous thrombosis, thrombotic stroke
- Thrombolytic agents include recombinant t-PA, urokinase, streptokinase (only tPA is widely available in the USA)
- Presence of fibrin degradation products and D-dimers, decreased fibrinogen and plasminogen, prolonged thrombin time, PT and PTT
- References: Clin Lab Med 2009;29:159
Diagrams / tables
Images hosted on other servers:
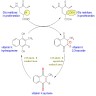
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Definition / general
- Therapeutic anticoagulant to prevent thromboembolism by impairing regeneration of active vitamin K (warfarin is a synthetic derivation based on coumarin)
- Name incorporates the acronym for the organization which funded the key research (WARF) and the ending -arin, indicating its link with coumarin (Wikipedia: Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation [Accessed 19 April 2021])
Clinical features
- Takes 4 - 5 days for complete therapeutic effect due to long half-life of factors II and X
- Must be supplemented with another anticoagulant such as heparin (bridged) until INR is in therapeutic range for 2 consecutive days to prevent Warfarin Skin Necrosis in those with low Protein C
- Therapeutic effect is measured by INR; goal is often INR between 2 and 3
- INR may be elevated by lupus anticoagulants or use of hirudin with warfarin
- Warfarin should not be used alone for acute heparin induced thrombocytopenia because it causes paradoxical thrombosis; must add a rapid acting anticoagulant (hirudin, danaparoid, argatroban) until INR is therapeutic
- PTT may be normal even if low warfarin levels
Treatment of bleeding / overdose
- Vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma
- Also prothrombin complex concentrates (J Clin Pathol 2004;57:1132, J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:1853)
Diagrams / tables
Images hosted on other servers: