Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Cai C, Kresak J, Yachnis A. Atypical meningioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumoratypicalmeningioma.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- A meningioma of intermediate aggressiveness between benign and malignant forms, comprising 5 - 15% of meningiomas
- WHO grade 2
- Diagnostic criteria: fulfilling either 1 of 2 major criteria or 3 of 5 minor criteria
- Major criteria:
- 4 - 19 mitotic figures/10 high power fields
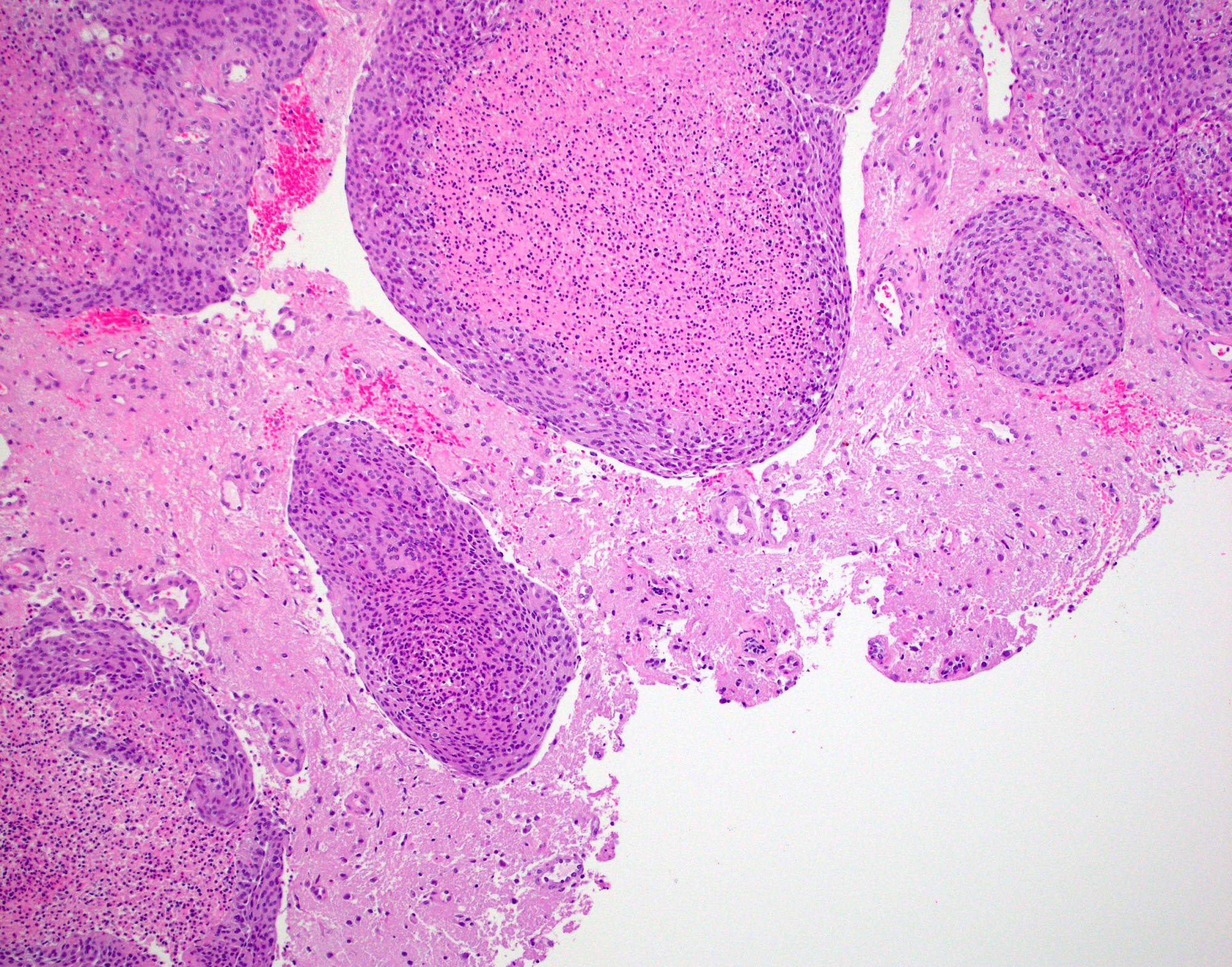
- Brain invasion
- Minor criteria:
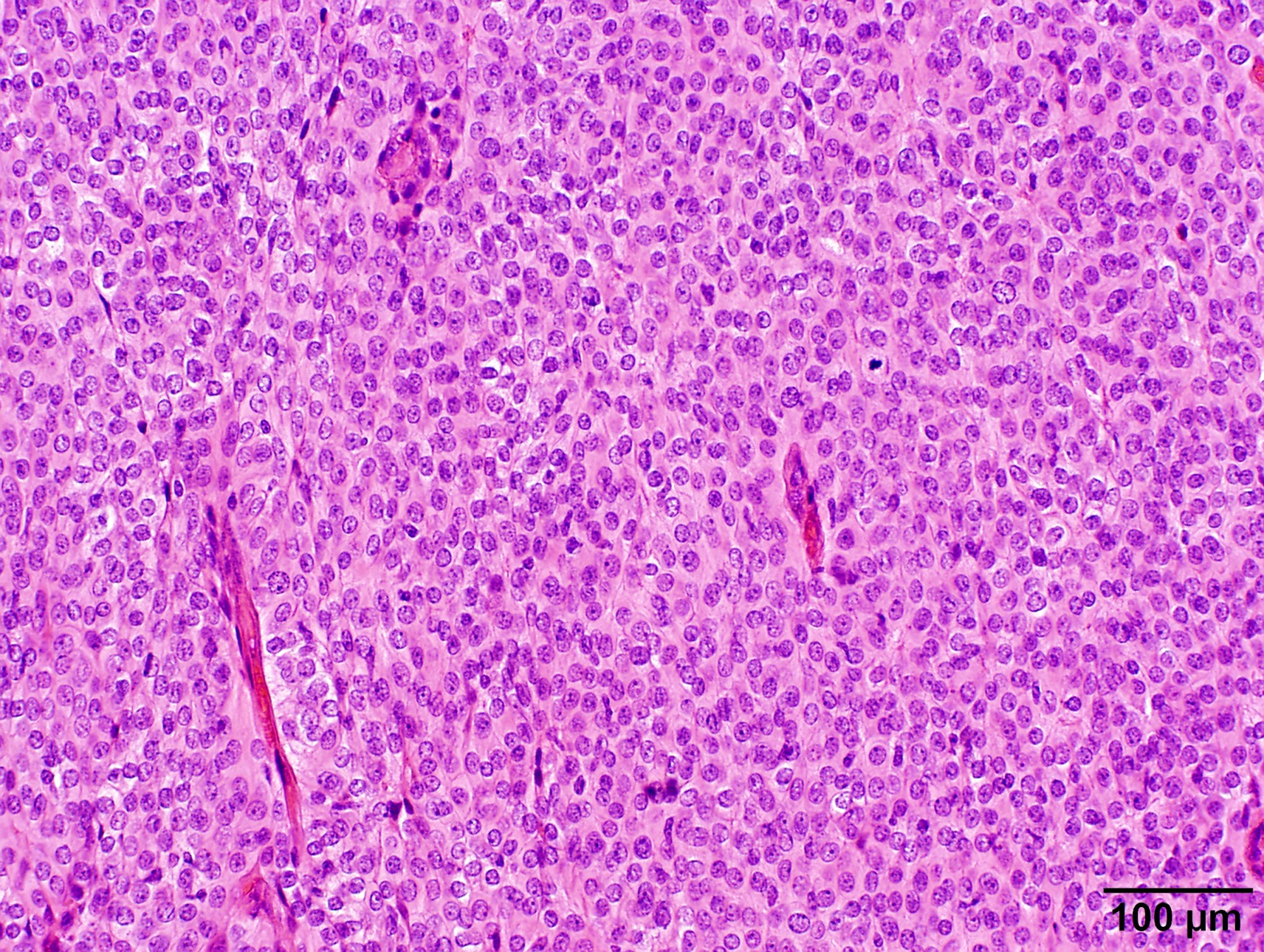
- Increased cellularity
- Small cells with high N/C ratio
- Large and prominent nucleoli
- Patternless or sheet-like growth (loss of lobular architecture)
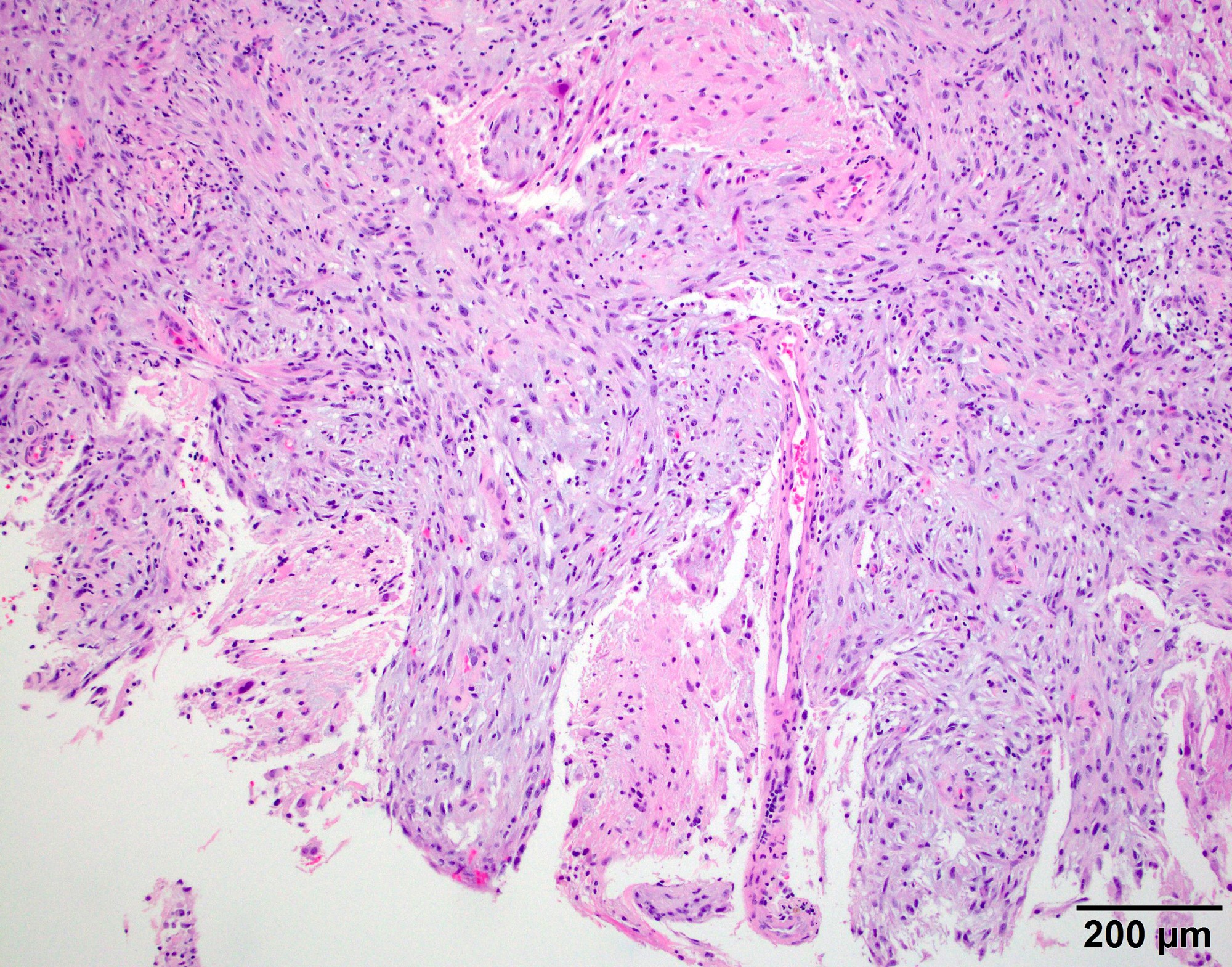
- Foci of spontaneous or geographic necrosis
- Major criteria:
- Invasion of dura, bone or soft tissue does not affect grading
- Pleomorphic or atypical nuclei do not affect grade
