Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Li JJX, Tse GM. Tubular adenoma . PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breasttubularadenoma.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign fibroepithelial tumor of the breast composed of compact bilayered tubules with sparse intervening stroma
Essential features
- Circumscribed / nodular benign tumor of the breast
- Closely packed tubules with sparse intervening stroma
Terminology
- Fibroadenomas variant (pericanalicular subtype), not recommended by WHO
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Found in 2.8% (n = 33/1,167) of cases in a series of breast biopsies (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Most identified in young (20 - 40 years old) women and rarely in postmenopausal age group (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
Sites
- Most commonly involve upper outer quadrants of the breast (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Also reported in accessory breast tissue (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:60)
Pathophysiology
- Arises from terminal duct lobular units
Etiology
- Unknown
- May be associated with reproductive hormones due to high incidence in women of reproductive age
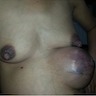
Clinical features
- Commonly presents as a firm, mobile, well defined and painless mass (Iran J Pathol 2015;10:17)
- Worrisome features (irregular borders, fixation to adjacent tissue and ulceration) uncommon (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Isolated case of tubular adenoma presenting with nipple discharge in a postmenopausal woman reported (Indian J Radiol Imaging 2017;27:112)
- No axillary lymphadenopathy reported
Diagnosis
- Histology recommended for definitive diagnosis (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Radiology and cytology usually allow identification of the benign nature of lesion but may not be sufficient in excluding differential diagnoses
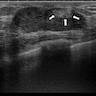
Radiology description
