Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Gyure K.A. Subacute combined degeneration. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnssubacutecombined.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Acquired myelopathy caused by vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency
Sites
- Posterior and lateral columns of spinal cord
Pathophysiology
- Adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin are metabolites of cobalamin; they are coenzymes in reactions which (a) convert methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA and (b) transfer methyl groups to homocysteine to form methionine, respectively
- Accumulation of methylmalonyl CoA causes a decrease in normal myelin synthesis and incorporation of abnormal fatty acids into neuronal lipids
Etiology
- Cobalamin deficiency: vegetarian diet
- Impaired absorption of cobalamin intrinsic factor (IF) complex: pernicious anemia / atrophic gastritis, partial gastrectomy, fish tapeworm infection, Imerslund-Gräsbeck syndrome (genetic defect of cobalamin IF complex receptor), Crohn disease
- Subacute combined degeneration can be triggered by exposure to nitrous oxide in B12 deficient patients
Clinical features
- Progressive sensory abnormalities, ascending paresthesias, weakness, ataxia, loss of sphincter control and gait impairment
Diagnosis
- Schilling test: radiolabeled cyanocobalamin is administered orally and its excretion is measured in the urine
- Increased serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine concentrations
- Decreased serum cobalamin concentration
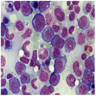
- Macrocytic / megaloblastic anemia
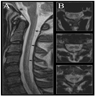
Radiology description
- Symmetric, increased T2 signal confined to posterior and lateral columns of the cervical and thoracic spinal cord
Prognostic factors
- Less severe disease at time of diagnosis, including absence of sensory dermatomal deficits, Romberg sign and Babinski sign, is associated with a higher rate of resolution following cobalamin replacement therapy
Case reports
- 23 year old man with vitamin B12 deficiency (BMJ Case Rep 2013;Sep 30:2013)
- 27 year old woman with subacute combined degeneration of the spinal from abusing nitrous oxide (Am J Health Syst Pharm 2015;72:952)
- Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord due to different etiologies (Case Rep Neurol Med 2013;2013:159649)
Treatment
- Intramuscular cobalamin injections
Gross description
- Shrunken spinal cord with discoloration of the posterior and lateral columns
Microscopic (histologic) description
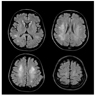
- Bilaterally symmetric myelin loss and degeneration in the posterior and lateral columns of the spinal cord
- Dense gliosis in longstanding cases
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Tabes dorsalis: does not affect lateral columns of spinal cord
- Vacuolar myelopathy of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: thought to be related to abnormal vitamin B12 metabolism but serum B12 levels are typically normal
Additional references