Table of Contents
Definition / general | Trade name | Clinical information | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Uses by pathologists | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Yeh YA. Larotrectinib (LOXO-101). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorlarotrectinib.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting tropomyosin receptor kinases TRKA, TRKB and TRKC encoded by NTRK1, NTRK2 and NTRK3, respectively (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:731)
- Discovered by Array BioPharma
- Licensed to Loxo Oncology in 2013
- Synonyms: LOXO-101, ARRY-470
Trade name
- Vitrakvi®
Clinical information
- Approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration on November 26, 2018 (Drugs 2019;79:201)
- Indications and usage (Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:731)
- Treatment of adult and pediatric patients with NTRK fusion positive cancers
- Metastatic solid tumors or when surgery would result in severe morbidity
- No alternative treatments or poor response to other treatments
- Adverse reaction (N Engl J Med 2018;378:731)
- General: fatigue, pyrexia, peripheral edema, weight gain
- Neurotoxicity: delirium, dysarthria, dizziness, gait disturbance, headache
- Hepatotoxicity: increased ALT and AST
- Embryofetal toxicity: malformations
- Cardiovascular: hypertension
- Respiratory: cough, dyspnea
- Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgia
- Discontinue larotrectinib if adverse reactions persist for 4 weeks
- Resistance to larotrectinib and selitrectinib has been reported in metastatic undifferentiated sarcoma with NTRK1 gene fusion (JCO Precis Oncol 2020;4:79)
- Approximate cost: $32,800 per month (oral capsules); $11,000 (liquid oral formulation)
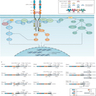
Pathophysiology
- Neurotrophins bind to TRK receptors
- NGF specific for TRKA (high affinity)
- BDNF and NT-4 for TRKB (high affinity)
- NT-3 for TRKA, TRKB, TRKC (highest affinity for TRKC)
- p75NTR for TRKA, TRKB, TRKC (low affinity)
- Binding of neurotrophins to extracellular domain (predominantly Ig2 domain) of TRK
- Homodimerization of ligand dependent receptors
- Transactivation of intracellular tyrosine kinase domains
- Recruitment of various cytoplasmic proteins
- Activation of the kinase domain by binding of SHC transforming protein (SHC), fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) and phosphoinositide phospholipase CƳ (PLCƳ)
- The adaptor proteins activate downstream signaling pathways including MAPK, PKC and PI3K signaling pathways
- The signaling pathways activate gene transcription involved in tumor cell survival, growth and differentiation
- Reference: Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:731
(See diagram below)
Diagrams / tables
Uses by pathologists
- NTRK gene fusions identified in human tumors (Target Oncol 2018;13:545, Cancer Discov 2015;5:25, Mod Pathol 2019;32:147, N Engl J Med 2018;378:731, FDA: Drug Approval Package - Vitrakvi (larotrectinib))
NTRK1 gene fusion Tumor type ARHGEF2-NTRK1 Glioblastoma BCAN-NTRK1 Glioblastoma CD74-NTRK1 Lung adenocarcinoma CHTOP-NTRK1 Glioblastoma CTRC-NTRK1 Pancreatic carcinoma GON4L-NTRK1 Melanoma IRF2BP2-NTRK1 Thyroid carcinoma LMNA-NTRK1 Spitzoid neoplasm, colorectal carcinoma,
congenital infantile fibrosarcomaMPRIP-NTRK1 Lung adenocarcinoma NFASC-NTRK1 Glioblastoma multiforme PDE4DIP-NTRK1 Soft tissue sarcoma PLEKHA6-NTRK1 Glioblastoma PPL-NTRK1 Papillary thyroid carcinoma RABGAP1L-NTRK1 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma SQSTM1-NTRK1 Non small cell lung carcinoma TFG-NTRK1 (TRKT-3) Papillary thyroid carcinoma TPM3-NTRK1 (TRK) Colon adenocarcinoma, papillary
thyroid carcinoma, pediatric glioma,
sarcoma, lung adenocarcinomaTPR-NTRK1(TRKT-1/2) Papillary thyroid carcinoma TP53-NTRK1 Spitzoid neoplasm TRIM63-NTRK1 Melanoma
NTRK2 gene fusion Tumor type AFAP1-NTRK2 Low grade glioma AGBL4-NTRK2 Pediatric glioma NACC2-NTRK2 Astrocytoma PAN3-NTRK2 Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma QK1-NTRK2 Astrocytoma SQSTM1-NTRK2 Low grade glioma STRN-NTRK2 Undifferentiated sarcoma TRIM24-NTRK2 Lung adenocarcinoma VCL-NTRK2 Pediatric glioma
NTRK3 gene fusion Tumor type BTB1-NTRK3 Pediatric glioma ETV6-NTRK3 Acute myeloid leukemia, papillary
thyroid carcinoma, pediatric
glioma, secretory breast
carcinoma, congenital
mesoblastic nephroma, mammary
analogue secretory carcinomaLYN-NTRK3 Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma RBPMS-NTRK3 Thyroid carcinoma TPM4-NTRK3 Sarcoma
- Pan-TRK immunohistochemical staining (IHC): sensitive (95 - 97%) and specific (98 - 100%)
biomarker for detecting NTRK fusions
(Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:1547, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:927)
- Colorectal carcinoma, mammary analogue secretory carcinoma, glioblastoma, melanoma, secretory breast carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma and sarcoma
- LMNA-NTRK1 fusions: nuclear membrane accentuation in 5/5 (100%) cases
- TPM3/4 fusions: cellular membrane accentuation in 4/4 (100%) cases
- ETV6-NTRK3 fusions: nuclear staining in 3/6 (50%) cases
- Staining in pediatric mesenchymal tumors: cytoplasmic in NTRK1, NTRK2 rearrangements; nuclear +/- cytoplasmic in NTRK3 rearrangements (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:927)
- Staining in secretory mammary carcinoma: diffuse or at least focally strong nuclear staining (Am J Surg Pathol 2019 Sep 6 [Epub ahead of print])
- References: J Clin Pathol 2019;72:460, Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:731
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following agents targets TRKA, TRKB and TRKC receptors?
- Erlotinib
- Trametinib
- Larotrectinib
- Trastuzumab
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- What type of tumors could be treated by Larotrectinib (LOXO-101)?
- NTRK fusion positive tumors
- BCR-ABL fusion positive tumors
- PD-L1 positive tumors
- EGFR mutations positive tumors
Board review style answer #2