Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Stuart L. CD31. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd31.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Cell adhesion molecule required for leukocyte transendothelial migration under most inflammatory conditions
- Most sensitive and specific endothelial marker in paraffin sections
Terminology
- Also known as platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM1, OMIM 173445), PECA1, GPIIA, endoCAM, CD31 / EndoCAM (Entrez Gene: platelet / endothelial cell adhesion molecule)
Pathophysiology
- Member of immunoglobulin superfamily
- Ligands are CD38 and vitronectin receptor (αvβ3 integrin, CD51 / CD61) (Cancer 2003;97:1914, J Cell Biol 1995;130:451)
- Cell adhesion molecule that is found on the surface of platelets, monocytes, neutrophils and some types of T cells
- Major constituent of endothelial intercellular junction
- Plays a key role in leukocyte trafficking across endothelium / transendothelial migration (Blood 2003;101:2816) and integrin activation
- Also important for angiogenesis and removal of aged neutrophils from body
- May mediate signal-transduction pathway regulating capacitation in spermatozoa (J Cell Sci 2005;118:4865)
- May act as a minor histocompatibility antigen in HLA identical stem cell transplantation (Bone Marrow Transplant 2005;36:151)
Clinical features
- CD31+ T cells (angiogenic T cells) have vasculoprotective and neovasculogenic qualities; undergo numerical and functional impairments with advancing age (J Appl Physiol 2010;109:1756)
- CD31+ Annexin V+ circulating microparticles are risk factor for cardiovascular disease (Eur Heart J 2011;32:2034)
Interpretation
- Membranous (not cytoplasmic) immunostain; endothelium is a positive internal control
- Potential pitfall: don't confuse CD31+ macrophages (granular, membranous expression) with a vascular tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1167)
Uses by pathologists
- Most sensitive and specific endothelial marker in paraffin sections; stains small and large vessels
- Confirms vascular origin of tumors, but may also stain nodal sinuses (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:638)
- Identifies/confirms vascular invasion (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:786, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:354), although D240 may be more sensitive (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:92, Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:1825)
- Assesses tumor microvessel density, a possible prognostic factor, although D240 and endoglin / CD105 (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;129:578) may be more sensitive
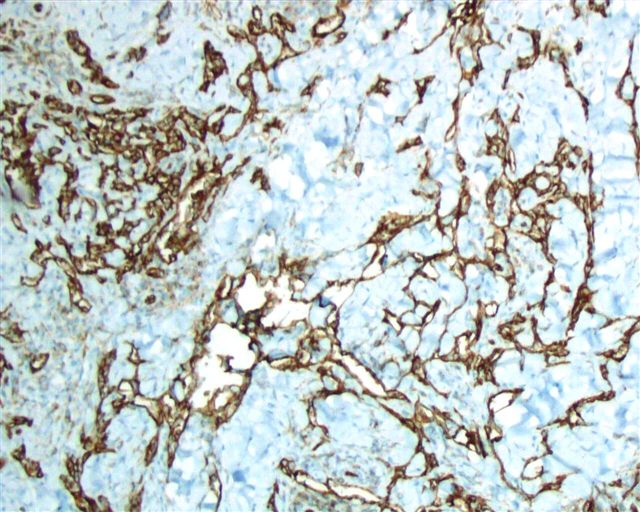
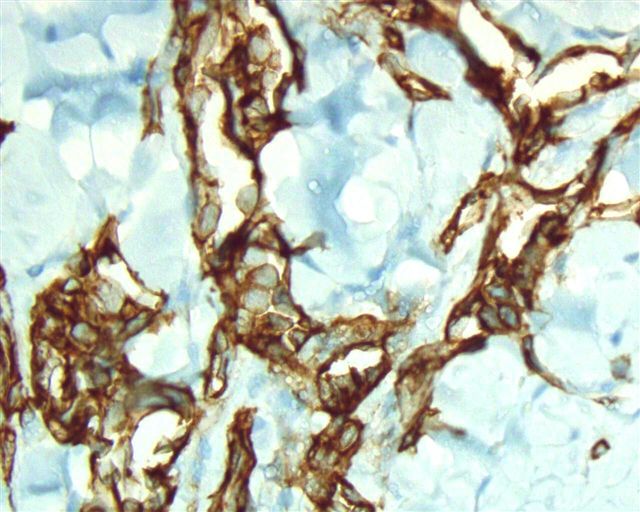
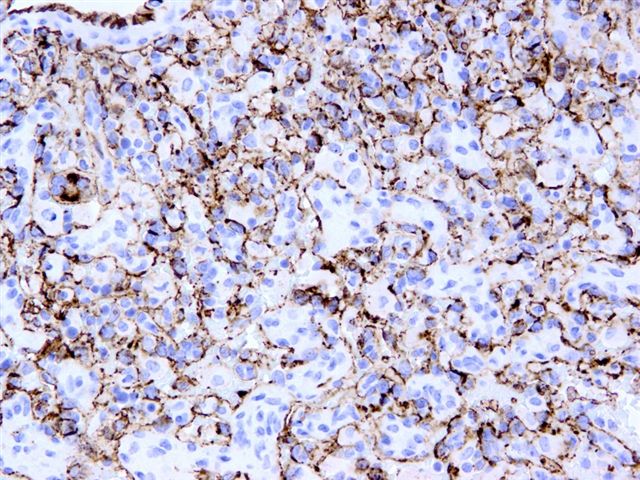
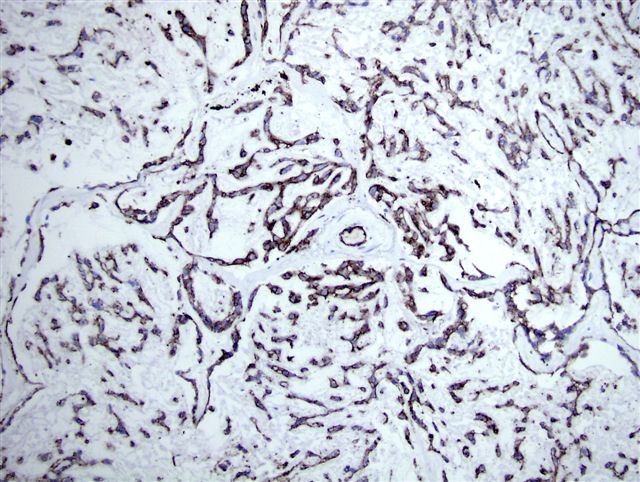
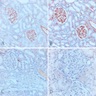
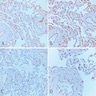
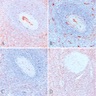
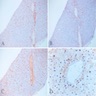
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cases #107, 187, 77
Images hosted on other servers:
Normal structure:
Benign vascular tumors / processes:
Positive staining - normal
- Endothelial cells at cell junctions, including alveolar wall capillaries, glomeruli, sinuses in liver, lymphatics, spleen (J Histochem Cytochem 2006;54:385), megakaryocytes (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002;126:618), pericytes, platelets
