Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Pathophysiology | Uses by pathologists | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative stainingCite this page: Pernick N. CD13. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd13.html. Accessed January 7th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Myeloid antigen, although CD33 is more specific (OMIM #151530)
- Also called aminopeptidase N (APN)
Clinical features
- CD13+ may be poor prognostic indicator in Ph' negative B cell ALL (Leuk Res 2013;37:759)
- Mediates tumor angiogenesis (J Histochem Cytochem 2011;59:47, Blood 2007;110:142)
- Viruses: acts as receptor for human coronavirus 229E (J Virol 1998;72:6511), mediates CMV infection (J Immunol 2004;173:4897)
- CD13 autoantibodies are associated with chronic graft versus host disease after bone marrow transplantation (Bone Marrow Transplant 2010;45:1653)
- Caution: may be easy to induce CD13 expression with in vitro culture (Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2002;33 Suppl 2:155)
Pathophysiology
- Cleaves peptides at brush border of small intestine, renal proximal tubules and placenta
- Cleaves antigen peptides bound to MHC class II molecules of presenting cells
- Degrades neurotransmitters at CNS synaptic junctions
- Regulates sperm motility (Asian J Androl 2010;12:899)
Uses by pathologists
- Differentiate acute myelogenous leukemia / AML in Down's syndrome patients (usually CD13+, CD11b+) from transient myeloproliferative disorder (usually CD13-, CD11b-, Am J Clin Pathol 2001;116:204)
- Differentiate AML M0 (CD13+) from ALL (CD13-, Am J Clin Pathol 2002;117:380)
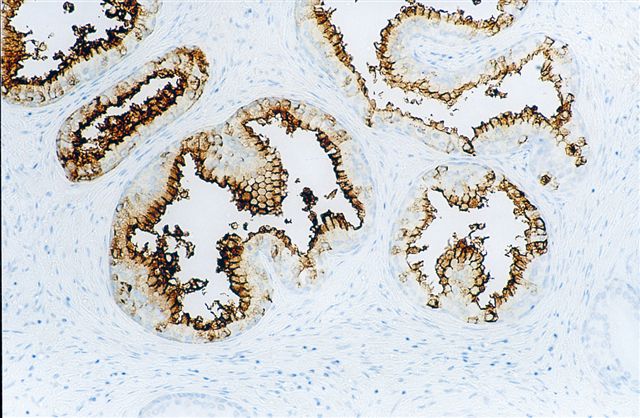
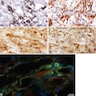
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Granulocytes (most, but low levels in newbornss, Mod Pathol 1993;6:414), interdigitating dendritic cells, large granular lymphocytes (some), macrophages, mast cells, monocytes, myelomonocytes and osteoclasts
- Also bile duct canaliculi, central nervous system synapses, endothelial cells, endometrial stromal cells, fibroblasts, liver, perineurium of peripheral nerves, placenta, prostate secretory cells, renal proximal tubules (PLoS One 2013;8:e66750), respitatory epithelium, small intestine and sperm
Positive staining - disease
- Tumor vasculature (J Histochem Cytochem 2011;59:47)
- Acute basophilic leukemia
- Acute panmyelosis with myelofibrosis
- AML M1-M5 (75-95%), AML-M6 (usually) and myeloid sarcoma
- Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (47%, Am J Clin Pathol 2003;119:205, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:1804, leukemic-Am J Clin Pathol 2003;120:617)
- CLL (Hematology 2012;17:1332)
- CML (90%), CML in blast transformation (Mod Pathol 1998;11:1211), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- Chronic B cell lymphoproliferative disorders (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1995;119:53)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (canalicular pattern, J Clin Pathol 2005;58:1069)
- Mast cell sarcoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1013)
- MFH (Int J Oncol 2013;43:57)
- Pre B ALL, pre T ALL (occasionally, Exp Mol Pathol 2007;83:471)
Negative staining
- CLL/SLL (rarely positive, Am J Clin Pathol 2003;119:824)
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma (usually, Am J Pathol 2004;165:1543)
- Transient myeloproliferative disorder of Down's syndrome (usually)