Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Dampier C, Cimino PJ. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnstumorDNET.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cortex based glioneuronal neoplasm that is often located in the mesial temporal lobe of adolescents and young adults and associated with medically refractory epilepsy, usually with activating mutations of FGFR1, CNS WHO grade 1 (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545)
Essential features
- Presents clinically with intractable seizures, usually in children and young adults (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545, Brain Pathol 2012;22:350)
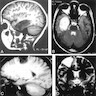
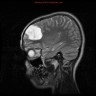
- Radiographically is sharply demarcated, nodular, cortical lesion(s) without edema or enhancement (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24:829, Neuroradiology 2009;51:433, J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2011;70:859)
- Composed of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes (or oligodendrocyte-like cells) and neurons with neurons often appearing to float in a myxoid matrix between columns of oligodendroglial cells (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545, Brain Pathol 2012;22:350)
- Activating genetic alterations in FGFR1 (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:847)
- CNS WHO grade 1 (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2011;70:859)
Terminology
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
- Simple dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
- Complex dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 1.2:1 = M:F (N Engl J Med 2017;377:1648)
- 5.9% of epilepsy surgery cases (N Engl J Med 2017;377:1648)
Sites
- Cerebral cortex
- Most common sites: temporal lobe, especially medial (67%), frontal lobe (16%), other cortex (16%) (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2011;70:859)
Pathophysiology
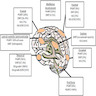
- Activating alteration in FGFR1 (receptor tyrosine kinase) > activation of MAPK pathway > dysregulated cell growth, proliferation and differentiation (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:847)
Etiology
- Most cases are sporadic (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:833)
- Germline mutations in MAPK pathway genes, including FGFR1, NF1 and PTPN11 (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:847, Epilepsy Res 2013;105:384, Am J Med Genet A 2017;173:1061)
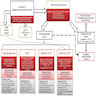
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Intractable seizures
- Absence of focal neurologic deficits (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545)
Diagnosis
