Table of Contents
CD150 | CD151 | CD152 | CD153 | CD154 | CD155 | CD156a | CD156b | CD156c | CD157 | CD158 | CD158a | CD158b | CD159a | CD159c | CD170 | CD171 | CD172a | CD173 | CD174 | CD175 | CD176 | CD177 | CD178 | CD179 | CD180 | CD181 / CD128 | CD182 / CXCR2 | CD183 / CXCR3 | CD184 | CD185 | CD186 | CD187 | CD188 | CD189 | CD190 | CD191 / CCR1 | CD192 / CCR2 | CD193 / CCR3 | CD194 / CCR4 | CD195 / CCR5 | CD196 / CCR6 | CD197 / CCR7 | CD198 / CCR8 | CD199 / CCR9 | CDw210 | CD211 | CD212 | CD213 | CD214 | CD215 | CD216 | CDw217 | CD218 | CD219 | CD220 | CD221 | CD222 | CD223 | CD224 | CD225 | CD226 | CD227 | CD228 | CD229 | CD240CE | CD240D | CD240DCE | CD241 | CD242 | CD243 | CD244 | CD245 | CD246 | CD247 | CD248 | CD249 | CD281 | CD282 | CD283 | CD284 | CD289 | CD303 | CD333 | CD351 | CD352 | CD353 | CD354 | CD355 | CD357 | CD358 | CD360 | CD361 | CD365 | CD366 | CD367 | CD368 | CD369 | CD370 | CD371 | Diagrams / tables | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Peripheral smear imagesCite this page: Pernick N. CD markers - other. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkersother.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
CD150
CD151
CD152
- Also known as cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4, CTLA4
- Negative regulator of T cell activation
- CTLA4 restriction fragment length polymorphisms are linked to various autoimmune disorders
- Shares sequence homology with CD28; also shares ligands CD80 and CD86 with CD28
- Positive staining - normal: activated but not resting T cells, activated B cells
- Reference: OMIM CD152
CD154
- Also known as CD40 ligand, CD40L, TNF related activation protein (TRAP)
- Regulates B cell function by engaging CD40
- Defective gene prevents immunoglobulin class switch and is associated with hyper IgM syndrome, autoimmune hematologic disorders, disorganized nodal follicular architecture and PAS positive plasmacytoid cells containing IgM, lymph nodes without germinal centers, shortened lifespan, often with gastrointestinal cancers (cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and adenocarcinoma) and Cryptosporidium parvum infection
- Positive staining - normal: T cells
CD155
CD156a
CD156b
CD156c
- Also known as ADAM10
- Protein belonging to a superfamily of metalloproteases (Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2015;2015:975436)
CD157
CD158
- Member of KIR (killer cell immunoglobulin like receptor) family, also called killer cell inhibitory receptors
- Binding by HLA class I molecules causes inhibition of NK or T cell cytotoxic activity
- Melanoma specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes may express KIR and regulate their ability to kill these tumors
- Terminology:
- CD158c: KIR2DS6 / KIRX
- CD158d: KIR2DL4
- CD158e1: KIR3DL1 / p70
- CD158e2: KIR3DS1 / p70
- CD158f: KIR2DL5 (Front Immunol 2017;7:698)
- CD158g: KIR2DS5
- CD158h: KIR2DS1 / p50.1
- CD158i: KIR2DS4 / p50.3
- CD158j: KIR2DS2 / p50.2
- CD158k: KIR3DL2 / p140
- CD158z: KIR3DL7 / KIRC1
- Positive staining - normal: natural killer cells (NK cells), some T cells
CD158a
CD158b
CD159a
CD159c
- Plays a role as a receptor for the recognition of MHC class I HLA-E molecules by natural killer cells and some cytotoxic T cells (Front Immunol 2018;9:686)
- Also known as NKG2C, KLRC2
- Positive staining - normal: natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells
CD170
CD171
- Aka L1
- Adhesion molecule required for normal neurohistogenesis
- Mutations cause CRASH (Corpus callosum hypoplasia / agenesis, Retardation, Aphasia, Spastic paraplegia / shuffling gait and Hydrocephalus due to stenosis of aqueduct of Sylvius), an X linked neurologic disorder
- May mediate kidney branching morphogenesis, maintenance of lymph node architecture during immune response, costimulation of T cell activation in vitro
- Positive staining - normal: postmitotic neurons, glia, epithelial cells (some), lymphoid cells (some), myeloid (some), monocytes
CD173
CD174
CD175
CD176
CD177
CD178
- Aka CD95 ligand, Fas ligand (FasL)
- Important role in T cell mediated cytotoxicity; induces apoptosis in Fas expressing target cells
- Cells in immune privileged sites (testis, anterior chamber of eye, placenta) constitutively express FasL, which induces apoptosis in Fas expressing infiltrating T cells, minimizing inflammatory responses that might damage important physiologic functions at these sites
- May influence interaction of tumor cells with host immune system; theory is that FasL+ tumor cells induce apoptosis in infiltrating Fas+ mononuclear cells
- Fas-FasL binding triggers apoptosis in lymphocytes
- Mutations may be related to some cases of Systemic Lupus Erythematosis (SLE)
- Processed by metalloproteases which cause shedding of extracellular portion into blood (sFas L)
- Positive staining - normal: activated and cytotoxic T cells, testis, anterior chamber of eye, placenta; also Sertoli cells, neurons, thyroid epithelial cells
- Positive staining - tumors: Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin’s lymphoma (nodular sclerosis and mixed cellularity) (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:388)
CD179
- CD179a:
- Aka VpreB1
- Associates noncovalently with CD179b to form surrogate light chain as component of preB cell receptor, which plays a critical role in early B cell differentiation
- CD179b:
- Aka lambda 5
- Associates noncovalently with CD179a to form surrogate light chain as component of preB cell receptor, which plays a critical role in early B cell differentiation
- Mutations impair B cell development and cause agammaglobulinemia
- Positive staining - normal: preB cells
CD180
- Also called RP105
- Regulates B cell recognition of lipopolysaccharide, a membrane constituent of gram-negative bacteria
- Positive staining - normal: mantle zone and marginal zone B cells (strong), other B cells (weak / negative); peripheral blood monocytes, dendritic cells
