Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Factors interfering with electrophoresis | Types of interferences | Fibrinogen | Hemolysis | Human antianimal antibodies (HAAAs) | IgG4 related disease (IgG4 RD) | Contrast dyes | Antifungals and antibiotics | Gelatin based plasma substitutes | Hydroxocobalamin | Monoclonal therapies | Monoclonal immunoglobulin rapid accurate molecular mass (miRAMM) assay | Diagrams / tables | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Farooq A, Zhu Y. Interference in protein electrophoresis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/chemistryelectrophoresis.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Interference causes a clinically significant difference in the assay result due to another component or property of the sample
- For serum electrophoresis, it can be exogenous or endogenous
Essential features
- Interference in serum electrophoresis can cause misinterpretation, leading to improper patient management
- Immunofixation, immunosubtraction and clinical assessment can mitigate most of the interferences
Factors interfering with electrophoresis
- Analytical interferences
- Important causes of laboratory error
- Clinically significant consequences, including over or undertreatment and misdiagnosis
Types of interferences
| Endogenous | Exogenous |
|
|
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
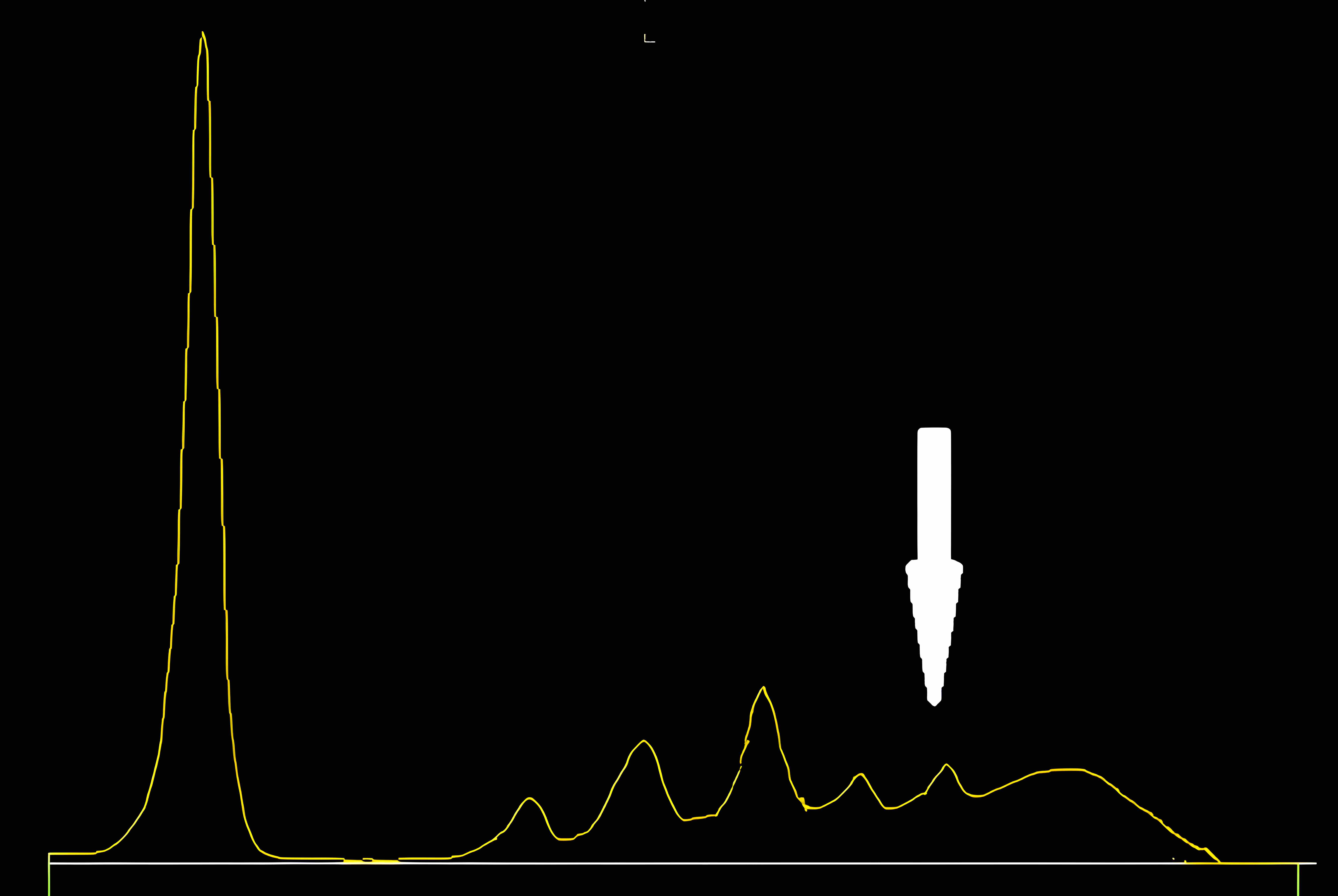
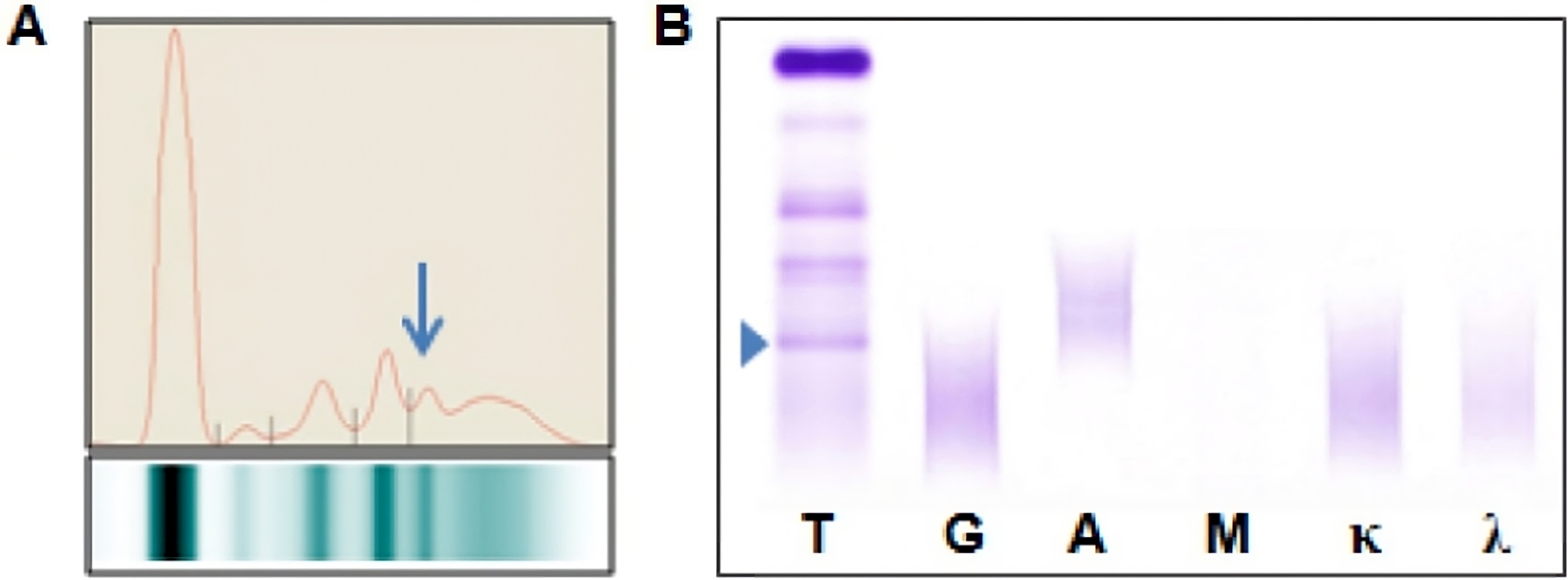
Fibrinogen
- Fibrinogen is not normally present in serum specimens if adequate preanalysis is performed
- Fibrinogen may be present in serum
- Disorders of coagulation
- Anticoagulation therapy
