Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Goyette ERJ, Muller KE. Molecular subtypes. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmolecularsubtypes.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Gene expression profiling and hierarchical cluster analyses have categorized breast cancer into 4 major intrinsic subtypes with distinct molecular characteristics, risk factors, treatment effectiveness and prognosis (Nature 2000;406:747, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001;98:10869, J Pathol 2010;220:263, Cancer Res 2018;78:6011)
- Traditional immunohistochemical biomarkers (ER, PR, HER2, Ki67 proliferative index) and pathologic features such as histological type and tumor grade serve as surrogates to classify tumors into molecular subtypes in clinical practice
Essential features
- Luminal subtype (subdivided into luminal A and luminal B)
- Luminal A (ER positive, PR positive, HER2 negative, Ki67 proliferative index low)
- Luminal B
- HER2 negative (ER positive, PR negative / low, HER2 negative, Ki67 proliferative index high)
- HER2 positive (ER positive, PR positive or negative, HER2 positive, Ki67 proliferative index varies)
- Triple negative subtype (ER negative, PR negative, HER2 negative)
- Umbrella term that includes basal-like (1 and 2), luminal androgen receptor positive, mesenchymal, mesenchymal stem-like and immunomodulatory
- HER2 enriched (HER2 positive; ERBB2 positive)
- ER negative, PR negative, HER2 / neu amplified or overexpressed
- Other rare subtypes: claudin low, normal breast-like
Terminology
- Intrinsic subtypes, molecular classification of breast cancer
Epidemiology
- Frequency and lifetime risk by molecular subtype and age (Cancers (Basel) 2015;7:908, Surg Oncol Clin N Am 2018;27:95)
- Lifetime risk
- Luminal A and B: 6.79%
- HER2 positive: 1.78%
- Triple negative: 1.2%
- Overall frequency
- Luminal A: 30 - 40%
- Luminal B: 20 - 30%
- HER2 positive: 12 - 20%
- Triple negative: 15 - 20%
- Molecular subtype by age
- < 40: triple negative > luminal B > HER2 > luminal A
- 40 - 59: triple negative > luminal B > HER2 > luminal A
- 60 - 69: luminal A > HER2 > luminal B > triple negative
- > 70: luminal A > luminal B and HER2 > triple negative
- Lifetime risk
- Triple negative
- Younger age, African ancestry, BRCA1 mutations (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;113:357)
- BRCA1, BRCA2, TP53 mutation carriers: triple negative
- 20 - 30% of triple negative patients have either BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations (Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:3254)