- Also basophils, granulocytes, Kupffer cells, macrophages, monocytes, NK cells, osteoclasts, plasma cells (extramedullary strong; bone marrow focal, J Clin Pathol 1997;50:490), T cells (some)
- Also brown fat (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:480), fibroblasts, spermatozoa, trophoblast (Mol Hum Reprod 1998;4:357)
Positive staining - disease
- Vascular lesions: angiosarcoma, benign vascular proliferations (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:328), blood vessels in tumors (usually), hemangioendothelioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:48, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:559), hemangioendothelioma-pseudomyogenic (variable, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:190), hemangioma, intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Hum Pathol 1996;27:986), Kaposi sarcoma (75% of AIDS-related cases, 58% of non AIDS related cases; Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:301), littoral cell angioma of spleen, lymphangioendothelioma (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1047), lymphangioma (Hum Pathol 2005;36:426), papillary endovascular angioendothelioma (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1004), primary cutaneous epithelioid angiosarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:60), sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of spleen (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1268), splenic hamartoma
- Other lesions: breast DCIS-high grade (J Pathol 2001;194:254), cardiac myxoma, epithelioid sarcoma (focal in 7%, Hum Pathol 1999;30:934, Virchows Arch 2003;443:93), Ewing sarcoma / PNET (focal in 5%, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:19), giant cell tumor of tendon sheath, granulocytic sarcoma (25%, Am J Clin Pathol 1994;102:55), hibernoma, histiocytes in granulomas, histiocytic sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1133), intimal sarcoma of large systemic vessels (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:1184), juvenile xanthogranuloma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis, lymphoblastic lymphoma (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2000;8:19), plasmacytomas (50%), sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:341); rare in carcinoma and mesothelioma (Am J Clin Pathol 1998;110:374)
Negative staining
- B cells, epidermal Langerhans cells, vascular adventitial fibroblastic cells, vas deferens (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;132:893)
- Adenomatoid tumor (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012;20:173), aneurysmal fibrous histiocytoma, cellular angiofibroma (Mod Pathol 2011;24:82), gastrointestinal stromal tumor, giant cell fibroblastoma, lipomatous hemangiopericytoma (Hum Pathol 2000;31:1108), mesothelial cyst (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:334), mycobacterial pseudotumor (Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:656), myeloma, nonvascular soft tissue tumors, peripheral T cell lymphoma, ovarian microcystic stromal tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1429), pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia of breast, sclerosing hemangioma of lung (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001;125:1335), sinonasal hemangiopericytoma, solitary fibrous tumor (Hum Pathol 1995;26:440)