Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Vora M, Richardson M. CD103. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsCD103.html. Accessed December 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- CD103 is a heterodimeric transmembrane surface receptor that is expressed by several cell types of the immune system and is involved in cell to cell or cell to matrix interactions
- CD103 mediates cell adhesion, migration and lymphocyte homing through interaction with E-cadherin, which is expressed in epithelial cells
Essential features
- Diagnostic tool in the detection of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) and hairy cell leukemia variant (HCL-v)
- Aids in distinguishing hairy cell leukemia from other types of B cell lymphoproliferative disorders (in conjunction with additional markers) (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:586, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- High CD103+ tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cell count is reported to be a favorable prognostic marker in a multitude of solid tumors (Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:6211, Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:434, J Immunol 2015;194:3475, Clin Cancer Res 2016;22:6290, Oncoimmunology 2014;3:e27668, J Urol 2015;194:556, Exp Ther Med 2018;15:4979, Sci Rep 2019;9:3808)
Terminology
- Integrin alpha Eβ7 (ITGAE)
- Integrin alpha E (αE)
- αE subunit first described as human mucosal lymphocyte 1 (HML1) antigen
Pathophysiology
- CD103 is a heterodimer complex; the integrin αE chain (CD103 in the strict sense) dimerizes exclusively with the β7 integrin subunit
- CD103 is the first integrin discovered that binds to a cadherin, namely E-cadherin
- Binding of CD103 is heterophilic
- αE subunit binds through its metal ion dependent coordination site (MIDAS) motif to the tip of the BC loop of E-cadherin (J Exp Med 2000;191:1555)
- β7 chain does not bind directly to E-cadherin but appears to have more of a regulatory function in this process
- CD103 mediates lymphocyte retention in epithelial tissues and allows immunocytes to maintain close contact with both peripheral lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissue (through binding to E-cadherin) (Nature 1994;372:190)
- Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) has been found to consistently upregulate its expression
- This cytokine induces CD103 on human cytotoxic lymphocytes in conjunction with T cell receptor (TCR) activation
Clinical features
- Interaction of E-cadherin with integrin αE(CD103)β7 plays a significant role in effective tumor cell lysis (J Exp Med 2007;204:559)
- CD103 plays a key costimulatory role in cytotoxic T cell activation (Int J Cancer 2011;129:2417, Cancer Res 2011;71:328)
Interpretation
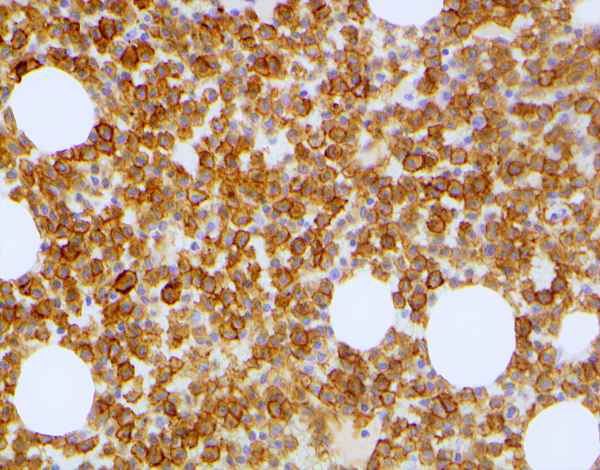
- Membranous (primarily) and cytoplasmic (variable intensity) with overlay of irregular cytoplasmic borders (consistent with projections) (Am J Clin Pathol 2013;139:220)
Uses by pathologists
- Diagnostic tool in the detection of hairy cell leukemia and hairy cell variant
- Aids in distinguishing hairy cell leukemia from other types of B cell lymphoproliferative disorders (in conjunction with additional markers) (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:586, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
Prognostic factors
- High CD103+ tumor infiltrating lymphocyte cell count is reported to be a favorable prognostic marker in a multitude of solid tumors (Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:6211, Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:434, J Immunol 2015;194:3475, Clin Cancer Res 2016;22:6290, Oncoimmunology 2014;3:e27668, J Urol 2015;194:556, Exp Ther Med 2018;15:4979, Sci Rep 2019;9:3808)