- BRCA1, BRCA2, TP53 mutation carriers: triple negative
- Younger age, African ancestry, BRCA1 mutations (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;113:357)
Pathophysiology
- Luminal
- Transformed from luminal progenitor cells (Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010;2:a003160)
- Nonobligate precursors: FEA, ADH, ER positive ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
- Triple negative (Annu Rev Pathol 2022;17:181, Cell Stem Cell 2010;7:403)
- Originally thought to arise from basal stem cells
- Most likely cell of origin for nonmetaplastic triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an ER negative luminal progenitor cell
- TNBC with metaplastic features likely arises from the myoepithelial progenitor cells
- Defects in homologous recombination (i.e., double stranded DNA repair)
- ~15% of all TNBCs harbor deleterious germline mutations in a homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) related gene (BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, CHK2, RAD51, PALB2, BRIP1)
- Nonobligate precursors
- Low grade: microglandular adenosis (MGA) and atypical microglandular adenosis, which contain nearly identical copy number variants and TP53 somatic variants to those seen in high grade TNBC
- High grade: ER negative ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotypes (~7% of all ductal carcinoma in situ)
- HER2 enriched (Oncologist 2002;7:2)
- HER2 is part of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, along with 3 other receptors: epidermal growth factor receptor HER1, HER2, HER3 and HER4
- HER2 gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 17 and encodes a 185 kDa transmembrane protein and an activator of several downstream signaling cascades, including the MAPK and PI3K pathways
Etiology
- Risk factors by subtype (Cancer Res 2018;78:6011, Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:373, Breast Cancer Res 2019;21:40)
- Luminal A and B
- Nulliparity, alcohol consumption, early menarche, use of menopausal hormones, increased BMI / weight, older age at first birth, late menopause
- For parous women, greater number of years between menarche and first birth
- Nulliparity, alcohol consumption, early menarche, use of menopausal hormones, increased BMI / weight, older age at first birth, late menopause
- Triple negative
- Ever parous (23% higher risk than nulliparous women), high BMI
- Breastfeeding might ameliorate the higher risk of triple negative breast cancer associated with parity (Ann Oncol 2015;26:2398)