CD181 / CD128
- Also called CXCR1, IL8Ralpha; previously called CDw128A
- Chemokine receptor, powerful neutrophil chemotactic factor
- Positive staining - normal: neutrophils, basophils, T cell subset, monocytes, keratinocytes
- Positive staining - disease: T cells in allergic rhinitis (J Immunol 2004;172:268)
CD182 / CXCR2
- Also called CXCR2; formerly called CD128b
- Interleukin 8 receptor beta subunit (IL8RB); binds multiple CXC chemokines including IL8 (CXCL8)
- Chemokine receptor, powerful neutrophil chemotactic factor, particularly to sites of inflammation
- Interpretation: cytoplasmic staining
- Uses by pathologists: no significant uses by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: mature granulocytes, keratinocytes, neuroendocrine cells, projection neurons (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:520)
- Positive staining - disease: carcinoid tumor (classic, atypical, metastatic), pituitary adenoma, pheochromocytoma, medullary carcinoma
- Negative staining: parathyroid cells; small cell carcinoma of lung / cervix, large cell lung neuroendocrine carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, neuroblastoma, melanoma
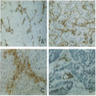
- See Diagrams / tables
- See Microscopic (histologic) images
CD183 / CXCR3
- Also called CXCR3
- Receptor for some chemokines; binding of chemokines to CD183 induces integrin activation, cytoskeletal changes and chemotactic migration in inflammation associated effector T cells
- CD183+ T cells detected in inflamed tissues of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, sarcoidosis, hepatitis C
- Positive staining - normal: T cells in inflamed tissue, eosinophils, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, hematopoietic progenitors
- Negative staining: naïve T cells in peripheral blood
CD184
- Also called CXCR4, stromal cell derived factor 1 (SDF1)
- Receptor for the CXC chemokine SDF1
- Also major HIV / SIV coreceptor (with CCR5 / CD195)
- Involved in B cell development, myelopoiesis, cardiac ventricular septum formation, blood vessel formation in GI tract, cerebellar granular cell development
- Positive staining - normal: all mature blood cells, blood progenitor cells, endothelial and epithelial cells, astrocytes, neurons
CD185
- Multipass membrane protein of CXC chemokine receptor family
- Also called CXCR5, BLR1 (Burkitt lymphoma receptor 1)
- Pathophysiology:
- Binds to B Lymphocyte Chemoattractant (BLC / CXCL13) (J Exp Med 1998;187:655)
- Involved in B cell migration into B cell follicles of spleen and Peyer patches (J Immunol 2009;182:2610)
- Critical for function of follicular helper T (TFH) cells
- May have role in survival and maintainance of cardiac structure upon pressure overload by regulating proteoglycans essential for correct collagen assembly (PLoS One 2011;6:e18668)
- May be important for ectopic mucosa associated lymphoid tissue neogenesis in chronic Helicobacter pylori induced inflammation (J Mol Med (Berl) 2010;88:1169)
- During HIV1 infection, altered expression of CXCR5 / CXCL13 may cause B cell dysfunction (Blood 2008;112:4401)
- Upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue and expressed in various cell types (Arthritis Res Ther 2005;7:R217)
- Interpretation: cytoplasmic staining
- Uses by pathologists: no significant uses by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: mature B cells
- Positive staining - disease: Burkitt's lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma; AIDS related non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Blood 2009;113:4604, AIDS Res Treat 2010;2010:164586)
- See Microscopic (histologic) images
CD191 / CCR1
- Member of beta chemokine receptor family; its major ligands are CCL3 / MIP1ɑ, CCL5 / RANTES and CCL7 / MCP3 (PLoS One 2011;6:e21772)
- Also called chemokine C-C motif receptor 1, CD191
- Note: maize protein cinnamoyl-CoA reductase 1 is also called CCR1 (J Exp Bot 2011;62:3837)
- Clinical features:
- Participates in pathogenesis of several renal diseases by orchestrating myeloid cell kidney infiltration (Am J Pathol 2012;180:1040)
- May play an important role in multiple myeloma (Future Med Chem 2011;3:1889)
- Antagonists are being developed for use in rheumatoid arthritis (Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011;89:726)
- Positive stains: monocytes / macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, dendritic cells, basophils (Allergy 2006;61:1054)
CD192 / CCR2
- Receptor for MCP1, MCP3, MCP4 chemokines; alternative coreceptor with CD4 for HIV1
- Abbreviation for chemokine C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2) chemokine C-C motif receptor 2
- Also known as CD192 but most publications use CCR2
- Inflammatory cytokine with 374 amino acids that mediates biologic effects of CCL2, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1); CCL2-CCR2 may be involved in neuroinflammation and chronic pain (J Neuroinflammation 2012;9:136)
- In astrocytes, CCL2 binding may be CCR2 independent (Brain Res 2012;1437:115)
- During chemotaxis, may act as scavenger consuming the chemokine (PLoS One 2012;7:e37208)
- Clinical features:
- Reduced levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (PLoS One 2012;7:e37208)
- Mutations associated with reduced risk for:
- Severe coronary artery disease (Intern Med 2011;50:2457)
- Delay in progression of HIV to AIDS (AIDS 2000;14:483)
- Mutations associated with increased risk for:
- Osteoporosis and osteopenia (Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2012;16:229)
- Chronic renal failure (Intern Med 2011;502457:649)
- Oral cancer (Oral Oncol 2011;47:577)
- Uses by pathologists: none
- Positive staining: neurons, monocytes; controversial if expressed on microglia or due to infiltrating monocytes
- See Diagrams / tables
CD193 / CCR3
- C-C chemokine receptor type 3; also known as CD193
- G protein coupled receptor for eotaxins
