Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Jaffer S. Pleomorphic adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmixedtumor.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Biphasic benign breast tumor with varying epithelial and stromal components
Essential features
- Similar to pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland in morphology, immunohistochemistry, prognosis and treatment, except rarer in breast
- Hypothesized to be a variant of intraductal papilloma
- Biphasic benign tumor easily misdiagnosed as mucinous or matrix producing metaplastic carcinoma
Terminology
- Also called benign mixed tumor, chondroid syringoma (in skin)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 1906 - current: < 100 case reports (Histopathology 2016;68:45)
Sites
- Periareolar, upper outer quadrant
Pathophysiology
- Breast and salivary glands are embryologically similar exocrine glands that originate from the same ectodermal layer and can differentiate towards dual epithelial myoepithelial cell differentiation
Etiology
- May derive from divergent differentiation of a single pluripotent stem cell resulting in epithelial myoepithelial cell differentiation and stroma (Hum Pathol 1991;22:1206)
- Periareolar location:
- Large ducts with numerous myoepithelial cells (Clin Oncol 1982;8:361)
- Arise in association with intraductal papilloma and therefore may be the same entity (Am J Surg Pathol 1990;14:913)
Clinical features
- Age range: 19 - 85 years
- F > M, only 3 case reports in men (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:497)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis may be made on core biopsy or FNA with radiologic correlation but definitive with excision
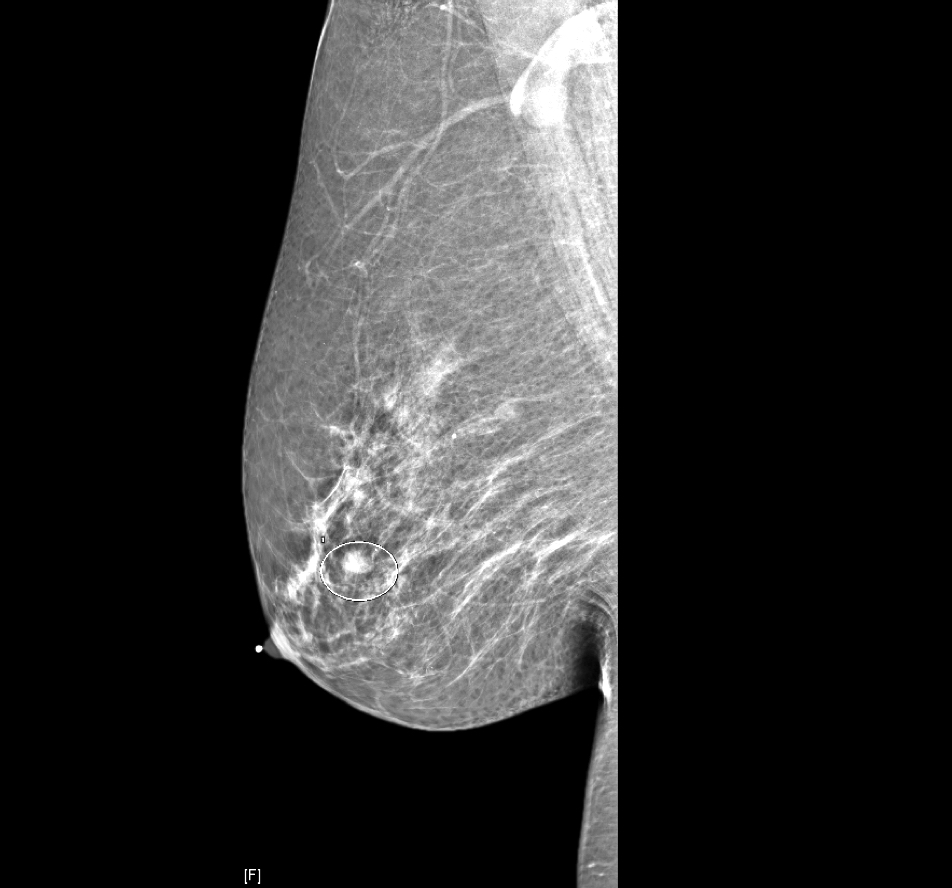
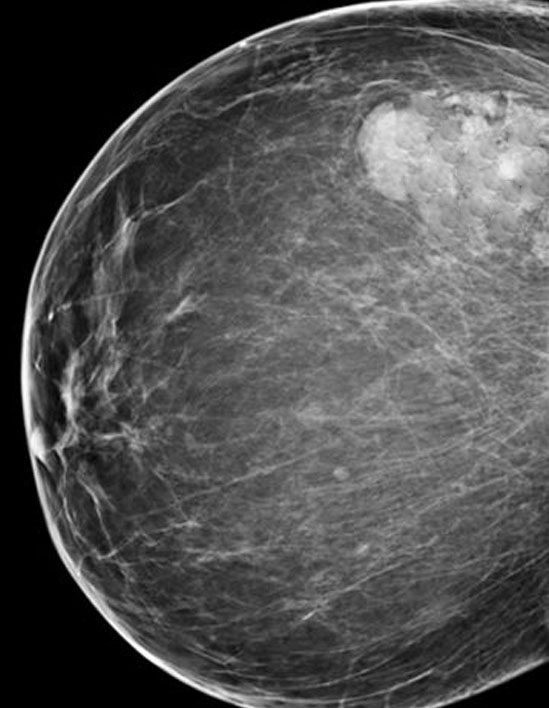
Radiology description
