Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Kresak J, Yachnis A. Clear cell meningioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorclearcellmeningioma.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare variant, 0.2 - 0.8% of all meningiomas (J Neurooncol 2007;81:315)
- WHO grade 2 due to aggressiveness
- 20 - 60% chance of recurrence even with gross total resection
- More common in younger patients (mean age 29 years)
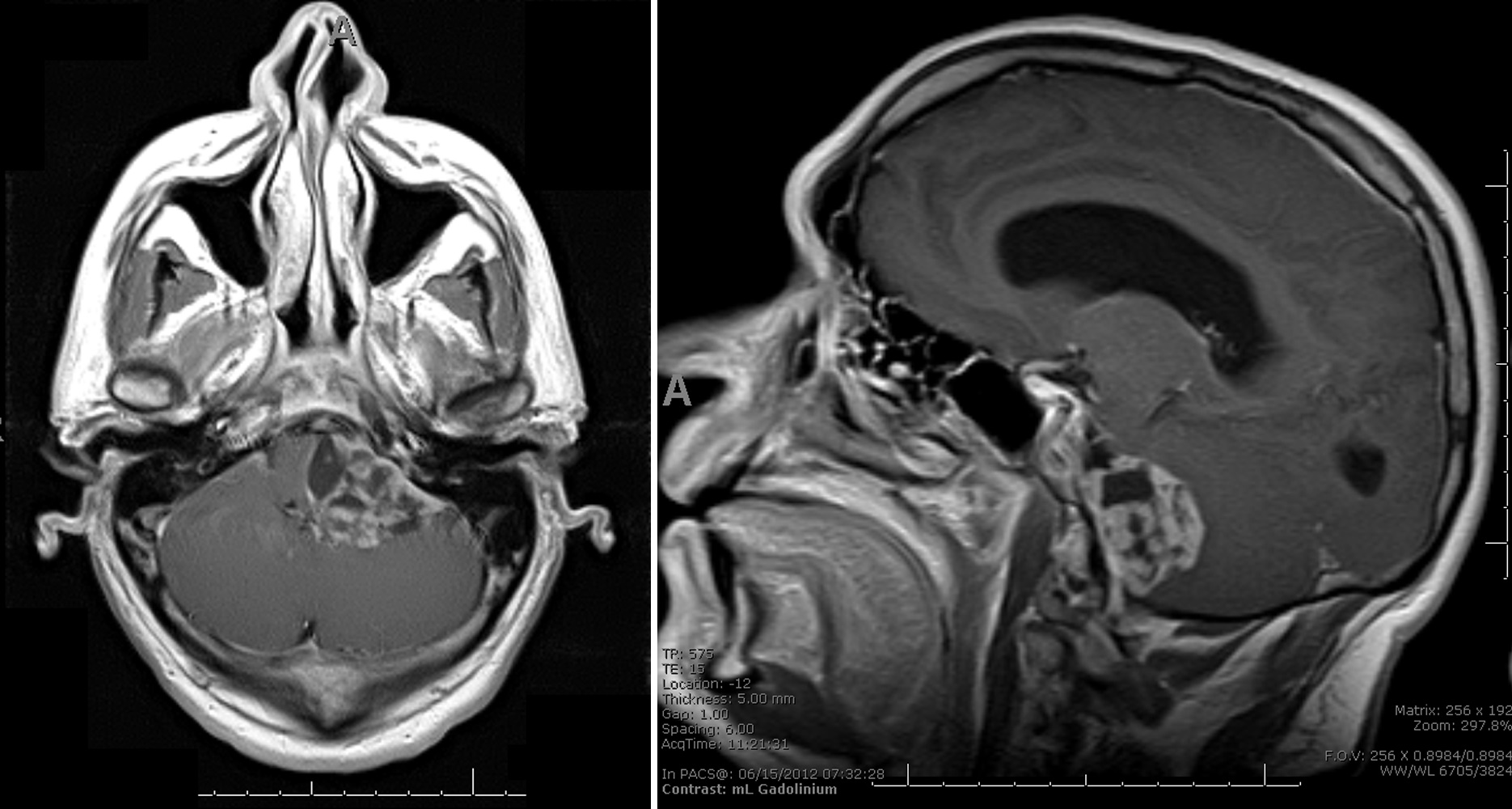
- Predilection for cauda equina and cerebellopontine areas
Sites
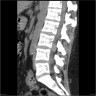
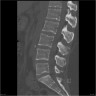
- Predilection for CP angle and cauda equina
Radiology description
- Indistinguishable from classic meningioma
- Dural based, homogenously enhancing