- When a plasma sample is erroneously provided instead of serum
- When serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) is performed on these samples, fibrinogen migrates to the β / γ region and it may be misinterpreted as a monoclonal immunoglobulin
- Following immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) the apparent monoclonal protein is absent, this combined with the characteristic localization of the band in the β / γ region should establish the identity of this band as fibrinogen
- Although not routinely performed in diagnostic practice, IFE with antifibrinogen antibodies provides solid proof that the band is indeed fibrinogen
- Commercial sources of antiserum used for IFE may contain antibodies with specificity towards proteins that are typically absent from serum, such as fibrinogen, which can produce clinically misleading results
- For proper M protein analysis of these rare cases, either another blood sample should be obtained or the fibrinogen should be selectively eliminated prior to SPEP (Clin Chim Acta 2006;368:192)
- See image 1
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
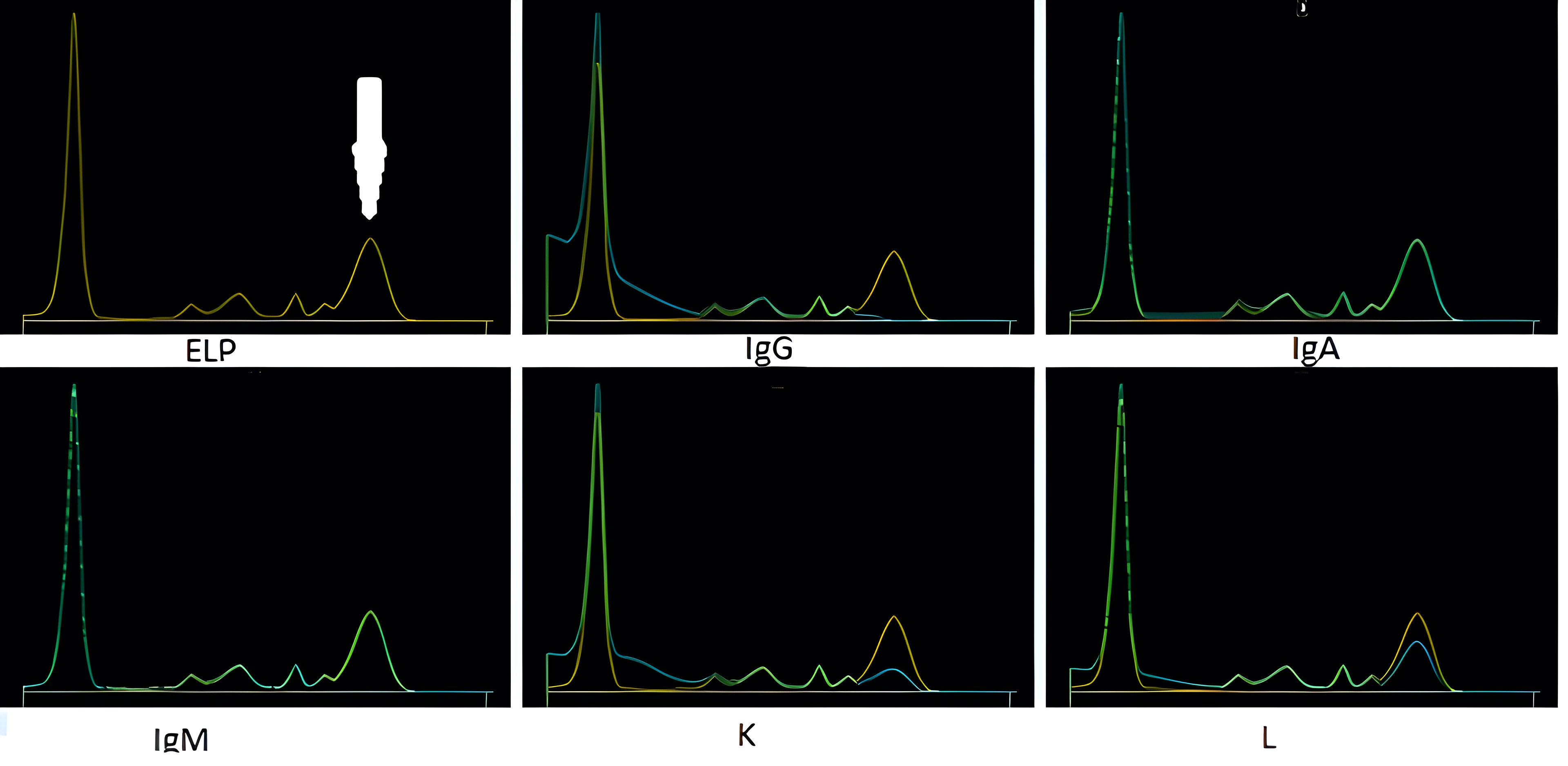
Hemolysis
- The 2 main interference mechanisms are spectral interference from high concentrations of hemoglobin and direct release of analytes from red blood cells
- Hemolysis can be broadly divided into either prephlebotomy (in vivo hemolysis) or during phlebotomy (in vitro) causes
- In SPEP, hemoglobin and hemoglobin complexes that show up as discrete bands in the α2 and β regions may be misinterpreted as monoclonal proteins