- High CD8+, CD103+ tissue resident memory T cells (TRM) are associated with metastasis and poorer clinical outcome in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) (J Immunother Cancer 2021;9:e001807)
Microscopic (histologic) description
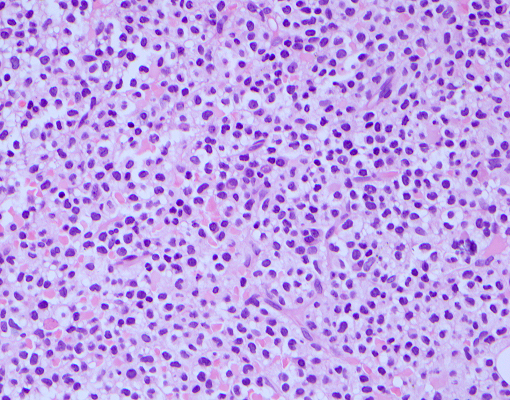
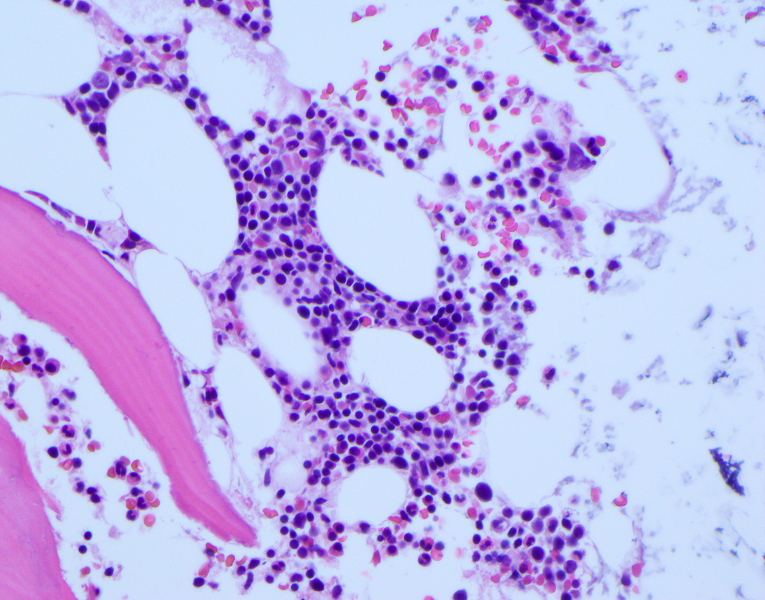
- CD103 expression is uniform with high intensity in cases of bone marrow involvement by hairy cell leukemia (in a diffuse interstitial pattern, ≥ 50% involvement)
- CD103 expression follows the distribution of neoplastic cells in cases of a patchy intrasinusoidal / interstitial pattern of bone marrow involvement (low level, 15% involvement)
- Reference: Am J Clin Pathol 2013;139:220
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs, T cells) (Eur J Immunol 1990;20:2201)
- Alloantigen induced regulatory CD8+ T cells (Tregs) (Hum Immunol 2008;69:737, J Immunol 2006;177:2775)
- Tissue resident memory T cells (TRM cells) (Nat Rev Immunol 2016;16:79, J Invest Dermatol 2018;138:23)
- FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) (Int J Cancer 2011;129:2417)
- Classic dendritic cells (cDCs) in nonlymphoid tissue (J Am Soc Nephrol 2016;27:1344)
- CD11chighMHC class IIhigh dendritic cells (mucosal and epithelial sites) (Immunol Rev 2010;234:268)
- CD4+ natural regulatory T cells (nTreg) (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006;118:1342)
Positive staining - disease
- Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:586, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Hairy cell leukemia variant (HCL-v) (Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2006;20:1051, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma (EATL) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1557)
- Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (ATLL) (Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:462, Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1557)
- Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma (MEITL) (Haematologica 2023;108:181)
Negative staining
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1557)
- T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (TLGL) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1557)
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) (Blood 2016;127:2072, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625, Mod Pathol 1998;11:601)
- < 10% cases positive by flow cytometry, < 25% cases by IHC
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma (SDRPL) (Histopathology 2002;40:22, Curr Oncol 2021;28:5148)
- Reports of cases that are positive
- 13/34 cases = 38% (Blood 2008;111:2253)
- 10/30 cases = 33% (Hematol Oncol 2011;29:47)
- Reports of cases that are positive
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- Follicular lymphoma (FL) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:625)
- Mycosis fungoides (MF) (16 - 24%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:1557, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:462)
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, posterior iliac crest, aspirate and core biopsy:
- Hypercellular marrow with involvement by CD103+ mature B cell neoplasm (see comment)
- Comment: The trephine core biopsy shows intravascular and patchy interstitial infiltration by small to intermediate sized lymphoid cells with asymmetric cytoplasmic projections and occasional nucleoli. These cells are positive for CD20, bright CD11c, bright CD22, CD103 and show kappa light chain restriction. These cells are negative for CD5, CD10, CD25 and CD38.