- Well defined and well circumscribed lesion (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:757)
- Hypoechoic on ultrasound
- Posterior acoustic enhancement sometimes seen
- Tiny, punctate and irregular microcalcifications may be present on mammography in older patients
Prognostic factors
- Benign, indolent lesions
- No increased risk of developing subsequent breast carcinoma
- Rare cases with incidental in situ and invasive carcinomas (Breast Cancer 2015;22:428, Pathol Int 2002;52:244)
Case reports
- 26 year old woman with a tubular adenoma in the accessory breast (Diagn Pathol 2015;10:60)
- 29 year old woman with a giant tubular adenoma (BMJ Case Rep 2018;2018:bcr2018224631)
- 33 year old woman with ductal carcinoma in situ in a tubular adenoma (Breast Cancer 2015;22:428)
Treatment
- Curable by complete surgical excision
- Observation acceptable for asymptomatic, low risk patients
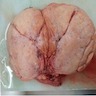
Gross description
- Well defined borders
- Tan to whitish cut surface (Clin Med Insights Pathol 2018;11:1179555718757499)
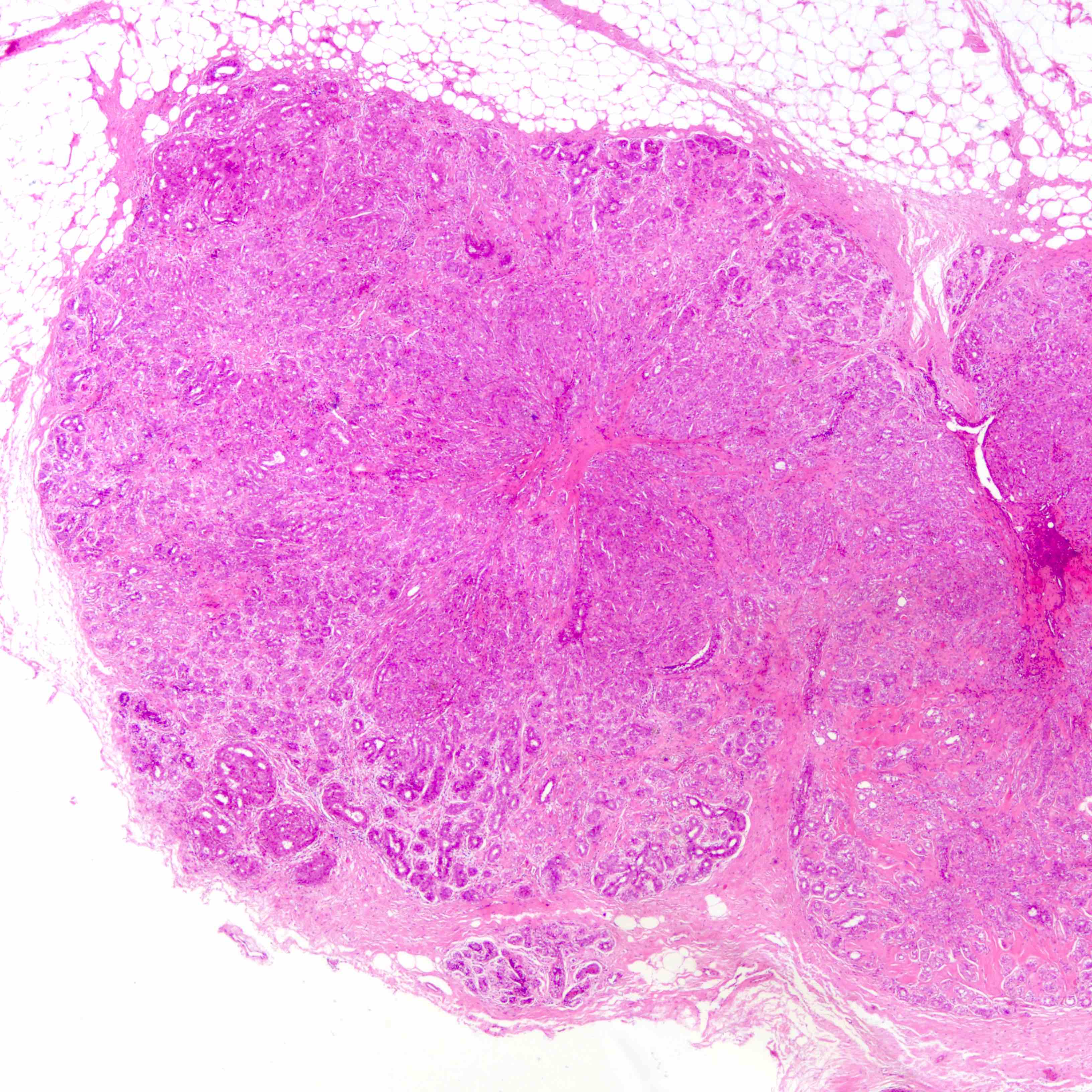
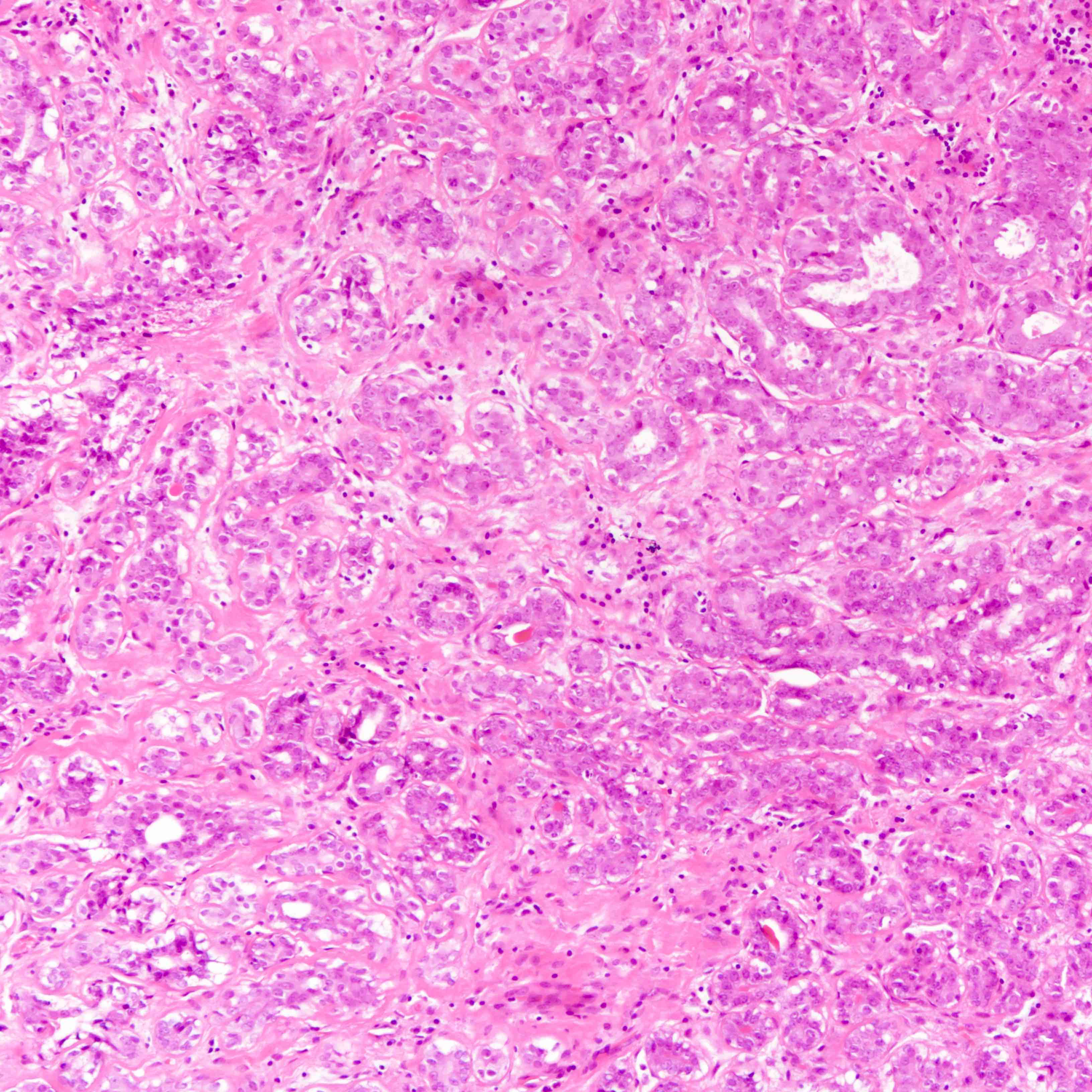
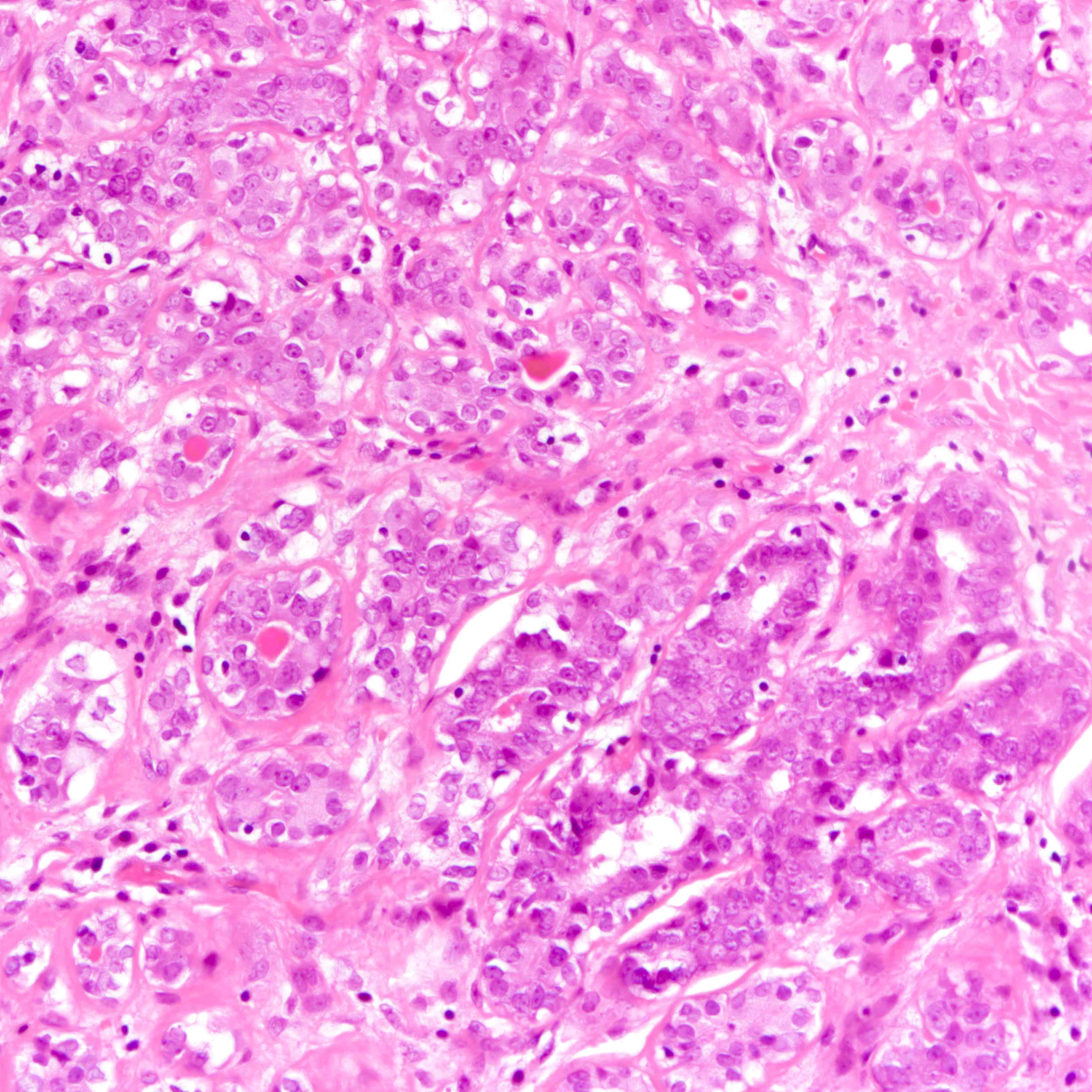
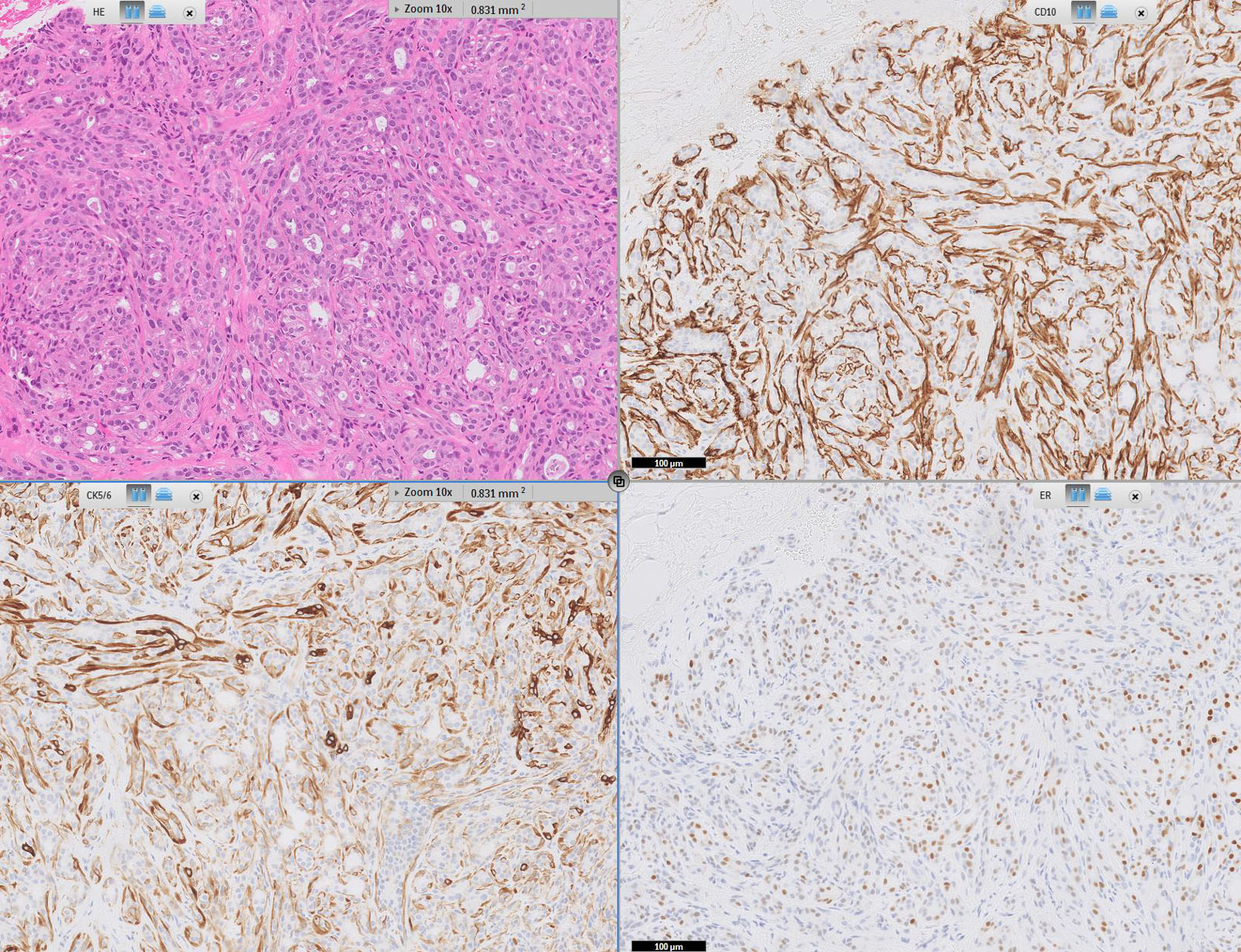
Microscopic (histologic) description
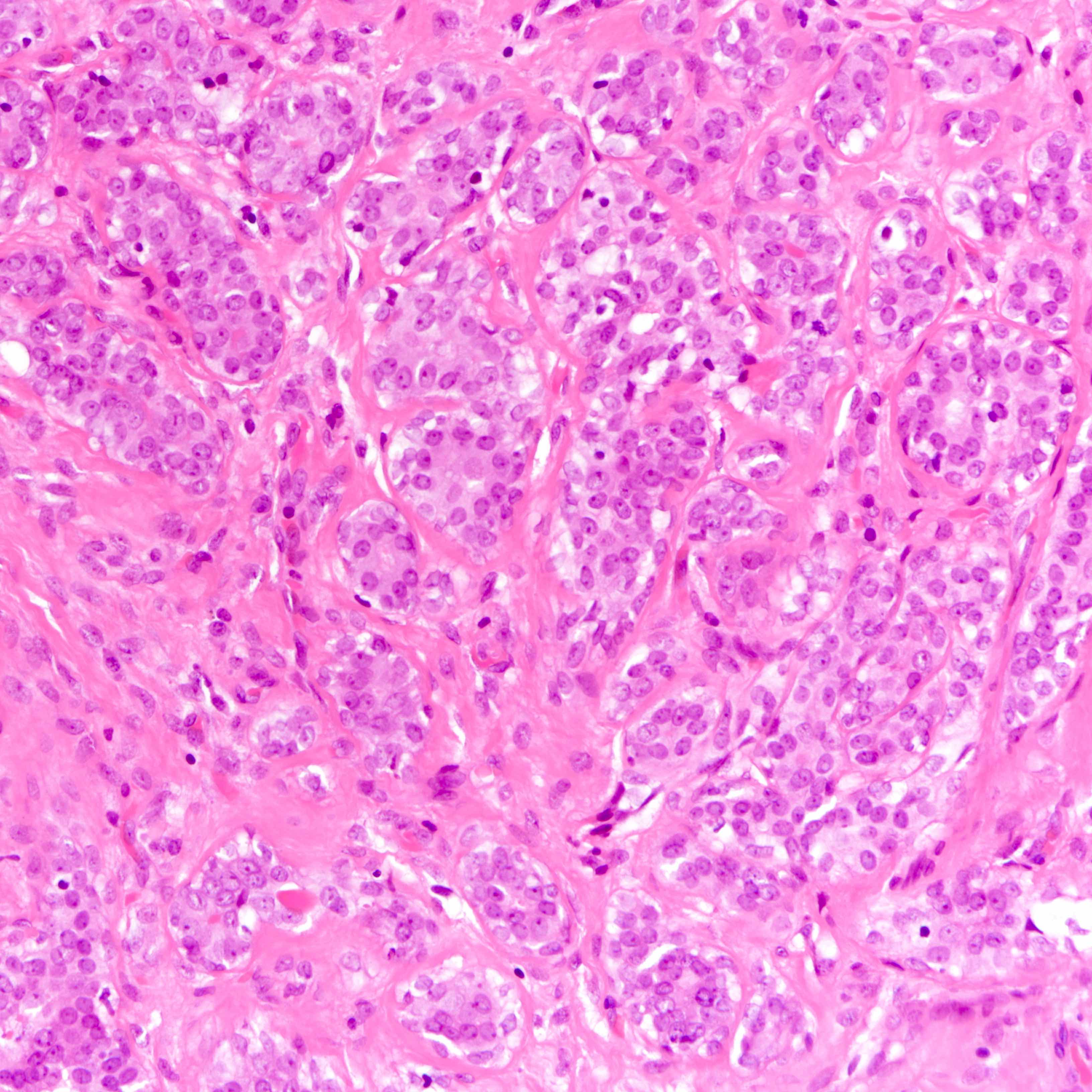
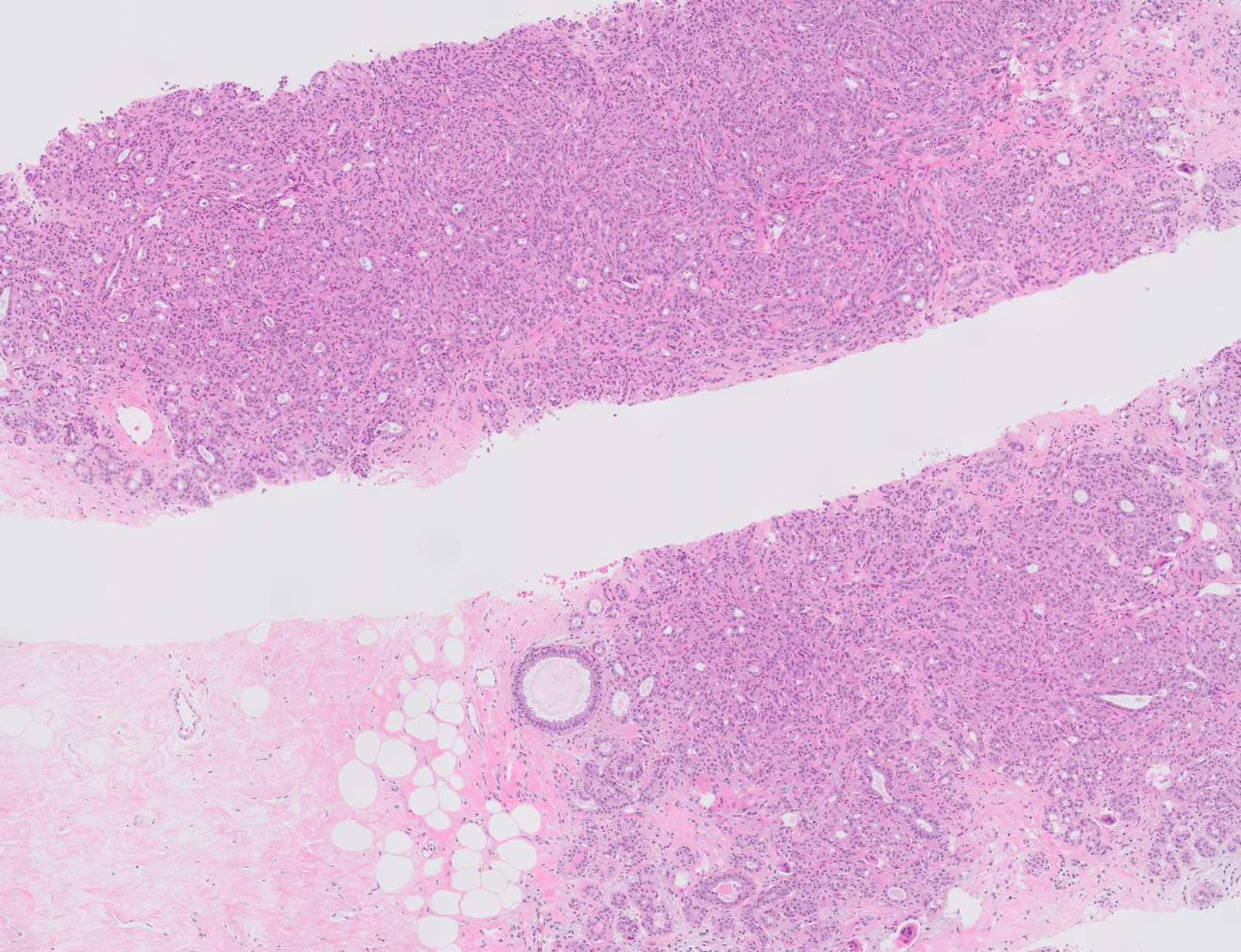
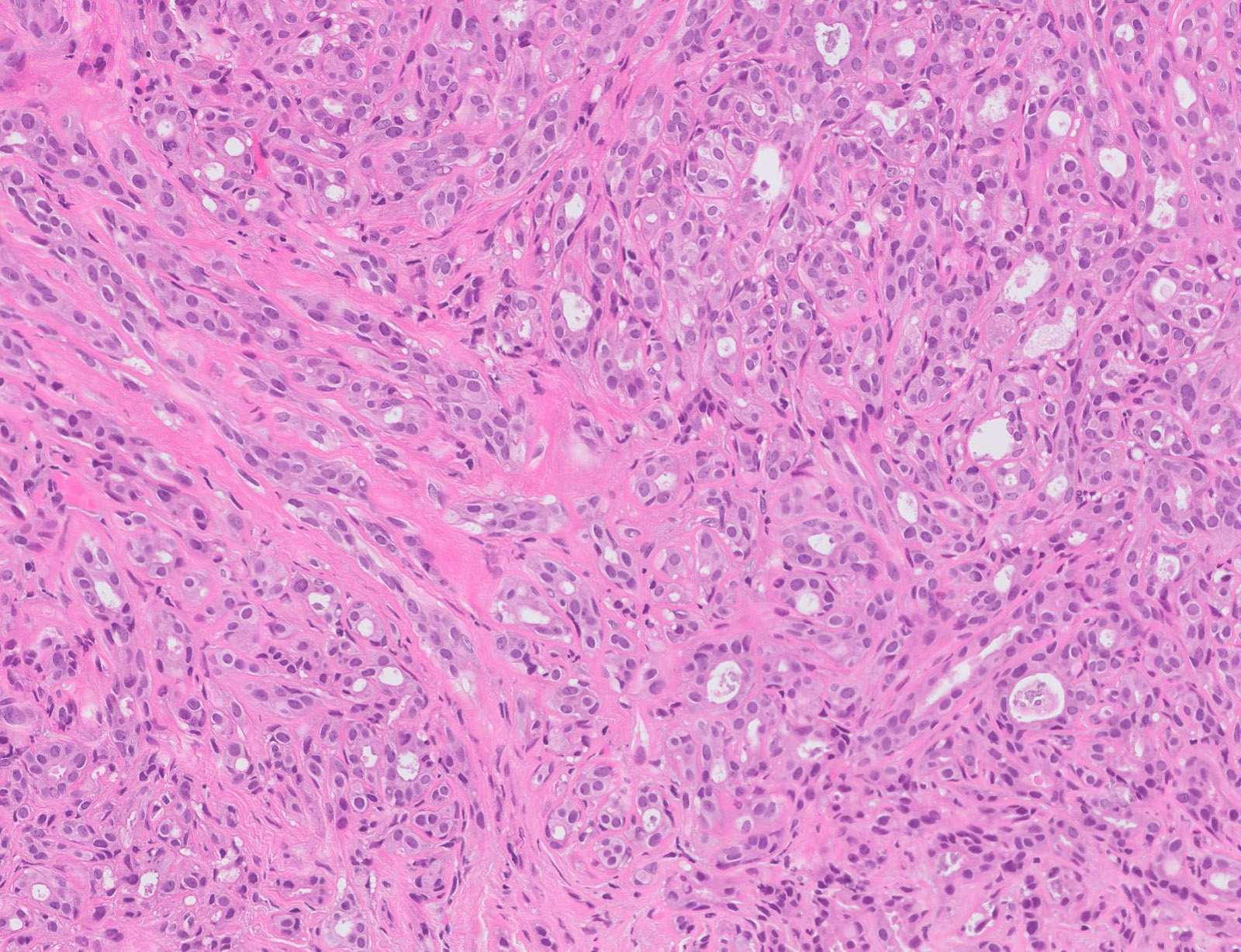
- Well defined borders
- Sparse fibrovascular stroma intervening tubules