Radiology images
Case reports
- 13 year old girl with pediatric spinal clear cell meningioma (J Neurosurg Pediatr 2009;3:57)
- 14 year old boy with clear cell meningioma of the fourth ventricle (Pediatr Neurosurg 2010;46:462)
- 38 year old woman and two 60 year old men with clear cell meningiomas (Neurosurgery 2010;67:E870)
- 41 year old woman with clear cell meningioma of the cauda equina (J Spinal Disord Tech 2005;18:539)
- 51 year old man with progressive hearing loss in the left ear, intermittent dizziness, difficulty walking (Case of the Month #514)
- Clear cell meningioma of the fourth ventricle (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:131)
Treatment
- Gross total resection
- Postsurgical radiation
Microscopic (histologic) description
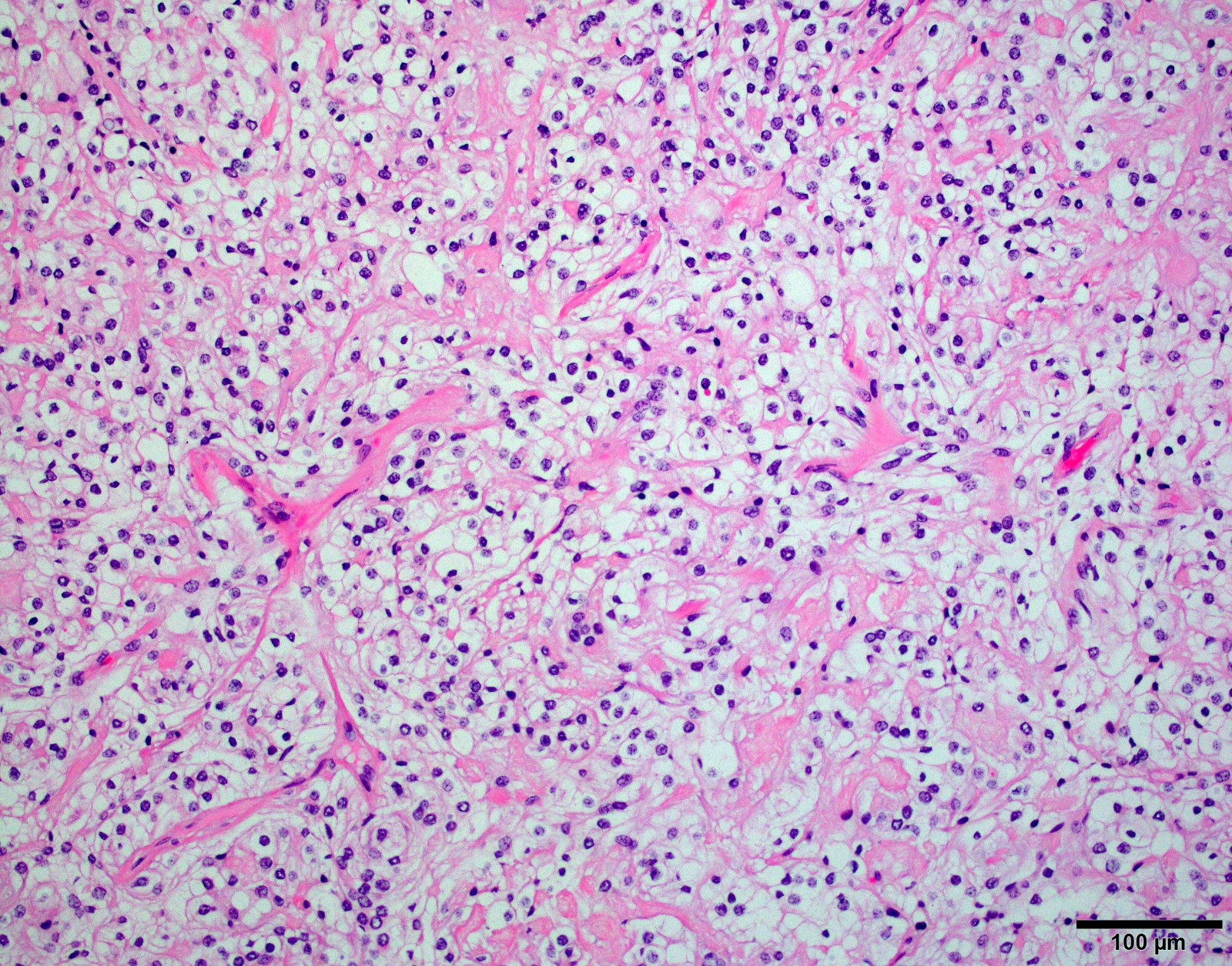
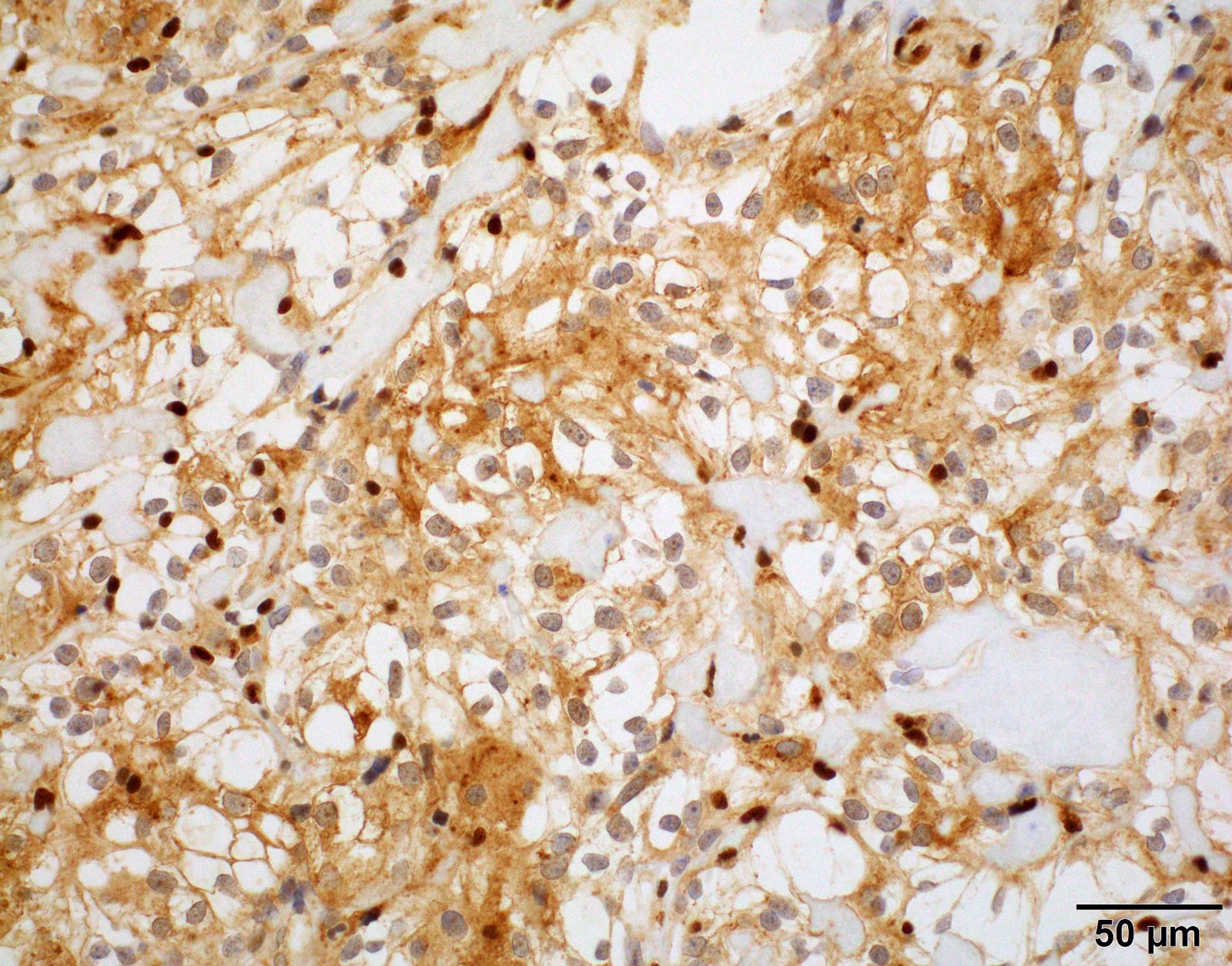
- Patternless arrangement of clear cells with sometimes distinct cell borders
- Prominent perivascular and interstitial collagen
- Little to no mitotic activity
- May not display any characteristic meningioma features (whorls, psamomma bodies, intranuclear inclusions)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Whorled, syncytial architecture composed of spindle to polygonal cells with vacuolated cytoplasm and bland nuclei (Diagn Cytopathol 1998;18:131)
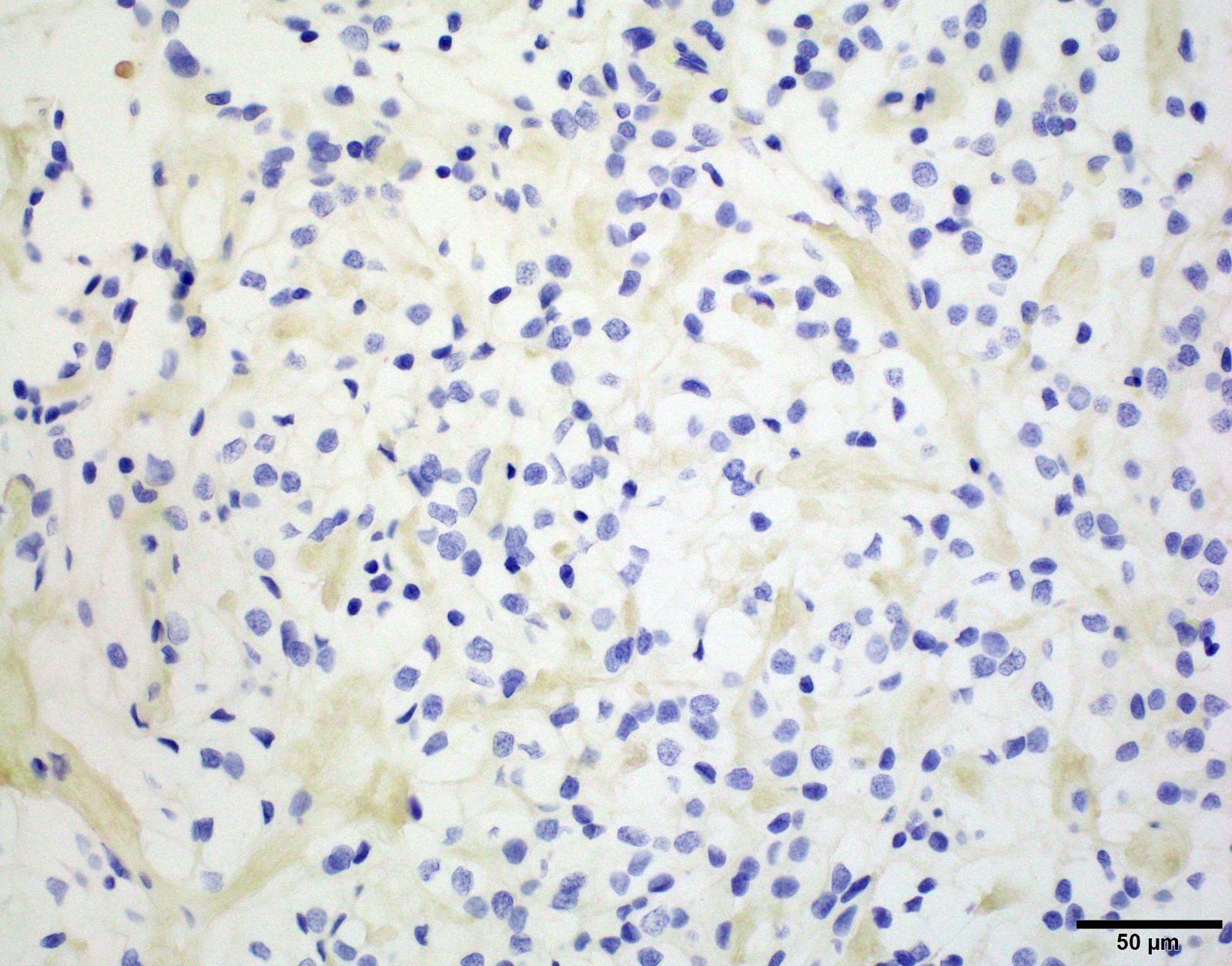
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Abundant cytoplasmic glycogen
- Intermediate filaments
- Interdigitation of cell membranes, desmosomes
- Occasional cytoplasmic lumina (Ultrastruct Pathol 1999;23:51)
Differential diagnosis
- Clear cell ependymoma: GFAP +
- Germinoma / seminoma: PLAP+, OCT3 / 4+, cKIT+
- Hemangioblastoma: inhibin+, NSE +
- Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: keratin+ (J Clin Neurosci 2005;12:685)
- Oligodendroglioma: GFAP +
Board review style question #1
Which of the following genetic alterations is characteristic of clear cell meningioma?
- AKT1 mutation
- BAP1 mutation
- NF2 mutation
- SMARCE1 mutation
- TRAF7 and KLF4 co-mutations
Board review style answer #1
D. SMARCE1 mutation. Clear cell meningioma is a rare variant characterized by loss of nuclear SMARCE1 protein expression.
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell meningioma
Comment Here
Reference: Clear cell meningioma