- This is easily avoided by identifying hemolyzed specimens prior to interpretation or by reflexing to IFE to confirm the presence of any abnormal bands
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Human antianimal antibodies (HAAAs)
- HAAAs are typically formed after exposure to animal proteins (either through occupational exposure or medical therapy)
- The most common HAAAs encountered are human mouse antibodies (HAMAs)
- Disorders affected by HAMAs include cases of organ transplantation, cancer, inflammation, infection and kidney disease, etc. (Clin Chem 1999;45:942)
- HAMAs interfere with serum IFE and may falsely appear as monoclonal proteins
- When SPEP / IFE in isolation are not sufficient to drive decision making, clinical awareness of this issue is the best course of action
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Contrast dyes
- Contrasts dyes, used in imaging testing, interfere with capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE)
- Migrate to α2 globulin fraction or less frequently the β2 globulin fraction
- Reflex testing to IFE or immunotyping can confirm absence of a monoclonal component
- Clinicians should be aware that imaging using contrast dyes should be done after blood collection
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
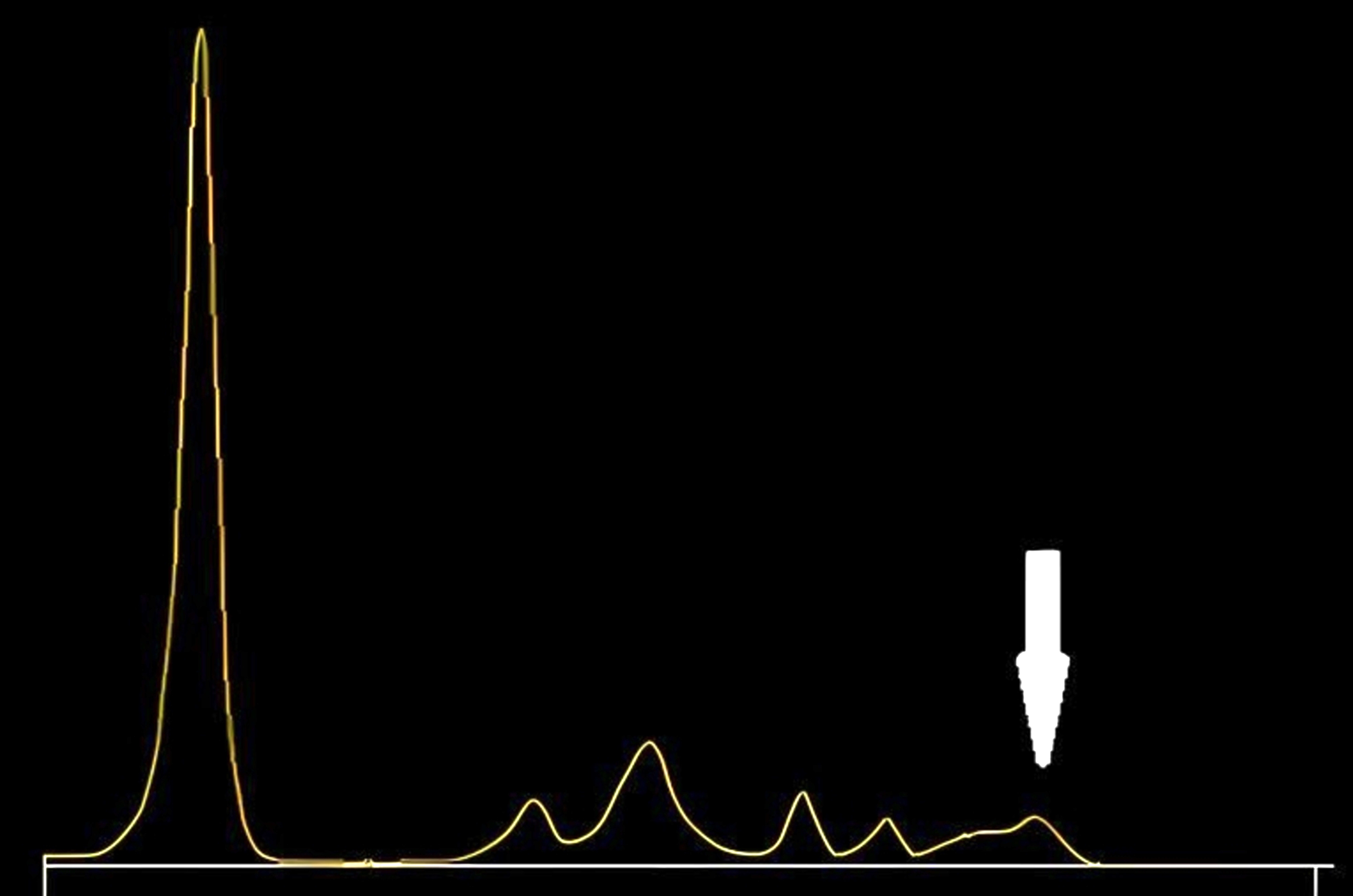
Antifungals and antibiotics
| Drugs | Peak zones on CZE |
| 5 fluorocytosine (5FC) | Cathodal region of γ globulin fraction |
| Ceftriaxone | Anodal region of the prealbumin fraction |
| Sulfamethoxazole | Albumin peak |
| Piperacillin with tazobactam | α2 β1 globulin region |
- These interferences are more likely to occur when blood samples are collected closer to the time of perfusion, especially in the context of renal failure and drug accumulation