- Ki67 is not a true diagnostic criteria; however, it is usually greater than 4% and up to 20%
Essential features
- Atypical meningiomas have an intermediate recurrence rate between benign and malignant meningiomas
- 29 - 52% recur (versus 7 - 25% of classic meningiomas and 50 - 94% of anaplastic meningiomas) (Louis: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 4th Edition, 2016)
- Molecular genetic and epigenetic signatures of atypical meningiomas are becoming increasingly important in predicting prognosis and new targeted therapy in progressive tumors
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D32.9 - benign neoplasm of meninges, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Similar to meningioma, overall
Sites
- Intracranial, intraspinal or intraorbital
Pathophysiology
- Arising from the meningothelial cells or the arachnoid layer
Etiology
- Risk factors include male gender and prior surgery (Louis: WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 4th Edition, 2016)
- Some risk factors may be similar to benign meningioma:
- Ionizing radiation (Acta Neuropathol 2017;134:155)
- Hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives (J Clin Oncol 2008;26:279, J Neurosurg 2013;118:649)
- Germline mutations in NF2 or SMARCB1 predispose to multiple meningiomas (Neurogenetics 2012;13:1, J Med Genet 2011;48:93)
Clinical features
- Clinical presentation of atypical and anaplastic meningioma is similar to their benign counterpart
- Common symptoms include headaches, seizures and focal neurological deficit due to tumor compression (Neurosurg Clin N Am 2016;27:239)
Diagnosis
- Diagnose by imaging and pathology of biopsy / resection specimen
Radiology description
- Extra-axial mass with dural tail
- Uniformly contrast enhancing
- Extensive peritumoral edema is associated with brain invasion (Neuro Oncol 2020 Aug 13 [Epub ahead of print])
- Several benign meningioma variants, including angiomatous, microcystic, secretory and lymphoplasmacyterich meningiomas may also have prominent peritumoral edema (J Neurooncol 2013;111:49)