- Cortical glioneuronal tumor with presence of specific glioneuronal component
- FGFR1 alteration or DNA methylation profile can help in challenging cases
- Preferable to make diagnosis in context of early onset focal epilepsy
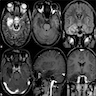
Radiology description
- Sharply demarcated, nodular, cortical lesion without edema or enhancement (AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24:829)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Benign lesion with low rate of recurrence after resection (J Neuroradiol 2001;28:230)
- Rare case reports of malignant transformation (Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7:240, J Neurooncol 2009;94:283, Radiol Case Rep 2022;17:939)
Case reports
- 18 year old woman with left parietal mass (Radiol Case Rep 2022;17:939)
- 26 year old woman with superficial right frontal mass (J Radiol Case Rep 2013;7:7)
- 27 year old man with right temporal mass (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013010469)
Treatment
- Surgical resection (Childs Nerv Syst 2015;31:847)
- Radiation or chemotherapy is generally not applicable
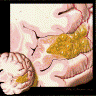
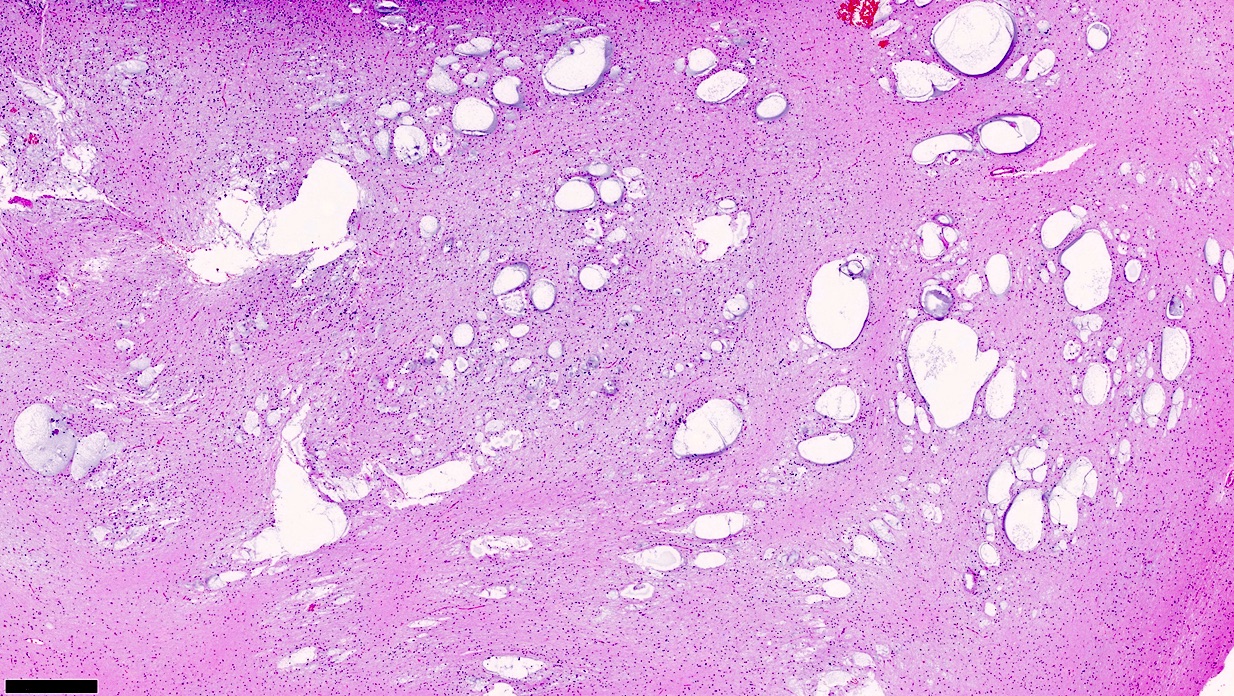
Gross description
- Usually poorly demarcated (Epileptic Disord 2002;4:99)
- Located predominantly in gray matter and subcortical white matter
- May contain solid, mucoid or cystic components
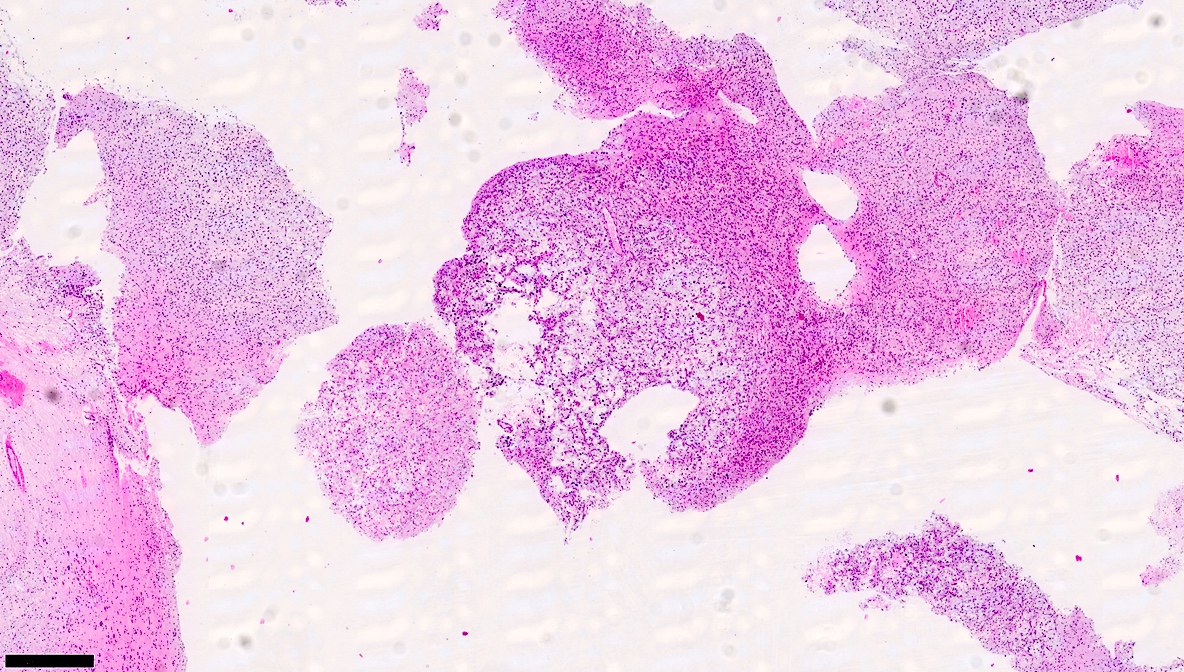