- Disproportionally affects African American women and germline BRCA1 and PALB2
- HER2 enriched
- Risk factors are less well defined than luminal and triple negative subtypes
- HER2 positive / enriched tumors overexpress HER2 and genes associated with the HER2 pathway or the HER2 amplicon on 17q12
- All subtypes: family history of breast cancer, personal history of benign breast disease, smoking (women who initiate smoking before first childbirth)
- Luminal A and B
Diagnosis
- Luminal (subdivided into luminal A and B)
- Luminal A (ER positive, PR positive, HER2 negative, Ki67 proliferative index low)
- Luminal B, HER2 negative (ER positive, PR negative / low, HER2 negative, Ki67 proliferative index high)
- Luminal B, HER2 positive (ER positive, PR positive or negative, HER2 positive, Ki67 proliferative index varies)
- Triple negative (ER negative, PR negative, HER2 negative)
- Umbrella term that includes basal-like (1 and 2), luminal androgen receptor positive, mesenchymal, mesenchymal stem-like and immunomodulatory
- HER2 enriched (ERBB2 positive)
- ER negative, PR negative, HER2 amplified or overexpressed
- Invasive breast tumors that are HER2 positive (amplification via FISH testing or overexpression via IHC)
- ER negative, PR negative, HER2 amplified or overexpressed
- Reference: J Pathol 2010;220:263
Radiology description
- Imaging findings do not distinguish between molecular subtypes; however
- Luminal subtype is associated with architectural distortion
- HER2 positive subtype is more likely to be associated with mammographic calcifications
- Triple negative subtype is most likely to be associated with a mammographic mass (Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:3247, Radiology 2008;246:367)
Prognostic factors
- Survival rate at 4 years from diagnosis (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2018;27:619)
- Luminal (92.5%) > luminal HER2 positive (90.3%) > HER2 enriched (82.7%) > triple negative (77.0%)
- Local regional recurrence and distant metastasis rates by molecular subtype (Cureus 2016;8:e924)
- Local regional
- Luminal A: 2%
- Luminal B: 4%
- HER2 positive: 8%
- Triple negative: 12%
- Distant
- Luminal A: 6.4%
- Luminal B: 12.1%
- HER2 positive: 19.2%
- Triple negative: 27.4%
- Local regional
- Luminal A
- Generally low grade, indolent and slow growing, favorable prognosis
- Less frequent and less extensive lymph node involvement
- Risk of late recurrence and mortality after 10+ years from diagnosis