- Small, uniform, closely packed round tubules (Clin Med Insights Pathol 2018;11:1179555718757499)
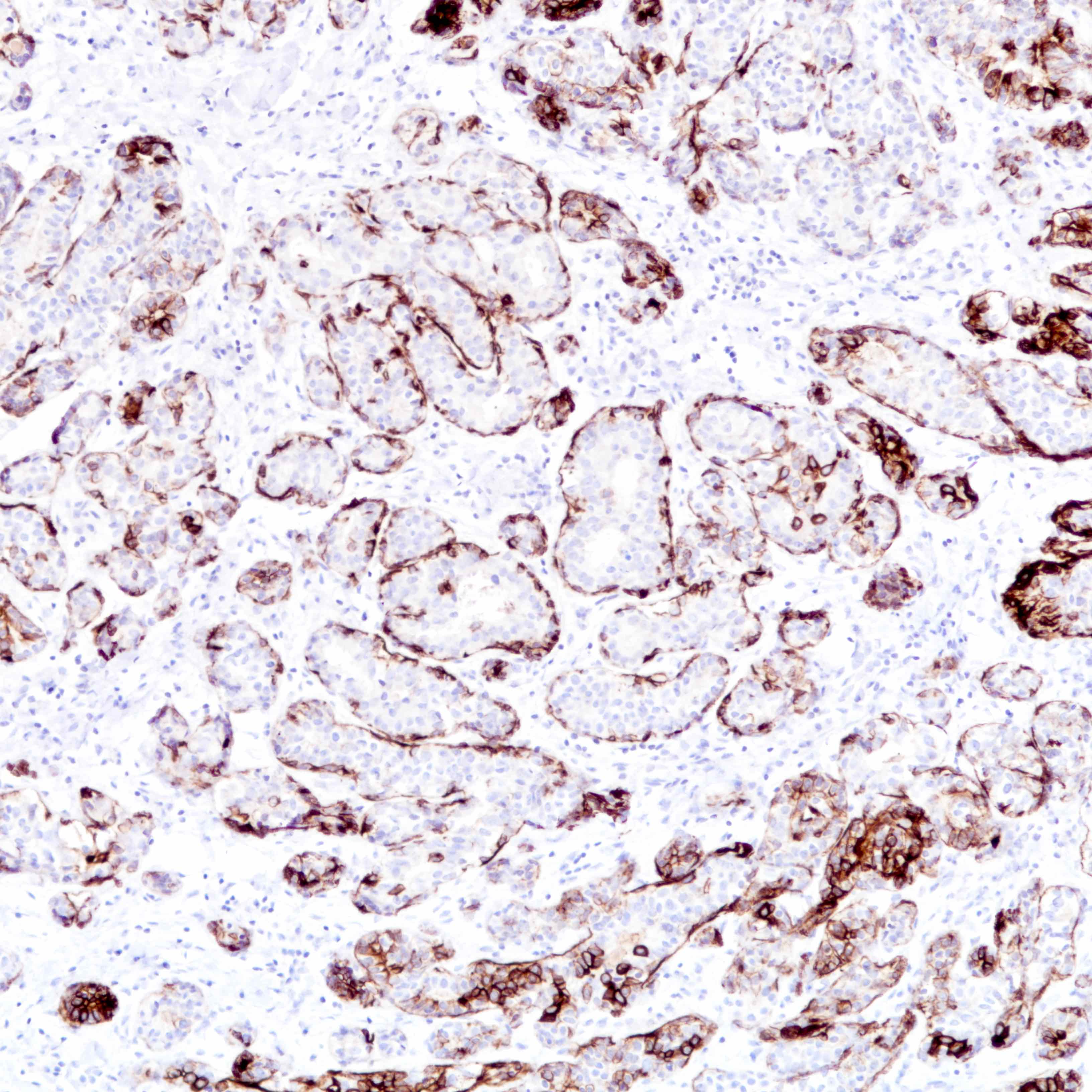
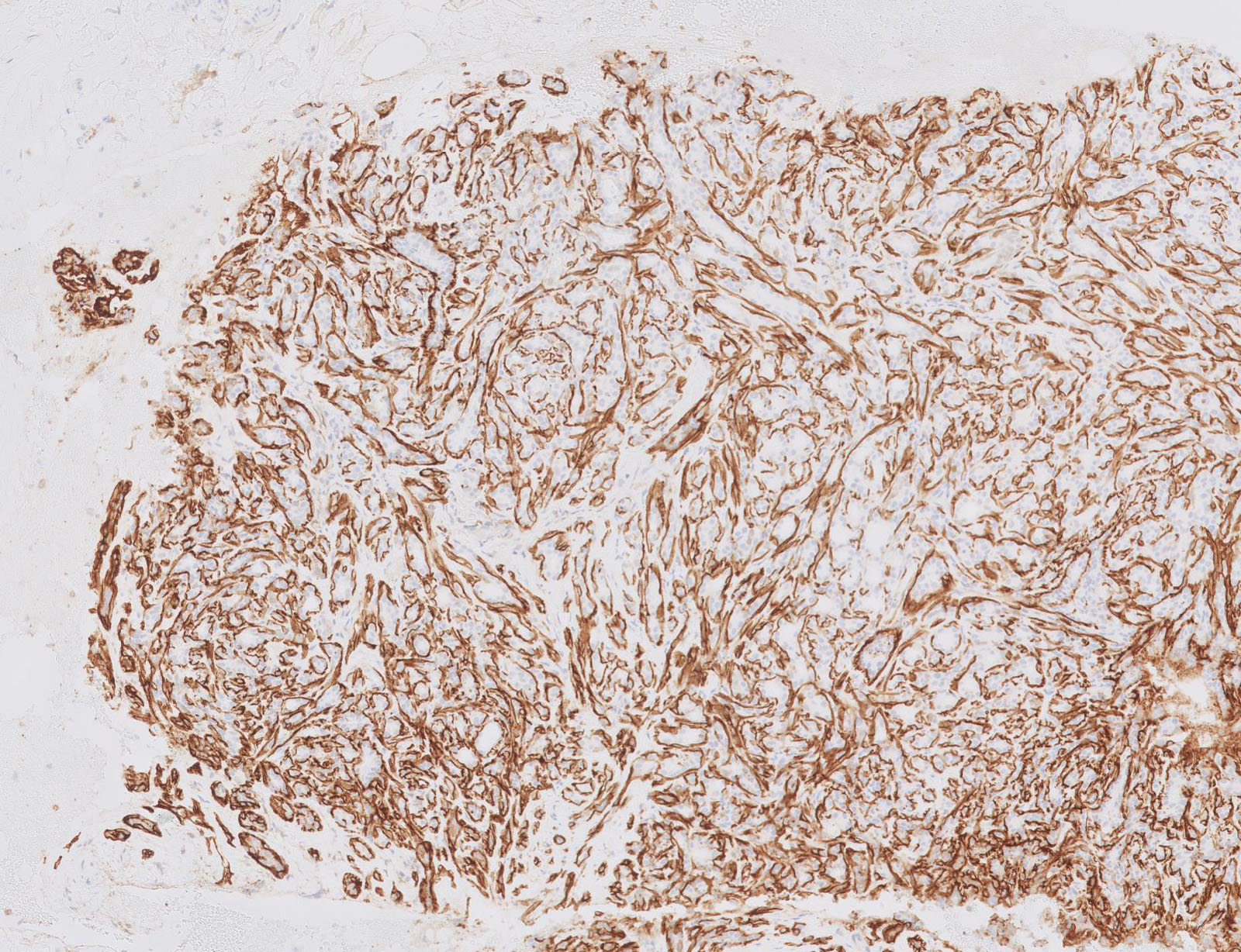
- Lined by an inner layer of luminal epithelial cells and an outer layer of myoepithelial cells
- Rare mild atypia and mitotic figures does not exclude diagnosis
- Occasional luminal eosinophilic secretion
- Lined by an inner layer of luminal epithelial cells and an outer layer of myoepithelial cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Joshua J.X. Li, M.B.Ch.B. and Gary M. Tse, M.B.B.S.
Contributed by Jijgee Munkhdelger, M.D., Ph.D. and Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D.
