Table of Contents
CD100 | CD101 | CD102 | CD103 | CD104 | CD105 | CD106 | CD107a | CD107b | CD108 | CD109 | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Pernick N. CD100-109. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/cdmarkerscd100.html. Accessed December 21st, 2024.
CD100
- Also called SEMA4D, semaphorin 4D
- Integral membrane protein and ligand for CD72 and plexin B1
- Functions:
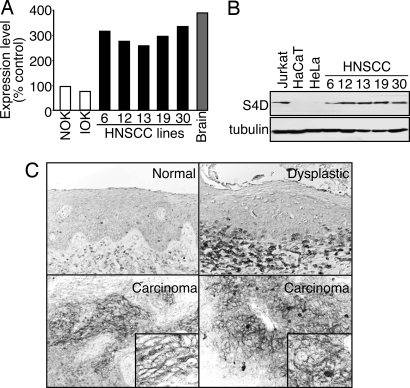
- Regulates axonal growth cone guidance in the developing CNS through its receptor plexin B1, which may be related to its expression in invading islands of transformed epithelial cells (but not normal and noninvasive dysplastic epithelium) (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103:9017)
- Evokes angiogenic responses from endothelial cells (Blood 2005;105:4321)
- Impairs monocyte migration
- After vascular injury, platelet associated CD100 binds to CD100 receptors on nearby platelets to promote thrombus formation (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:1621)
- Increases CD45 induced T cell adhesion
- Down regulates B cell expression of CD23
- Expression may have prognostic value in soft tissue sarcoma (Cancer 2007;110:164)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: most hematopoietic cells including platelets, increased expression after T cell activation
- Negative staining: immature bone marrow cells
- References: OMIM: 601866 [Accessed 30 April 2021], Wikipedia: Semaphorins [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD101
- Also called immunoglobulin superfamily member 2 (IGSF2), V7
- Inhibits T cell activation induced by CD3 by:
- Inhibiting IL2RA expression on activated T cells and IL2 secretion (J Immunol 1998;161:209)
- Inducing IL10 production (Eur J Immunol 2000;30:3132)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: monocytes, granulocytes, dendritic cells, activated T lymphocytes in small intestine
- Positive staining - disease:
- CD4+ CD56+ blastic tumor cells (J Invest Dermatol 2005;124:668)
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Histopathology 2000;36:229)
- References: OMIM: 604516 [Accessed 30 April 2021], J Immunol 1998;161:2780
CD102
- Also called ICAM2
- Binds the leukocyte integrins LFA1 (CD11a / CD18) and Mac1 (CD11b / CD18)
- Provides costimulatory signal in immune response
- Important in lymphocyte recirculation (J Immunol 2003;171:2588)
- Endothelial ICAM2 mediates angiogenesis (Blood 2005;106:1636)
- Elevated serum levels in:
- Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (Viral Immunol 2006;19:565)
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (Inflammation 2004;28:359)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: resting lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets, vascular endothelial cells
- Positive staining - disease: some lymphomas
- Negative staining: neutrophils
- Reference: OMIM: 146630 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD103
- See CD103
CD104
- Also called integrin beta 4 chain
- Tends to associate with alpha 6 subunit (CD49f)
- Adhesion receptor (for laminins) in normal epithelia that plays a critical role in structure of hemidesmosomes; associated with intermediate filaments
- May contribute to tumor progression via VEGF stimulation (Cancer Metastasis Rev 2005;24:413, J Cell Biol 2002;158:165)
- Overexpressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (J Histochem Cytochem 2005;53:799)
- Mutations are associated with epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia (Exp Dermatol 2004;13:61)
- Uses by pathologists: no significant clinical use by pathologists
- Positive staining - normal: epithelium, thymocytes, Schwann cells
- Positive staining - disease: carcinomas (some)
- Reference: OMIM: 147557 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD105
- See CD105
CD106
- Also called VCAM1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1); alpha 4 beta 1 ligand
- Interacts with beta 1 integrin VLA4
- Adhesion molecular in activated endothelium; plays a role in migration of white blood cells (J Exp Med 2006;203:2763)
- May mediate endothelial progenitor cell recruitment to rheumatoid arthritis synovium (Arthritis Rheum 2007;56:1817)
- Associated with type II rheumatic disease (Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2002;48:OL243)
- Important in initiation of atherosclerosis (J Clin Invest 2001;107:1255)
- Renal cell carcinoma may exploit VCAM1 overexpression for immune system escape (Cancer Res 2007;67:6003)
- On the other hand, down regulation in breast cancer is associated with nodal metastases (Pathol Oncol Res 2002;8:125)
- Increased expression: in placentas of women with pregnancy induced hypertension complicated by intrauterine growth restriction (Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao 2002;22:1022)
- Increased plasma levels associated with:
- Breast cancer [high stage] with circulating cancer cells (Neoplasma 2006;53:538)
- Cancer (general): early stage or preclinical (Eur J Cancer 2005;41:2355)