- Marker for Th2 cells (type 2 helper T cells, which promote humoral immune system)
- Constitutively expressed at high levels in eosinophils; primary chemokine receptor responsible for eosinophil recruitment to inflamed tissues (Exp Mol Med 2012;44:268)
- Clinical features:
- May play an integral role in pathogenesis of allergic diseases including asthma, allergic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis (Respir Res 2010;11:17)
- Important drug target for inflammatory diseases
- May also play a role in:
- Neovascular age related macular degeneration (Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011;52:8271, J Mol Cell Biol 2009;1:17)
- Ulcerative colitis (Clin Exp Immunol 2010;162:337)
- CCR3 expression on peripheral blood lymphocytes is associated with EBV related infectious mononucleosis (Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi 2010;24:355)
- CCR3 gene polymorphisms may contribute to aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease (Respir Med 2010;104:626)
- May play an integral role in pathogenesis of allergic diseases including asthma, allergic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis (Respir Res 2010;11:17)
- Uses by pathologists: possible basophil selection marker for flow cytometry (Allergy 2011;66:85, Cytometry A 2011;79:102)
- Positive staining - normal:
- Bronchial smooth muscle and epithelium (Clin Exp Allergy 2012;42:1040)
- Eosinophils, basophils, mast cells
- Th2 helper cells
- Epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts
- Positive staining - disease:
- Cutaneous melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma (Ann Dermatol 2010;22:412)
- Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (J Invest Dermatol 2010;130:2304)
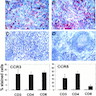
- See Diagrams / tables
CD194 / CCR4
- CC chemokine receptor 4
- Seven transmembrane G protein coupled receptor, selectively expressed on Th2 cells and regulatory T cells
- CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex is key eukaryotic regulator of gene transcription and cytoplasmic mRNA degradation (Protein Cell 2011;2:755, FEBS Lett 2011;585:2182)
- Catalyzes removal of mRNA poly(A) tails, repressing translation and committing mRNA to degradation (RNA Biol 2013;10:228)
- Receptor for CCL2 (MCP1), CCL4 (MIP1), CCL5 (RANTES), CCL17 (TARC), CCL22 (macrophage derived chemokine) (Wikipedia: CCR4 [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Clinical features:
- Tumor cells may function as Treg cells with CCR4 expression, contributing to tumor survival by downregulating host immunity; tumor cells also produce CCR4 ligands which attract other CCR4+ Treg cells to tumor site (Cancer Sci 2011;102:44)
- Humanized anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody, mogamulizumab (KW-0761), is being studied to treat peripheral T cell lymphoma (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2012;7:235)
- Uses by pathologists: none
- Positive staining - normal: Th2 cells and regulatory T cells
- Positive staining - disease:
- Carcinomas of breast and stomach (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012;131:837, Cancer Sci 2011;102:1264)
- Lymphoma:
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (60% of nodal ALK tumors) (Mod Pathol 2002;15:838)
- CLL in peripheral blood (low levels) (Eur J Haematol 2011;87:80)
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma, including adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:216)
- Dermis based lymphomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1111)
- See Diagrams / tables
CD195 / CCR5
- Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5; also known as CD195
- Surface receptor and attachment site for HIV and SIV into CD4+ cells, along with CXCR4 (CD184) (Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2011;236:637)
- Those with CCR5-Δ32 mutation may have HIV resistance (Wikipedia: CCR5 [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Receptor for CD8 chemokines RANTES, MIP 1 alpha, MIP 1 beta, monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (MCP2)
- Also receptor for Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin ED (Nature 2013;493:51)
- Uses by pathologists: none
- Positive staining - normal: T cells, macrophages
- See Diagrams / tables
CD196 / CCR6
- C-C chemokine receptor type 6 gene
- Note: also refers to Clostridium difficile isolate
- Member of G protein coupled receptor superfamily at 6q27, 374 amino acids (MW 42K Da) (Wikipedia: C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 6 [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Binds only a single ligand, CCL20 / macrophage inflammatory protein 3 alpha / MIP3 alpha (Exp Cell Res 2011;317:613)
- Important for B lineage maturation, antigen driven B cell differentiation
- Mediates recruitment of T cells to inflamed sites (Arthritis Res Ther 2012;14:R73, J Dermatol 2012;39:838)
- CCL20-CCR6 axis mediates migration of circulating regulatory T cells into tumor microenvironment; may cause tumor progression in colon, liver, lung, prostatic carcinomas (PLoS One 2011;6:e24856, PLoS One 2011;6:e24671)
- Clinical features:
- CCR6 polymorphisms are risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis in Asian females but a protective factor in males (DNA Cell Biol 2012;31:607)
- Associated with chronic GVHD and invasive fungal disease (Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011;17:1443)
- May be favorable prognostic factor in lung adenocarcinoma (Tumour Biol 2011;32:197)
- Some statins may help treat psoriasis by inhibiting CCL20 / CCR6 interaction (Exp Dermatol 2011;20:855)
- Memory CCR6+ CD4+ T cells are preferential targets for productive HIV1 infection (J Immunol 2011;186:4618)
- CCR6 polymorphisms are risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis in Asian females but a protective factor in males (DNA Cell Biol 2012;31:607)