- ~30% of ER positive patients will eventually develop anti-estrogen resistant metastatic or locally advanced breast cancer
- Luminal B
- More aggressive clinical behavior and worse prognosis compared to luminal A
- Higher histologic grade than luminal A
- Loss of PR expression adverse prognostic factor (J Clin Oncol 2013;31:203)
- Triple negative
- Aggressive phenotype with shorter time to relapse and metastasis compared to stage matched HR positive / HER2 positive tumors, despite more aggressive therapy (Breast J 2009;15:454)
- African American women are twice as likely to die from triple negative breast cancer even when controlling for treatment, stage and socioeconomic factors (Cancer J 2021;27:8)
- Of note, a subset of TNBC with distinct histomorphology is associated with significantly better prognosis (Am J Pathol 2017;187:2133)
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma, secretory carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, low grade metaplastic carcinomas (adenosquamous carcinoma, fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma)
- HER2 enriched
- Associated with aggressive biology and poor prognosis with high risk of recurrence and metastasis in the absence of targeted therapies (Science 1987;235:177)
- HER2 positivity is a predictive factor for response to anti-HER2 agents
- Anti-HER2 agents drastically improve outcomes in HER2 positive breast cancer (PLoS One 2011;6:e21030, J Clin Oncol 2023;41:1638, Lancet Oncol 2011;12:236)
Treatment
- Luminal
- Standard of care surgery and adjuvant endocrine therapy with or without irradiation (depending on surgical, pathological and clinical factors)
- Endocrine therapy for 5 - 10 years (tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitor) with or without ovarian suppression
- Duration and choice of endocrine therapy is dependent upon menopausal status at time of diagnosis
- Luminal tumors are less sensitive to chemotherapy compared to triple negative and HER2 enriched (pathologic complete response rates for neoadjuvant chemotherapy is 10 - 20% compared to 50 - 60%, respectively) (Lancet 2014;384:164)
- Neoadjuvant endocrine therapy is not widely used (Ann Surg Oncol 2017;24:418)
- Trials such as neoadjuvant aromatase inhibitor (NAOMI) therapy for ER positive breast cancer evaluate the effects of neoadjuvant aromatase inhibitor (letrozole) in postmenopausal women with stage I - III ER positive, HER2 negative breast cancer
- The NCCN Guidelines allow for the use of breast conserving surgery (pathologically negative margin required) with 5 years of tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, without breast irradiation, for patients over 70 years of age with clinically negative lymph nodes and ER positive T1 breast cancers