Prognostic factors
- Extent of surgery and WHO grading
- DNA methylation profiling may better predict tumor recurrence and prognosis than histologic classification (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:682)
Case reports
- 36 and 70 year old women with optic nerve seeding of atypical meningiomas presenting with subacute visual loss (J Neurosurg 2013;119:494)
- 44 year old man with atypical primary meningioma in the nasal septum with malignant transformation and distant metastasis (BMC Cancer 2012;12:275)
- Elderly man with metastatic atypical meningioma (J Clin Neurosci 2000;7:69)
Treatment
- Gross total resection
- Postsurgical radiation is often offered for atypical meningiomas, especially after a subtotal resection (J Neurooncol 2013;115:241)
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
Gross description
- Rubbery, well circumscribed mass firmly attached to the inner surface of the dura
- Brain invasive meningiomas readily adherent to adjacent brain tissue
- Reference: Perry: Practical Surgical Neuropathology - A Diagnostic Approach, 1st Edition, 2010
Frozen section description
- Similar to meningioma
Microscopic (histologic) description
- May have histology of any grade 1 variant meningioma with increased mitoses (4 - 19/10 high power fields)
- Mitotic rate is defined as the highest count over 10 consecutive high power fields (1 high power field = 0.16 mm²)
- May have increased cellularity or areas of small cell collections
- May have sheet-like growth pattern
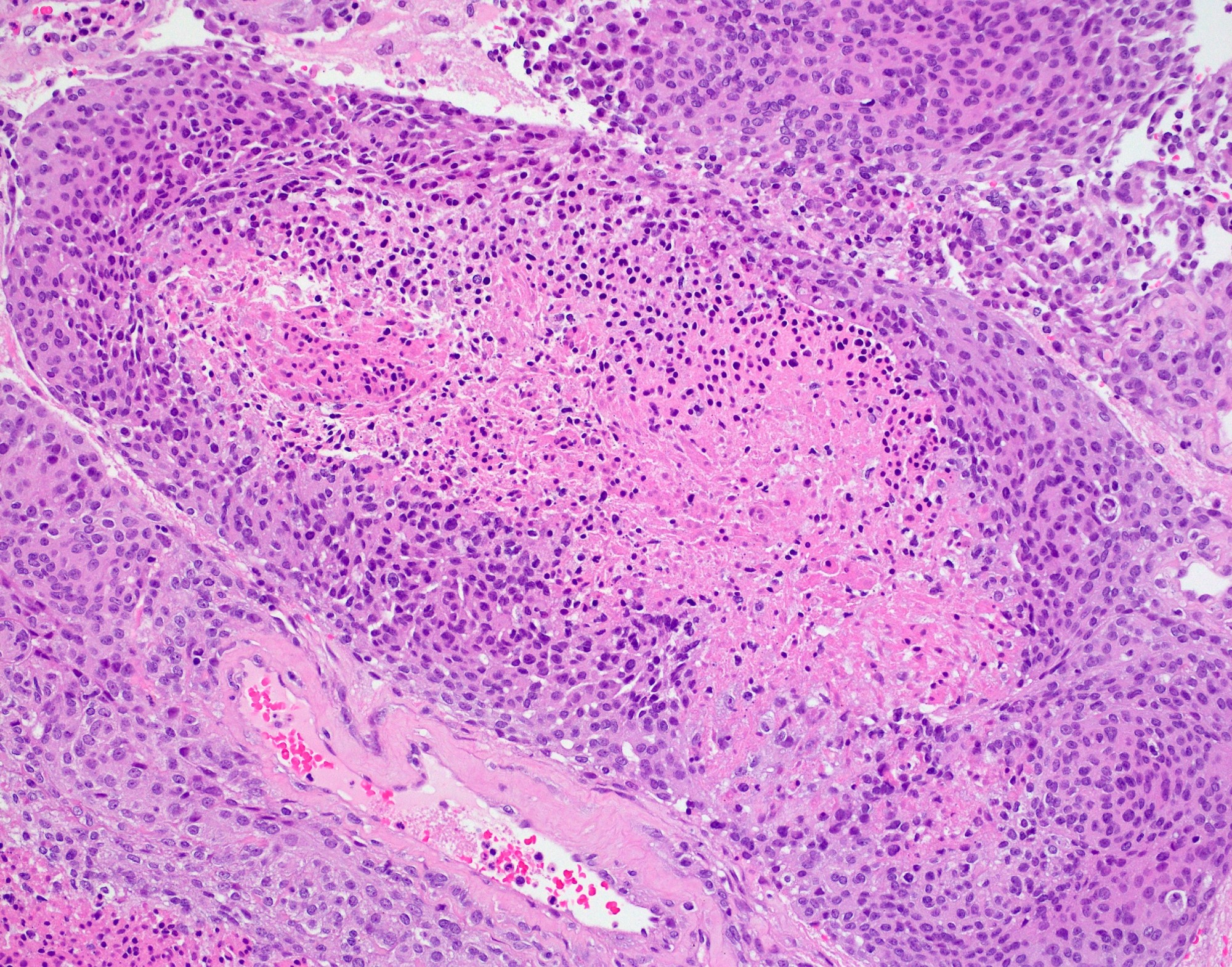
- May have areas of spontaneous necrosis
- May have macronucleoli
- Brain invasion is defined as irregular projections of tumor cells into adjacent CNS parenchyma without an intervening layer of leptomeninges at the tumor to brain interphase (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1455)
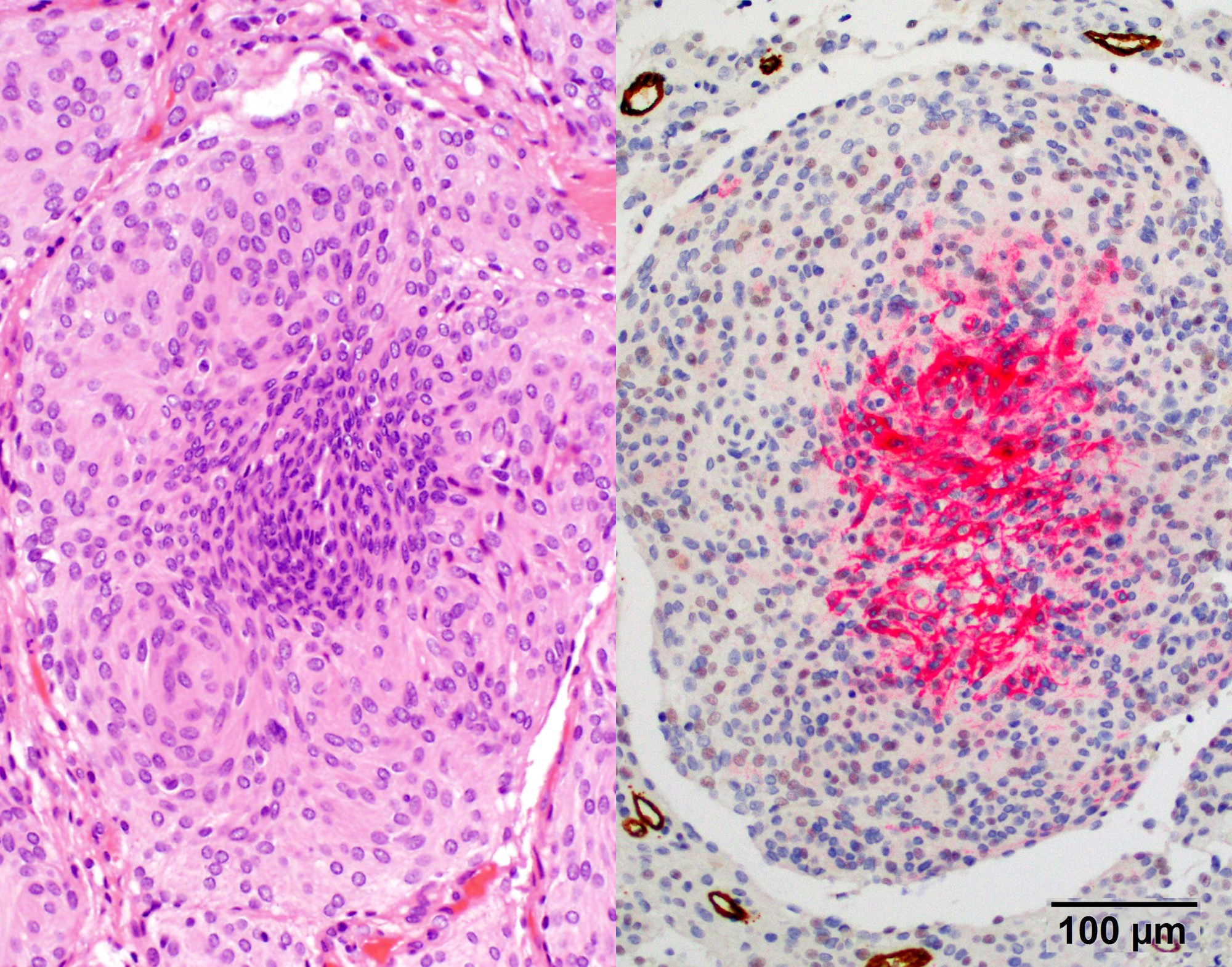
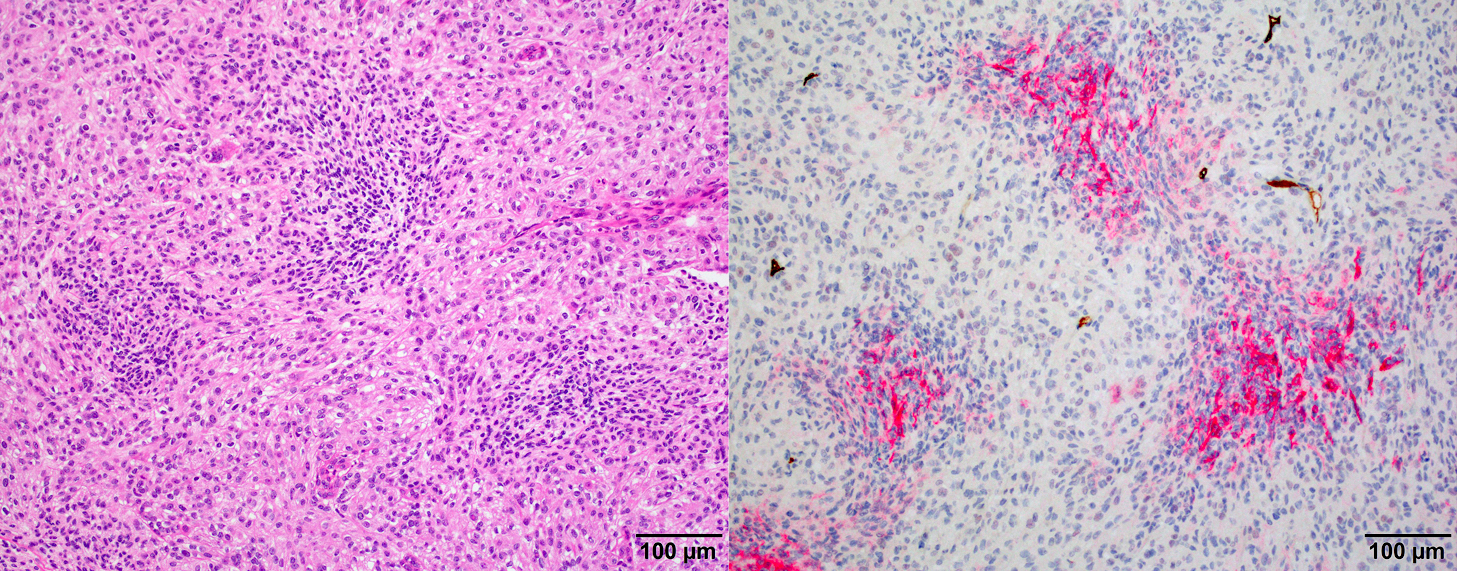
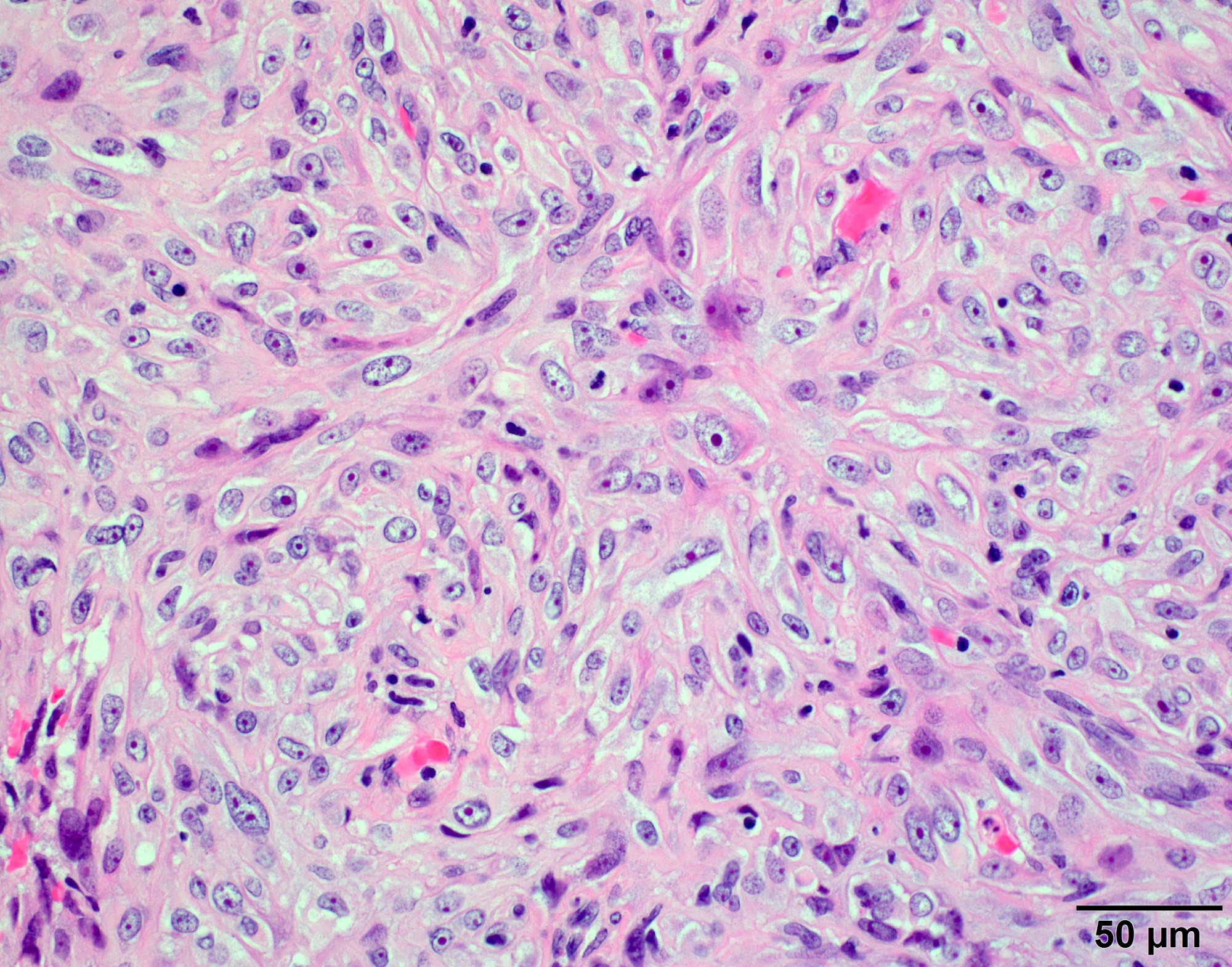
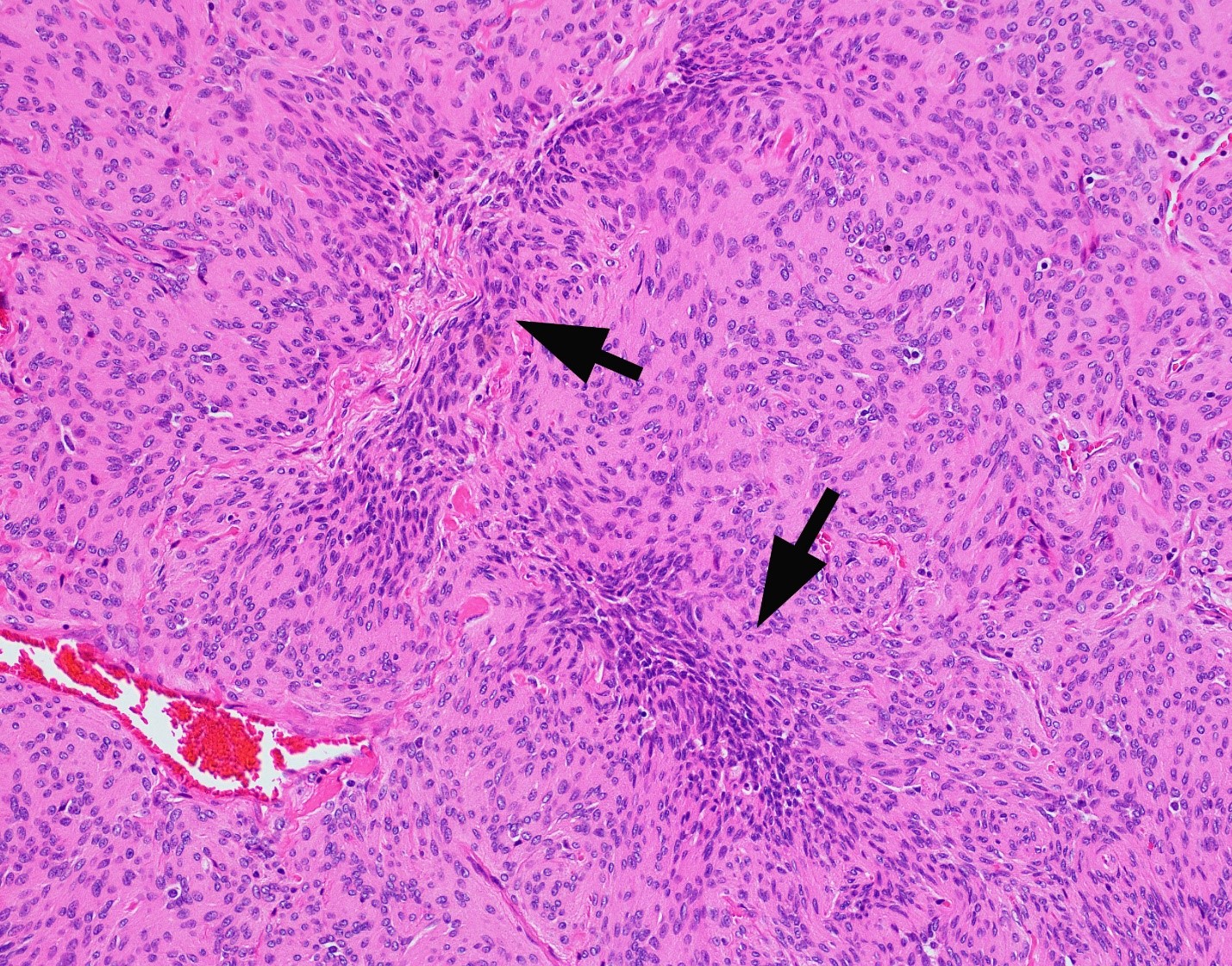