- Uses by pathologists: none
- Positive staining - normal:
- Immature dendritic cells, memory T cells that produce IL17 or IL22 (Th17 or Th22) (J Exp Med 2011;208:1875)
- Lymphoid tissue in GI tract
- Positive staining - disease:
- Gastric carcinoma (Pathol Int 2011;61:645)
- Lymphoma: mantle cell, marginal zone, MALT (Hum Pathol 2002;33:1227)
- See Diagrams / tables
CD197 / CCR7
- C-C chemokine receptor type 7
- Ligands are CCL19 and CCL21 (Wikipedia: C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Chemokine receptor that is 7 transmembrane domain G protein-coupled receptor
- Facilitates T cell migration to and compartmentation within secondary lymph nodes (J Immunol 2011;187:5645, PLoS One 2011;6:e18183)
- Promotes cell proliferation via extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) pathway; may prevent apoptosis by upregulating BCL2 and downregulating bax and caspase3 (PLoS One 2012;7:e33262)
- Clinical features:
- Aberrant CCR7 expression in various malignancies has been linked to prosurvival, invasive and metastatic pathways (J Biol Chem 2012;287:3581)
- CCR7-CCL21 pathway may have role in rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis (Arthritis Rheum 2012;64:2471)
- Macrophages participate in lymphangiogenesis in idiopathic diffuse alveolar damage through CCL19-CCR7 signal (Hum Pathol 2009;40:1553)
- 85 year old man with primary cutaneous aggressive epidermotropic CD8+ T cell lymphoma which transformed from indolent to aggressive phase in association with CCR7+ conversion (Dermatol Online J 2012;18:5)
- Uses by pathologists: tumor infiltration by CCR7+ T cells may be favorable prognostic marker in advanced colorectal carcinoma (Clin Cancer Res 2012;18:850)
- Positive staining - normal:
- Dendritic cells (Mediators Inflamm 2012;2012:320953)
- Macrophages (some)
- T lymphocytes (some) (Oncoimmunology 2012;1:531, Am J Clin Pathol 2010;133:281)
- Positive staining - disease:
- Various carcinomas including:
- Breast (J Cell Physiol 2013;228:341)
- Esophagus (Ann Surg Oncol 2012;19:3606)
- Head and neck: squamous cell (J Biol Chem 2012;287:3581)
- Lung (PLoS One 2012;7:e33262)
- Melanoma (Microcirculation 2011;18:172, Hum Pathol 2007;38:768)
- MALT lymphoma and some diffuse large B cell lymphomas (Mod Pathol 2013;26:182)
- Various carcinomas including:
- See Diagrams / tables
CD198 / CCR8
- Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 8; also known as CDw198
- Chemokine receptor associated with asthma / allergic diseases via Th2 pathway
- Ligand is CCL1 (Wikipedia: CCR8 (gene) [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Antagonists may have efficacy against asthma
- May play a role in macrophage recruitment and activation in:
- Type 1 diabetes (J Immunol 2007;179:5760)
- COPD (Clin Vaccine Immunol 2011;18:2050)
- Endometriosis (Fertil Steril 2007;88:317)
- May be alternate coreceptor for HIV1 and HIV2 (Virology 2010;408:174)
- Uses by pathologists: no uses at this time
- Positive staining - normal:
- Dendritic cells (Biochem Pharmacol 2012;83:778)
- Eosinophils
- T cells (particularly Th2) (Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011;407:764)
- Thymus
CD199 / CCR9
- Also known as CDw199, GPR28, CC chemokine receptor 9
- Chemokine receptor; mediates chemotaxis in response to thymus expressed chemokine (TECK) selectively expressed in thymus and small intestine
- Clinical features:
- Abnormal regulation of chemokine TECK and its receptor CCR9 in endometriotic milieu is involved in pathogenesis of endometriosis (Cell Mol Immunol 2010;7:51)
- Has role in inflammatory bowel disease (Expert Opin Ther Targets 2009;13:297)
- CCR9 and its ligand CCL25 have important role in breast cancer cell survival and resistance to cisplatin (World J Surg Oncol 2011;9:46)
- Plays pivotal role in drug resistance and invasion in T-ALL, ovarian cancer (World J Surg Oncol 2010;8:62, J Ovarian Res 2010;3:15)
- Uses by pathologists: none at this time
- See Diagrams / tables
CDw210
- Aka IL10 receptor
- Interleukin 10 produced by B cells, T helper cells and monocyte / macrophages, exhibits diverse activities on different cell lines (OMIM 124092)
- IL10 inhibits macrophage activation by interferon gamma
- Positive staining - normal: monocytes, B and T cells, large granular lymphocytes, spleen, thymus, placenta, lung, liver
CD212
- Aka IL12 receptor
- Interleukin 12 promotes cell mediated immunity to intracellular pathogens by inducing type 1 helper T cell responses and interferon gamma production
- Lack of IL12 associated with severe, idiopathic mycobacterial and Salmonella infections, mature granulomas
- Positive staining - normal: T cells, NK cells
CD213
- CD213a1:
- Aka IL13 receptor, alpha 1
- Binds IL13 with low affinity
- With IL4r-alpha, can form a functional receptor for IL13
- Positive staining - normal: ubiquitous, B cells, T cells and endothelial cells, highest levels in heart, liver, skeletal muscle and ovary
- CD213a2:
- Aka IL13 receptor, alpha 2
- Inhibits binding of interleukin 13 to the IL13 cell surface receptor
- Positive staining - normal: placenta
CDw217
CD221
CD222
CD223
- Aka Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3 (LAG3)
- Homologous to CD4
- Associates with MHC class II molecules on monocytes/dendritic cells, which are subsequently activated
- May help activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to fully activate monocytes and dendritic cells, leading to optimized MHC class I and class II T cell responses
- Positive staining - normal: activated T cells, activated NK cells
CD224
CD225
CD226
- Aka DNAM1, Platelet and T cell Activation antigen 1 (PTA1)
- Mediates adhesion to an unknown ligand
- T cell expression increased in some patients with autoimmune disease and viral infection
- Positive staining - normal: NK cells, platelets, monocytes, subset of B and T cells
- Negative staining: granulocytes, erythrocytes
CD227
- See EMA / MUC1
CD228
CD240CE