- Reflex testing to IFE or immunotyping can confirm the absence of a monoclonal component
- See image 3
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Gelatin based plasma substitutes
- Gelatin based plasma substitutes can increase the γ globulin fraction, with a polyclonal pattern shifted to the β2 globulin fraction, simulating a βγ block in CZE
- Reflex testing to IFE or immunotyping can confirm absence of monoclonal component
- SPEP is rarely performed in an emergency context of infusion of gelatin based substitutes; together with their short half life (~2.5 hours), the risk of this type of interference is uncommon
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Hydroxocobalamin
- Interference with SPEP concerning the α1 globulin fraction
- Hydroxocobalamin is the standard therapy for cyanide poisoning
- Interference will be much easier to detect on SPEP as hypoproteinemia is very frequently associated with severe burns
- Reflex testing to IFE or immunotyping can confirm absence of a monoclonal component
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
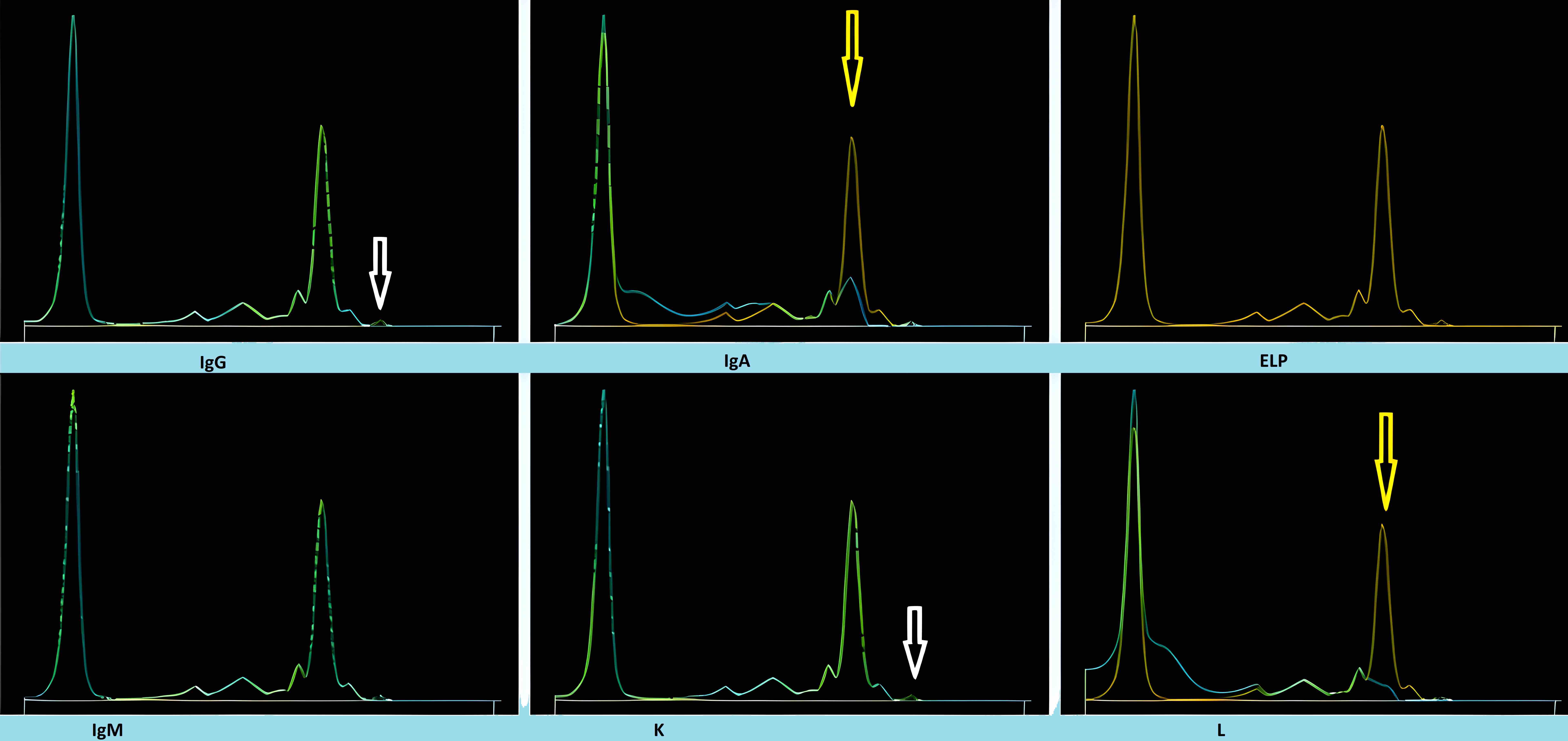
Monoclonal therapies
- Many of the available monoclonal therapeutics can appear as monoclonal IgG kappa by IFE
- Of the monoclonal drugs used for non-plasma cell dyscrasia based diseases, only rituximab and bevacizumab in therapeutic doses produced a visible M protein on SPEP / IFE
- Drugs like siltuximab, daratumumab and elotuzumab (all IgG kappa monoclonal antibodies) can appear as a small M protein, most often in concentrations of no more than 1 g/L or 0.1 g/dL, when used in therapeutic doses (Clin Chem 2010;56:1897)
