Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Abdelzaher E. Papillary glioneuronal tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorpapillaryglioneuronal.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Low grade glioneuronal tumor with a biphasic pattern composed of pseudopapillary glial structures and interpapillary neuronal components; also characterized by PRKCA gene fusion (mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion)
- Corresponds to WHO grade 1
Essential features
- Rare, low grade glioneuronal neoplasm with biphasic histological and immunophenotypic pattern characterized by pseudopapillae lined by GFAP positive glial cells with interpapillary synaptophysin positive neuronal elements (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- First described by Komori et al. (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171)
- Papillary glioneuronal tumor (PGNT) is characterized by PRKCA gene fusion (mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion) and a distinctive methylation profile
- Supratentorial, well delineated and often cystic tumors with predilection for young adults
- Favorable prognosis with gross total resection
Terminology
- Not recommended by WHO: pseudopapillary ganglioneurocytoma, pseudopapillary neurocytoma with glial differentiation
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9509/1 - papillary glioneuronal tumor
- ICD-11: 2A00.21 & XH3XU4 - mixed neuronal glial tumors & papillary glioneuronal tumor
Epidemiology
- Rare (J Cancer Res Ther 2023;19:1426)
- Age: predilection for young adults (median age at diagnosis is 16 years, range: 6 - 54 years) (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, Debinski: Gliomas, 1st Edition, 2021, World Neurosurg 2017;107:534)
- No gender predilection (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080)
Sites
- Supratentorial, with predilection for temporal and frontal lobes (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, World Neurosurg 2017;107:534, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Propensity for the ventricular system, with > 60% of tumors in a periventricular or intraventricular location (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, World Neurosurg 2017;107:534, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- It can occur anywhere in the cerebrum, cerebellum or brainstem (World Neurosurg 2017;107:534)
Pathophysiology
- PRKCA gene fusion is the hallmark of PGNT, mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion; less frequently NOTCH1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Reciprocal translocation t(9;17)(q31;q24) results in the canonical SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion with consequent generation of a constitutively expressed oncoprotein (Brain Pathol 2013;23:121)
- PRKCA encodes protein kinase C alpha (PKCA) involved in MAPK signaling pathway (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Principal manifestations include headache and seizures and mass effects (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695, Debinski: Gliomas, 1st Edition, 2021)
- Occasionally asymptomatic (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080)
- Hemorrhagic onset has been reported (Neuropathology 2006;26:206, Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013;115:200)
Diagnosis
- Neuroimaging: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT)
- Biopsy: diagnosis should be heavily weighted toward molecular findings because morphological analyses frequently result in mistyping (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- WHO diagnostic criteria
- WHO essential diagnostic criteria
- Biphasic histological and immunophenotypic pattern with pseudopapillary glial lining and interpapillary neuronal components
- PRKCA gene fusion (mostly SLC44A1::PRKCA)
- For unresolved lesions: methylation profile of papillary glioneuronal tumor
- WHO desirable diagnostic criteria
- Well delineated, solid and cystic tumor
- WHO essential diagnostic criteria
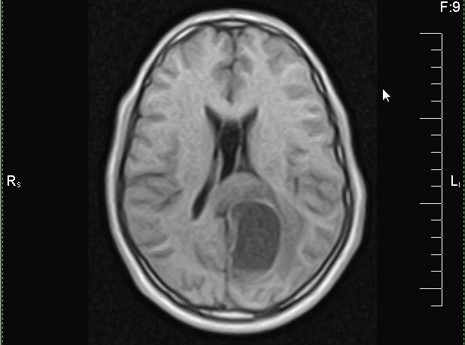
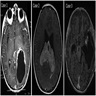
Radiology description
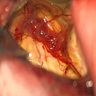
- MRI
- Supratentorial, well delineated
- Cystic and / or solid, some cases are cystic with a mural nodule (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695, Debinski: Gliomas, 1st Edition, 2021, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080, Brain Pathol 2013;23:121)
- Solid component is hypo to isointense on T1 weighted images and iso to hyperintense on T2 weighted images (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080)
- Contrast enhancing (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695)
- Most tumors show no or only minimal peritumoral edema and little mass effect; peritumoral edema was reported in 25% of cases (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080, Neurosurg Rev 2024;47:179)
- No diffusion restriction (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Outcome is usually favorable, with a reported median 5 year progression free survival > 80% (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- Gross total resection constitutes the main prognostic factor; male sex and low Ki67 proliferation index were also reported as positive prognostic indicators (World Neurosurg 2017;107:534, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080)
- Recurrence was reported in one molecularly confirmed case, while it was documented in 11.8% of morphologically diagnosed cases, with higher rates associated with incomplete resection (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2014;156:627)