- Triple negative
- Surgery and chemotherapy with or without irradiation (depending on surgical, pathological and clinical factors)
- Endocrine therapy and anti-HER2 therapies are ineffective due to absent expression of ER, PR and HER2
- While surgery and postoperative radiation remains standard of care, chemotherapy, either in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting, is also recommended
- Neoadjuvant therapy is preferred in individuals with ≥ cT2 or ≥ cN1 TNBC and can be considered in those with cT1c, cN0 TNBC as well
- Pathologic complete response (pCR) is associated with extremely favorable disease free and overall survival (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1796, Lancet 2014;384:164)
- Preferred therapeutics include anthracyclines, taxanes, antimetabolites, microtubule inhibitors, platinum based therapy, cyclophosphamide
- If recurrent / unresectable or metastatic, additional testing for
- PDL1 expression (first line) variable
- Germline BRCA1 / BRCA2 testing (second line) variable
- Directed biomarkers (i.e., MSI high, TRK, mTOR inhibitors, RET, etc.) are warranted (Oncol Lett 2021;22:512, Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:1665)
- If any are positive, the relevant targeted agents can be utilized in concert with the standard chemotherapy regimen
- In PDL1 positive TNBC, pembrolizumab and chemotherapy significantly increased event free survival in high risk early stage TNBC patients (N Engl J Med 2020;382:810)
- HER2 enriched
- Surgery, anti-HER2 agents and chemotherapy with or without irradiation (depending on surgical, pathological and clinical factors)
- Neoadjuvant therapy may be employed; pathologic complete response (pCR) in HER2 positive (nonluminal) tumors is associated with excellent prognosis (J Clin Oncol 2012;30:1796, Cancer Treat Rev 2020;84:101965)
- Chemotherapy and anti-HER2 agents (i.e., trastuzumab / Herceptin®, pertuzumab / Perjeta®) show marked clinical benefit for HER2 positive patients (N Engl J Med 2005;353:1659, Lancet Oncol 2011;12:236, Lancet 2017;389:1195)
- Patients may develop de novo and acquired resistance to anti-HER2 agents (Front Oncol 2012;2:62)
- Additional agents for advanced HER2 positive breast cancer include neratinib, lapatinib and T-DM1 (Am J Cancer Res 2020;10:1045, Cancer 2020;126:4278)
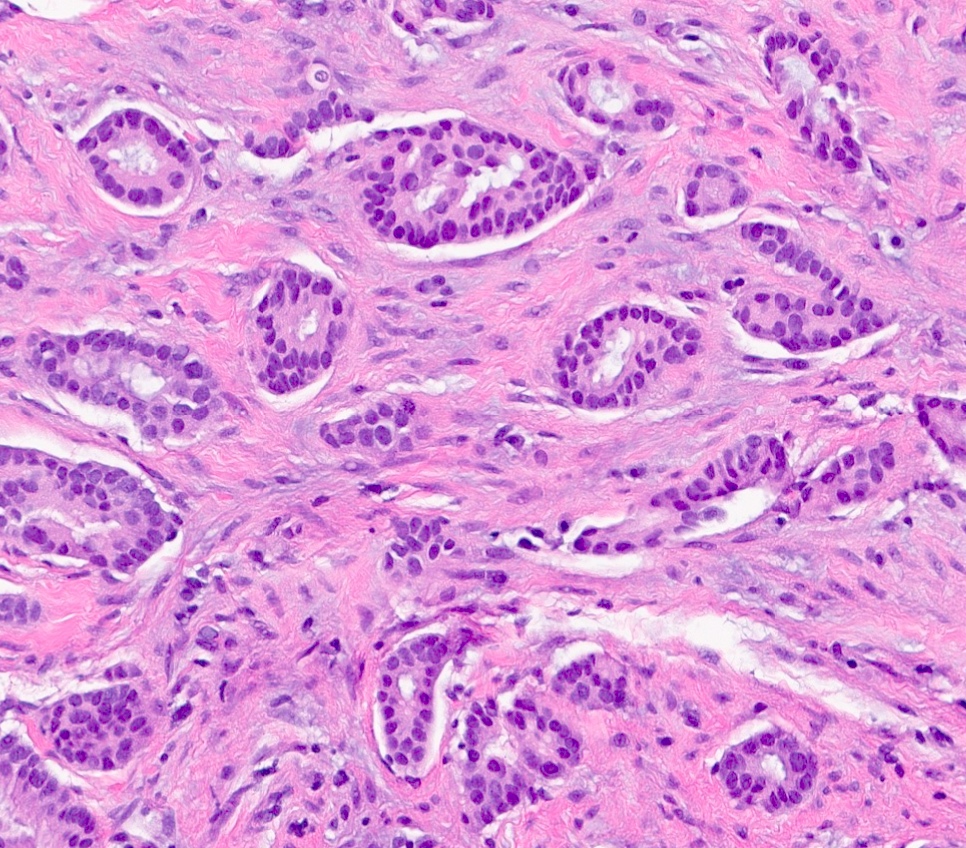
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Luminal