- The main concern with the presence of these therapies is misclassification of disease response as having a very good partial response (VGPR) as opposed to a complete response
- Practically applicable mitigation response to monoclonal therapy varies with subtype of clonal immunoglobulin produced by plasma cell neoplasm
| IgG plasma cell neoplasm | Plasma cell neoplasm other than IgG |
|
|
- Daratumumab specific immunofixation electrophoresis reflex assay (DIRA) using an antibody targeting daratumumab to alter the migration of daratumumab during electrophoresis should be utilized
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Monoclonal immunoglobulin rapid accurate molecular mass (miRAMM) assay
- miRAMM assay uses affinity purification followed by microflow LC-ESI-Q-TOF MS to determine the exact mass of monoclonal immunoglobulin chains
- This method is effectively immune to interferences including those from a monoclonal therapy because it will resolve each immunoglobulin peak by its unique mass and allow for it to be identified and differentiated (Methods 2015;81:56)
- Reference: Clin Biochem 2018;51:72
Diagrams / tables
Board review style question #1
Which of the following statements regarding electrophoreses after initiation of monoclonal therapy is true?
- Electrophoresis studies should be done before administration of monoclonal antibodies
- Immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) will show a peak in the anodal part of the γ region with daratumumab
- Short time interval between serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) and drug administration should decrease chances of interference
- SPEP showing a peak of 300 mg/dL will always mean a very good partial response (VGPR)
Board review style answer #1
A. Electrophoresis studies should be done before administration of monoclonal antibodies. Before each dose, the concentration of therapeutic monoclonal will be lowest and thus give less interference.
Answer C is incorrect because with longer intervals between the dose and testing, interference will be less.
Answer B is incorrect because daratumumab usually migrates to the cathodal part of the γ region.
Answer D is incorrect because a value of < 1 g/dL can be due to therapeutic monoclonal therapy.
Comment Here
Reference: Interference in protein electrophoresis
Comment Here
Reference: Interference in protein electrophoresis
Board review style question #2
Serum electrophoresis of a 60 year old man identifies a peak. Immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE) is performed. Which most the following is most consistent with the findings?
- Patient has multiple myeloma
- Plasma sample of patient with macrocytic anemia
- Serum sample obtained immediately after monoclonal therapy
- Serum sample of patient with IgG related disease
Board review style answer #2
B. Plasma sample of patient with macrocytic anemia. Plasma contains fibrinogen; plasma sample was erogenously run instead of serum.
Answer C is incorrect because IFE shows no monoclonal antibody.
Answer D is incorrect because the band is in β / γ region.
Answer A is incorrect because IFE shows no monoclonal antibody.
Comment Here
Reference: Interference in protein electrophoresis
Comment Here
Reference: Interference in protein electrophoresis