- Mammogram: circumscribed round lesion simulating fibroadenoma, variable calcifications (Case Rep Pathol 2015;2015:172750)
- Ultrasound: homogeneously smooth lobulated internal mass or complex cystic mass, resembling intraductal papilloma
- Tomography: isointense mass with internal septations
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Low grade indolent tumor
- Recurrences (3 case reports) due to inadequate margins or multifocal tumors (Hum Pathol 1991;22:1206, Cancer 1988;61:997, Breast J 2007;13:418)
Case reports
- 55 year old woman with subareolar breast mass (Pathol Res Pract 2005;201:333)
- 57 and 78 year old women with breast masses (BMJ Case Rep 2015;2015:bcr2015210906)
- 59 year old woman with pleomorphic adenoma of the breast (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:474)
- 70 year old woman with 2 cm mass, electron microscopy study (Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93:795)
- 71 year old woman with fine needle aspiration of 23 mm breast mass (Diagn Cytopathol 2018;46:56)
Treatment
- Wide excision with clear margins (2 - 5 mm) (Breast J 2007;13:418)
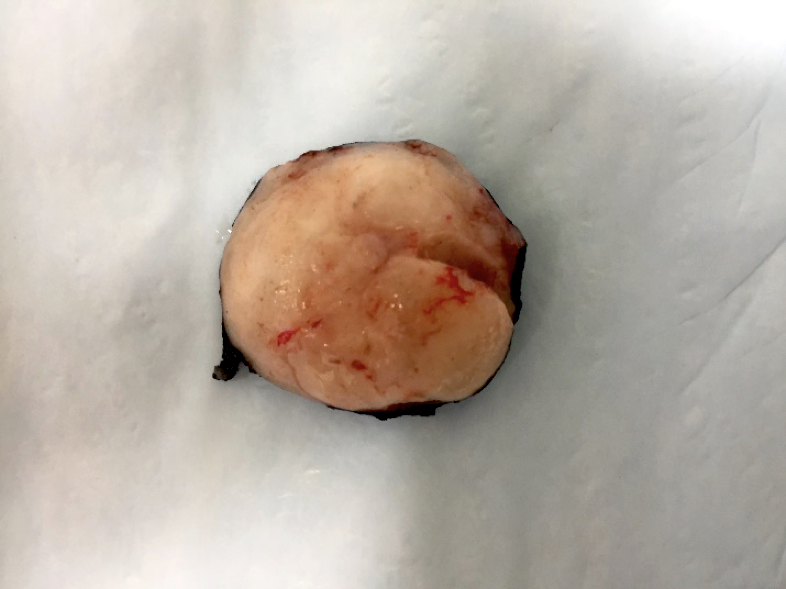
Gross description
- Circumscribed yellow white gritty solid nodules > polypoid, multinodular or satellite lesions
- Size: typically 0.8 - 4.5 cm (mean = 2.0 cm) (South Med J 1975;68:97)
- Intraductal nodule with cystification
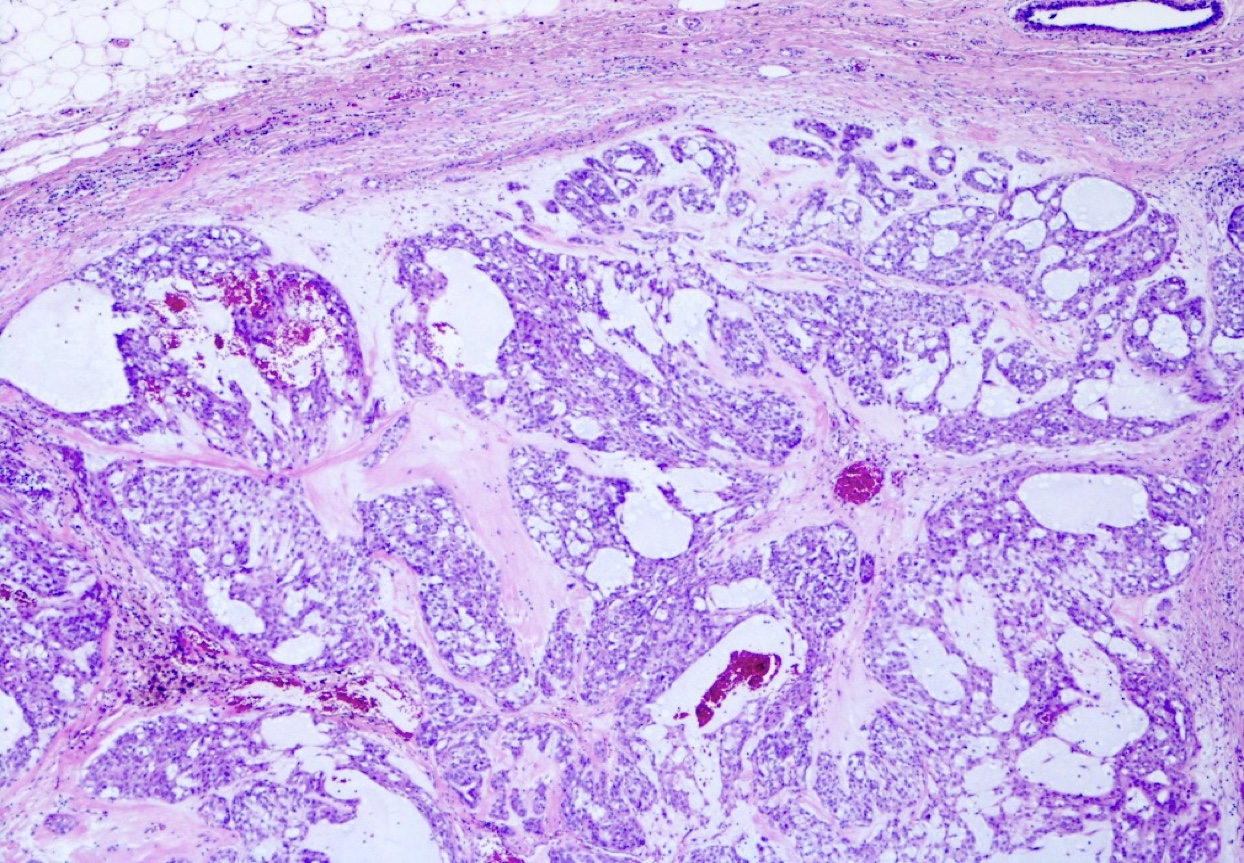
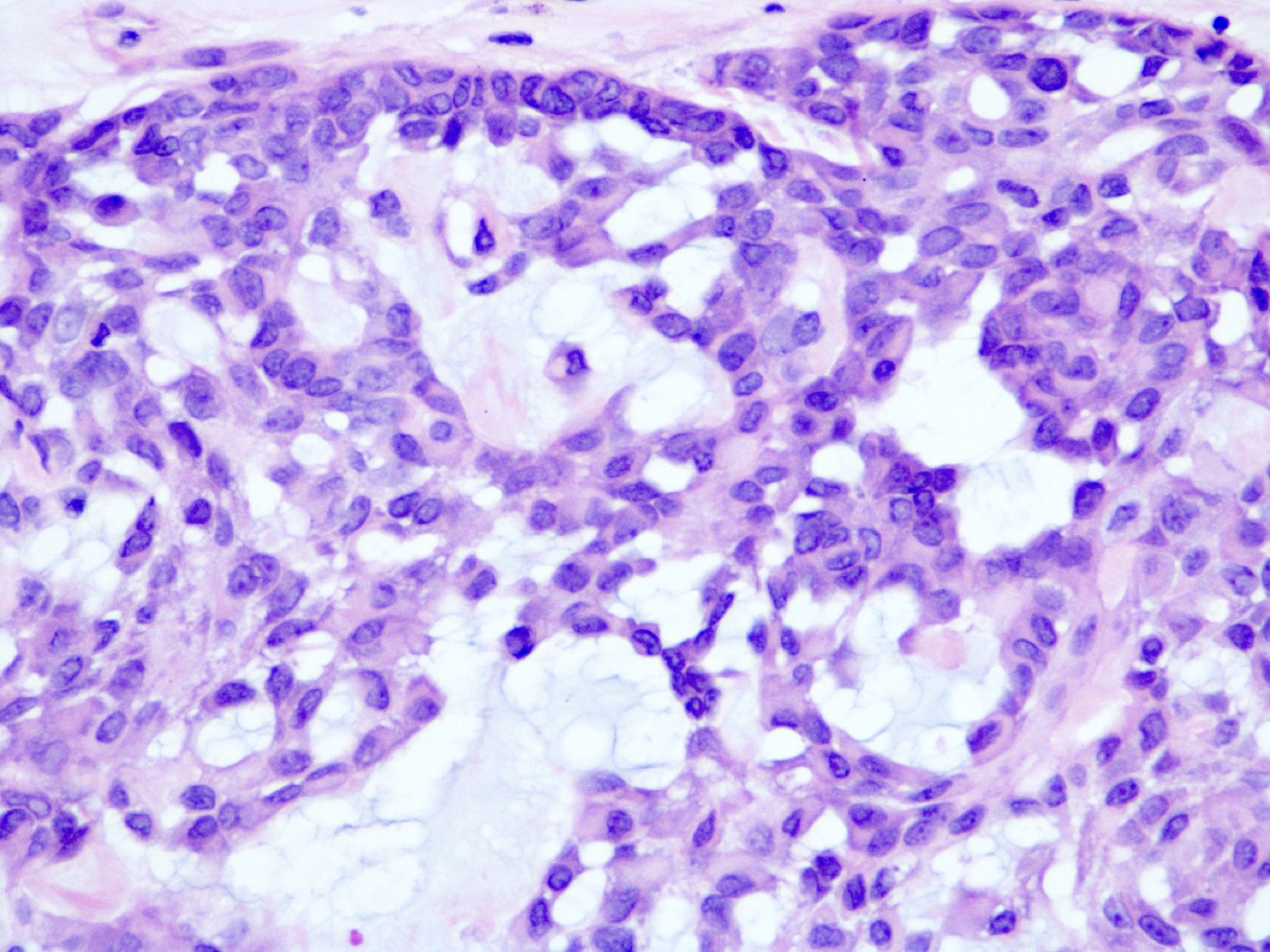
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Admixture of epithelial and myoepithelial cells embedded in a chondromyxoid stroma, may show chondroid or osseous metaplasia
- Architecture includes tubules, islands, cords, trabeculae, sheets or pseudoglandular structures lined by 2 cell types
- Inner epithelial cells: cuboidal or columnar epithelial cells, with or without apocrine or squamous metaplasia