- Also called RH 30 CE, Rh blood group Cc and Ee blood group antigens; encodes RhC and RhE antigens on a single polypeptide
- On #1p36.11 adjacent to RH D gene
- Rh (rhesus) blood group system is second most clinically significant blood group after ABO; is most polymorphic blood group, with variations due to deletions, gene conversions and missense mutations
- Rh antigens are carried by an oligomer of two major erythroid specific polypeptides, the Rh (D and CcEe) proteins and the RhAG glycoprotein
- Rh proteins form a core complex critical to structure of erythrocyte membrane (Blood Rev 2006;20:93)
- May play a role in ammonia transport (J Biol Chem 2002;277:12499, Transfus Clin Biol 2006;13:132)
- Discrepant or doubtful serologic results can be resolved by sequence specific primer (PCR SSP) technique (Transfusion 2007;47:54S)
- Rarely causes hemolytic disease of newborn (Transfus Med 2000;10:305)
- Uses by pathologists: blood typing
- Positive staining - normal: erythroid cells
- References: Blood 2000;95:375, OMIM 111700
CD240D
- Also called RH30 D, Rh blood group D blood group antigen; is major antigen of the Rh system
- On #1p36.11 adjacent to RHCE gene
- Rh (rhesus) blood group system is second most clinically significant blood group after ABO; is most polymorphic blood group, with variations due to deletions, gene conversions and missense mutations
- Weak D, formerly called D(u), occurs in 0.2 to 1% of whites
- Exhibits reduced expression of D antigen (Blood 1999;93:385)
- Should not be labeled as Rh negative (Curr Opin Hematol 2006;13:476)
- Individuals are classified as Rh positive or negative based on presence or absence of highly immunogenic D antigen on red cell surface
- May have arisen historically by duplication of RHCE gene (Blood 2002;99:2272)
- Discrepant or doubtful serologic results can be resolved by sequence specific primer (PCR SSP) technique (Transfusion 2007;47:54S)
- Hemolytic disease of fetus and newborn: usually due to Rh negative woman whose partner is Rh+ or heterozygous and fetus is Rh+; woman has preexisting anti-RhD antibodies that cross placenta and harm fetus (Immunohematol 2006;22:188)
- Can use maternal plasma in alloimmunized pregnancies to determine fetal RhD status or for RHD and RHCE genotyping (Fetal Diagn Ther 2006;21:404, Prenat Diagn 2005;25:1079)
- Genotyping from amniotic fluid or chorionic villi sampling was performed in past but is more invasive (N Engl J Med 1998;339:1734, Clin Exp Med 2002;2:77)
- Rh positive mothers may rarely (0.15%) develop new antibodies (other than anti-RHD) in third trimester but no clinical significance (J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2007;20:59)
- Having Rh negative mother may be risk factor for autistic children, due to use of mercury containing Rho-immune globulin (J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2007;20:385)
- Uses by pathologists: blood typing
- Positive staining - normal: erythroid cells
- References: OMIM 111680, Wikipedia, eMedicine (Rh incompatibility)
CD240DCE
CD241
- Also called RH50 glycoprotein, RHAG, Rhesus blood group associated glycoprotein
- Located at #6p21.1 - p11
- Is a strictly required posttranscriptional factor regulating Rh membrane expression (Blood 2002;100:1038)
- Also appears to be an ammonium transporter and a CO2 channel (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004;101:17222, FASEB J 2008;22:64)
- Defects cause Rh-null phenotype, associated with a chronic hemolytic anemia and spherostomatocytosis (OMIM 268150, J Biol Chem 1998;273:2207)
- Uses by pathologists: blood typing
- Positive staining - normal: erythroid cells
- Reference: OMIM 180297
CD242
- Also called intercellular adhesion molecule 4 (ICAM4), Landsteiner-Wiener (LW) blood group protein
- Discovered with antibody raised in guinea pigs injected with the cells of rhesus monkeys but Rh designation had already been taken
- Binds to CD11a / CD18, CD11b / CD18 and CD11c / CD18 (Blood 2007;109:802)
- May be critical in erythroblastic island formation, where erythroid progenitors differentiate (Blood 2006;108:2064)
- May be ligand for platelet activated alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (J Biol Chem 2003;278:4892)
- In sickle cell disease, contributes to red cell endothelial cell adhesion and vasoocclusion (Transfus Clin Biol 2006;13:44)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: erythroid cells
- References: OMIM 111250
CD243
- See Stains-MDR
CD244
- Also called Natural Killer cell receptor 2B4
- Regulates NK and T cell function in multiple ways (J Immunol 2005;175:2045)
- Coexpression of 2B4 and CD160 defines a CD8+ T lymphocyte subpopulation with high cytolytic effector activity (Eur J Immunol 2006;36:2359)
- Binds to CD48 (J Immunol 2006;176:4646)
- CD244 - CD48 interactions prevent NK cells from killing each other (Blood 2007;110:2020)
- Functional changes are associated with X linked lymphoproliferative disease (J Exp Med 2000;192:337, J Immunol 2000;165:2932)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal:
- NK cells
- CD8+ T cells
- Monocytes and basophils (Eur J Immunol 1999;29:1676)
- Eosinophils (J Immunol 2005;174:110)
- Spleen (Tissue Antigens 1999;54:27)
- Reference: OMIM 605554
CD245
- Also called p220 / 240
- Very little information is available for CD245 directly; appears to be identical to NPAT (nuclear protein, ataxia-telangiectasia locus)
- NPAT links S phase cyclin E / Cdk2 kinase activity to replication dependent histone gene transcription (Biochemistry 2006;45:15915, Mol Cell Biol 2005;25:6140)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: T cells (some), other white blood cells with varying intensity
CD246
- See Stains-ALK
CD247
- Also called T cell receptor zeta chain
- Forms T cell-CD3 receptor complex with TCR alpha / beta and gamma / delta heterodimers and CD3 (gamma, delta and epsilon) (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988;85:9709)