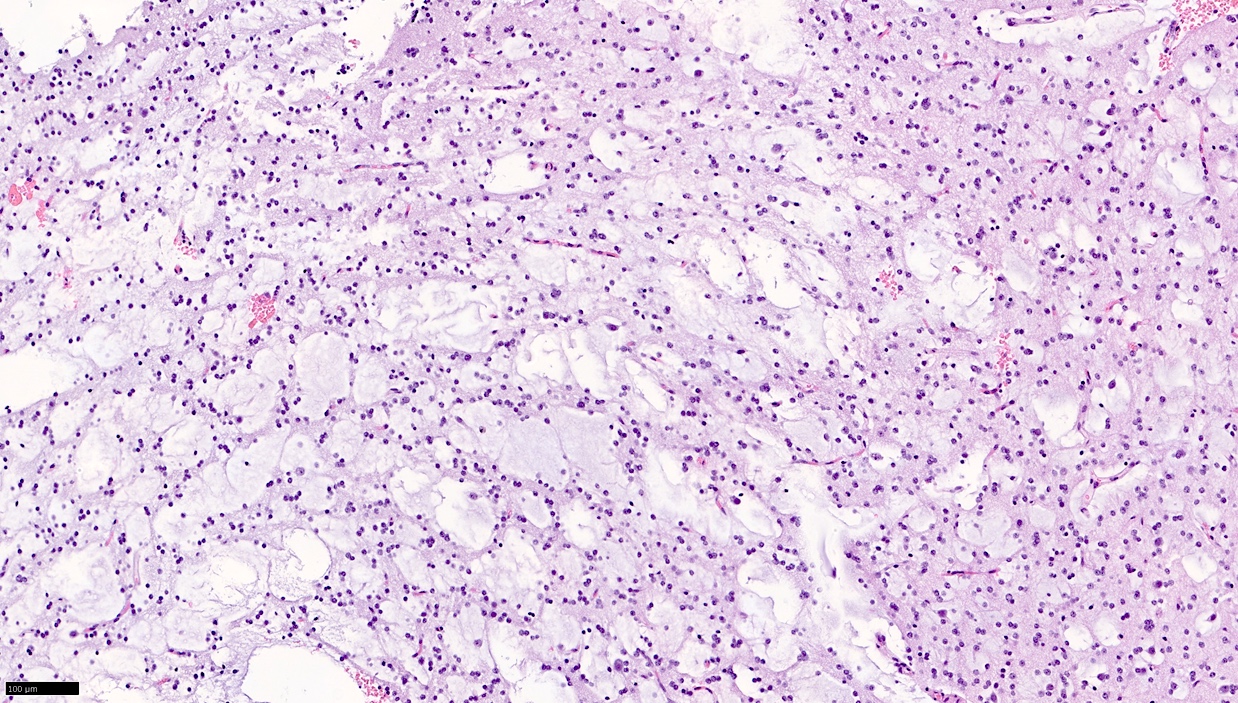
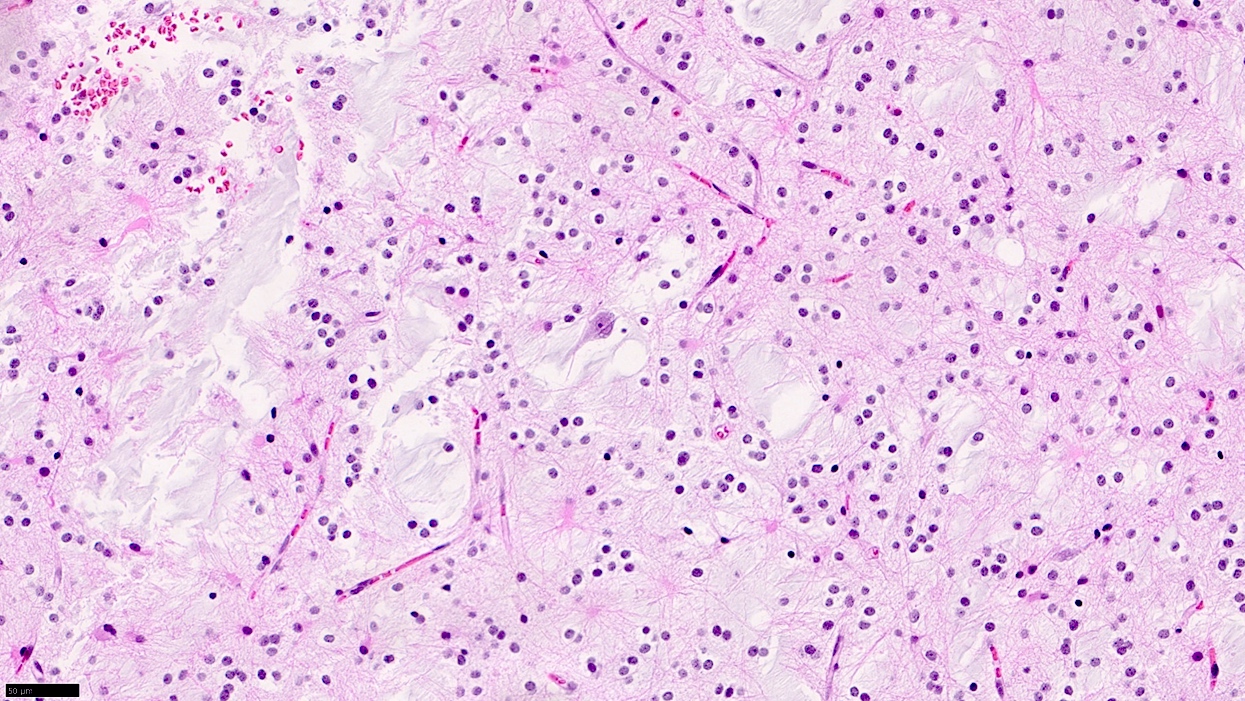
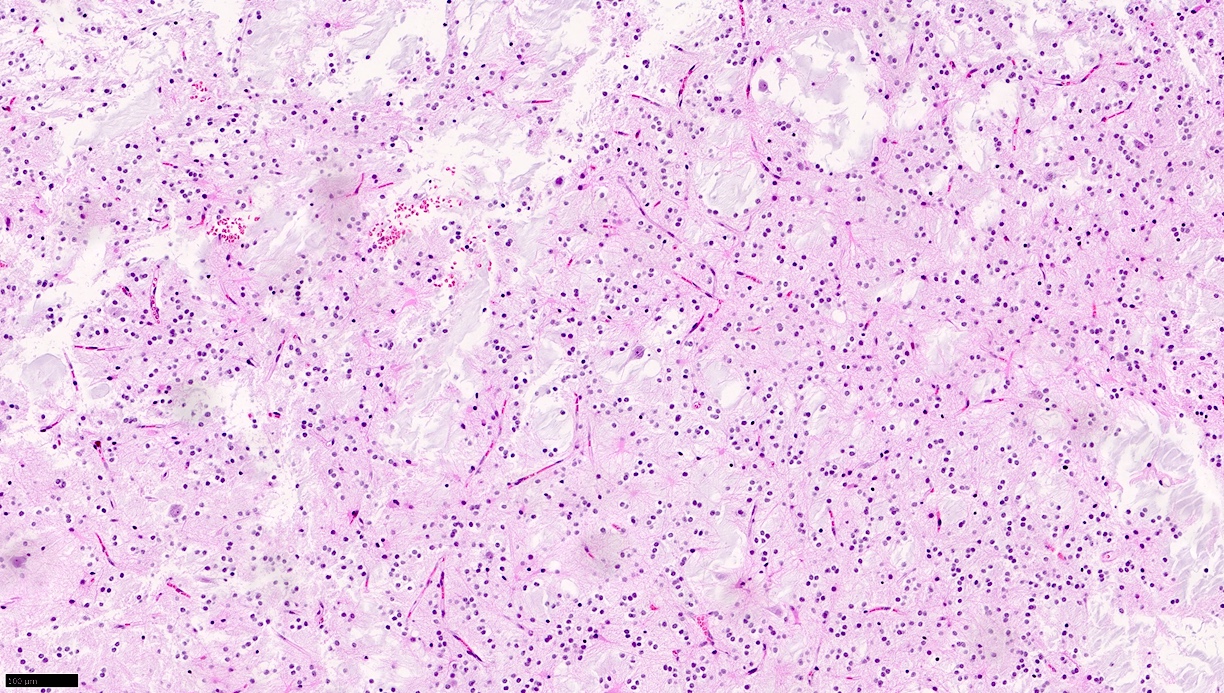
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Growth pattern
- Intracortical and multinodular (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545)
- Pathognomonic appearance
- Bundles of axons lined by small oligodendroglia-like cells form columns oriented perpendicularly to the cortical surface with intervening cytologically normal neurons floating in a myxoid matrix (Neurosurgery 1988;23:545)
- Absence of the following:
- Dysplastic ganglion-like cells
- High cellularity
- Necrosis
- Perivascular lymphoid infiltrates
- Eosinophilic granular bodies
- Simple form
- Pathognomonic component alone
- Complex form
- Pathognomonic component along with glial nodules, resembling other glioma types (J Neurooncol 1999;41:267)
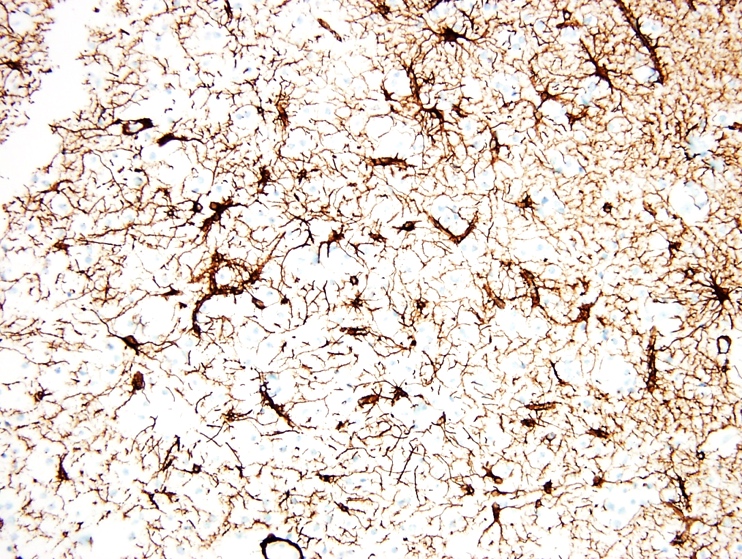
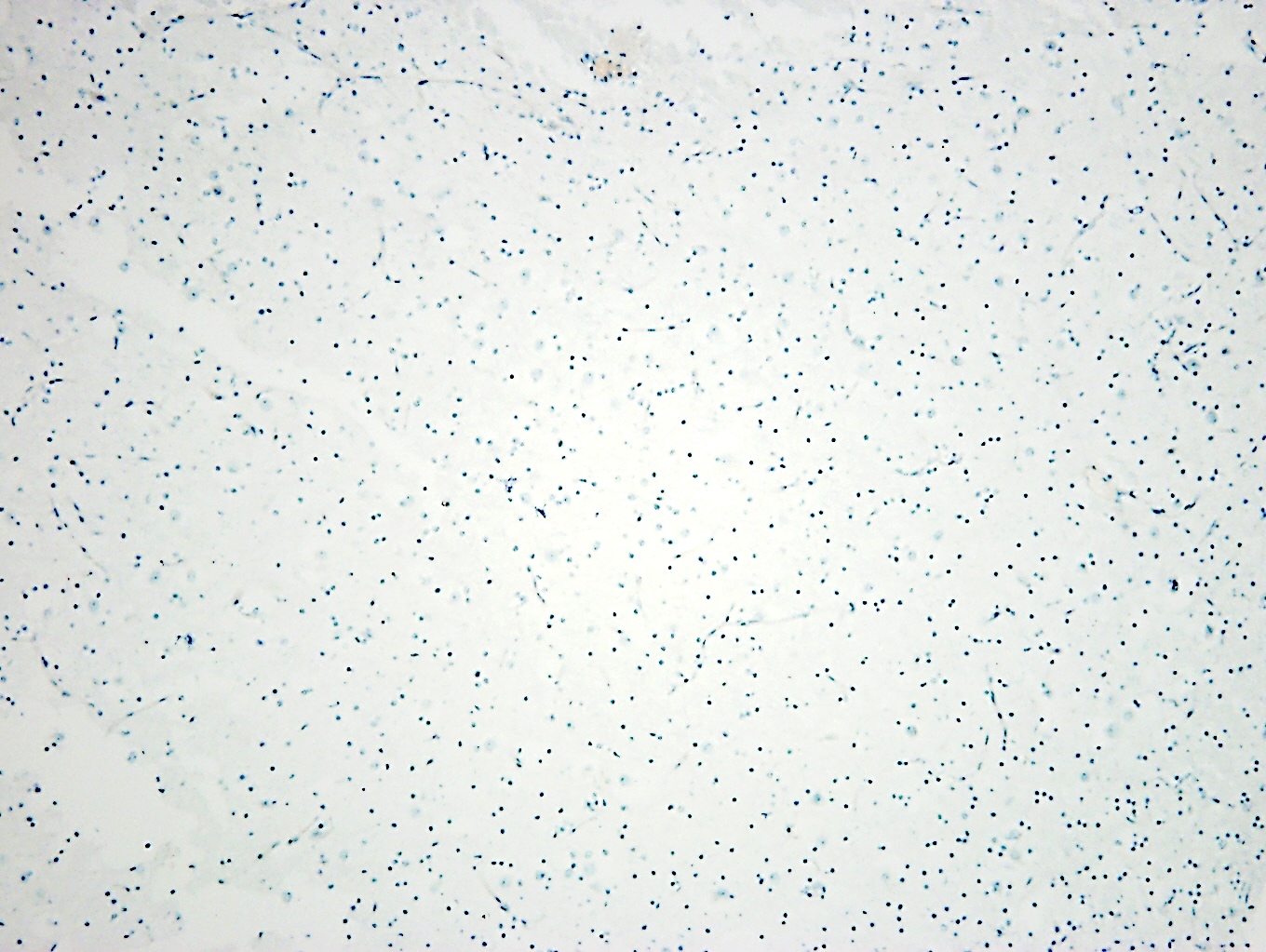
Microscopic (histologic) images
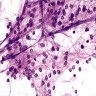
Cytology description
- Smear preparation (alcohol fixed, H&E stained) (Acta Cytol 2022;66:142)
- Uniform round cells
- Mucinous and fibrillary background
Cytology images
Positive stains
- S100 (in the oligodendroglial-like cells) (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:438)
- Olig2 (in the oligodendroglial-like cells) (Neuropathology 2013;33:246)
