Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Kearns K, Dioufa N. Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixmesonephrichyper.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Vestigial elements of the distal ends of the Wolffian ducts that fail to regress
- Small tubules or cysts that are usually located deep in the lateral aspects of the cervix
Essential features
- Usually an incidental finding; rarely can cause nodularity, induration, an erosion or an abnormal Pap smear (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2008)
- Several small, well circumscribed lobular aggregates of small to medium sized, round shaped tubules typically found in the lateral aspects of the cervix (3 o'clock and 9 o'clock)
- Tubules contain eosinophilic, colloid-like, PAS positive intraluminal secretions
- No stromal response, no atypia, no / minimal mitotic activity
Terminology
- Wolffian duct remnants
- Wolffian hyperplasia
Epidemiology
- Mean age of 35 - 47 years; range of 21 - 72 years (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100)
- 1 - 22% of adult cervices
- Up to 40% of the cervices of newborns and children
Sites
- Lateral aspects of the uterine cervix
- Vagina
- Broad ligament
Pathophysiology
- In the embryo, the mesonephric ducts serve as temporary kidneys that are later replaced by permanent kidneys (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100)
- Mesonephric ducts degenerate; however, small remnants may persist giving rise to cysts and rarely neoplasms (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100)
Etiology
- Persistence of Wolffian ducts
Clinical features
- Generally asymptomatic / incidental finding
- Has been implicated in vaginal or postcoital bleeding on rare occasions (Gynecol Oncol 1993;49:41)
Diagnosis
- Usually an incidental finding
- Mesonephric hyperplasia may present as nodularity or mass, if florid
- Rarely can cause induration, an erosion or an abnormal Pap smear (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2008)
Case reports
- 24 year old woman with a history of recurring high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) after loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) (Pathology 2022;54:378)
- 37 year old woman with atypical glandular cells found on a routine cervical smear (Int J Gynecol Pathol 2003;22:121)
- 49 year old woman with routine hysterectomy (Int J Gynecol Pathol 1985;4:245)
Gross description
- Rarely can present as cervical nodularity, induration or erosion (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 2nd Edition, 2008)
Microscopic (histologic) description
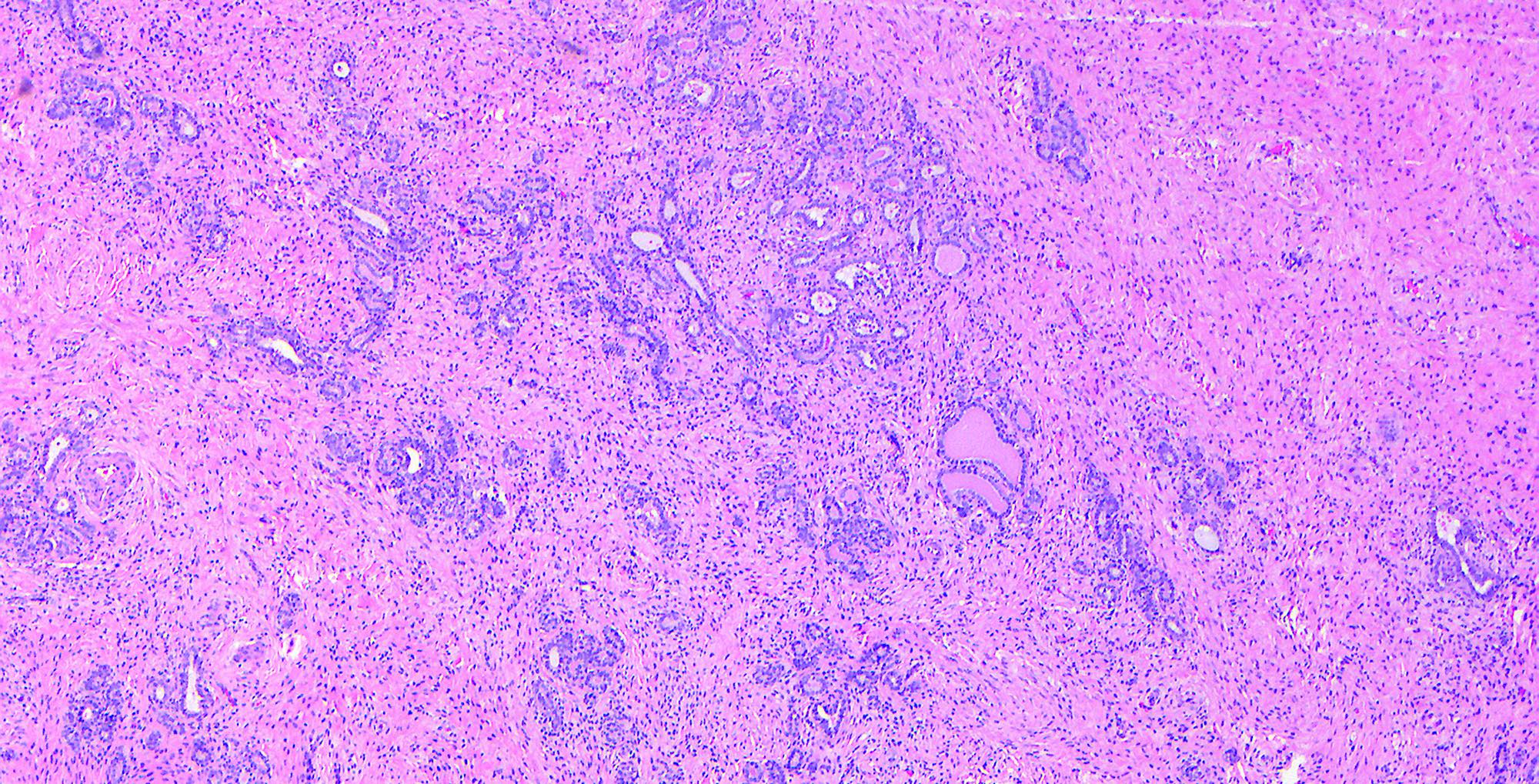
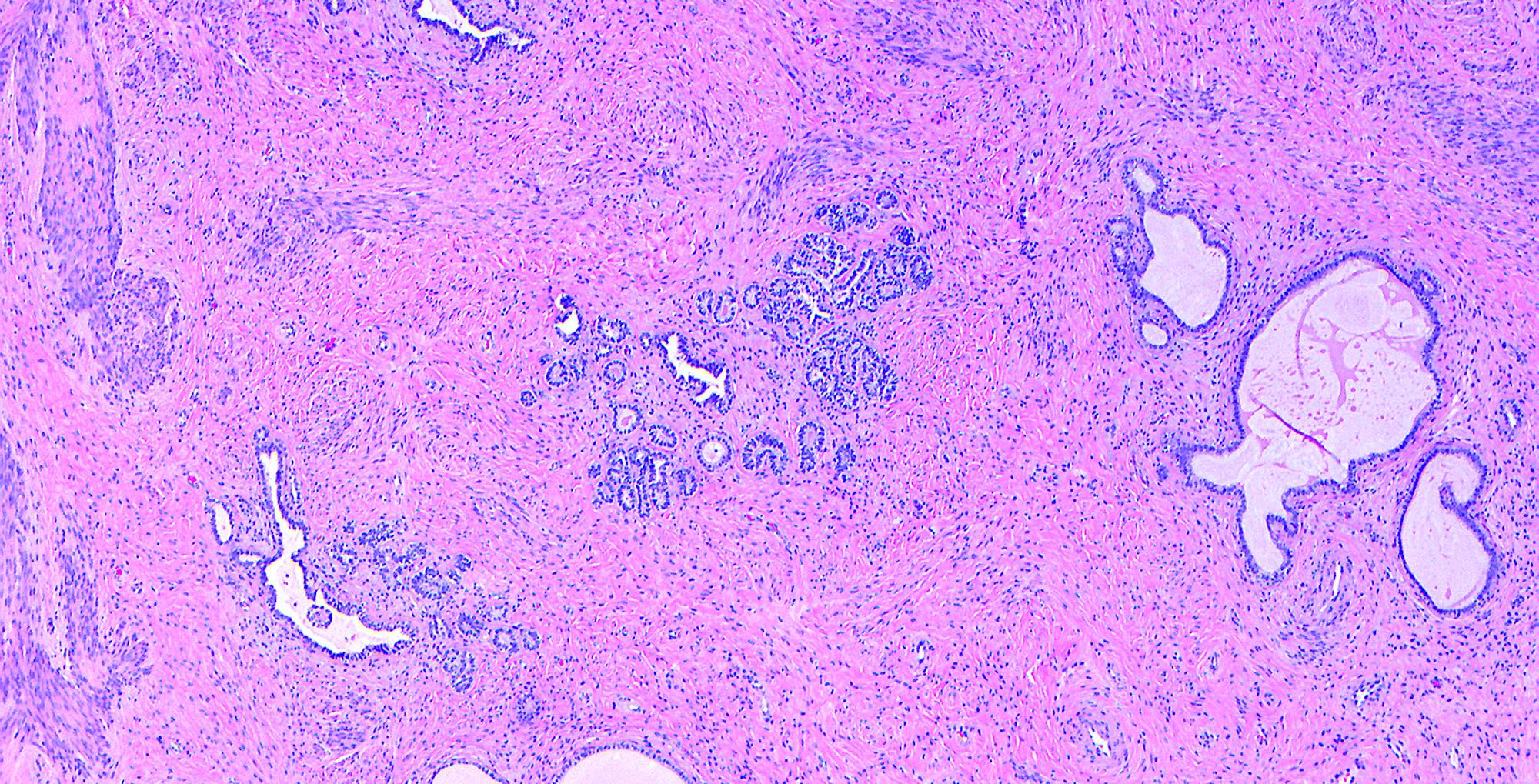
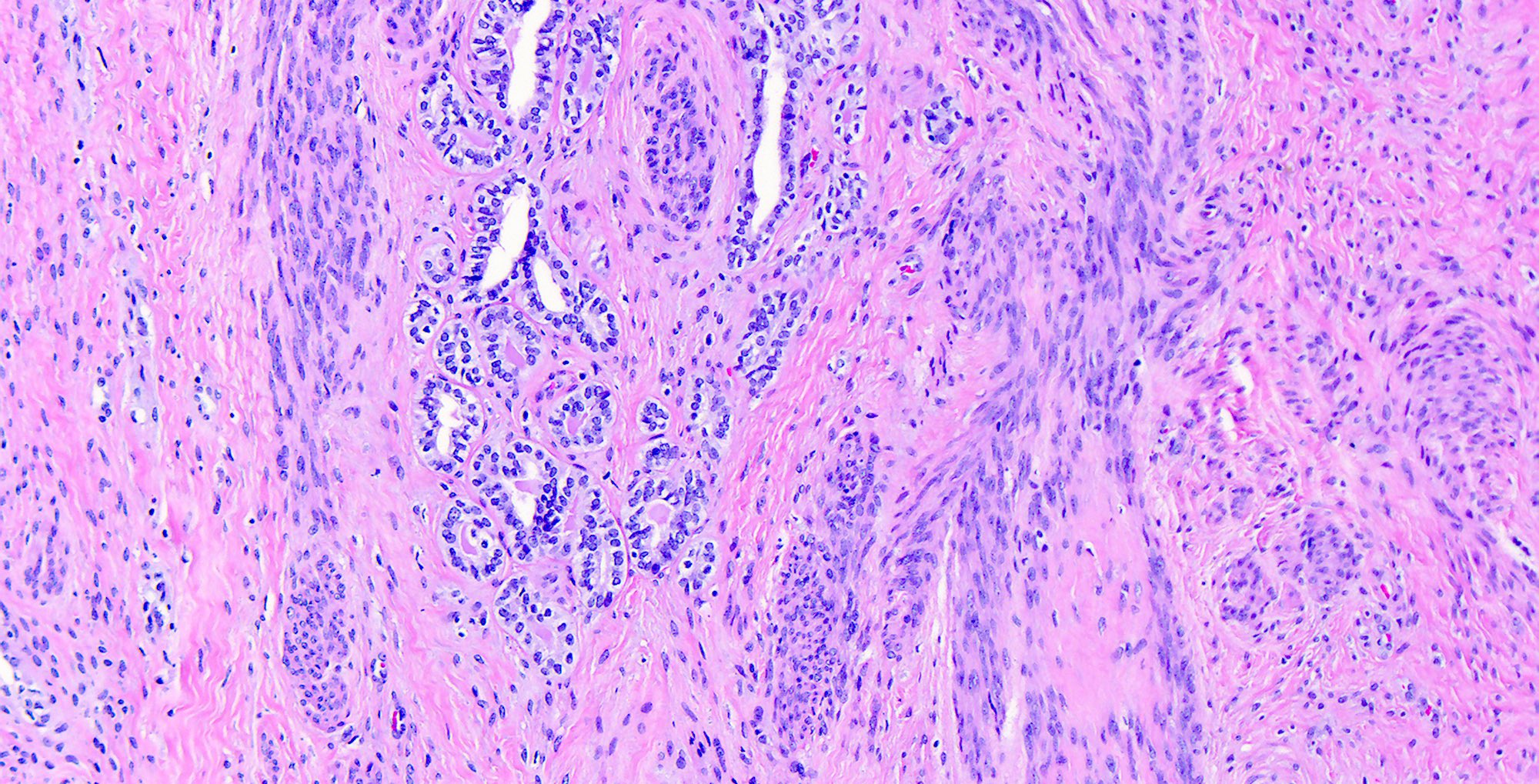
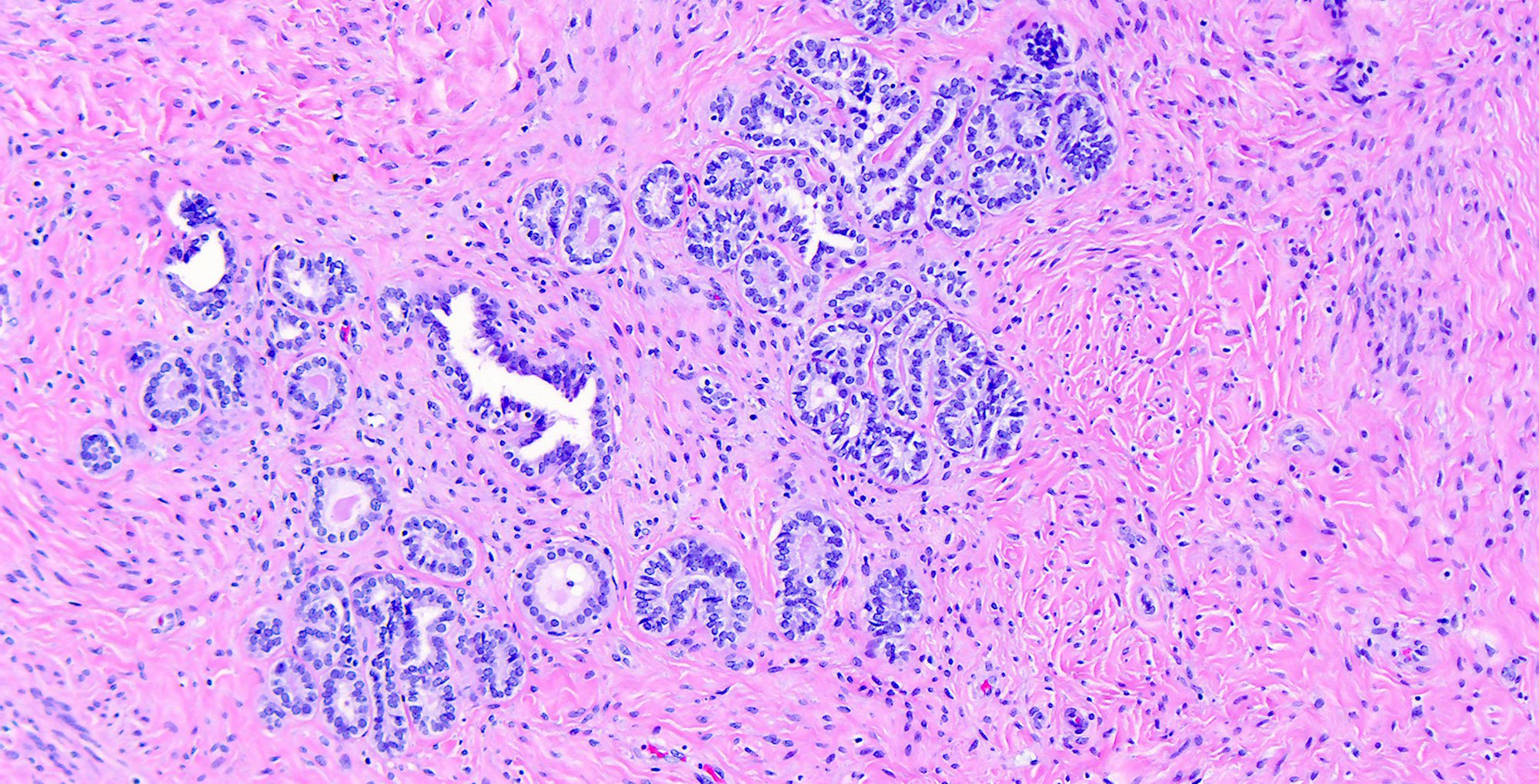
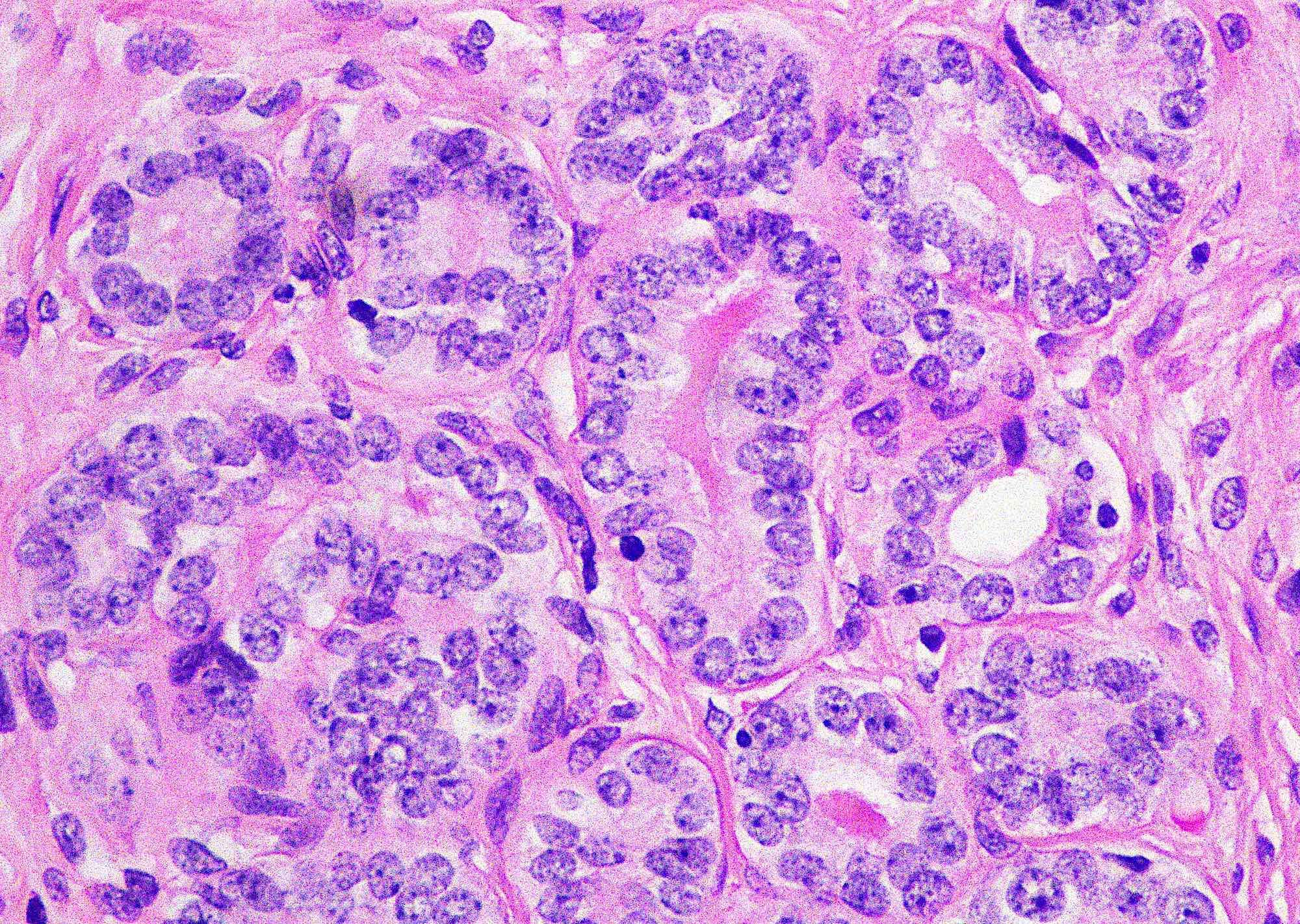
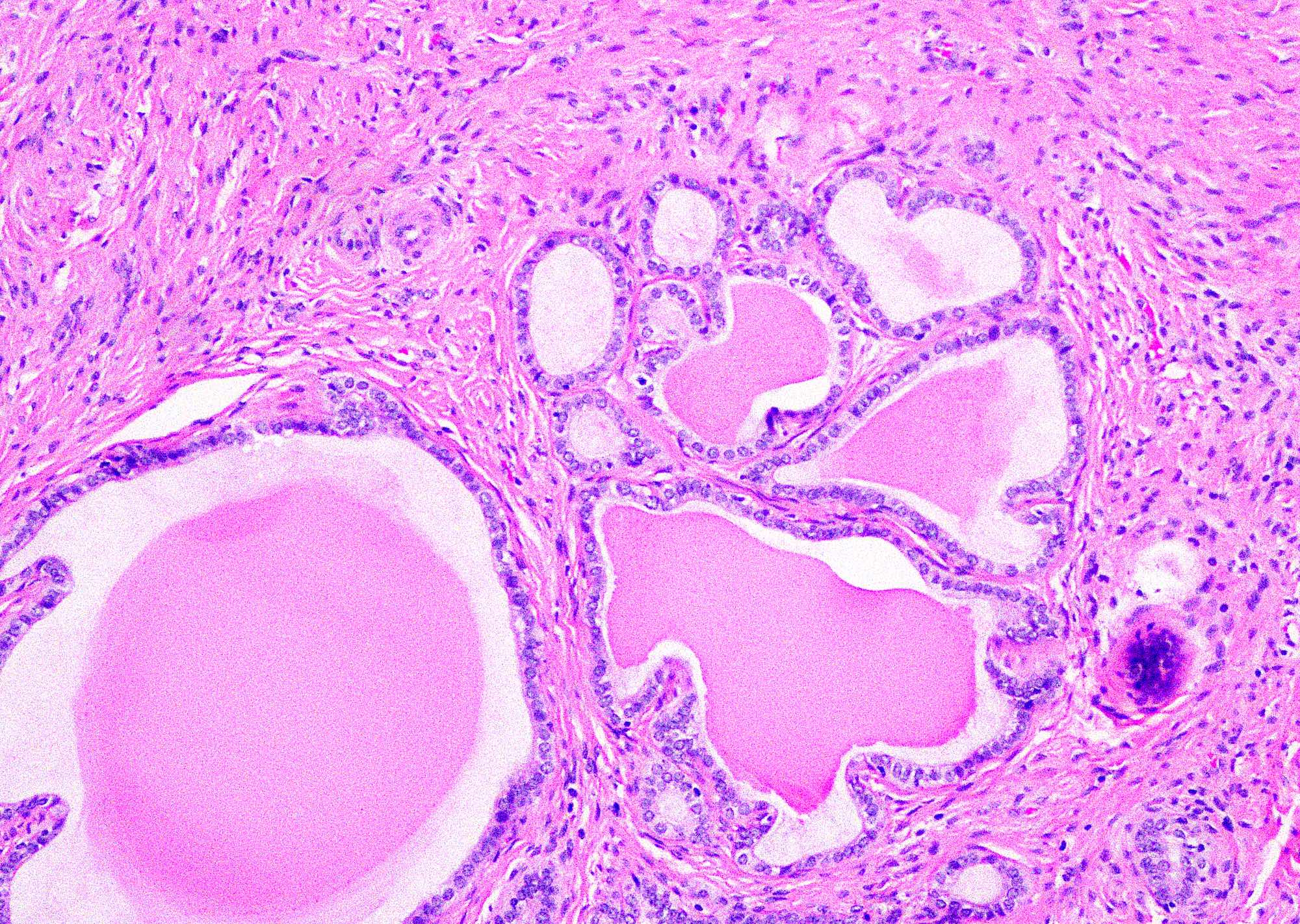
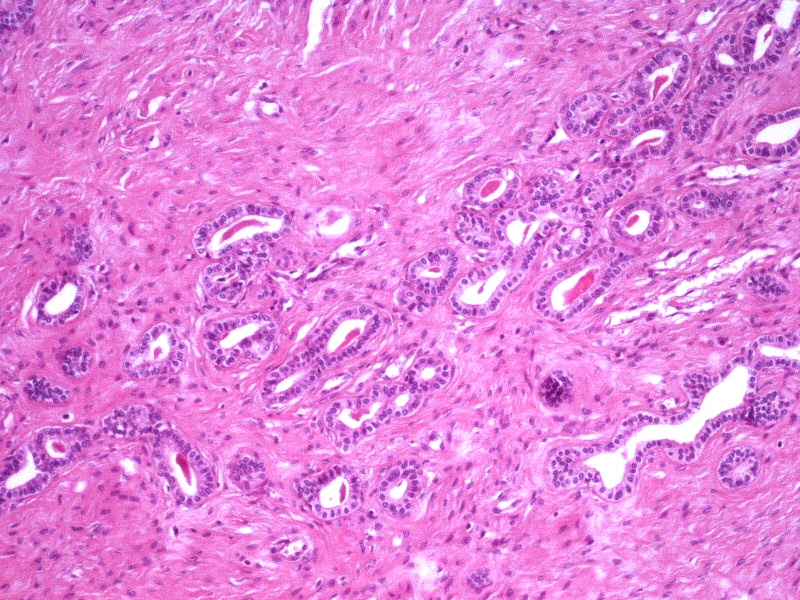
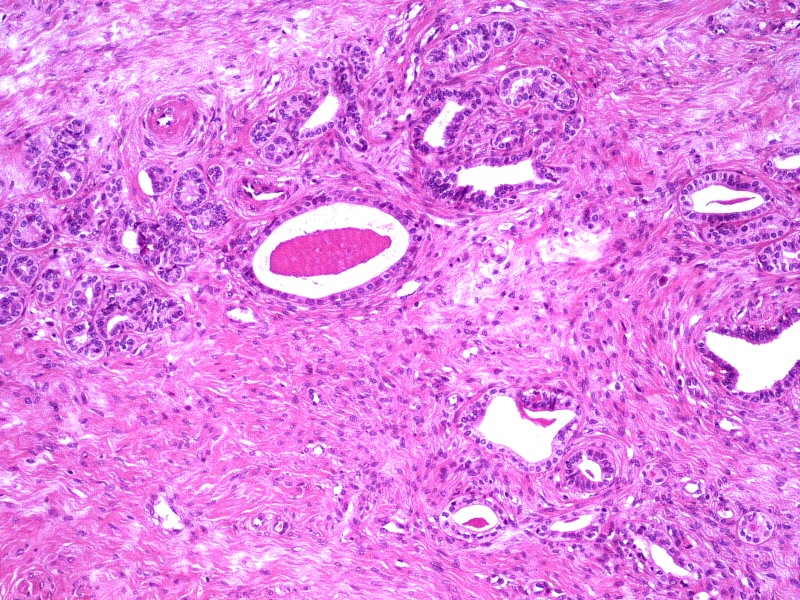
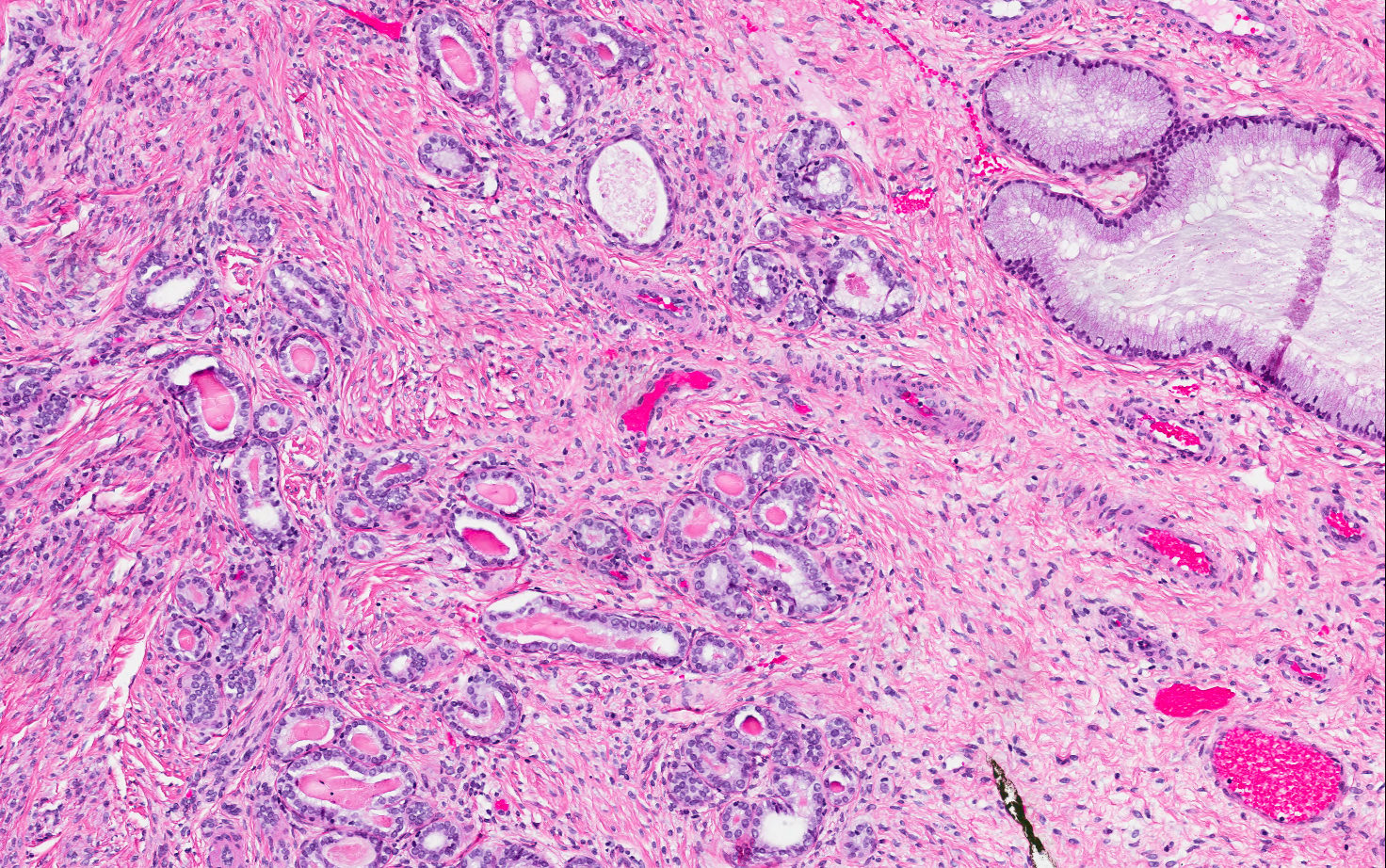
- Small tubules or cysts that are located deep in the lateral cervical wall and arranged in small clusters (Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract, 6th Edition, 2011)
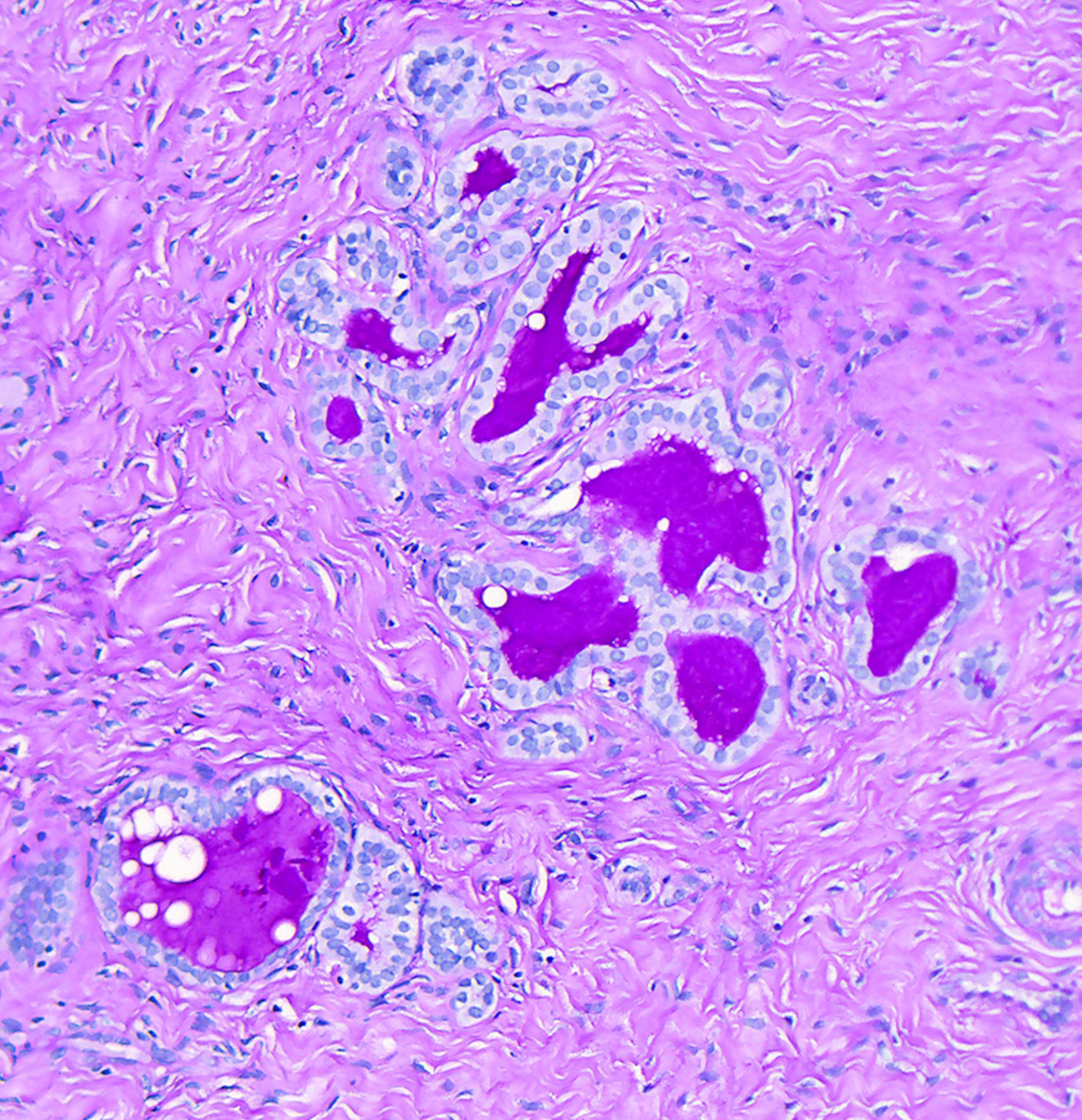
- Tubules usually contain characteristic eosinophilic, colloid-like, PAS positive luminal secretion (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2013)
- No stromal response (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2013)
- Cells lining the tubules are cuboidal with scant eosinophilic cytoplasm, round, cytologically bland nuclei with no atypia or mitotic activity
- Mesonephric hyperplasia classification (not clinically relevant)
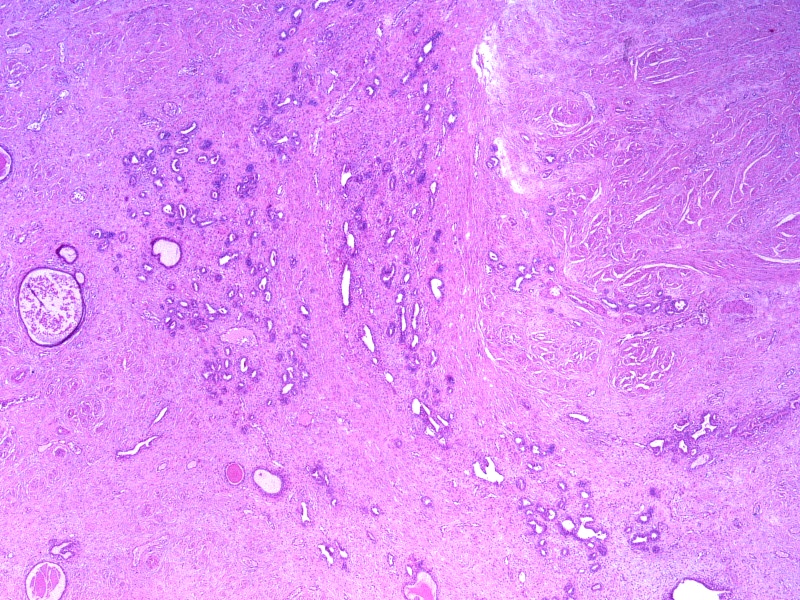
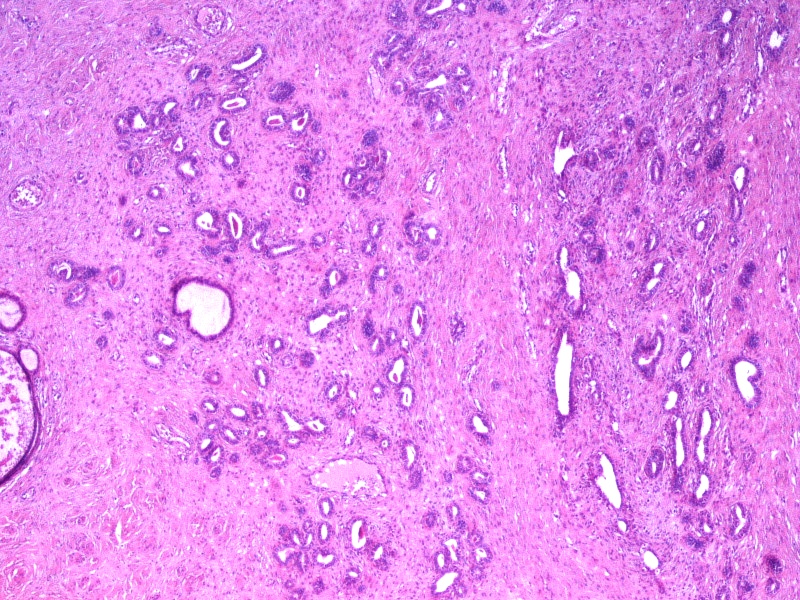
- Lobular type: clustered mesonephric tubules, with or without a centrally placed duct and variable amounts of stroma; occurs at a younger age, is less extensive and tends to arise deeper in the cervical stroma
- Diffuse type: diffuse proliferation of uniformly well spaced mesonephric tubules, occasionally cystic (Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract, 6th Edition, 2011)
- Separately described is mesonephric ductal hyperplasia (least common): mesonephric duct lined by hyperplastic epithelium typically in the form of micropapillary projections / tufts; lacks the eosinophilic luminal secretions (Clement: Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2013)
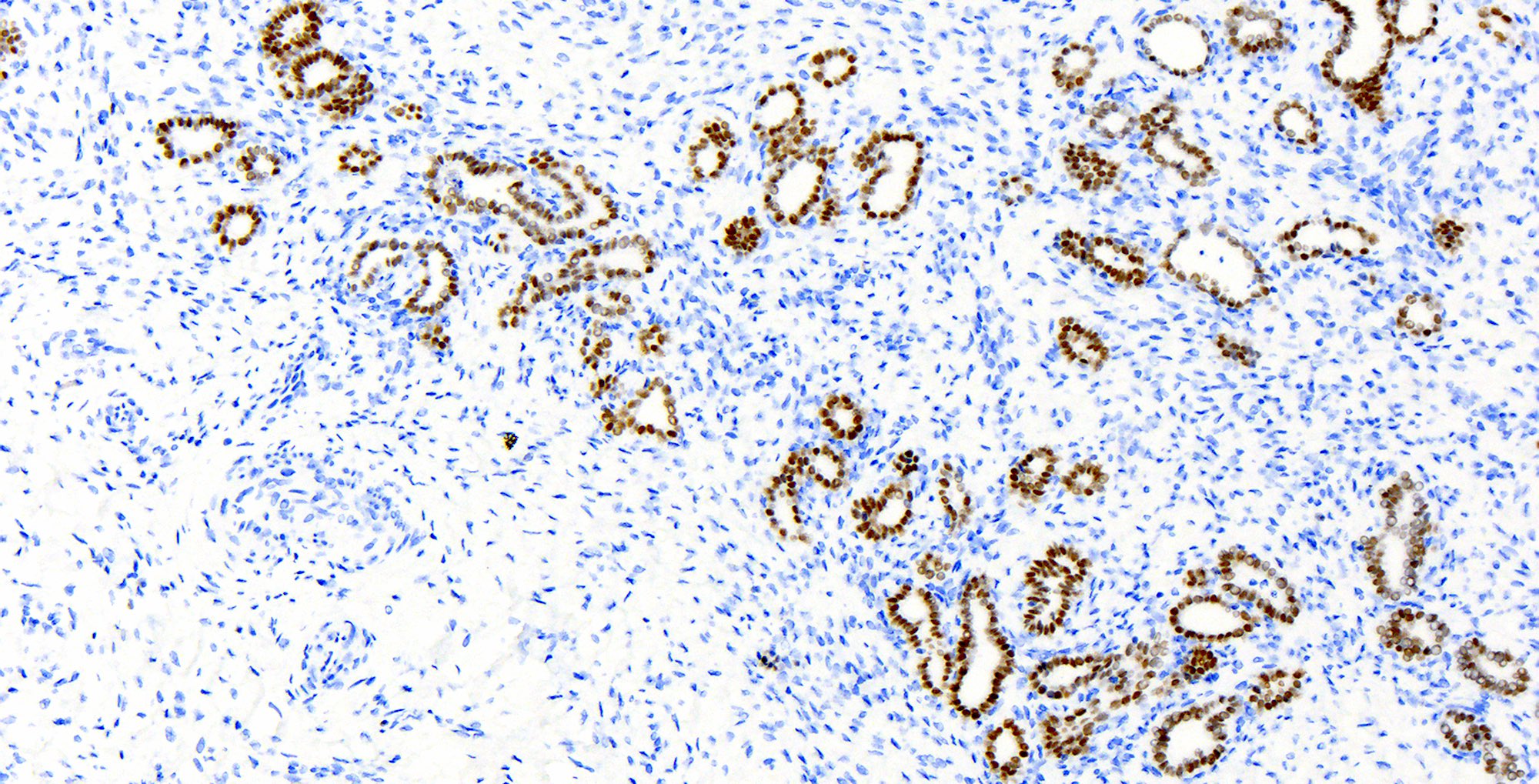
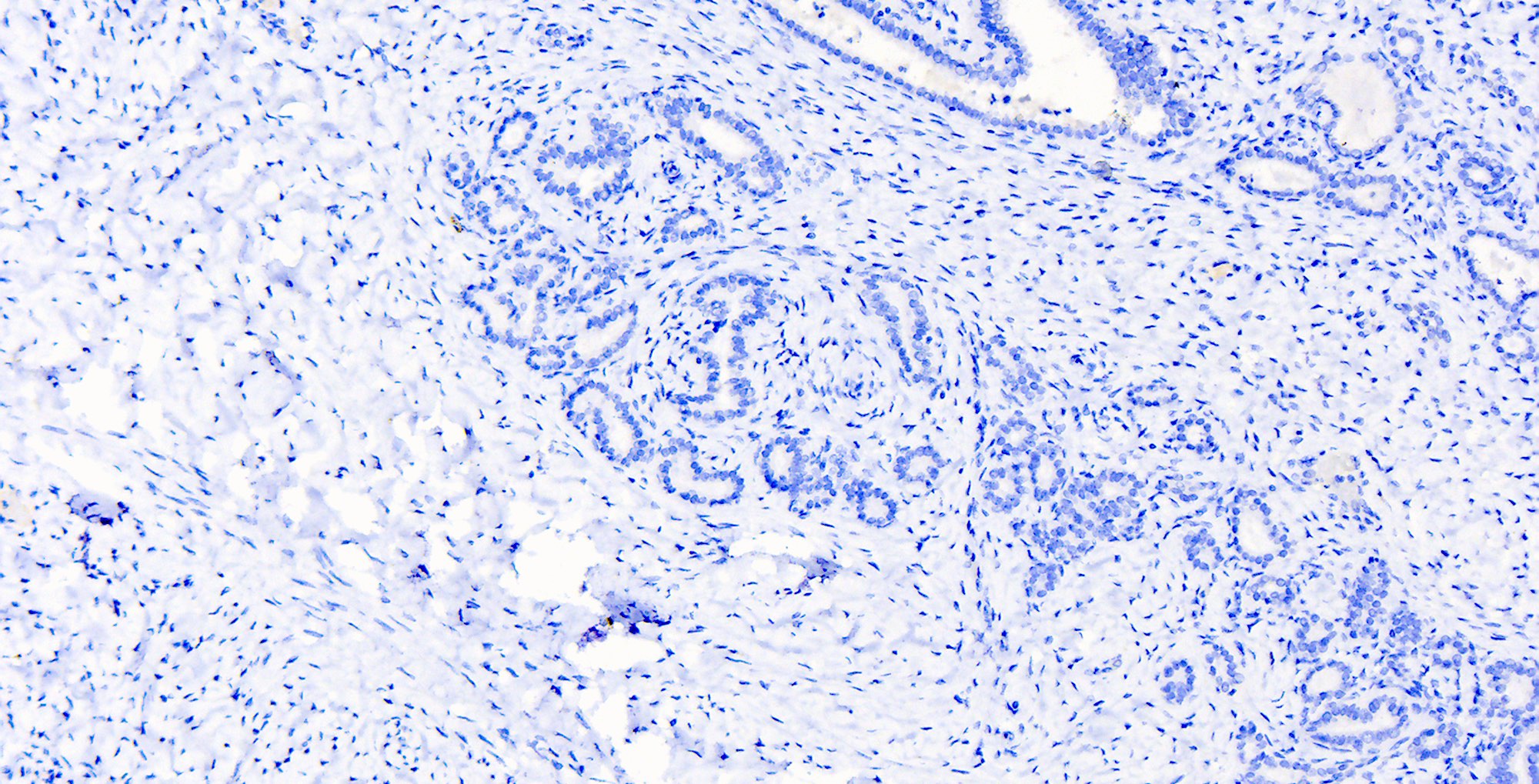
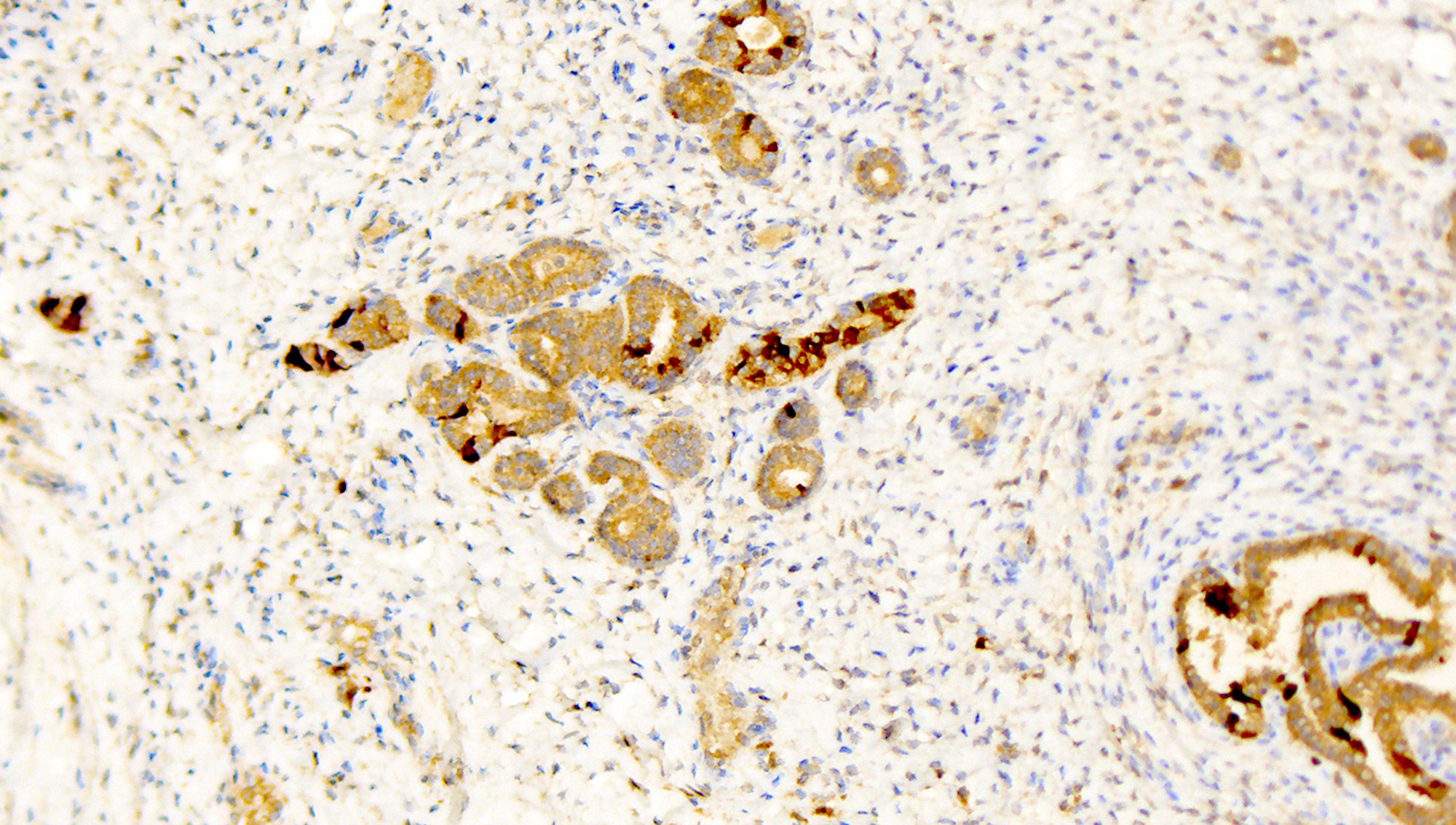
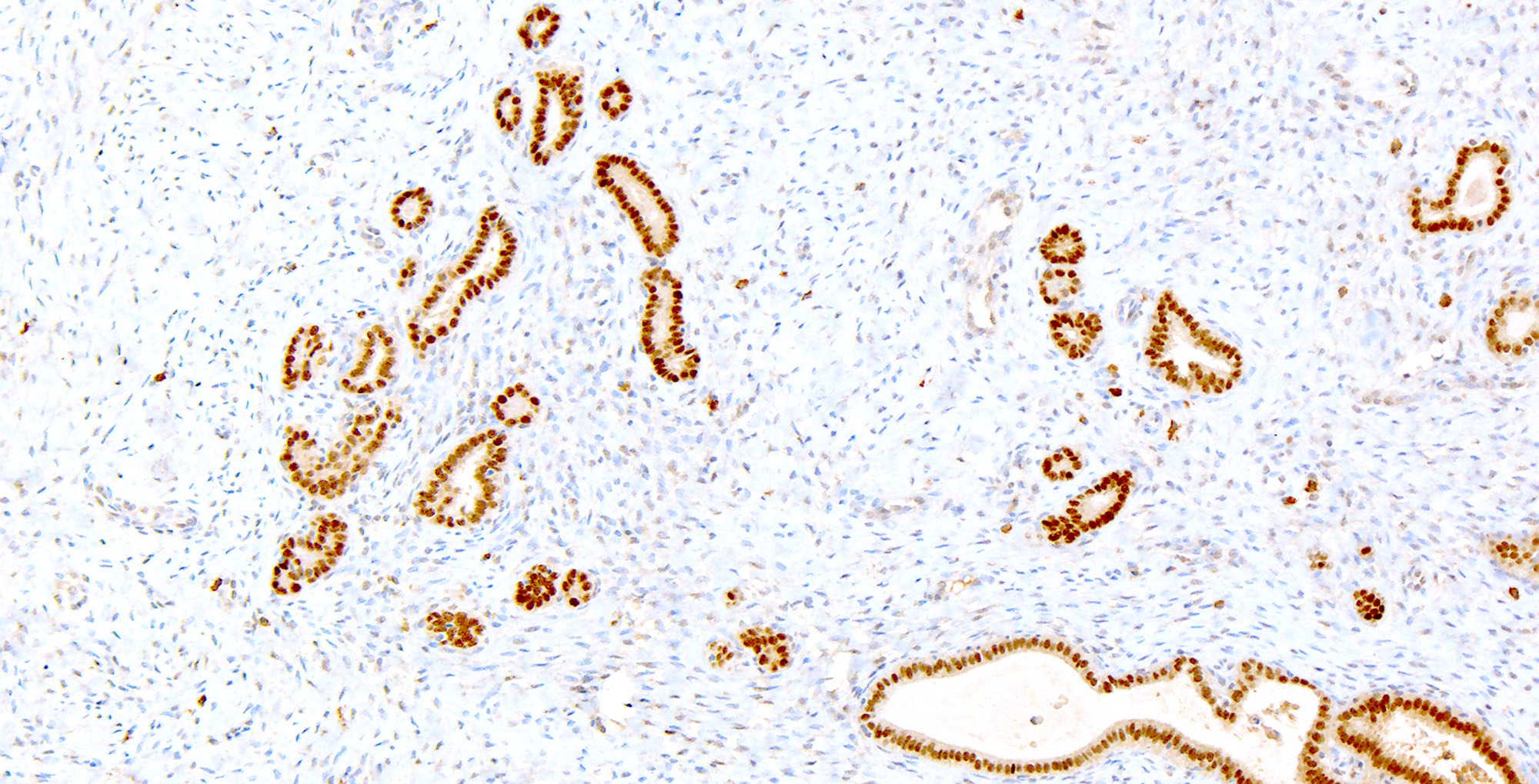
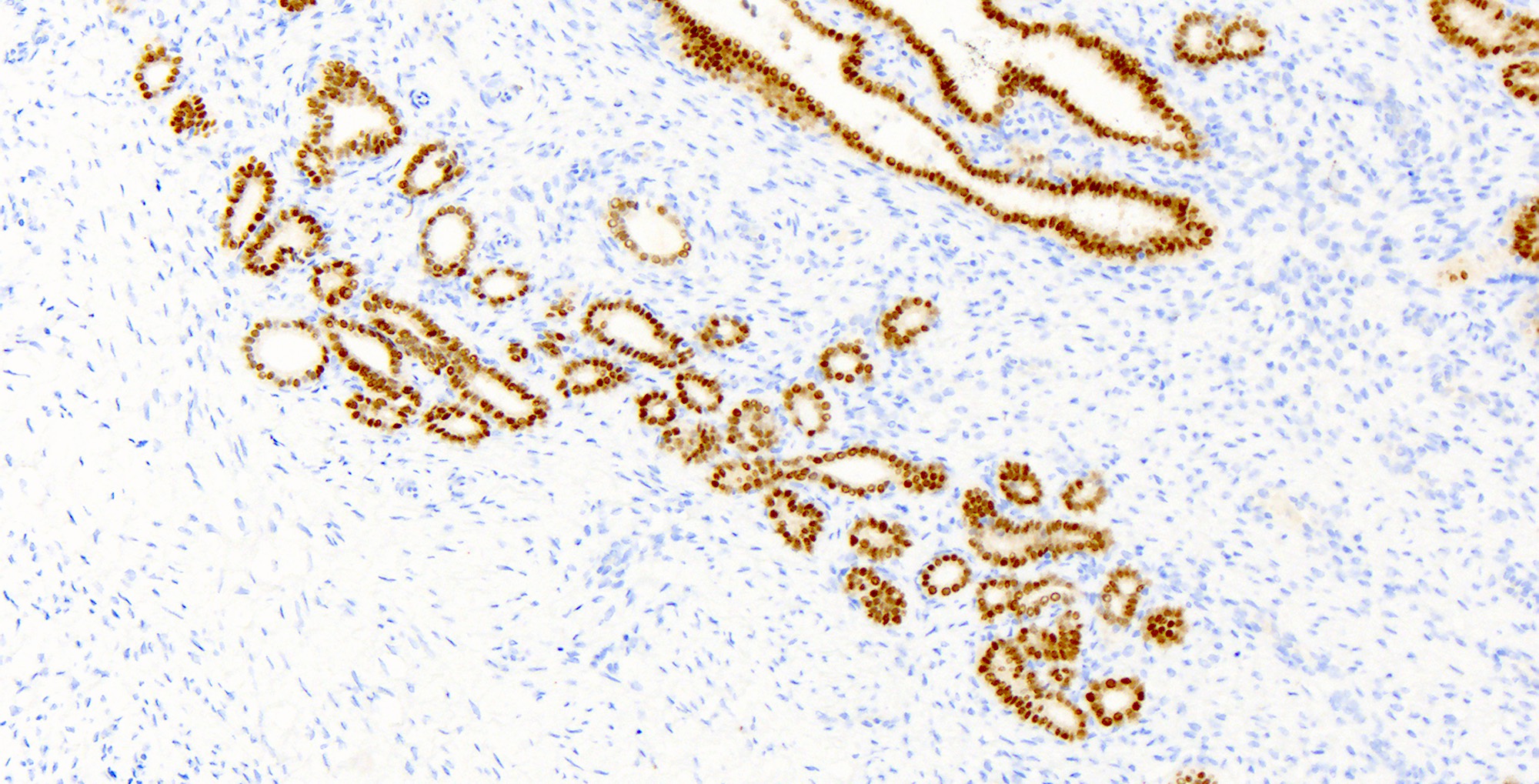
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Katerina Kearns, M.D., Michela Campora, M.D., Carlos Parra-Herran, M.D. and Nikolina Dioufa, M.D.
Cytology description
- May cause abnormal Pap smears (Cytopathology 2005;16:240, Int J Gynecol Pathol 2003;22:121)
- Abnormal glandular cells in loose clusters with cuboidal outlines and no significant anisocytosis
Positive stains
- CD10 (apical cytoplasm and luminal secretions)
- EMA
- Calretinin
- PAX2 (strong nuclear)
- PAX8, GATA3 frequently positive
- MIB1 / Ki67 (rare cells)
- p16 (weak to moderately positive) (Gynecol Oncol 2010;116:468)
- Reference: Nucci: Diagnostic Pathology: Gynecological, 3rd Edition, 2023
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Mesonephric hyperplasia with atypia: KRAS mutation, 1q gain (Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2020;17:813)
- Mesonephric hyperplasia without atypia: lack of KRAS (Histopathology 2017;71:1003)
Sample pathology report
- Cervix, loop electrosurgical excision procedure:
- Cervix with mesonephric hyperplasia
- Negative for dysplasia and malignancy
Differential diagnosis
- Mesonephric hyperplasia with atypia:
- Acknowledged by a few authors (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:1100, Int J Gynecol Pathol 1985;4:245, Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2020;17:813)
- Mild to moderate nuclear atypia (e.g., pleomorphism, larger nuclei, nuclear membrane irregularities) (Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2020;17:813)
- No architectural abnormalities such as destructive stromal infiltration, confluent growth, back to back glandular arrangement and cribriform pattern (Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2020;17:813)
- HPV associated endocervical adenocarcinoma, usual type:
- Clear cell carcinoma (CCC):
- Typically centered in the mucosa
- Papillary, tubulocystic and solid growth pattern
- Clear glycogen rich cytoplasm (PAS+ / diastase sensitive)
- Hobnail cells
- Moderate to marked nuclear atypia
- High proliferation index in endometrium CCC; lower rates in early stage CCC of the ovary but can be elevated in higher grade tumors (Front Oncol 2021;11:732782, PLoS Med 2008;5:e232)
- Mesonephric adenocarcinoma:
- Admixture of architectural patterns, (i.e., solid, ductal, tubular, retiform, spindled, etc.), with irregular, frankly infiltrative borders and minimal intervening stroma
- Significant nuclear atypia and mitoses
- Lymphovascular invasion
- KRAS / NRAS mutations (up to 80%)
- ARID1A / ARID1B / SMARCA4 mutations (up to 60%)
- Lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia:
- Presence of intra and extracellular mucin
- Localized at the mucosal aspect, in contrast to the often more deeply seated mesonephric remnants / hyperplasia
- Tunnel clusters:
- Presence of intra and extracellular mucin
- Localized at the mucosal aspect, in contrast to the often more deeply seated mesonephric remnants / hyperplasia
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. PAX2+, ER-, CD10+ (apical), p16+ (patchy). The image shows a case of mesonephric hyperplasia which is typically PAX2+, ER-, CD10+ (apical) and p16+ (patchy). Answer B is incorrect because mesonephric hyperplasia shows apical cytoplasmic staining of CD10. Answers C and D are incorrect because mesonephric hyperplasia shows positivity for PAX2, CD10 and p16 (patchy) and negativity for ER.
Comment Here
Reference: Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia
Board review style question #2
What is the most common presentation of mesonephric hyperplasia of the cervix?
- Abnormal Pap smear
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Cervical mass
- Incidental finding
Board review style answer #2
D. Incidental finding. Mesonephric hyperplasia is almost always asymptomatic and is detected incidentally on either cervical biopsy, cone biopsy or hysterectomy specimens. Answer A is incorrect because it is rarely associated with abnormal Pap smears. Answers B and C are incorrect because abnormal vaginal bleeding and the presence of a cervical mass are associated more with mesonephric adenocarcinoma rather than mesonephric hyperplasia.
Comment Here
Reference: Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia
Comment Here
Reference: Mesonephric rests and mesonephric hyperplasia