- The overall morphologic and immunophenotypic features are consistent with involvement by a splenic origin lymphoma. Absence of CD25 coexpression argues against a diagnosis of classical hairy cell leukemia. The primary diagnostic considerations include hairy cell leukemia variant and splenic marginal zone lymphoma. An additional differential may include splenic diffuse red pulp lymphoma (SDRPL). The morphologic features reflect a low grade process. There is no overt large cell transformation observed.
- Correlation with clinical findings and additional pertinent laboratory and radiographic studies is recommended for comprehensive assessment. This case (core biopsy) was submitted for internal quality assurance review.
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 59 year old man visits his primary care doctor to be evaluated for progressive weakness and decreased exercise tolerance. Physical examination shows splenomegaly and petechial bruises on the upper limbs bilaterally. Laboratory studies reveal pancytopenia. Peripheral smear reveals the findings in the image above and flow cytometry shows a mature monotypic B cell population coexpressing bright CD20, CD22, CD25, CD11c, CD103, FMC7, CD200 and lambda light chain restriction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Adult T cell leukemia / lymphoma (ATLL)
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL)
- Hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
- Splenic diffuse red pulp small B cell lymphoma (SDRPL)
- T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (TLGL)
Board review style answer #1
C. Hairy cell leukemia (HCL). The immunoprofile (particularly coexpression of CD11c, CD25 and CD103) and cytologic features (intermediate sized lymphocytes with circumferential cytoplasmic projections) are most consistent with hairy cell leukemia. The alternate disease entities listed either do not (or seldomly) coexpress CD103 with the other markers listed above (i.e., AITL, TLGL, SDRPL) or have different cytologic features in the peripheral blood (i.e., ATLL shows multilobed nuclei flower cells in the peripheral blood).
Comment Here
Reference: CD103
Comment Here
Reference: CD103
Board review style question #2
A 40 year old man presents to his physician with fever and left upper quadrant pain. Subsequent clinical evaluation shows anemia and monocytopenia. A bone marrow biopsy evaluation reveals a B cell lymphoproliferative disorder with the following immunoprofile: CD20+, CD25+, CD103+, annexin A1+, DBA44+. A diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia is made. Which of the following is the characteristic staining pattern of CD103 in this disease entity?
- Cytoplasmic
- Membranous (primarily) and cytoplasmic
- Nuclear
- Perinuclear dot-like
- Perinuclear golgi
Board review style answer #2
B. Membranous (primarily) and cytoplasmic. The most characteristic immunohistochemical pattern of CD103 staining is described in the literature as membranous (primarily) and cytoplasmic (variable intensity) with overlay of irregular cytoplasmic borders (consistent with projections). Since CD103 is a transmembrane surface receptor, the CD103 antibody would bind primarily to the cell membrane; therefore, the alternate choices (nuclear, perinuclear golgi or dot-like and cytoplasmic) are incorrect.
Comment Here
Reference: CD103
Comment Here
Reference: CD103