- PDGFRA (in the oligodendroglial-like cells)
- NeuN (in the floating neurons) (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:438)
- Alcian blue (extracellular)
Negative stains
- GFAP (in the oligodendroglial-like cells) (J Pathol Transl Med 2015;49:438)
- MAP2 (in the oligodendroglial-like cells) (Acta Neuropathol 2004;108:89)
- CD34 (76.5% of cases are negative) (World Neurosurg 2019;121:e761)
- BRAF p.V600E
- IDH1 p.R132H (Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:241)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Activating alterations in FGFR1 (Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:847)
- Internal tandem duplication
- Missense mutations
- FGFR1::TACC1 fusion (rare)
- Complete duplication of FGFR1 (rare)
- PTPN11 alteration (rare) (Am J Med Genet A 2017;173:1061)
- NF1 alteration (rare) (Epilepsy Res 2013;105:384)
- Chromosomal polysomies (gains of chromosome 5, chromosome 6, chromosome 7; loss of chromosome 22) unusual but reported (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2015;41:743, Acta Neuropathol 2016;131:847)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Videos
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET)
Sample pathology report
- Brain, temporal lobe, biopsy:
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor, CNS WHO grade 1
- Positive for FGFR1 alteration
Differential diagnosis
- Neoplastic
- Oligodendroglioma:
- IDH1/2 mutation
- Codeletion of whole chromosome arms 1p and 19q
- Ganglioglioma:
- Dysplastic ganglion-like cells
- Perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate
- Eosinophilic granular bodies
- BRAF p.V600E alteration (Acta Neuropathol 2011;121:397)
- Myxoid glioneuronal tumor:
- Located primarily in the septum pellucidum
- PDGFRA p.K385 alteration (Brain Pathol 2020;30:479)
- Multinodular and vacuolating neuronal tumor:
- Predominant neuronal component (Brain Pathol 2013;23:515)
- MAP2K1 or BRAF alteration
- Polymorphous low grade neuroepithelial tumor of the young:
- Diffuse growth pattern (Acta Neuropathol 2017;133:417)
- Extensive CD34 immunopositivity
- BRAF p.V600E or FGFR2/3 fusion
- Diffuse astrocytoma, MYB or MYBL1 altered:
- Monomorphic glial neoplasm (Acta Neuropathol 2020;139:193)
- MYB or MYBL1 alteration
- Angiocentric glioma:
- Perivascular orientation of tapered cells
- MYB::QKI fusion or other MYB alteration (Nat Genet 2016;48:273)
- Diffuse glioneuronal tumor with oligodendroglioma-like features and nuclear clusters:
- Specific methylation profile (Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2020;46:422)
- Monosomy chromosome 14
- Oligodendroglioma:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. FGFR1 alteration.
TP53 mutations are uncommon in dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (E). IDH1 R132H is the most common mutation in IDH mutant astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas but should be negative in dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (C). BRAF p.V600E mutation has been reported in dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor but methylation profiling indicates such tumors are probably a distinct entity (A). NF1 loss may occur in dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor but is rare (D).
Comment Here
Reference: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors?
- Associated with NF2
- Associated with seizures
- Harbor several cytogenetic alterations
- Most frequently occur in adults
- Show diffuse CD34 immunoreactivity
Board review style answer #2
B. Associated with seizures.
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor should not show significant CD34 immunopositivity (E). Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor usually occurs in children (D). Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor is generally without chromosomal losses or gains, resulting in a flat copy number profile (C). Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor has rarely been associated with NF1 but not NF2 (A).
Comment Here
Reference: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
Comment Here
Reference: Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor