Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Cytology description | Cytology images | Negative stains | Videos | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Hasteh F. Atrophy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cervixcytologyatrophy.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- May resemble SIL
- Increased number of basal and parabasal cells, associated with diagnosis of ASCUS
Clinical features
- May cause increased incidence of ASCUS in Pap smears of peri- and post-menopausal women (Cancer 2001;93:100)
- Associated with scanty smears (Cytopathology 1997;8:274), ASCUS in postmenopausal women (Diagn Cytopathol 2001;24:132)
- Changes may disappear after topical estrogen
Prognostic factors
- New guidelines recommend HPV testing as initial triage management of postmenopausal women with cytologic result of LSIL (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:1276)
Treatment
- Estrogen will cause atypical atrophic cells to mature, but dysplastic cells will not respond (Cancer 1998;84:218)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- No atypia in upper epithelial layers, no mitotic figures
- Pseudokoilocytosis, immature but bland epithelium
- May resemble urothelial metaplasia
- May have focal nuclear enlargement and hyperchromasia
- Cells have prominent intercellular bridges
- Nuclei are uniform, evenly spaced, often elongated with grooves
Cytology description
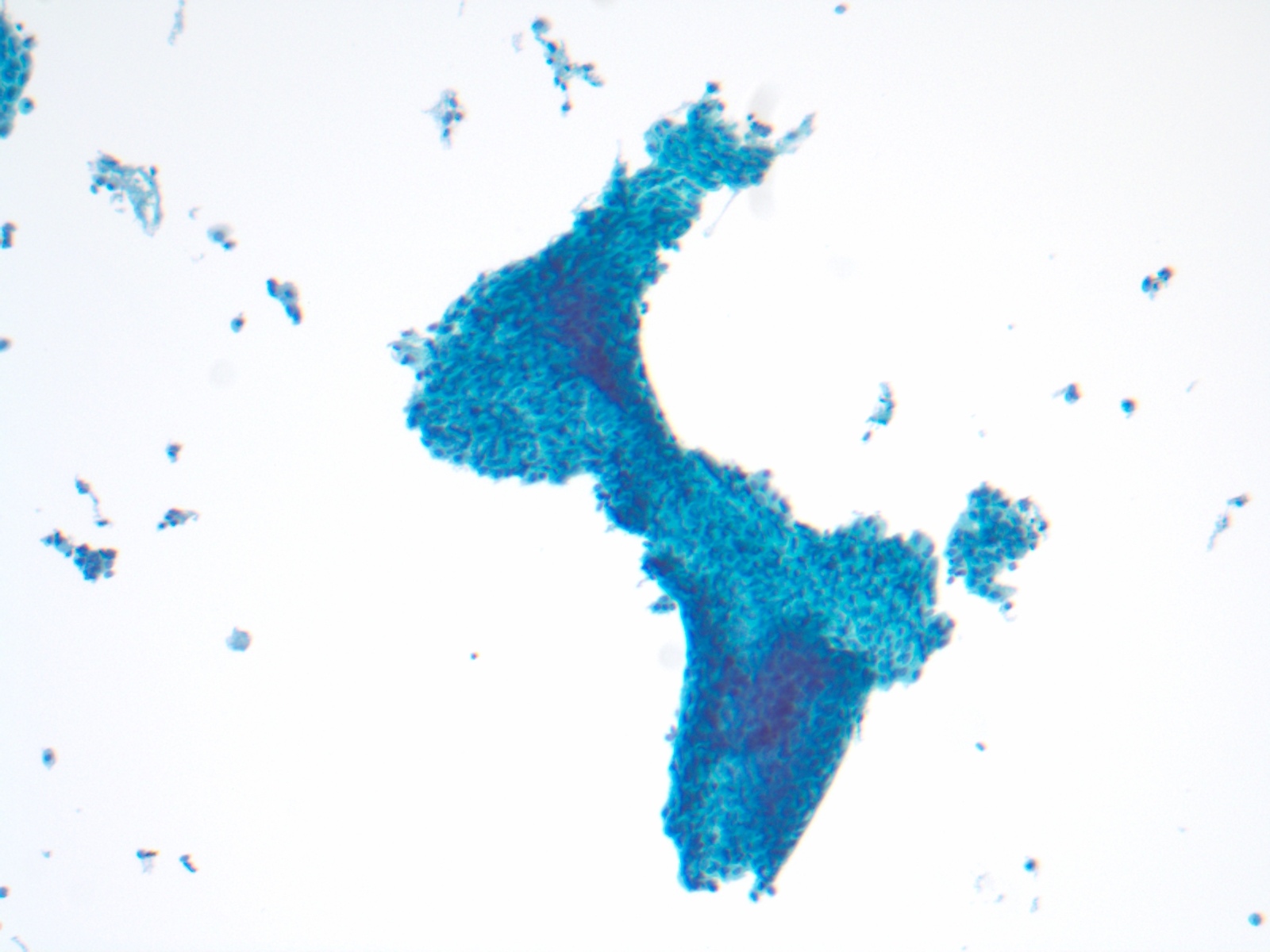
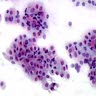
- Increased number of parabasal cells and basal cells, which form sheets and syncytial-like aggregates or hyperchromatic crowded groups
- Naked nuclei (small cells) may be seen
- Cells have high N/C ratio but uniform chromatin
- Pseudokeratinized cells (pink to orangophilic cytoplasm) are due to degeneration
- Severe atrophy can show dirty background with inflammation, debris, old blood, blue blobs and giant cells
- In liquid based cytology, background of atrophic smear is cleaner
- May resemble urothelial metaplasia, but cells have prominent intercellular bridges
- Nuclei are uniform, evenly spaced, often elongated with grooves
Cytology images
Negative stains
- Ki67 (Gynecol Oncol 2000;79:225, J Pathol 2000;190:545), cyclin E, p16
Videos
Differential diagnosis
- SIL: strong Ki67+ and p16 staining in 75-80%, strong cyclin E+ in 31% (J Low Genit Tract Dis 2005;9:100)
- Dirty background of severe atrophy can mimic tumor diathesis