Cite this page: Parsons JC. D-dimer / dimerized plasmin fragment D. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/coagulationdimerizedplasminfragmentD.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Marker of ongoing procoagulant activity
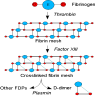
- Fibrin degradation products (fibrin split products) that are formed only by plasmin degradation of fibrin, not by plasmin degradation of intact fibrinogen, thus indicating that fibrin has been formed
- D-regions of fibrinogen are crosslinked by factor XIII after the fibrin clot is formed
- Plasmin cannot cleave the bond between the D-regions, so dimers are also found when a clot is broken down
- Normal plasma level is probably due to physiologic clotting activity
- Specimen:
- Usually plasma with citrate anticoagulant
- Values < 0.5 mg/L with quantitative ELISA assays have good negative predictive value for thromboembolic disorders
- Other values are not predictive (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:519)
- Suggested guidelines for D-dimer testing to rule out pulmonary emboli in patients with low clinical suspicion (if moderate or high clinical suspicion, should do imaging studies):
- Age < 70 years, and no unexplained hypoxemia, unilateral leg swelling, recent surgery, hemoptysis, pregnancy or prolonged duration of symptoms (Acad Emerg Med 2005;12:20)
- Elevated levels are sensitive but not specific for DIC
- Elevated levels after completion of oral anticoagulation are associated with venous thromboemboli
- LIA assay:
- Mix patient plasma with latex particles coated with monoclonal anti-D-dimers or fibrin degradation product antibodies
- Detect agglutination with coagulation analyzer and semiquantitate with dilutions
- Although this is called a Latex ImmunoAssay, it differs from the qualitative latex agglutination assay that is NOT predictive of pulmonary emboli
- ELISA method:
- Also available
- False positives:
- Recent surgery
- HIV+ Castlemans disease due to interference from monoclonal gammopathy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:328)
- High rheumatoid factor
- Liver disease
- Cancer patients
- Pregnancy
- Note: Some platforms use fibrinogen equivalent units, which are 50% the numerical value of D-dimer units