Table of Contents
Definition / general | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Immunostains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Pernick N. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumormetastaticcarcinoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Most common brain tumors in community hospitals are metastases (50% of intracranial tumors in hospitalized patients)
- Primary is usually known: melanoma or carcinoma (lung, breast, kidney and GU), occasionally germ cell tumor
- Common with choriocarcinoma
- Common presentation is adult with seizures or ataxia
- Dural metastases are often from breast and prostate, but also unusual primaries; may have survival of 2+ years (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001;125:880)
- Metastases to vertebral column: often prostate, breast or hematopoietic neoplasm
- Metastases with unknown primary: lung, colon, kidney
- Multiple lesions are suggestive of metastasis vs. primary CNS tumor
- Usually to cerebrum, but no distinct patterns
Meningeal carcinomatosis:
- Represents 4-8% of metastatic brain tumors
- Diffuse spread of tumor in subarachnoid space
- Associated with carcinoma of lung and breast and ALL
- Poor prognosis
- Repeat lumbar punctures and immunocytochemistry may be helpful in differentiating from aseptic meningitis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:759)
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognostic factors: single metastasis, younger age, surgical resection of metastasis, primary in lung (non-small cell), breast, melanoma, renal cell or ovary
Case reports
Meningeal carcinomatosis:
- 18 year old woman with primary alveolar soft part sarcoma in tongue when 8 years old and multiple pulmonary metastases (Case #222)
- 26 year old man with metastatic renal collecting duct carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:638)
- 37 year old man with metastatic salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma to spinal cord (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:887)
- 38 year old man with contralateral adenoid cystic carcinoma of external ear canal (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:87)
- A middle aged woman with a history of lung carcinoma presented with a single cerebellar mass (Case #425)
- 77 year old woman with obstructive hydrocephalus due to gallbladder carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001;125:1120)
- Leptomeningeal melanomatosis due to shoulder melanoma (Hum Pathol 2003;34:625)
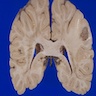
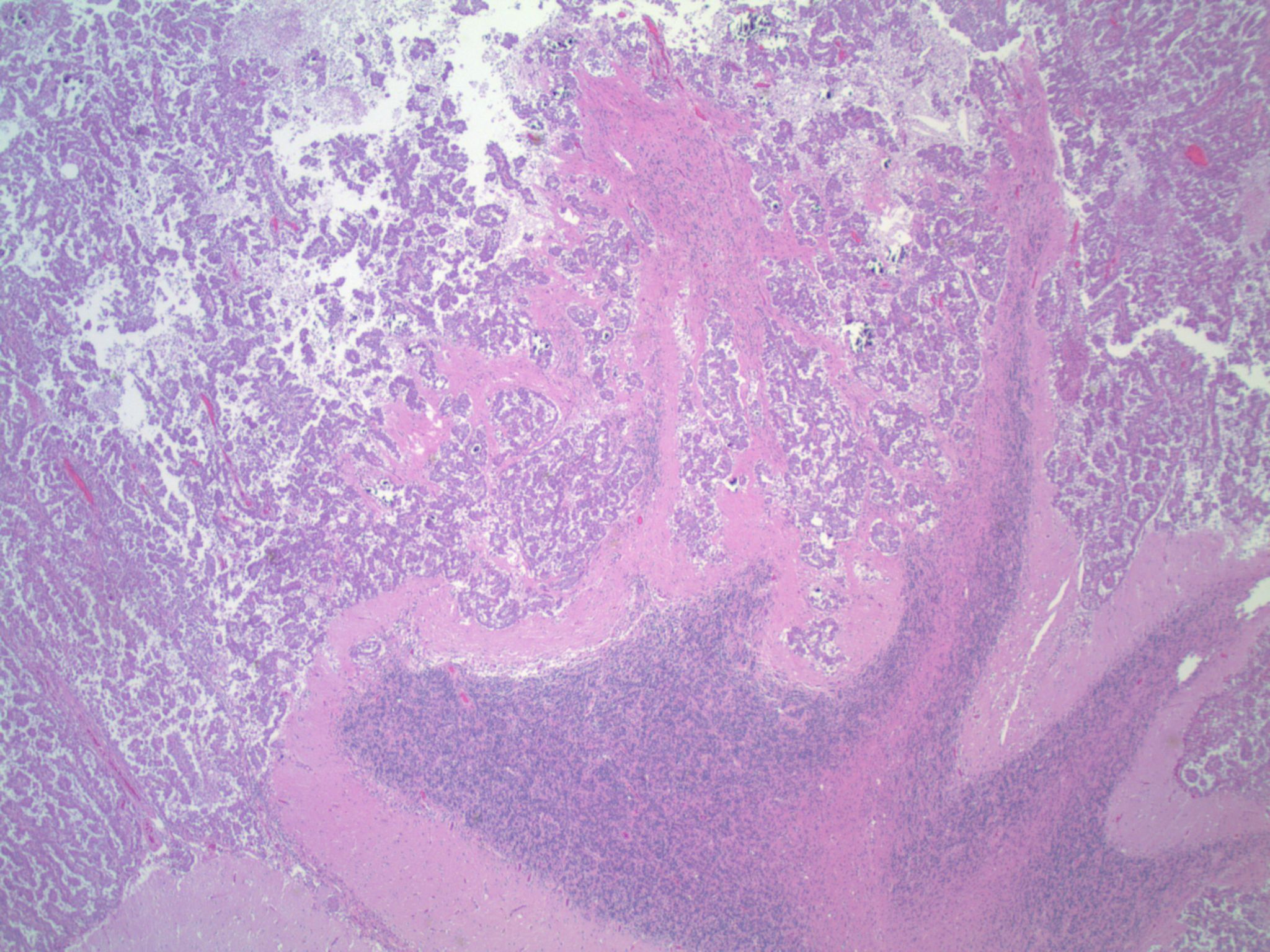
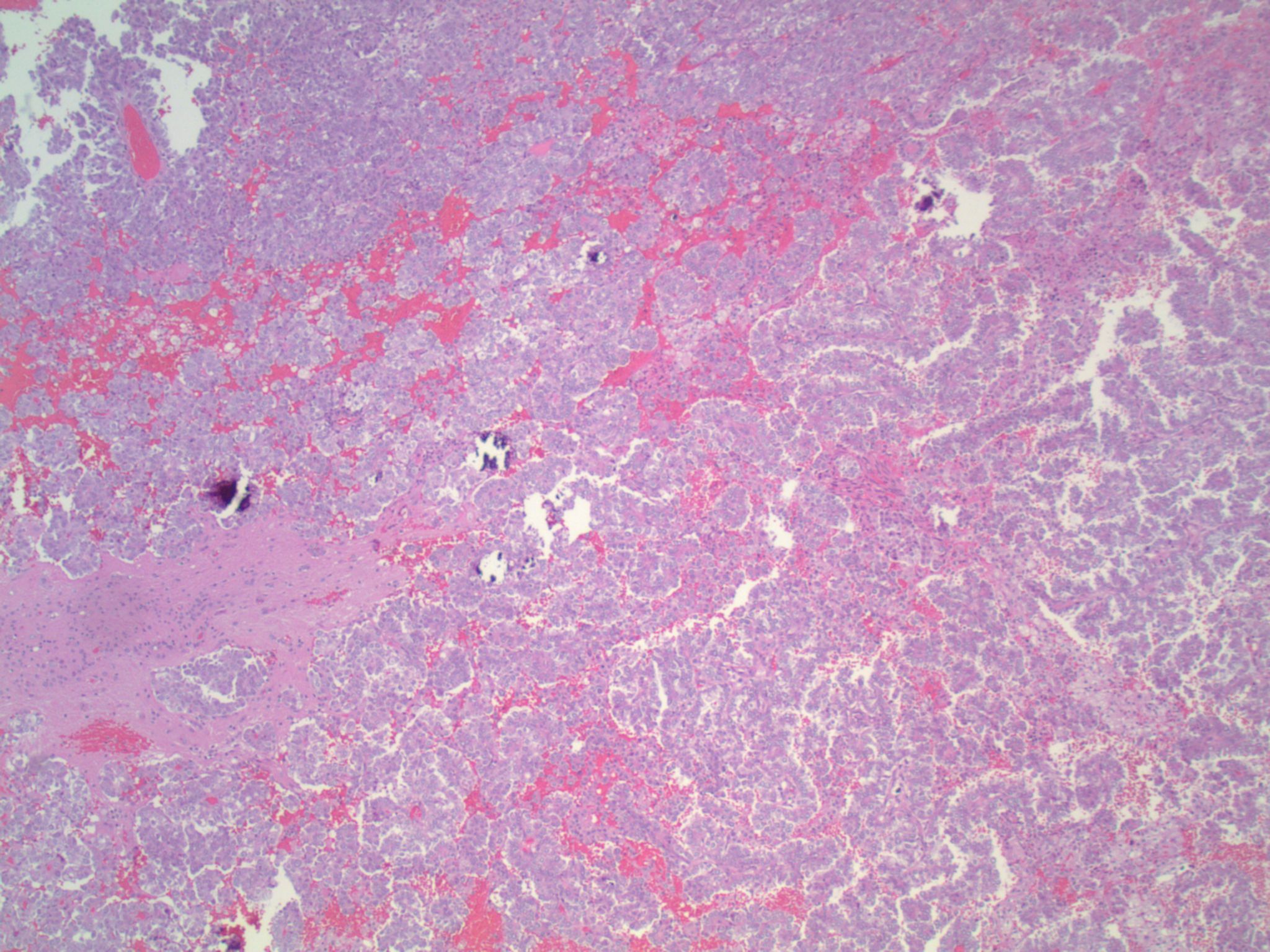
Gross description
- Sharply demarcated lesion at gray-white matter junction, surrounded by edema
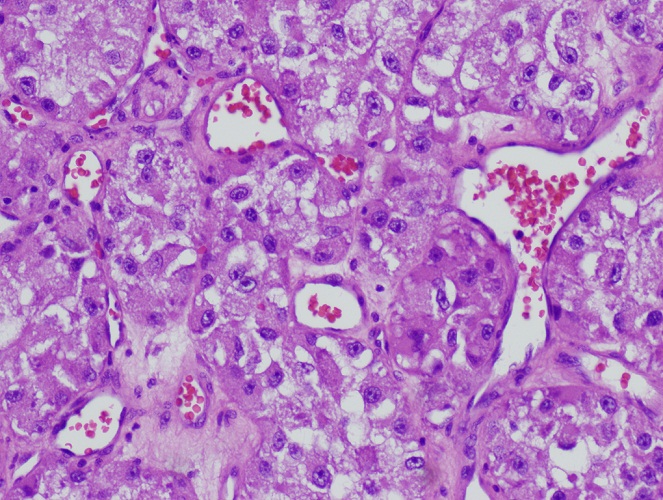
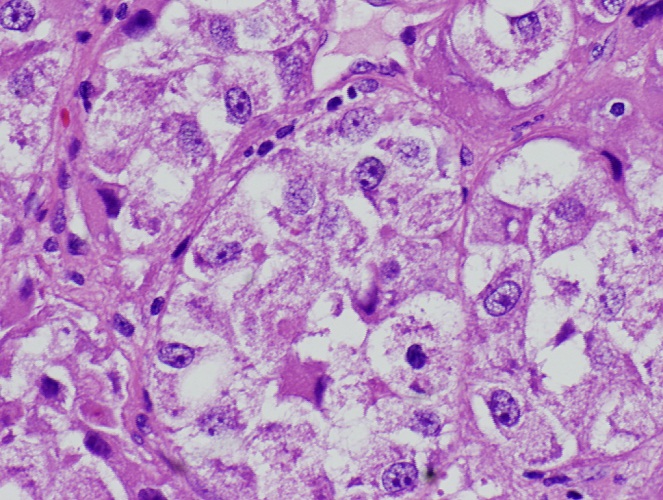
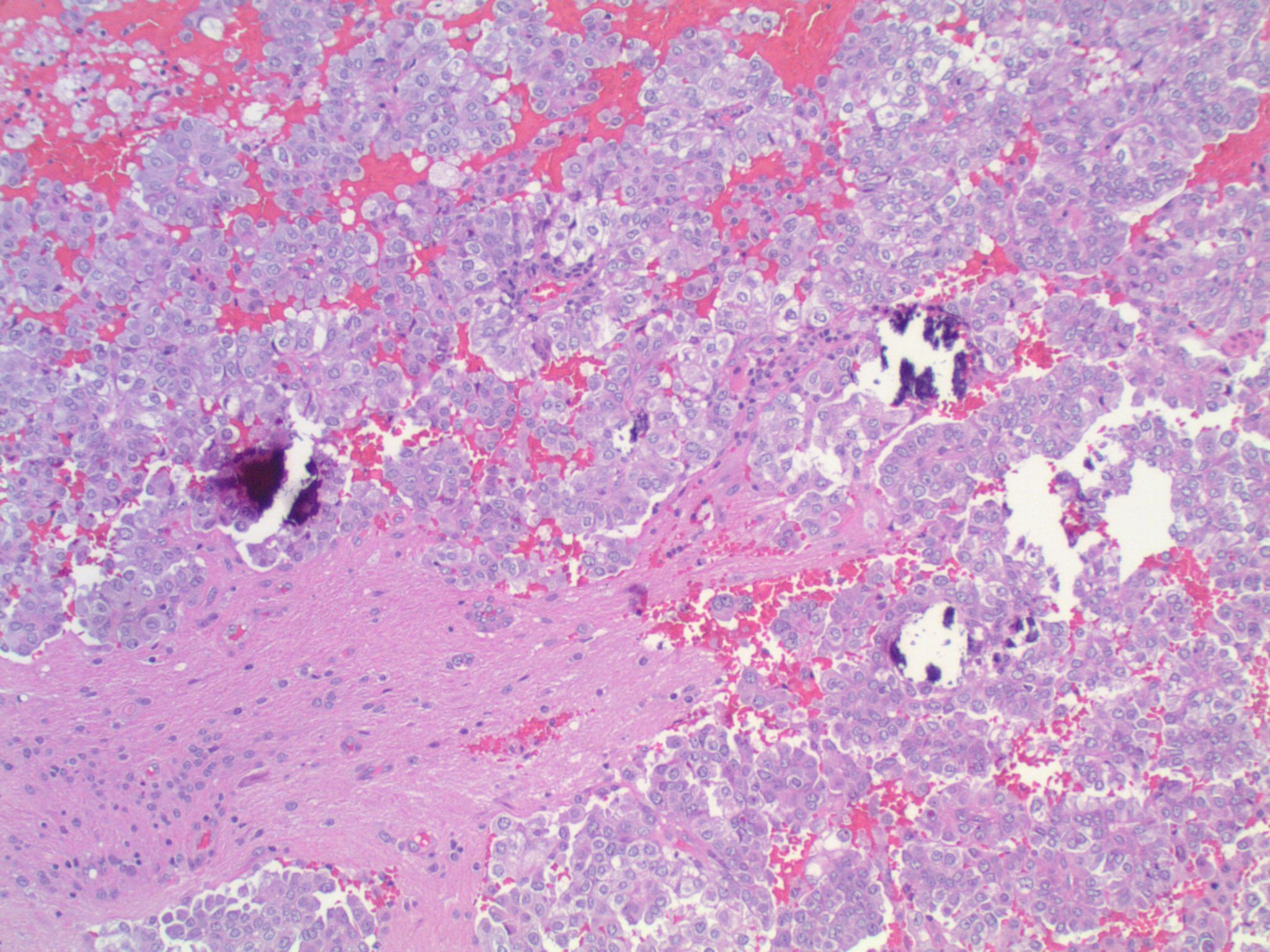
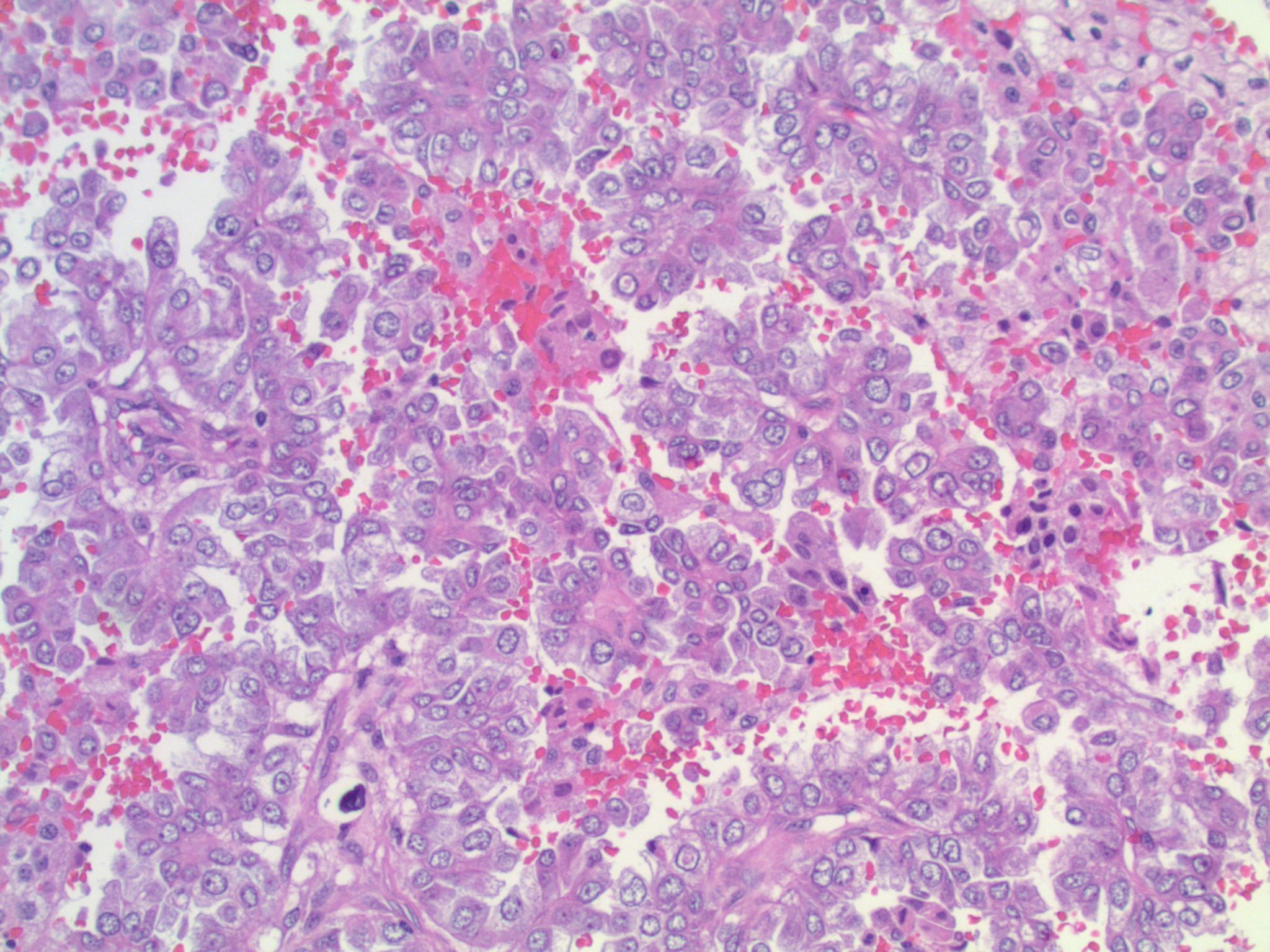
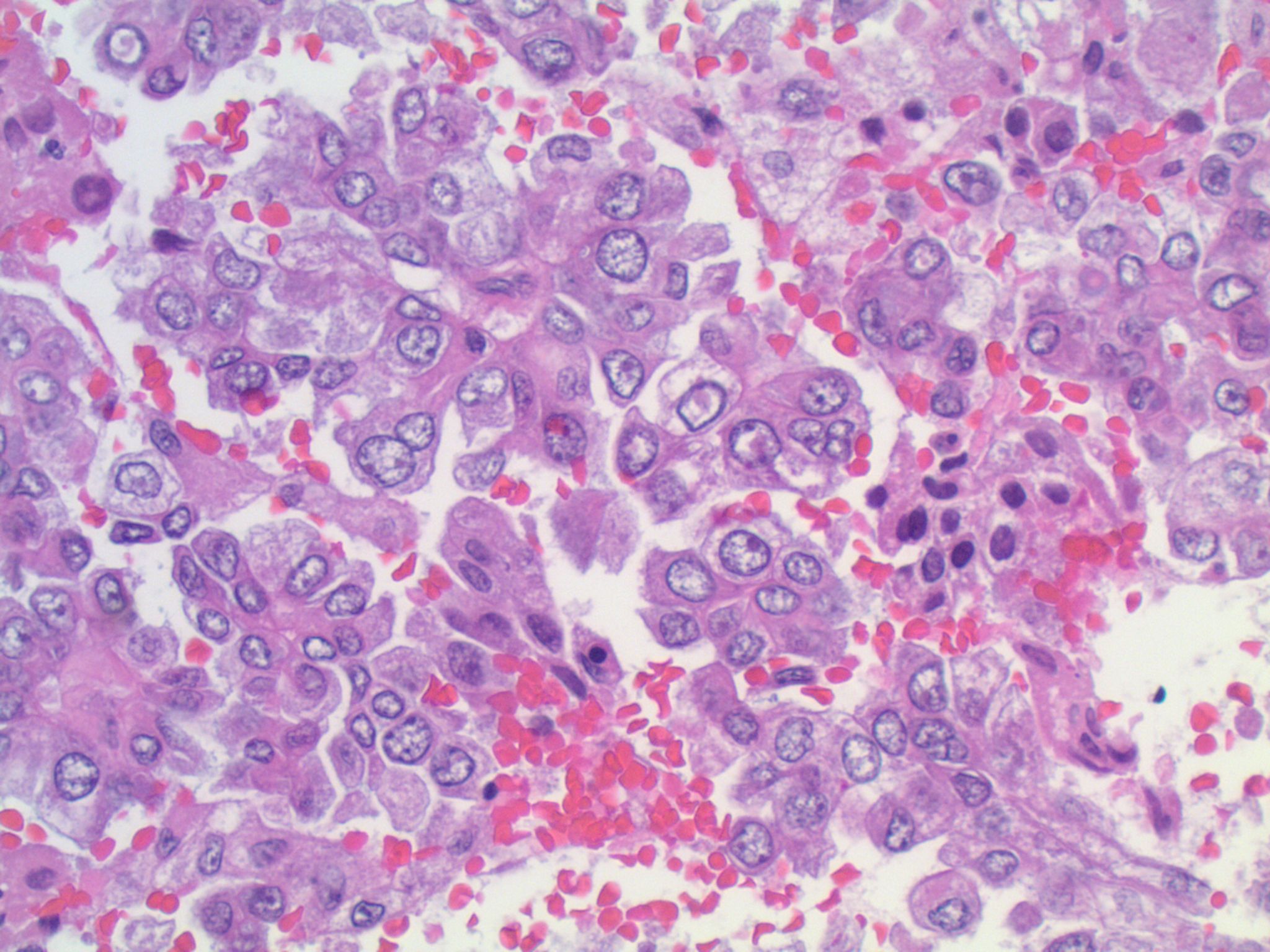
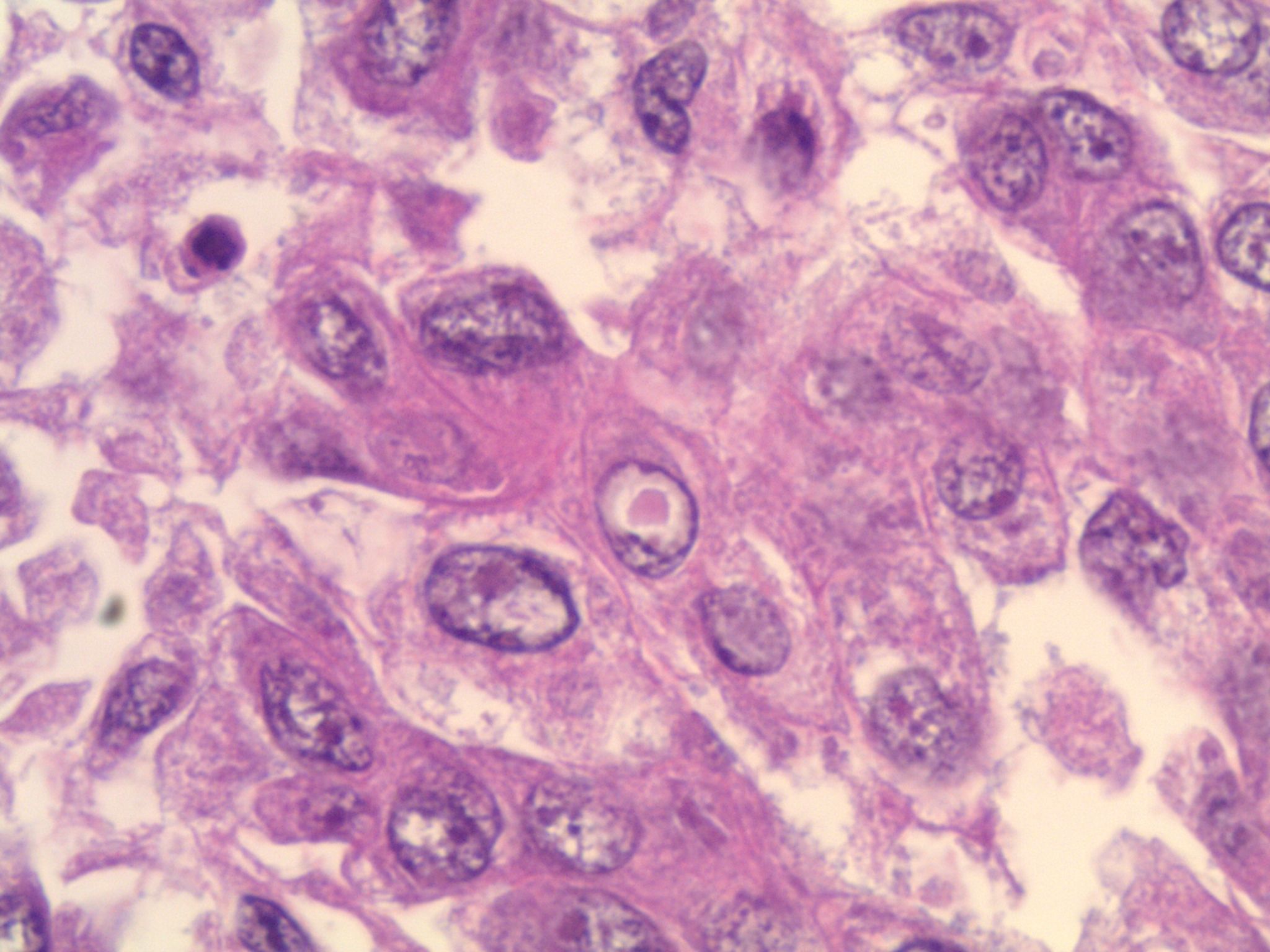