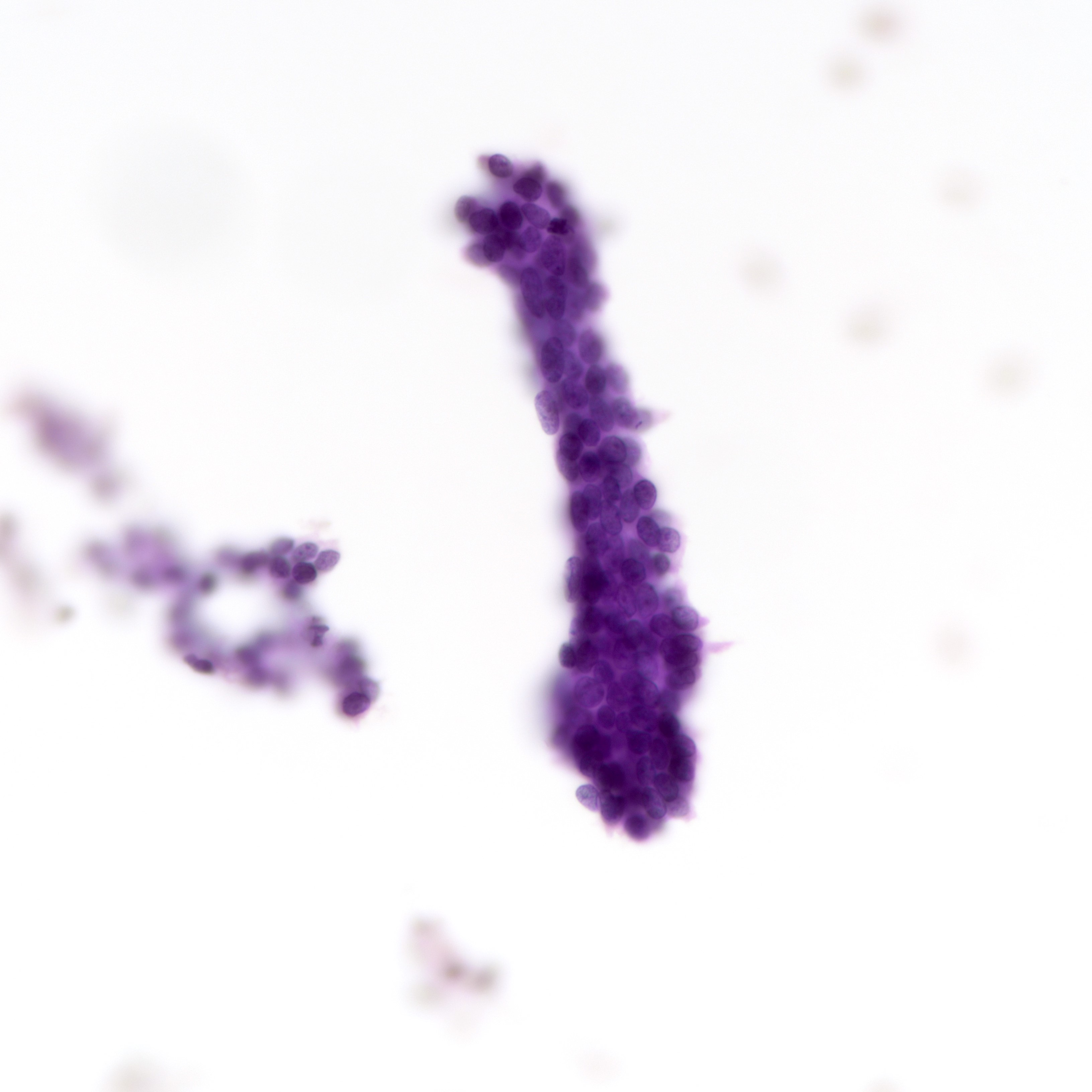
Cytology description
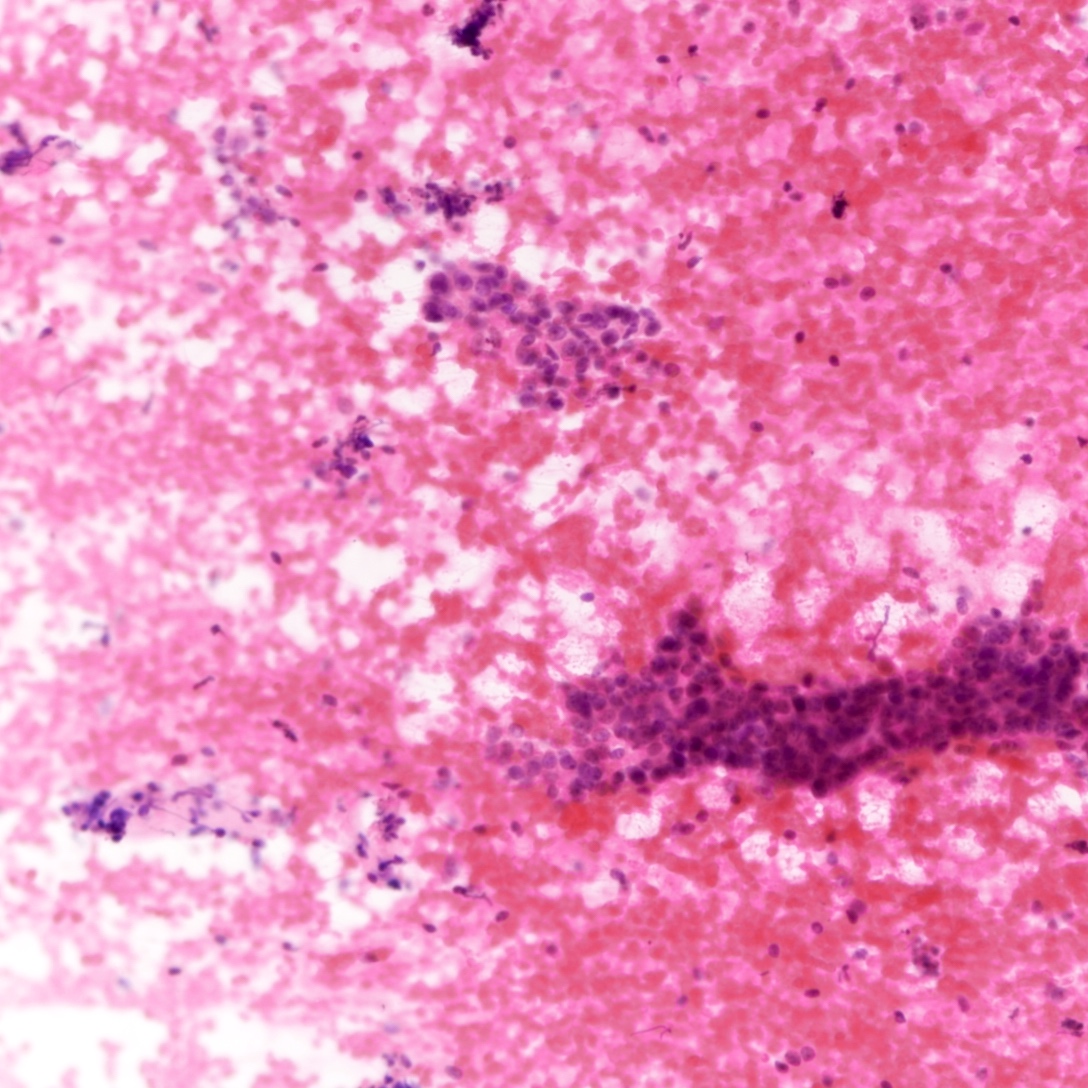
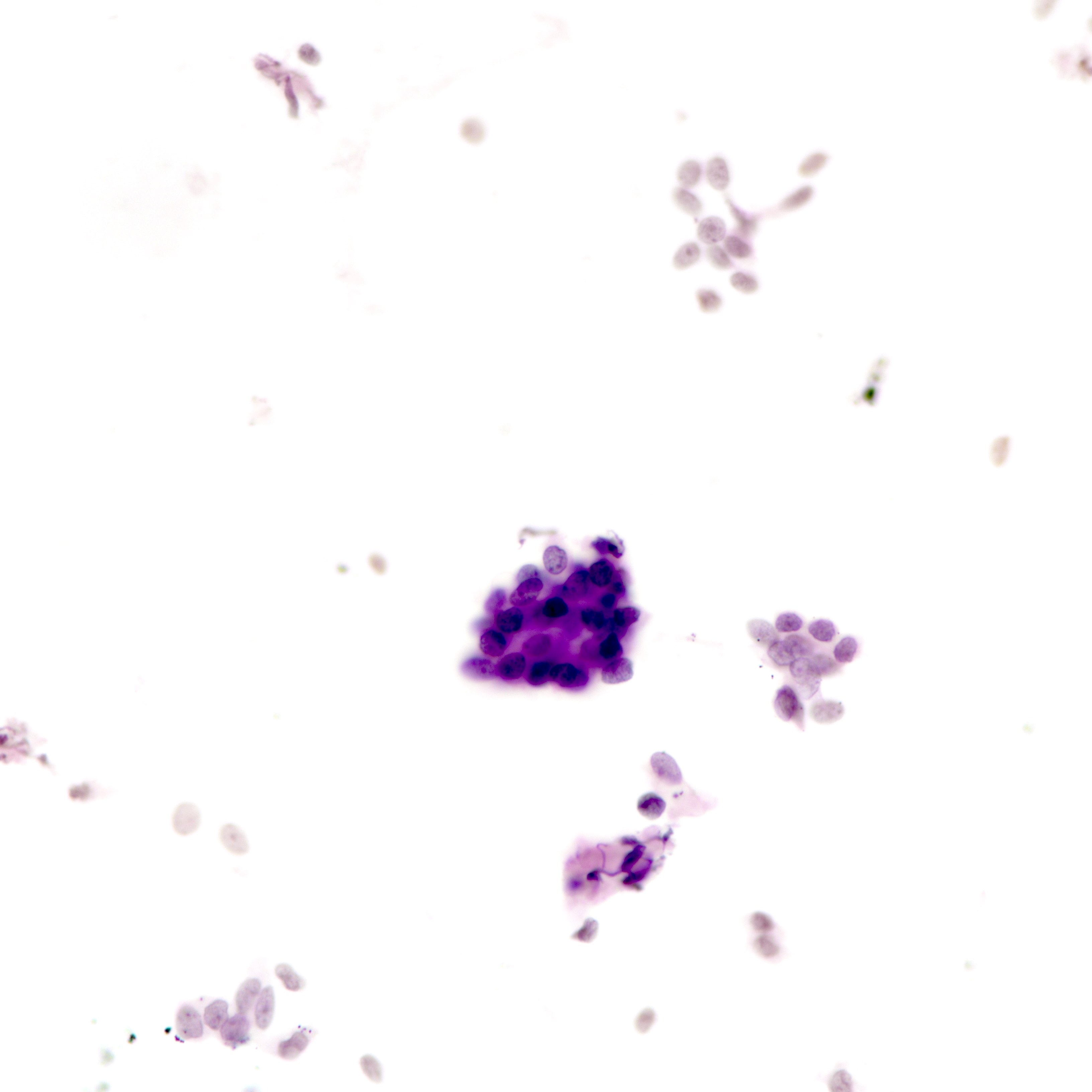
- Tubular fragments (tissue fragments containing multiple tubular structures with or without stroma) is a pathognomonic feature of tubular adenoma (Acta Cytol 2022 Dec 14 [Epub ahead of print])
- Naked nuclei (myoepithelial cells) in the background (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Fibrous fragments scanty (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
- Epithelial cells arranged in 3 dimensional ball-like structures and probable acinar formations (Acta Cytol 1998;42:657)
- Epithelial cells mostly show bland nuclear features
- Diagnosis based on cytologic assessment only not recommended (N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:219)
Cytology images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- Luminal secretions: α-lactalbumin (J Pathol 1982;137:13)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Recently, next generation sequencing demonstrated that tubular adenomas and fibroadenomas show different mutation profiles (J Cell Biochem 2019;120:182)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, excisional biopsy:
- Tubular adenoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show a proliferation of small, crowded tubules with minimal intervening stroma, composed of bland epithelial cells with an intact myoepithelial cell layer. Occasional eosinophilic luminal secretions are noted.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibroadenoma:
- Expanded stromal component in between ducts
- Ducts distorted and compressed by stroma (intracanalicular pattern)
- Presence of MED12 mutations
- Lactating adenoma:
- Luminal epithelium shows secretory changes (hobnail changes, granular or vacuolated cytoplasm)
- Luminal secretions positive for α-lactalbumin
- Nipple adenoma:
- Haphazardly distributed tubular ducts
- Lacks circumscription
- Located at the superficial aspect of nipple, often with epidermal connection
- Adenomyoepithelioma:
