Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Gyure K.A. Heroin leukoencephalopathy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cnsheroin.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Toxic leukoencephalopathy secondary to the use of inhaled heroin or "chasing the dragon"
Sites
- White matter including cerebellar white matter
Pathophysiology
- Heating of heroin is thought to activate a lipophilic compound that damages white matter
Clinical features
- Stage 1: predominantly cerebellar symptoms
- Stage 2: cerebellar and extrapyramidal symptoms
- Stage 3: progressive spasms, akinetic mutism and death
Radiology description
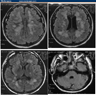
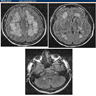
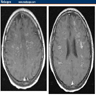
- Increased signal on T2 weighted and FLAIR MR images in white matter, including cerebellar white matter with sparing of the dentate nucleus
Radiology images
Case reports
- 36 year old man with worsening altered mental status (MedGenMed 2007;9:14)
- 43 year old woman with fatal case of spongiform leukoencephalopathy (J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 2003;41:887)
- 49 year old man with leukoencephalopathy from "chasing the dragon" (Neurology 2005;64:1755)
Treatment
- Supportive care
Microscopic (histologic) description
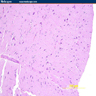
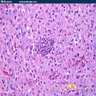
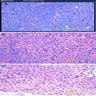
- Myelin loss / vacuolation - "spongiform encephalopathy"
- Inflammatory infiltrate consisting of macrophages with associated perivascular chronic inflammation
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Leukodystrophies
- Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases
Additional references