- Increased Ki67 proliferation index (> 20%) or anaplastic features with tumoral progression or dissemination have been reported in morphologically diagnosed cases but have not been described in PRKCA fused cases (World Neurosurg 2017;107:534, J Neurosurg Pediatr 2009;3:46, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2014;156:627)
Case reports
- 14 year old boy with intraventricular papillary glioneuronal tumor (J Cancer Res Ther 2023;19:1426)
- 16 year old girl with suprasellar papillary glioneuronal tumor mimicking craniopharyngioma (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:85)
- 38 year old man with papillary glioneuronal tumor growing slowly for 26 years (J Neurosurg Case Lessons 2021;2:CASE21266)
- 48 year old woman with papillary glioneuronal tumor masquerading as malignant brain tumor (Yonago Acta Med 2023;66:385)
- 64 year old man with papillary glioneuronal tumor with an excessive angiomatous component (Chin Med J (Engl) 2018;131:243)
Treatment
- Gross total resection is optimal (Debinski: Gliomas, 1st Edition, 2021)
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are used rarely, on a case by case basis (World Neurosurg 2017;107:534)
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, solid and / or cystic lesions
- Calcification and hemorrhage may be observed
Microscopic (histologic) description
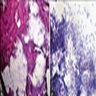
- Characterized by a biphasic pattern created by a glial pseudopapillary component and an interpapillary neuronal component with variable proportions of both components (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171)
- Glial component is composed of a single or pseudostratified layer of small cuboidal glial cells with round nuclei and scant cytoplasm, lining pseudopapillary structures (present in 93% of molecularly confirmed PGNTs) with hyalinized vascular cores (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- Neuronal component is composed of uniform neurocytes or medium sized neurons disposed in a neuropil background (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171)
- Ganglion cells (21.4%), microcalcifications (35.7%) may be seen (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- Rarely, eosinophilic granular bodies may be encountered (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Occasional mitoses may be seen (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- Microvascular proliferation and necrosis are absent (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171)
- Anaplastic features were rarely reported in nonmolecularly confirmed cases (J Neurosurg Pediatr 2009;3:46, Clin Neuropathol 2007;26:119)
- Peritumoral reactive gliosis
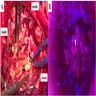
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Eman Abdelzaher, M.D., Ph.D.
Cytology description
- Nonspecific
- May exhibit vague papillary structures with hyalinized cores lined by bland tumor cells (J Cancer Res Ther 2023;19:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1794)
- Loosely cohesive clusters and singly scattered tumor cells with mildly pleomorphic round to oval nuclei with stippled chromatin, small nucleoli and scant to moderate cytoplasm (Ann Diagn Pathol 2021;53:151757, J Cancer Res Ther 2023;19:1426, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1794)
Cytology images
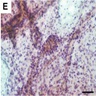
Positive stains
- Biphenotypic immunophenotype: glial in pseudopapillary structures and neuronal in interpapillary areas
- GFAP: positive in glial cells ensheathing pseudopapillae and in scattered cells in interpapillary areas (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695, Brain Pathol 2013;23:121)
- S100: positive in glial cells (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2022;43:1080, Brain Pathol 2013;23:121)
- Olig2: positive in glial cells; in some cases, oligodendrocyte-like cells (Olig2+ and GFAP-) may be seen (Acta Neuropathol 2005;110:39)
- Synaptophysin: positive in neuronal component (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695)
- NeuN: positive in neuronal component (Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2016;158:695)
- NFP / neurofilament: mostly confined to ganglioid / ganglion cells
Negative stains
- Chromogranin A: variable (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- CD34: may be focally positive (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- p53 (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- H3K27 (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- BRAF V600E (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- EMA (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:85)
- IDH1 (R132H) (NMC Case Rep J 2020;7:85, J Neurosurg Case Lessons 2021;2:CASE21266)
Electron microscopy description
- Pseudopapillae are surrounded by elongated astrocytes containing polarized bundles of intermediate filaments (Acta Neuropathol 2000;99:321)
- Other cell types include neuronally differentiated cells with microtubule containing processes and / or true but aberrant synapses characterized by synaptic vesicles and synaptic junctions; dense core granules are rare (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1171, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1794)
- Poorly differentiated or uncommitted primitive cells are also detected (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1794)
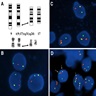
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PRKCA gene fusions (mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA and less frequently NOTCH1::PRKCA) invariably occur in PGNT but very rarely in other entities (Brain Pathol 2013;23:121, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85, Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- No PRKCA recurrent point mutation has been reported in PGNT
- Notably, PRKCA is involved in the MAPK signaling pathway; however, PGNTs lack the BRAF mutations that are found in other neuronal and glioneuronal tumors with mutations in the MAPK pathway (StatPearls: Neuronal Brain Tumors [Accessed 29 April 2024])
- PGNTs exhibit a highly characteristic and diagnostic methylation profile (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837, Acta Neuropathol Commun 2020;8:27)
- Copy number variation analysis reveals flat profiles or only focal abnormalities on the chromosomal arm 17q involving the PRKCA locus (in 50% of cases), possibly as a genomic scar of the translocation formation (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Case 4, papillary glioneuronal tumor
Sample pathology report
- Left temporal lobe mass lesion, gross total resection:
- Papillary glioneuronal tumor, CNS WHO grade 1
- Molecular genetics: PRKCA gene fusion (SLC44A1::PRKCA)
Differential diagnosis
- PGNT diagnosis is challenging and it should be heavily weighted toward molecular findings because morphological assessment frequently results in mistyping which reflects the morphological heterogeneity of PGNT (Acta Neuropathol 2019;137:837)
- Ganglioglioma:
- CD34+ (70 - 80%) (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- BRAF V600E positive (40%) (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Astroblastoma:
- EMA+
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- MN1 alteration
- Neurocytic tumors:
- No perivascular GFAP+ neoplastic glial component, only scattered reactive astrocytes
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor:
- Intracortical lesion with distinctive nodular pattern
- Floating neurons
- Myxoid background
- Pilocytic astrocytoma:
- Biphasic compact and spongy pattern with microcysts
- Rosenthal fibers
- Widespread GFAP positivity
- KIAA1549::BRAF fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Rosette forming glioneuronal tumor:
- Synaptophysin+ neuropil cores of neurocytic rosettes and neuropil of perivascular pseudorosettes
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (J Clin Neurosci 2016;23:73)
- Ependymoma:
- GFAP+, which is accentuated in perivascular pseudorosettes (Pathol Res Pract 2007;203:613)
- Often Olig2- (Histol Histopathol 2016;31:95)
- EMA+ with a paranuclear dot-like pattern and along luminal surfaces of true ependymal rosettes
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- ZFTA (C11orf95) or YAP1 rearrangements in supratentorial ependymomas
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma:
- Tumor of infancy occurring in the hypothalamic / chiasmatic region
- Monomorphic piloid cytology
- Diffusely myxoid background
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma:
- Pleomorphic tumor cells, spindle cells, xanthomatous (lipidized) cells
- Reticulin deposition
- BRAF mutation
- Angiocentric glioma:
- Negative for neuronal markers
- Olig2-
- No SLC44A1::PRKCA fusion (Acta Neuropathol Commun 2015;3:85)
- Oligodendroglioma:
- Diffuse infiltration, with secondary structures
- 1p/19q codeletion
- Choroid plexus papilloma:
- True, rather than pseudopapillae
- Cytokeratin+
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 26 year old man presented with seizures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a left temporal lobe mass lesion with an enhancing cyst mural nodule pattern. Gross total resection of the tumor was done and the histopathological features of the tumor are shown in the image above. Which of the following genetic abnormalities is the hallmark of this tumor?
- 1p/19q codeletion
- KIAA1549::BRAF fusion
- MN1 alteration
- PRKCA gene fusion
Board review style answer #1
D. PRKCA gene fusion (mainly SLC44A1::PRKCA) is the hallmark of papillary glioneuronal tumor (PGNT). Answer A is incorrect because 1p/19q codeletion is characteristic of oligodendroglioma. Answer B is incorrect because KIAA1549::BRAF fusion is characteristic of pilocytic astrocytoma. Answer C is incorrect because MN1 alteration is the hallmark of astroblastoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary glioneuronal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary glioneuronal tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is the most distinctive histological feature of papillary glioneuronal tumor?
- Biphasic with compact elongated piloid cells alternating with loosely textured spongy areas
- Biphasic with pseudopapillary gliovascular structures associated with intervening neuronal cells ranging from neurocytes to ganglion cells
- Intracortical lesion with a distinctive nodular pattern with a myxoid background and floating neurons
- Neurocytic rosettes or perivascular pseudorosettes with synaptophysin+ neuropil
Board review style answer #2
B. Biphasic with pseudopapillary gliovascular structures associated with intervening neuronal cells ranging from neurocytes to ganglion cells. Papillary glioneuronal tumor is histologically characterized by a biphasic pattern composed of pseudopapillary glial structures and interpapillary neuronal components. Answer A is incorrect because pilocytic astrocytoma is histologically characterized by a biphasic pattern with compact elongated piloid cells alternating with loosely textured spongy areas. Answer C is incorrect because dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor is histologically characterized by being an intracortical lesion with distinctive nodular pattern with a myxoid background and floating neurons. Answer D is incorrect because neurocytic rosettes or perivascular pseudorosettes with syanptophysin+ neuropil are the histological hallmarks of rosette forming glioneuronal tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary glioneuronal tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary glioneuronal tumor