- Biphasic lesion with multilayered or solid nests of myoepithelial cells
- Mixed nontubular patterns, including lobular and spindle patterns
- Sclerosing adenosis:
- Hyalinized and occasionally expanded stroma
- Ducts compressed and distorted by stroma
- Collagenous spherulosis:
- Intraductal proliferation with cribriform pattern
- Spherules containing basement membrane material enclosed by myoepithelial cells
- Usually associated with benign proliferative lesions
- Microglandular adenosis:
- Infiltrative, haphazardly distributed small round glands
- Lacks myoepithelial cells
- Lacks circumscription
- Tubular carcinoma:
- Infiltrative angulated tubules with tapering ends
- Lacks myoepithelial cells
- Stroma shows desmoplastic reaction
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Tubular adenoma is most commonly but not exclusively located at the upper outer quadrant of the breast and presents in young women. Attachment to the nipple is a feature of nipple adenoma. Axillary lymphadenopathy, an irregular border and fixation are malignant features not commonly associated with tubular adenomas.
Comment Here
Reference: Tubular adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Tubular adenoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following features favors the diagnosis of tubular adenoma over fibroadenoma?
- Detection of MED12 mutation
- Minimal intervening fibrous stroma between tubules
- Presence of myoepithelial layer
- Presence of rare mitotic figures
- Tubules arranged in an intracanalicular pattern
Board review style answer #2
B. Minimal intervening fibrous stroma between tubules. Fibroadenomas often demonstrate expansion of fibrous stroma, which compresses tubules and produces an intracanalicular pattern. MED12 mutation is associated with fibroepithelial lesions of the breast, in particular fibroadenomas. Myoepithelial layer is present in both lesions and rare mitotic figures are allowed in both lesions.
Comment Here
Reference: Tubular adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Tubular adenoma