- Couples antigen recognition to several intracellular signal transduction pathways; low expression causes impaired immune response
- Low expression in tumor infiltrating T cells in various disorders:
- Cancer of kidney (Cancer Invest 2004;22:871)
- Cancer of stomach (Cancer 2002;94:1437)
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma (Blood 1996;88:236)
- Active tuberculosis (J Infect Dis 2006;194:1385)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (J Immunol 2002;169:6048, Adv Med Sci 2006;51:181)
- Normal pregnancy but not preeclampsia (Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:843)
- Defects cause primary T cell immunodeficiency (OMIM 610163)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: T cells
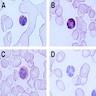
- See Diagrams / tables
- See Microscopic (histologic) images
- Reference: OMIM 186780
CD248
- Also called endosialin, tumor endothelial marker 1 (TEM1)
- Cell surface glycoprotein associated with tumors: traditionally thought present in vascular endothelial cells (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:10832, J Biol Chem 2001;276:7408)
- May actually be marker of stromal fibroblasts (FEBS Lett 2005;579:2569)
- Not present (or weak) in nontumor associated endothelium
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal:
- Endometrium
- Embryos (Cancer Res 2001;61:6649)
- Fibroblasts and pericytes during lymphoid tissue development (FEBS Lett 2007;581:3550)
- RNA at low / moderate levels in many organs
- Positive staining - disease:
- MFH and other sarcomas, some capillaries and fibroblasts in carcinomas
- Endothelium of high grade brain tumors (J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2004;63:1274)
- RNA at low / moderate levels in carcinomas (Cancer Immun 2005;5:10)
- See Microscopic (histologic) images
- Reference: OMIM 606064
CD249
- Also called ENPEP, glutamyl aminopeptidase, differentiation antigen gp160, aminopeptidase A
- Regulates blood pressure via renin-angiotensin system (J Biol Chem 2006;281:23503)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: kidney; also brain, heart, liver, lung, placenta, skeletal muscle, pancreas (Genomics 1993;17:657)
- Positive staining - disease:
- Cervical neoplasia (Lab Invest 2004;84:639)
- Renal cell carcinoma-some (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90:7069)
- Reference: OMIM 138297
CD281
- TLR1_HUMAN (Q15399, OMIM 601194)
- TLR1, toll-like receptor 1 (toll / interleukin 1 receptor-like) (TIL)
CD282
- TLR2_HUMAN (O60603, OMIM 603028)
- TLR2, TIL4, toll-like receptor 2 (toll / interleukin 1 receptor-like protein 4)
CD283
- TLR3_HUMAN (O15455, OMIM 603029)
- TLR3, toll-like receptor 3
CD284
- TLR4_HUMAN (O00206, OMIM 603030)
- TLR4, toll-like receptor 4
CD289
- TLR9_HUMAN (Q9NR96, OMIM 605474)
- TLR9, toll-like receptor 9
CD333
- Also known as FGFR3
CD351
- Identified in 2011 at HLDA9 (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Also known as FCAMR, Fcα/μR
- Fc receptor for both IgA and IgM (Mol Immunol 2013;56:23, Mol Immunol 2011;48:1818, GeneCards: FCAMR Gene [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Positive staining: intestinal lamina propria of appendix, small bowel, colorectum (macrophages, plasma cells, Paneth cells); follicular dendritic cells (Eur J Immunol 2007;37:3540) of germinal centers of some lymphoid follicles (Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009;381:148)
CD352
- First described as CD352 at HLDA9 in 2011 (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Also known as Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule F6 (SLAMF6), Ly108 and NTBA
- Member of SLAM (CD150) family of receptors, which are leukocyte cell-surface glycoproteins involved in leukocyte activation; these molecules and their adaptor protein SAP contribute to germinal center formation, generation of plasma cells and memory B cells (Immunol Lett 2011;134:129)
- Costimulatory molecule with CD28 implicated in formation of Th17 lymphocytes and IL17A expression (J Biol Chem 2012;287:38168)
- One of several risk loci for Graves disease of thyroid (Hum Mol Genet 2013;22:3347)
- Increased expression on surface of T cells in system lupus erythematosus (J Immunol 2012;188:1206); this pathway may be defective in SLE T cells (Autoimmunity 2011;44:211)
- No usage for pathologists at this time
- Positive staining (normal): B cells, plasma cells (Immunol Lett 2011;134:122); also NK, T cells (Wikipedia)
CD353
- Also known as SLAMF8
- First described at HLAD9 in 2011 (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Member of CD2 family of cell surface proteins involved in lymphocyte activation (Wikipedia)
- Cell surface receptor expressed upon activation of macrophages by IFN-γ or bacteria
- Negatively regulates inflammatory responses via very high NADPH oxidase (Nox2) enzyme activity (J Immunol 2012;188:5829)
- Higher baseline expression in postmenopausal women with ER+ breast cancer is associated with poor antiproliferative response to neoadjuvant anastrozole (Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:2775)
- No uses by pathologists at this time
- Positive staining: lymphoid tissue (GeneCards: SLAMF8 Gene [Accessed 14 November 2022])
CD354
- Triggering REceptor on Myeloid cells; member of Ig superfamily
- sTREM1: soluble levels of TREM1
- Part of family of immune sensors which signal innate immune system and amplifies immune responses that promote pro-inflammatory cytokine production; neutrophils are major source of TREM1
- TREM1 is an activating receptor and requires association with transmembrane adapter molecule DAP12 (DNAX-associated protein 12) for cell signaling (PLoS One 2013;8:e82498, J Leukoc Biol 2013;93:209)
- TREM1 and MMPs orchestrate an "adaptive" form of innate immunity by modulating the monocyte response to endotoxin (J Leukoc Biol 2012;91:933)
- Dendritic cells: TREM1 induction by hypoxic microenvironment activates immature dendritic cells and regulates Th1 cell trafficking (Eur J Immunol 2013;43:949)
- Positive staining: Myeloid cells
- Acute bacterial infection: TREM1 mRNA levels inversely correlate with severity (Int J Med Sci 2014;11:215, Jpn J Infect Dis 2012;65:376)
- Asthma: elevated plasma levels of sTREM1 reflect its severity, state of exacerbation and presence of respiratory tract obstruction (Mediators Inflamm 2012;2012:628754)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma: TREM1 may be related to tumor's aggressive behavior (Cancer Sci 2012;103:984)
- Kidney injury: overlapping role with TLR2/4 and MyD88 signaling pathways in myeloid cell activation (PLoS One 2013;8:e68640)
- Labor: elevated sTREM1 levels in spontaneous term and preterm labor (PLoS One 2013;8:e56050); also in premature rupture of membranes and subclinical chorioamnionitis (Mol Med Rep 2012;5:663)
- Lung disease, non tuberculous mycobacterial: may be helpful in diagnosing and predicting outcome (Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2011;15:1415)
- Obstructive sleep apnea: increased levels (Sleep 2013;36:923)
- Periodontitis: increased oral and systemic levels of sTREM1 (J Dent Res 2013;92:161, PLoS One 2013;8:e75784)
- Rheumatoid arthritis: correlates with disease activity and severity (J Rheumatol 2012;39:933)
- Sarcoidosis: increased TREM1 and TREM2 cell surface expression (Respirology 2013;18:455)
- Sepsis: sTREM1 is a marker of severe sepsis and a sepsis risk factor (Mediators Inflamm 2013;2013:969875); patients with E coli sepsis express TREM1 on blood neutrophils (Diagn Pathol 2013;8:24); also associated with myocardial dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis (Mediators Inflamm 2013;2013:819246)
CD355
- Class I MHC Restricted T cell Associated Molecule
- First identified at 9th Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens Workshop in 2011 / HLDA9 (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Expressed in epithelial cells along lateral membrane; important for early cell-cell contacts and cell-substrate interactions (J Cell Biochem 2010;111:111)
- Binds to cell adhesion molecule nectin-like 2 (Necl2) (Structure 2013;21:1430)
- Rapidly induced in NK, NKT and CD8+ T cells (Mol Immunol 2009;46:3379); may promote cytotoxic function of NK cells and lead to IFN-γ secretion by CD8+ T cells through interaction with Necl2 (J Immunol 2013;190:4868, Curr Opin Immunol 2012;24:246)
- 3 common variants of CRTAM gene are associated with an increased rate of asthma exacerbations based on a low circulating vitamin D level (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012;129:368)
- No uses by pathologists at this time
- Positive staining: Epithelial cells; activated CD8+ and natural killer T cells
CD357
- Also called GITR / Glucocorticoid Induced Tumor necrosis factor Receptor family related protein
- Type I transmembrane protein belonging to the TNFR superfamily
- After activation, may influence effector and regulatory T cells (ScientificWorldJournal 2012;2012:308265, Wikipedia), causing autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmune thyroid disease (Clin Dev Immunol 2013;2013:340751)
- Ligand is GITRL
- Antibodies may serve as effective anti-tumor therapy (Curr Opin Immunol 2012;24:217)
- Polymorphisms are associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis prognosis (Clin Exp Immunol 2011;165:141)
- Inactivated during tumor progression in myeloma (PLoS One 2013;8:e66982)
- May have role in Sjogren syndrome (Reumatismo 2012;64:293)
- No significant uses by pathologists at this time
CD358
- Also called TNFRSF21, death receptor 6, DR6
- Member of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
- First characterized at Ninth HLDA Workshop (HLDA9) (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Different from HLA-DR6 and protein product of direct repeat 6 (associated with HHV6A and HHV6B) (Int J Rheum Dis 2014;17:268, J Virol 2010;84:2648, Virology 2014;452:254)
- Induces apoptosis when overexpressed (FEBS Lett 1998;431:351)
- Highly expressed in brain
- Induces axon pruning and neuron death (J Neurodev Disord 2013;5:10); binds to amyloid precursor protein (APP); may be involved in development of Alzheimer's disease (J Mol Biol 2011;409:189, Proteins 2011;79:1376, Nature 2009;457:981)
- Regulates brain vascular development (Dev Cell 2012;22:403)
- May be involved in pathogenesis of endometriosis (Am J Reprod Immunol 2013;70:485)
- No specific uses by pathologists at this time
- Positive staining:
- Serum DR6 protein levels elevated in ovarian carcinoma (Cancer Biol Ther 2011;12:169)
- Also adult sarcoma, particularly synovial sarcoma (PLoS One 2012;7:e36525)
- Negative staining: serum DR6 levels not elevated in uterine carcinosarcoma, bladder, liver or pancreatic cancer
CD360
- Type I cytokine identified during 9th HLDA Workshop (Wikipedia: Type I Cytokine Receptor [Accessed 11 November 2022], Immunobiology 2009;214:41, Immunol Lett 2011;134:104)
- Produced when immune reaction reaches its peak by CD4+ T cells
- Regulates T cell, B cell, NK cell and myeloid cell functions (Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010;392:171)
- Binds to a receptor complex of IL21R and the common gamma chain receptor subunit (CD132 / IL2R gamma)
- Also induces PD1 expression on T cells and plays a role in an immunologic cascade (Korean Circ J 2013;43:38)
- IL21 and IL21R gene polymorphisms may be associated with: Hashimoto thyroiditis, HBV infection (BMC Endocr Disord 2013;13:26, Hum Immunol 2013;74:567)
- Kawasaki disease (Korean Circ J 2013;43:38)
- Multiple sclerosis (Genes Immun 2010;11:279)
- Osteoporosis (J Bone Miner Res 2010;25:1042)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:2402)
- No specific uses for pathologists at this time
- Positive staining - normal: mature B cells, also T cells, NK cells, keratinocytes, some myeloid cells.