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, no special type (IDC, NST)
- Also tubular, mucinous, invasive lobular carcinoma (classic and variants), cribriform, invasive carcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation, micropapillary, some apocrine / oncocytic carcinomas
- Luminal A: IDC, NST, grade 1 or 2
- ER positive, PR positive, HER2 negative, Ki67 low
- Luminal B: IDC, NST, grade 2 or 3
- ER positive, HER2 positive (Ki67 and PR can show any degree of expression)
- ER positive, PR negative or low, HER2 negative, Ki67 high
- Luminal A: IDC, NST, grade 1 or 2
- Triple negative (J Pathol 2008;216:141, Breast Care (Basel) 2020;15:327, Semin Cancer Biol 2021;72:136)
- ER negative, PR negative, HER2 negative, includes high and low grade tumors
- High grade TNBC: IDC, NST grade 3, spindle cell metaplastic breast carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, apocrine carcinoma
- Low grade TNBC: salivary gland-like tumors (secretory carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, acinic cell carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma), tall cell carcinoma with reverse polarity, low grade metaplastic carcinomas (adenosquamous carcinoma, low grade fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma)
- Broken down into basal-like type 1, basal-like type 2, mesenchymal and luminal androgen receptor
- Debated distinct subtypes include immunomodulatory (IM) (high rates of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes [TILs]) and mesenchymal stem-like (MSL) (high levels of tumor associated mesenchymal tissue)
- Immunomodulatory and mesenchymal stem-like characteristics that may be present in different degrees of all TNBC subtypes
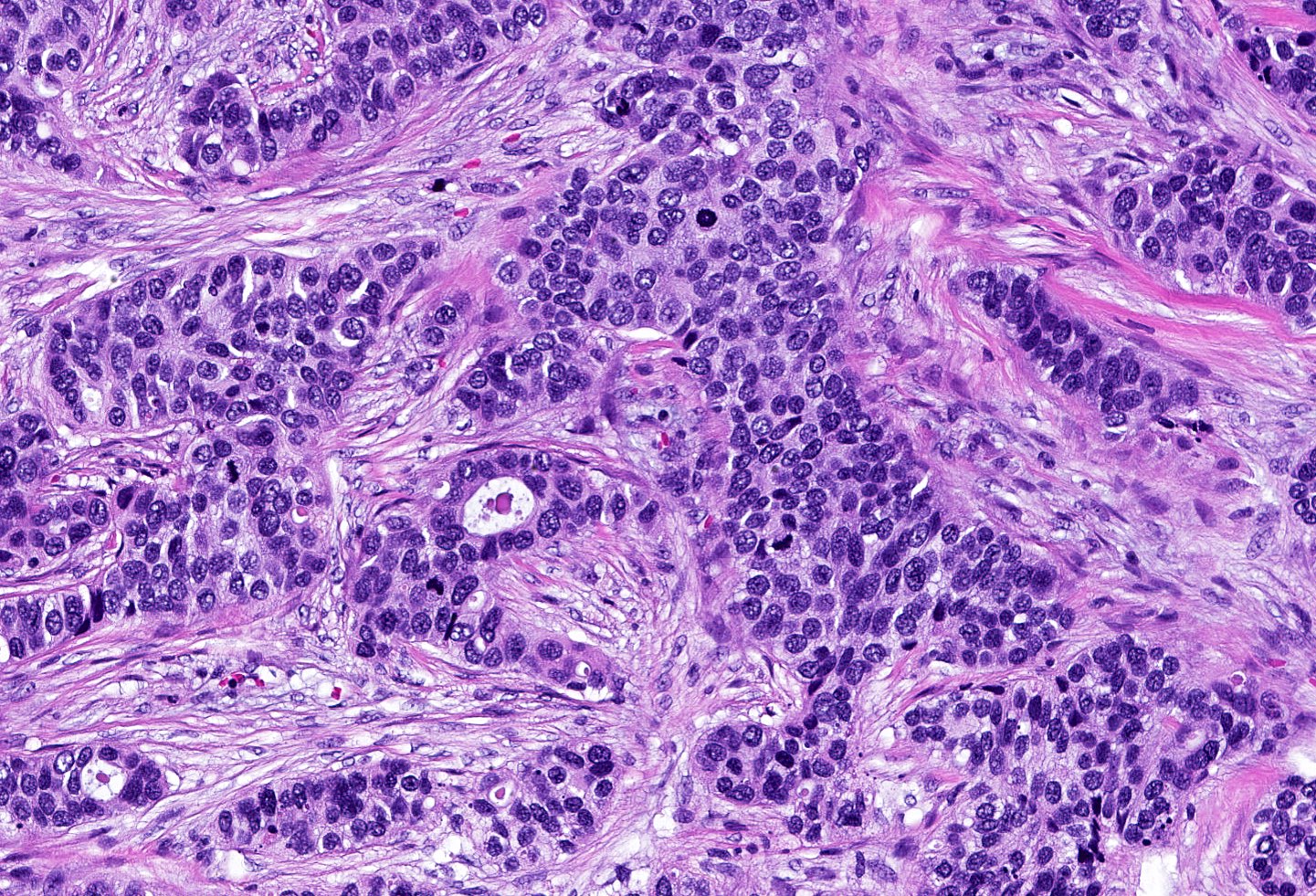
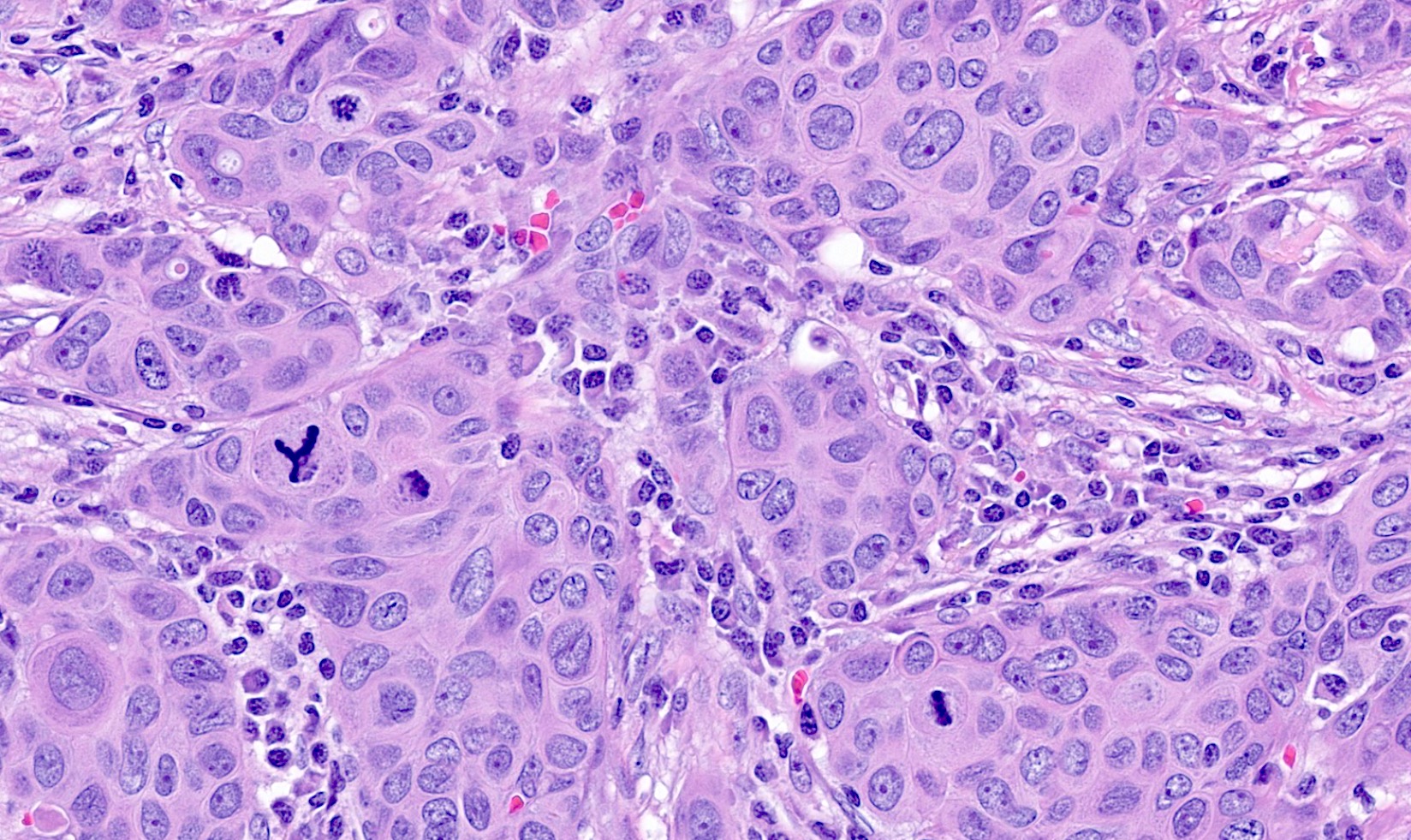
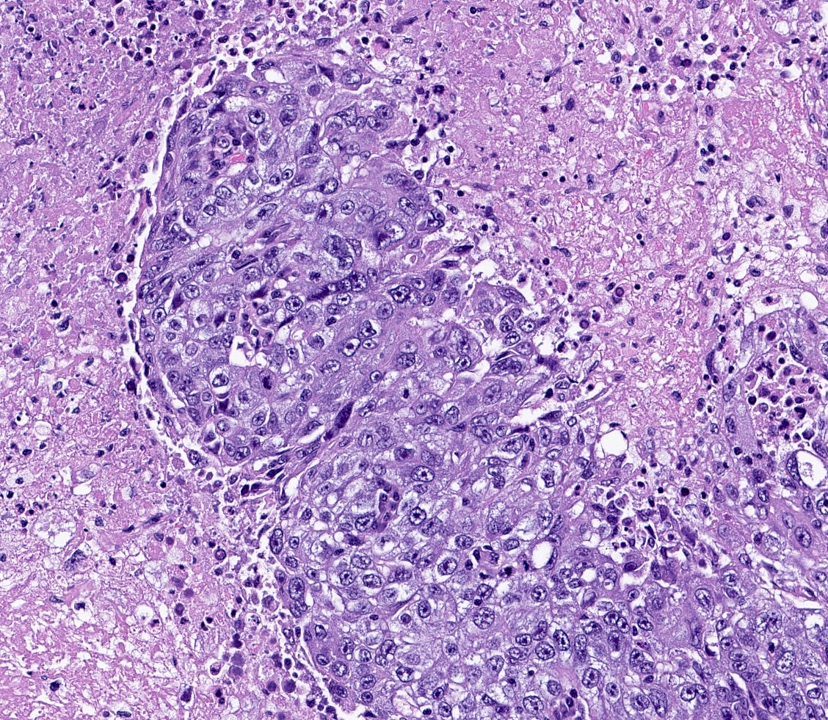
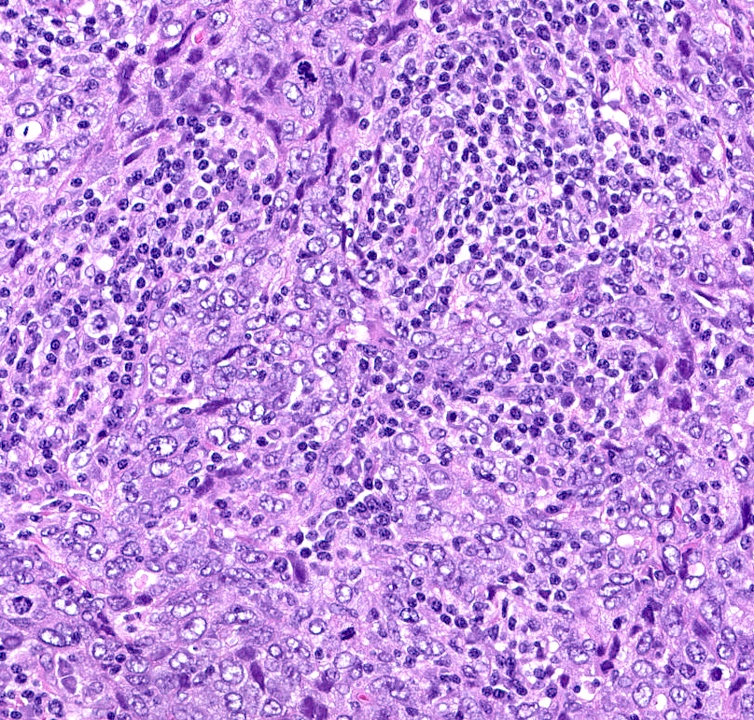
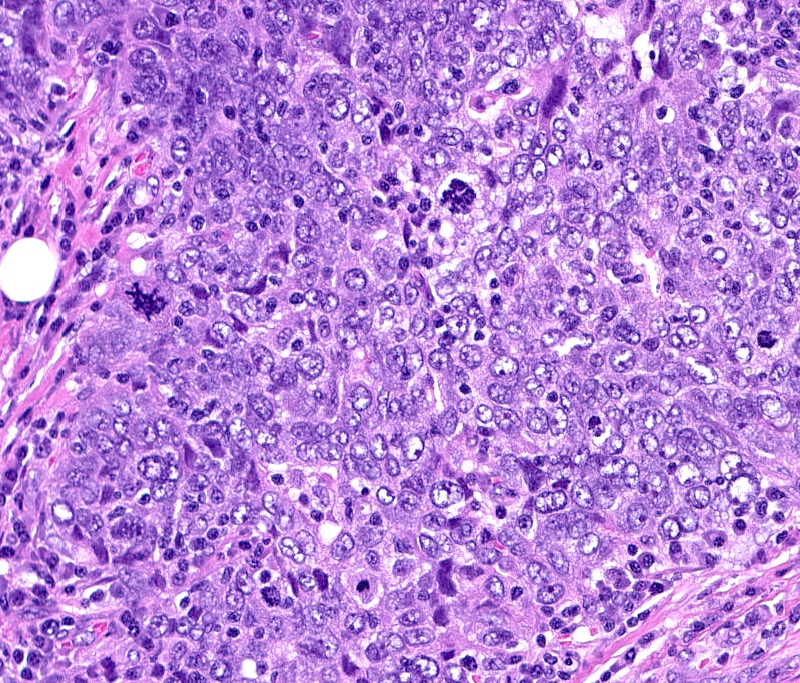
- Basal-like: high grade IDC, NST, solid tumor growth with pushing borders, geographic necrosis, nuclear pleomorphism, brisk inflammatory infiltrate, high mitotic index, high Ki67
- Most express basal cytokeratins (keratin 5/6, 14, 17) and EGFR
- Medullary (immunomodulatory), metaplastic (mesenchymal and mesenchymal stem-like), adenoid cystic, acinic cell, secretory carcinoma
- Molecular apocrine: invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) (pleomorphic), apocrine
- Breast carcinomas with apocrine differentiation may cluster into several intrinsic subtypes, including luminal (ER positive), HER2 enriched and molecular apocrine (also known as luminal AR)