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Squash prep shows similar histology as standard meningioma but may also show occasional mitoses or macronucleoli
Positive stains
Negative stains
- GFAP (useful in highlighting tumor brain interphase in cases with brain invasion)
- STAT6 (useful to distinguish meningioma [negative] from solitary fibrous tumor / hemangiopericytoma [positive]) (Clin Neuropathol 2017;36:56)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Majority of atypical meningiomas have loss of NF2 combined with either genome instability (large scale chromosomal alterations) or loss of SMARCB1 (Nat Commun 2018;9:16215)
- Recurrent losses of chromosome 1p, 6q, 14q,18q and gain of 1q are indicators of poor prognosis (Acta Neuropathol 2017;133:431)
- Non-NF2 meningiomas are enriched in mutations in TRAF2, KLF4, AKT1 and SMO, most of which are benign and preferentially locate in skull base (Science 2013;339:1077)
- DNA methylation profiling of meningioma distinguished 6 methylation classes (MCs), benign (ben) 1 - 3, intermediate (int) A and B and malignant (mal)
- DNA methylation based meningioma classification is reported to better predict tumor recurrence and prognosis than the WHO histological classification (Lancet Oncol 2017;18:682)
- NF2 mutant atypical meningiomas display increased H3K27me signal and a hypermethylated phenotype due to increased polycomb repressive complex 2 (PCR2) / EZH2 activity (Nat Commun 2018;9:16215)
Sample pathology report
- Brain, right frontal lobe mass, excision:
- Atypical meningioma (see comment)
- Comment: Section shows a meningioma with predominant meningothelial morphology and rare psammoma bodies. Multiple atypical features are present, including variably increased mitotic index up to 7 mitoses/10HPF (A7), multifocal microscopic necrosis, widespread small cell change, hypercellularity, and sheeted architecture. No macronucleoli or brain invasion is identified. Ki67 proliferation index is 12.7% per 1,000 nuclei count.
Differential diagnosis
- Hemangiopericytoma:
- Anaplastic meningioma:
- With mitoses greater than 20/10 high power fields
- Meningioma:
- With atypical features insufficient for criteria above
- Necrosis:
- Due to prior radiation therapy or embolization (which are not considered spontaneous)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Small cell change
The image shows an atypical meningioma with small cell change, characterized by reduced cytoplasm and increased N/C ratio in these regions. These regions may resemble lymphoplasmacytic inflammation on low power but on high power show nuclei that are similar to adjacent tumor cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical meningioma
The image shows an atypical meningioma with small cell change, characterized by reduced cytoplasm and increased N/C ratio in these regions. These regions may resemble lymphoplasmacytic inflammation on low power but on high power show nuclei that are similar to adjacent tumor cells.
Comment Here
Reference: Atypical meningioma