Cite this page: Abdelzaher E. Ectodermal cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorepidermoidcyst.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Epidermoid cyst
Definition / general
Terminology
Sites
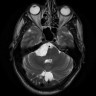
Radiology description
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Benign cyst lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and lacking skin adnexa (eMedicine: Brain Epidermoid Imaging [Accessed 19 December 2024])
- More common than dermoid cyst (1% of intracranial masses)
Terminology
- Also called epidermoid or epidermoid tumor
Sites
- Occurs throughout neuriaxis
- Favored site: cerebellopontine angle
- Other sites: brainstem, cranial diploe, intraspinal, pineal gland, sella, temporal lobe
- Rarely undergoes malignant degeneration
Radiology description
- Discrete, extra-axial with signal characteristics reflecting keratinous contents
- Diffusion MRI helps distinguish from arachnoid cysts
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Case reports
- 68 year old man with cyst and sudden death (Am J Forensic Med Path 2002;23:368)
- Woman with cerebellopontine angle cyst that degenerated into squamous cell carcinoma (Neurosurg 2002;97:1237)
Gross description
- Well defined round mass, thin walled, pearly white
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Fibrous wall lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium; contains anucleate squames but no skin adnexae and no hair
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Craniopharyngioma, adamantinous:
- Wet keratin, adamantinomatous epithelium
- Craniopharyngioma, papillary:
- No anucleate squames
- Dermoid cyst:
- Skin adnexa
- Rathke cleft cyst or endodermal cyst with extensive sqaumous metaplasia:
- Have residual columnar epithelium but no anucleate squames
Dermoid cyst
Definition / general
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis
- Developmental lesions arising from embryologic displacement of ectoderm into meninges, ventricles or rarely parenchyma (eMedicine: Imaging in CNS Dermoid Tumors)
- Benign cyst lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium and cutaneous adnexa
- Uncommon; much less common than epidermoid cyst
- Usually affects children
- Distribution more restricted than epidermoid cysts, usually affects midline (mostly fontanelle or posterior fossa as midline cerebellar lesions or within the 4th ventricle), may affect spinal canal
- May have sinus tract to skin surface in nasofrontal or occipital regions
- May rupture and cause chemical meningitis
Gross description
- Thick walled with greasy pilosebaceous contents
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Fibrous wall lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium with skin adnexa, cyst contains squames, hair, sebum
- Hair shafts highlighted with polarized light
- May be hair matrix differentiation (shadow cells)
- Rupture may cause granulomatous inflammation with foreign body giant cell reaction
Positive stains
Differential diagnosis