- Positive staining - disease: increased expression in systemic sclerosis; expressed in rheumatoid arthritis by synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages (Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:856, Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:1468)
- Reference: Int J Mol Med 2005;16:609
CD361
- Initially described at Ninth HLDA Workshop (Immunol Lett 2011;134:104, Immunol Lett 2011;134:145)
- Ecotropic Viral Integration site 2B (GeneCards: EVI2B Gene [Accessed 14 November 2022])
- Involved in melanocyte and keratinocyte differentiation
- Hemizygosity in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), due to its codeletion with NF1 gene, may contribute to disease process (Am J Hum Genet 2001;69:516, Genomics 2000;66:93)
- Increased levels of EVI2B mRNA are present in fibroblast-like cells derived from neurofibroma (DNA Cell Biol 1999;18:345)
- Colorectal carcinoma: gene overexpression may predict relapse (DNA Cell Biol 2012;31:625)
- CLL: associated with 11q23 deletion (Leukemia 2001;15:1721)
- Melanoma: downregulated in melanoma cells by agouti signalling protein/ASIP (Pigment Cell Res 2003;16:65)
- No specific uses for pathologists at this time
CD365
- New CD marker designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1)
- Antibodies 10-14 (clone FAB1750P) and 10-67 (clone 1D12) recognizing TIM1 (HAVCR1) were tested in the HLDA10 workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- TIM1 is a single pass type 1 membrane glycoprotein and a member of the Ig superfamily
- The antibodies bind to transfectants expressing TIM1 but show little reactivity to fresh healthy blood cells
- CD365 (HAVCR1) and mHavcr1 may be functional HAV receptors that mediate HAV infection (J Virol 2018;92:e02065, J Virol 2019;93:e01793, J Virol 2019;93:e02040)
CD366
- New CD marker designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as HAVCR2, T cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin domain containing protein 3 / TIM3 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Originally identified as a receptor on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells functioning as coinhibitory receptor
- Recent studies have shown that TIM3 is part of a module that contains multiple coinhibitory receptors (checkpoint receptors), which are coexpressed and coregulated on dysfunctional or 'exhausted' T cells in chronic viral infections and cancer
- Coblockade of TIM3 and programmed cell death 1 (PD1) can cause tumor regression in preclinical models and can improve anticancer T cell responses in patients with advanced cancers (Nat Rev Immunol 2020;20:173, J Immunother Cancer 2020;8:e000911)
- Presence on CD8+ T cells correlates with poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma (J Vis Exp 2018;(132):56606)
- May be useful for detecting minimal residual disease (JCI Insight 2018;3:e98561)
CD367
- New CD marker designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as CLEC4A, DCIR (Dendritic Cell Immunoreceptor), CLECSF6 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- A pattern recognition receptor expressed on dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, B cells and neutrophils ( BMC Immunol 2015 Oct 23;16:64)
- DCIR binds endogenous carbohydrates as well as pathogenic and viral antigens
- Antibodies 10-13 (clone 216110) and 10-71 (clone 111F8.04) bind to transient transfectants expressing DCIR (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Antibodies recognize a type II transmembrane protein that is a member of the C type lectin family
CD368
- New CD marker designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as CLEC4D, MCL, CLECSF8, Dectin3 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Strong binding to myeloid populations within peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- Antibodies recognize a type II transmembrane protein that is a member of the C type lectin family
- Key molecule in antimycobacterial host defense (Cell Host Microbe 2015;17:252)
CD369
- New CD marker designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as CLEC7A, dectin1 (dendritic cell associated C type lectin 1), beta glucan receptor and C type lectin superfamily member 12 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Pattern recognition receptor expressed primarily on cells of myeloid origin, including macrophages, dendritic cells and neutrophils (J Cell Sci 2020;133:jcs236166)
- Promotes wound healing by inducing early phase neutrophil accumulation (J Invest Dermatol 2021;141:164)
- Recognizes β-glucan on Candida albicans cell wall, leading to phagocytosis, oxidative burst, cytokine and chemokine production (J Cell Sci 2020;133:jcs236166)
- Variations may play a role in autism spectrum disorder due to genetic control of innate immune response (PLoS One;2015;10:e0137339)
CD370
- Designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Type II transmembrane glycoprotein member of the C type lectin family that functions as an endocytic receptor, particularly for the uptake and processing of dead cells through its ability to bind filamentous actin (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Also known as CLEC9A, DNGR, DNGR1 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
- Links F-actin exposed by dying cells to favor cross presentation of dead cell associated antigens to CD8+ T cells; also exerts feedback to temper neutrophil recruitment and prevent additional tissue damage (Front Immunol 2020;11:251, Front Immunol 2020;10:3146)
- Binds thymic CD141+ dendritic cells in peripheral blood
- Part of an investigational anti-tumor vaccine due to its binding CD141+ dendritic cells and activating CD8+ T cells (Clin Transl Immunology 2020;9:e1141)
CD371
- Designated at the Tenth Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigen (HLDA10) Workshop (Clin Transl Immunology 2015;4:e47, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57, Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e61)
- Also known as CLEC12A (C type lectin-like receptor), MICL (myeloid inhibitory C type lectin-like receptor), CLL , CLL1 (Clin Transl Immunology 2016;5:e57)
Diagrams / tables
Virtual slides