- Dengue virus infection severity (J Med Virol 2004;72:445)
- Diabetes with poor control (high HbA1c) (Diabetes Care 2007;30:159)
- Arteriosclerosis obliterans (Clin Chim Acta 2007;377:198)
- Endometriosis: advanced (J Soc Gynecol Investig 2002;9:98)
- Sickle cell trait in athletes (J Appl Physiol 2007;102:169)
- Uses by pathologists: marker of endothelial damage (Endothelium 2006;13:335)
- Positive staining - normal: activated endothelial cells, lymphocytes, monocytes, neural cells, hematopoietic cells
- Positive staining - disease: renal cell carcinoma
- Reference: OMIM: 192225 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD107a
- Also called lysosome associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1)
- Note: DC-LAMP is CD208
- Functions:
- Surface antigen transiently present on cell surface of CD8+ T cells after release of cytolytic granules (J Immunol Methods 2003;281:65)
- Basophil activation antigen (Cell Res 2005;15:325)
- Expression correlates with aggressiveness of melanocytic neoplasms (Melanoma Res 2006;16:235)
- Critical to phagosomes acquiring microbicidal capabilities (Cell Microbiol 2007;9:2153)
- Ligand to E-selectin mediated cell adhesion
- Uses by pathologists: defective CD107a surface expression discriminates between genetic subtypes of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (Blood 2006;108:2316)
- Positive staining - normal:
- Primarily endosome lysosome membranes, 1 - 2% on plasma membrane
- Degranulated platelets (Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2003;14:249)
- Activated neutrophils, T cells, endothelium
- Reference: OMIM: 153330 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD107b
- Also called lysosome associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2)
- X linked
- Major constituent of lysosomal membranes (also LAMP1)
- Functions:
- Mutations cause Danon disease, a lysosomal glycogen storage disease with cardiomyopathy in adult women and men before age 20 years (N Engl J Med 2005;352:362, Circulation 2005;112:1612)
- Also, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, myopathy, variable intellectual disability and retinopathy (Arch Ophthalmol 2007;125:231)
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells have intracytoplasmic vacuoles containing glycogen and autophagic material
- Levels decrease with age (J Cell Sci 2007;120:782)
- Binding of substrates to LAMP2 is limiting step in chaperone-mediated autophagy, a selective mechanism for the degradation of soluble cytosolic proteins in lysosomes (EMBO J 2006;25:3921)
- May be involved in infection induced involution of thymus via autophagy (Acta Biol Hung 2006;57:315)
- Facilitates MHC class II presentation of cytoplasmic antigens (Immunity 2005;22:571)
- Basophil activation antigen (Cytometry A 2004;61:62)
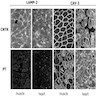
- Uses by pathologists: help differentiate cardiomyopathy due to Danon disease (LAMP2 negative) from other causes (LAMP2 positive) (Intern Med 2007;46:757)
- Positive staining - normal: lysosome membranes of various tissues, platelets (Thromb Haemost 1996;75:623)
- Negative staining: cardiac and skeletal muscle in Danon disease (Neuromuscul Disord 2003;13:708)
- Reference: OMIM: 309060 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD108
- Also called semaphorin 7A (SEMA7A) or John Milton Hagen (JMH) human blood group antigen
- A semaphorin (Wikipedia: Semaphorin [Accessed 30 April 2021])
- Receptors are plexin C1 and beta1 integrins
- Functions:
- Genetic variations may play a role in decreased bone mineral density and risk of vertebral fracture (J Hum Genet 2006;51:112)
- Extremely potent monocyte activator; stimulates chemotaxis and cytokine production (Scand J Immunol 2002;56:270)
- Stimulates axon growth and guidance during development (Nature 2003;424:398)
- Negative regulator of T cell responses (Immunity 2006;24:591)
- Expression is correlated with the establishment of dentin-pulp complex terminal innervation (Matrix Biol 2005;24:232)
- Positive staining - normal: erythrocytes, activated lymphocytes, odontoblasts, monocytes, keratinocytes, fibroblasts
- Reference: OMIM: 607961 [Accessed 30 April 2021]
CD109
- Also called platelet activation factor
- Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored cell surface protein
- Carries the biallelic platelet-specific Gov antigen system
- Alloantibodies to HPA-15 residing on CD109 are implicated in refractoriness to platelet transfusion, fetal / neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia and posttransfusion purpura (Blood 2002;99:1692)
- Positive staining - normal:
- Activation antigen for platelets and T cells
- Subset of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (Exp Hematol 1999;27:1282)
- Myoepithelial cells (breast, prostate [basal cells] salivary and lacrimal glands) (Pathol Int 2007;57:245)
- Widely expressed in other tissues
- Negative staining: invasive ductal carcinoma (breast), prostate adenocarcinoma
- Reference: OMIM: 608859 [Accessed 30 April 2021]