Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Kresak J, Yachnis A. Rhabdoid meningioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorrhabdoidmeningioma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- WHO grade 3 due to aggressive behavior and metastatic potential
- High rate of recurrence
- Rhabdoid morphology may increase with recurrences
Sites
- May be supratentorial, infratentorial or spinal
Radiology description
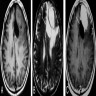
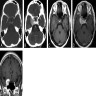
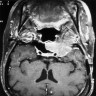
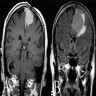
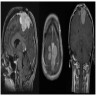
- MRI may show irregular tumor borders, cystic component, heterogenous tumoral enhancement and peritumoral edema suggesting a high grade meningioma (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007;28:1462)
Radiology images
Case reports
- 8 year old girl (Med Arh 2010;64:123) and 15 year old boy (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:964)
- 47 year old woman with recurrent tumor (Skull Base 2003;13:51)
- 55 year old woman with intraventricular tumor (J Clin Neurosci 2007;14:672)
- 60 year old man with recurrent extracerebral tumor (University of Pittsburgh: A Male in His Late 60's with Recurrent Extracerebral Tumor)
- Lacking malignant features (Clin Neuropathol 2004;23:16)
- Intraspinal tumor with metastasis to liver (J Clin Neurosci 2011;18:714)
Treatment
- Gross total resection
- Postsurgical radiotherapy (Front Oncol 2013;3:227)
- Radiosurgery (Radiat Oncol 2014;9:38)
Gross description
- Dural based
- May be well circumscribed or readily adherent to brain parenchyma
- Size can vary
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Sheets of loosely cohesive cells with eccentric nuclei and hyaline, paranuclear inclusions
- Nuclei may show pleomorphism, with vesicular chromatin and prominent nucleoli
- May retain meningothelial features including whorl formation and nuclear pseudoinclusions
- May have brain invasion
- Often increased mitotic activity (greater than 4/10 HP)
- May have papillary features
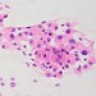
Cytology description
- Rhabdoid cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, cytoplasmic hyaline inclusions, eccentric nuclei
- Stout processes consistent with meningioma; however distinct cell borders
- Often vesicular nuclei with prominent nucleoli
- May see mitoses on smear
- May see pseudonuclear inclusions (Diagn Cytopathol 2010;38:594)
Positive stains
- EMA (variable), PR (in a subset; helpful if positive, not ruled out if negative), vimentin
- INI1 (Mod Pathol 2005;18:951)
- Cytokeratins may pick up cytoplasmic inclusions
- Ki67 (often 10% or more)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cytoplasmic whorls of intermediate filaments often entrapping lysosomes or other organelles
- Interdigitating cell membranes and intercellular junctions
Differential diagnosis