Microscopic (histologic) description
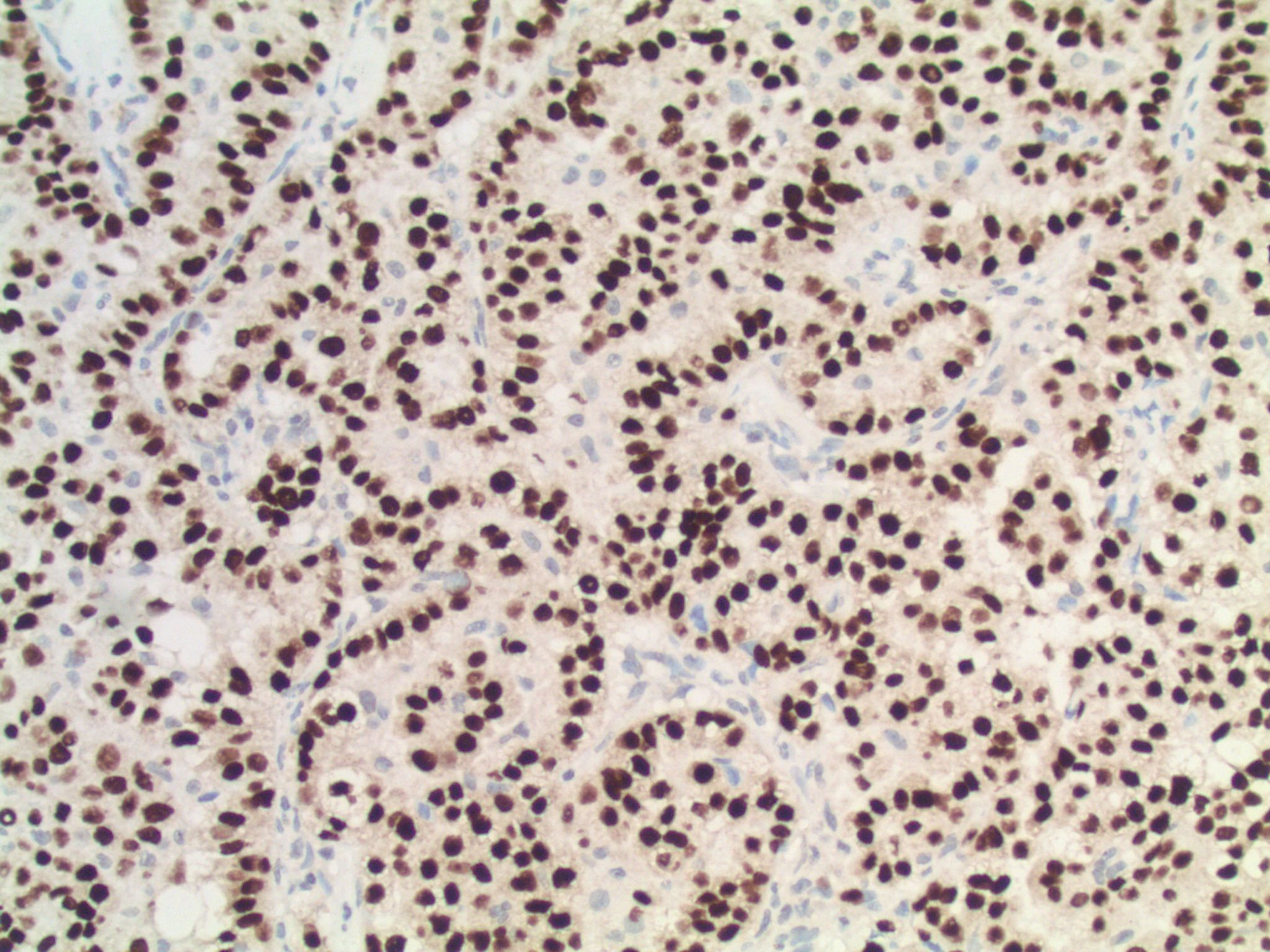
- Epithelial cells with discrete cell boundaries, pushing margin except for small cell carcinoma (infiltrative)
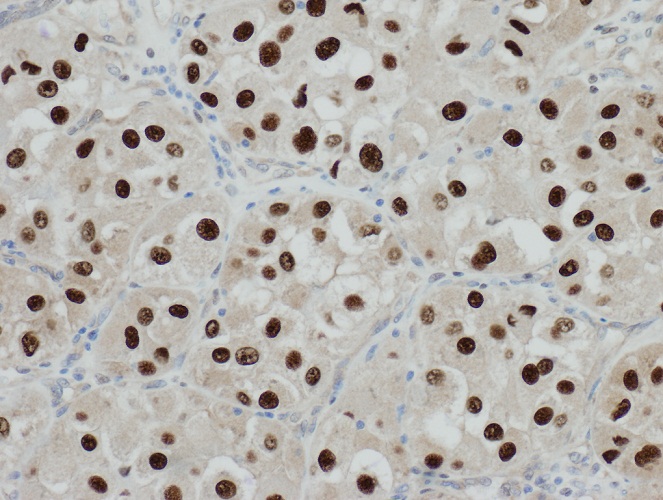
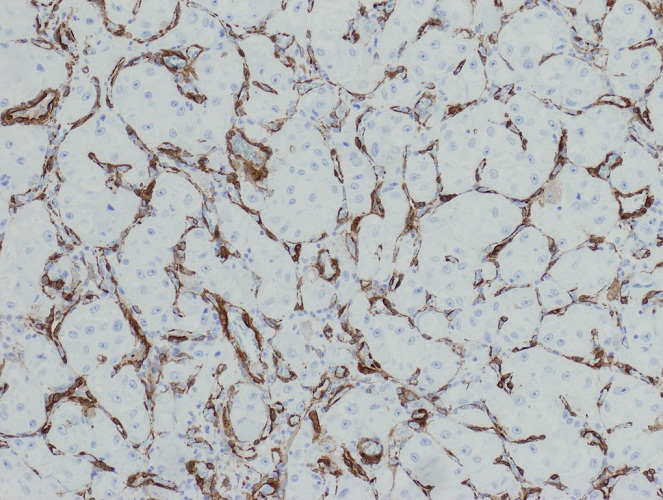
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunostains
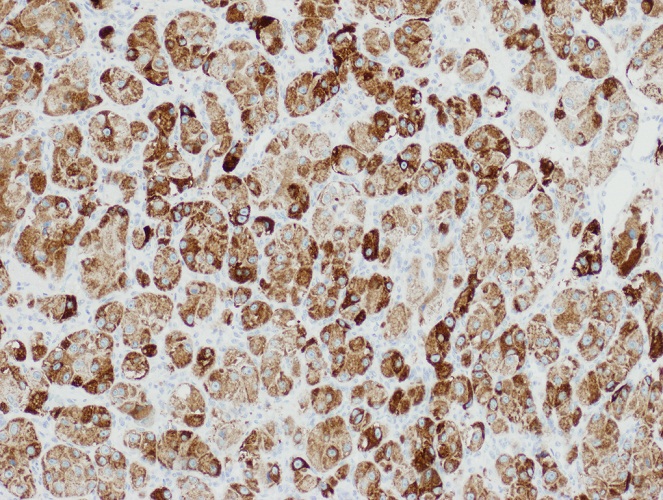
Recommended stain panels
- General: TTF1 (lung and thyroid, Hum Pathol 2002;33:642), cytokeratin and CAM 5.2, CK7, CK20 and PSA
- Breast carcinoma: CK7+, CAM5.2+, CK20-, TTF1-
- Lung adenocarcinoma: CK7,+ CAM5.2+, TTF1+, CK20-
- Colon carcinoma: CK20+, CK7-, TTF1-
- Renal cell carcinoma: RCC+, CAM5.2+, vimentin+
Differential diagnosis
- Anaplastic glioma: no distinct borders, have fibrillary cytoplasmic processes
- Glioblastoma
- Hemangioblastoma vs. metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Meningioma: syncytial borders
- PNET vs. metastatic small cell carcinoma: nonfibrillar cells