- ER negative, PR negative, HER2 negative, includes high and low grade tumors
- HER2 enriched
- Predominantly IDC, NST of high histological grade
- Tumor cells frequently have pleomorphic nuclei and more abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm than triple negative cancers
- Ki67 proliferative rate is high (20 - 60%)
- Frequently associated with high grade comedo ductal carcinoma in situ
- Some pleomorphic invasive lobular carcinoma are HER2 positive
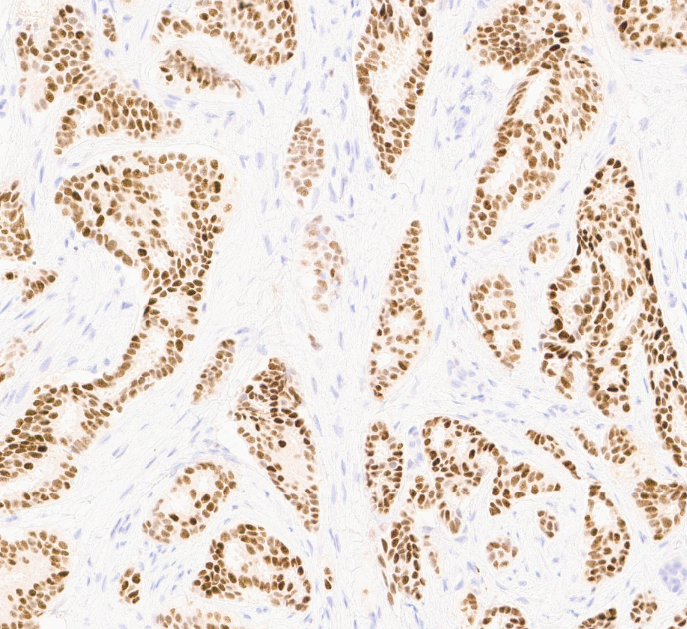
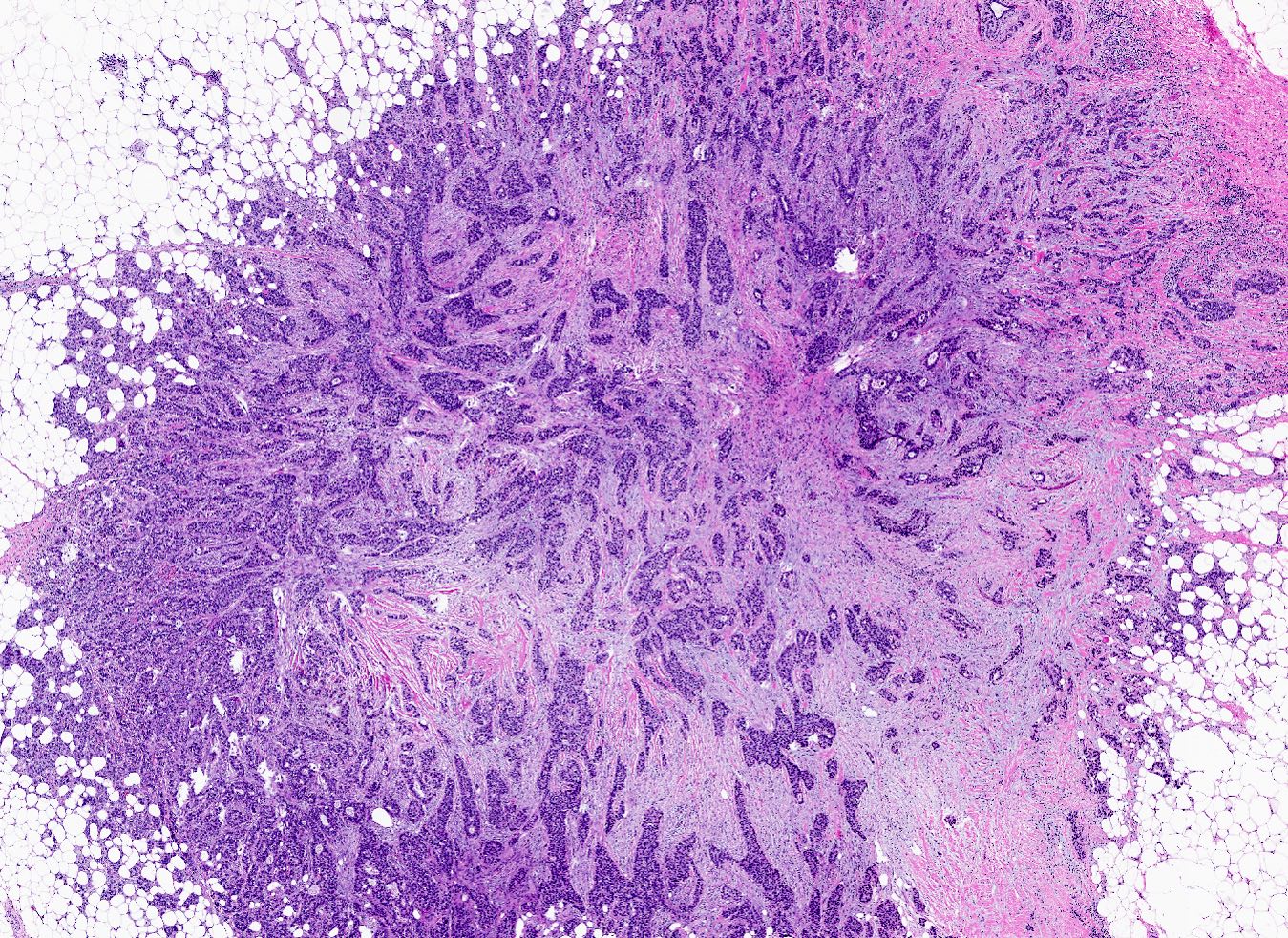
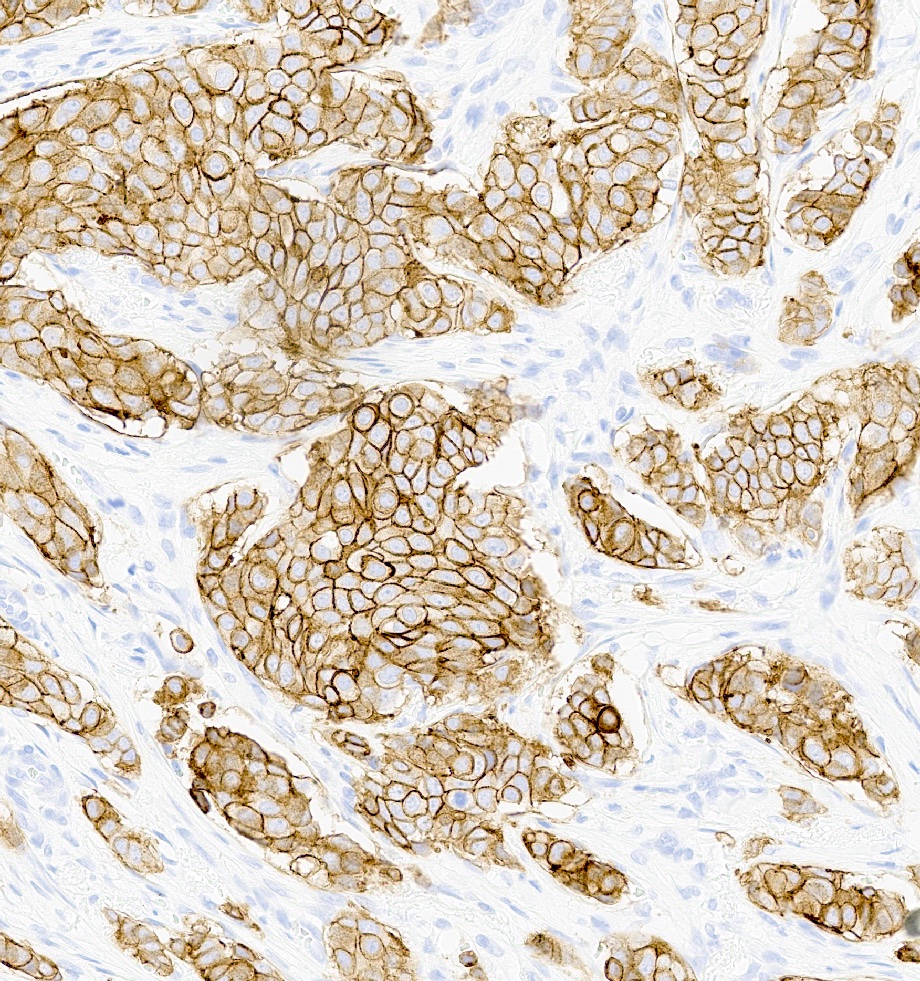
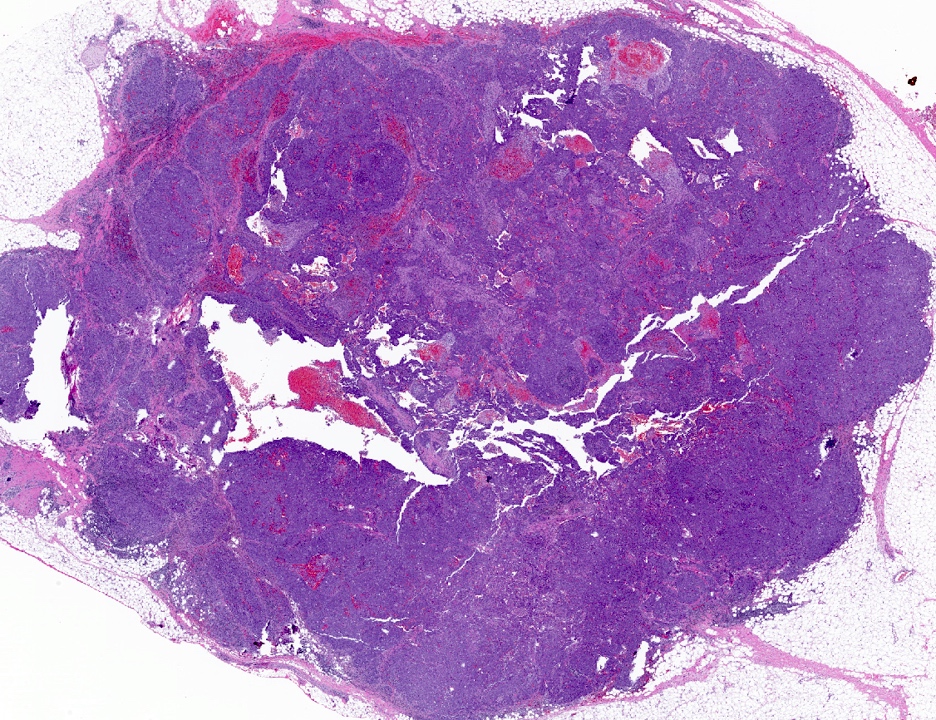
Microscopic (histologic) images
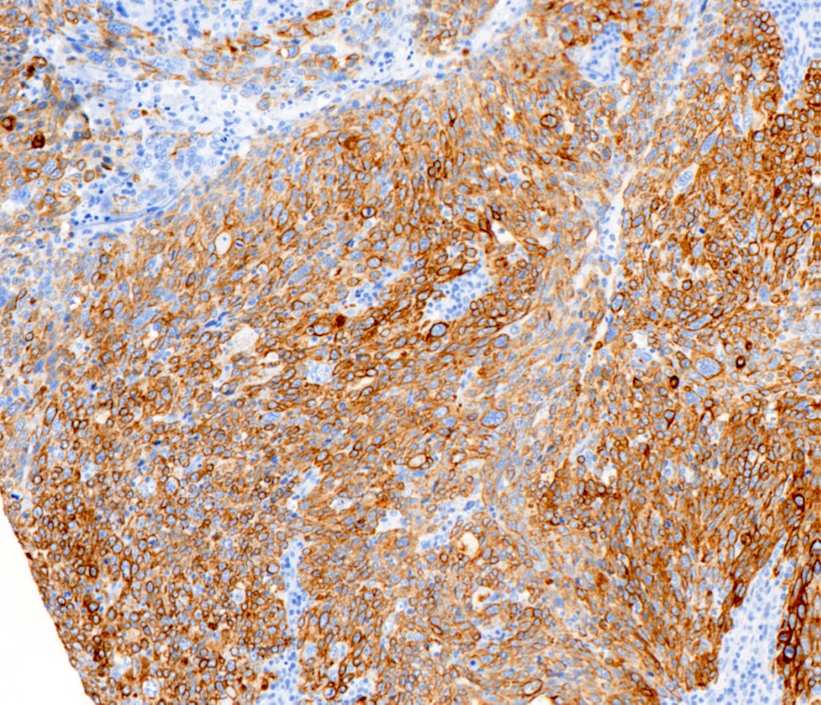
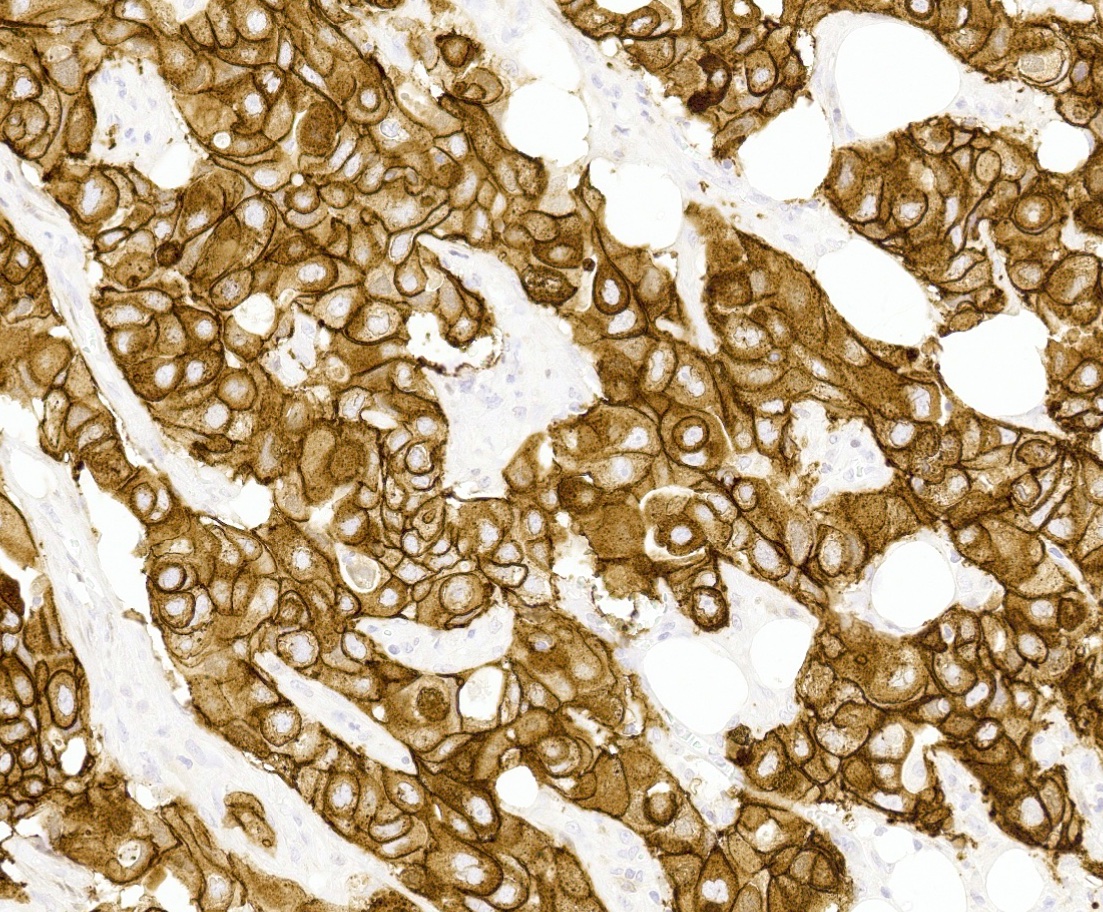
Positive stains
- Luminal
- Triple negative
- High molecular weight basal cytokeratins: CK5/6, CK14, CK17 (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429)
- EGFR (J Lab Physicians 2015;7:79)
- TRPS1 (positive in 86% of triple negative and metaplastic carcinomas)
- GATA3 (nonmetaplastic: 51%, metaplastic: 21%)
- HER2 enriched
- Reference: Mod Pathol 2021;34:710
Negative stains
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Luminal A (Nature 2012;490:61)
- PIK3CA (45%) > GATA3 (14%) > TP53 (12%)
- Gains 1q and 16p, loss 16q
- Luminal B (Nature 2012;490:61)
- PIK3CA (29%) and TP53 (29%) > GATA3 (15%)
- Gains 1q, 8q, 17q, 20q; losses 1p, 3q, 8p, 13q, 16q, 17p, 22q
- Triple negative (J Clin Invest 2011;121:2750, Nature 2012;490:61, PLoS One 2016;11:e0157368, Semin Cancer Biol 2021;72:136, Annu Rev Pathol 2022;17:181)
- TP53 (80%) > PIK3CA (9%) > GATA3 (2%)
- Many gains and losses across the entire genome
- Distinct gene profiles are associated with each TNBC subtype
- Basal-like 1
- Cell cycle and cell division pathways, BRCA1 / BRCA2 in minority
- Basal-like 2
- Growth factor signaling (EGFR, NGF, MET, Wnt / beta catenin)
- Luminal androgen receptor positive
- Steroid synthesis, androgen metabolism
- Mesenchymal-like
- Cell motility, cell differentiation
- Mesenchymal stem-like
- Cell motility, cell differentiation, genes associated with stem cells
- Growth factor signaling pathways (EGFR / PDGF)
- Low levels of claudin expression
- Epithelial mesenchymal transition
- Immunomodulatory
- Immune cell processes (TH1 / TH2, NK cell, B, T cell, antigen processing and presenting cytokine signaling)
- Basal-like 1
- HER2 enriched (Nature 2012;490:61)
- TP53 (72%) > PIK3CA (39%) > GATA3 (2%)
- Many gains and losses across entire genome
- HER2 / neu gene is a member of a family of genes encoding transmembrane receptors for growth factors, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), HER2, HER3 and HER4 (N Engl J Med 2005;353:1652)
- Amplification of the HER2 gene (ERBB2 gene) at the DNA level results in protein overexpression (Science 1989;244:707)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. Luminal A. Invasive breast tumors classified as luminal A by gene expression profiling are typically low grade invasive ductal carcinomas. By definition, the luminal A intrinsic subtype shows strong expression of hormone receptors (ER and PR) and is negative for HER2 / neu overexpression and amplification. Special histologic subtypes that cluster with the luminal A subtype include tubular, mucinous and cribriform carcinomas. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because basal-like, HER2 enriched and luminal B tumors are characteristically high grade.
Comment Here
Reference: Molecular subtypes
Comment Here
Reference: Molecular subtypes
Board review style question #2
A 67 year old woman underwent a partial mastectomy for a breast tumor shown in the image. Microscopic sections revealed a high grade invasive ductal carcinoma growing as a solid mass with pushing borders, areas of necrosis, brisk mitoses and abundant tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. The tumor was negative for ER, PR and HER2 and was classified as basal-like by gene expression profiling. What other immunostain(s) might be positive?
- Androgen receptor (AR)
- EGFR
- KIT
- Synaptophysin
Board review style answer #2
B. EGFR. Basal-like breast cancers are typically high grade invasive ductal carcinoma of no special type that show solid tumor growth with pushing borders, geographic necrosis, nuclear pleomorphism, a brisk inflammatory infiltrate, a high mitotic index and a high proliferative index with Ki67. Most basal-like breast cancers express basal cytokeratins (keratin 5/6, 14, 17) and EGFR. Answer A is incorrect because while a minor proportion of triple negative breast cancers can express androgen receptor, the prototypical AR positive breast tumor has apocrine features (apocrine carcinoma). Answer C is incorrect because KIT is not characteristically expressed in breast carcinomas. Answer D is incorrect because synaptophysin may be expressed in breast tumors with neuroendocrine differentiation, which typically cluster within the luminal category.
Comment Here
Reference: Molecular subtypes
Comment Here
Reference: Molecular subtypes