- Outer myoepithelial cells: polygonal, plasmacytoid, fusiform or stellate with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm
- No atypia, mitoses, necrosis or infiltrative growth
- Rare malignant transformation
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma = 3 cases (Virchows Arch 2005;446:142)
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma = 1 case (Med J Armed Forces India 2011;67:74)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Cellular smears consisting of epithelial and myoepithelial cell clusters and sheets arranged in branched glandular structures
- Epithelial cells: round cells with abundant cytoplasm
- Myoepithelial cells: stellate, plasmacytoid
- Stroma: myxochondroid, light green on Pap, metachromatic (red-purple) on Giemsa
- No atypia, mitoses or necrosis
- Pitfall for misdiagnosis as mucinous or matrix producing metaplastic carcinoma (Breast Dis 2017;37:105)
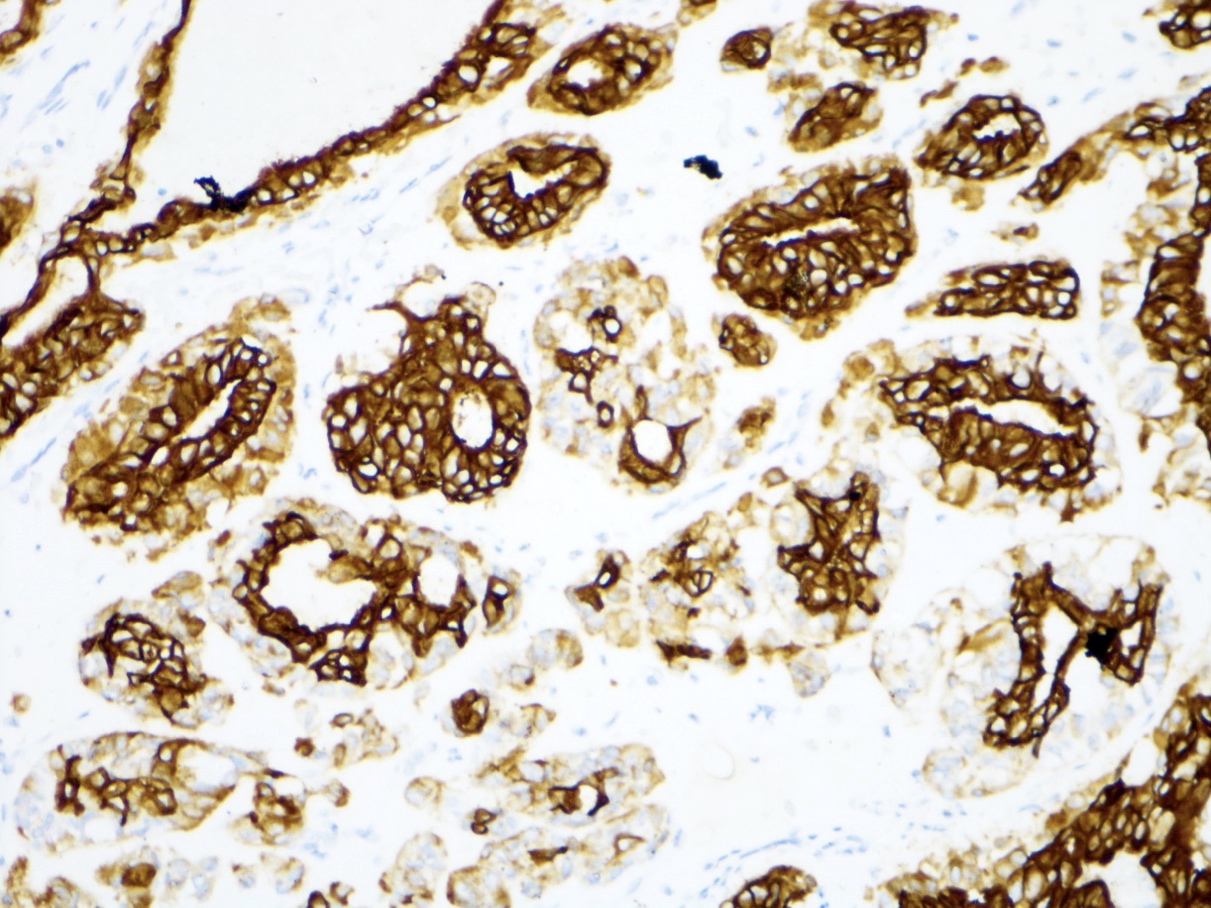
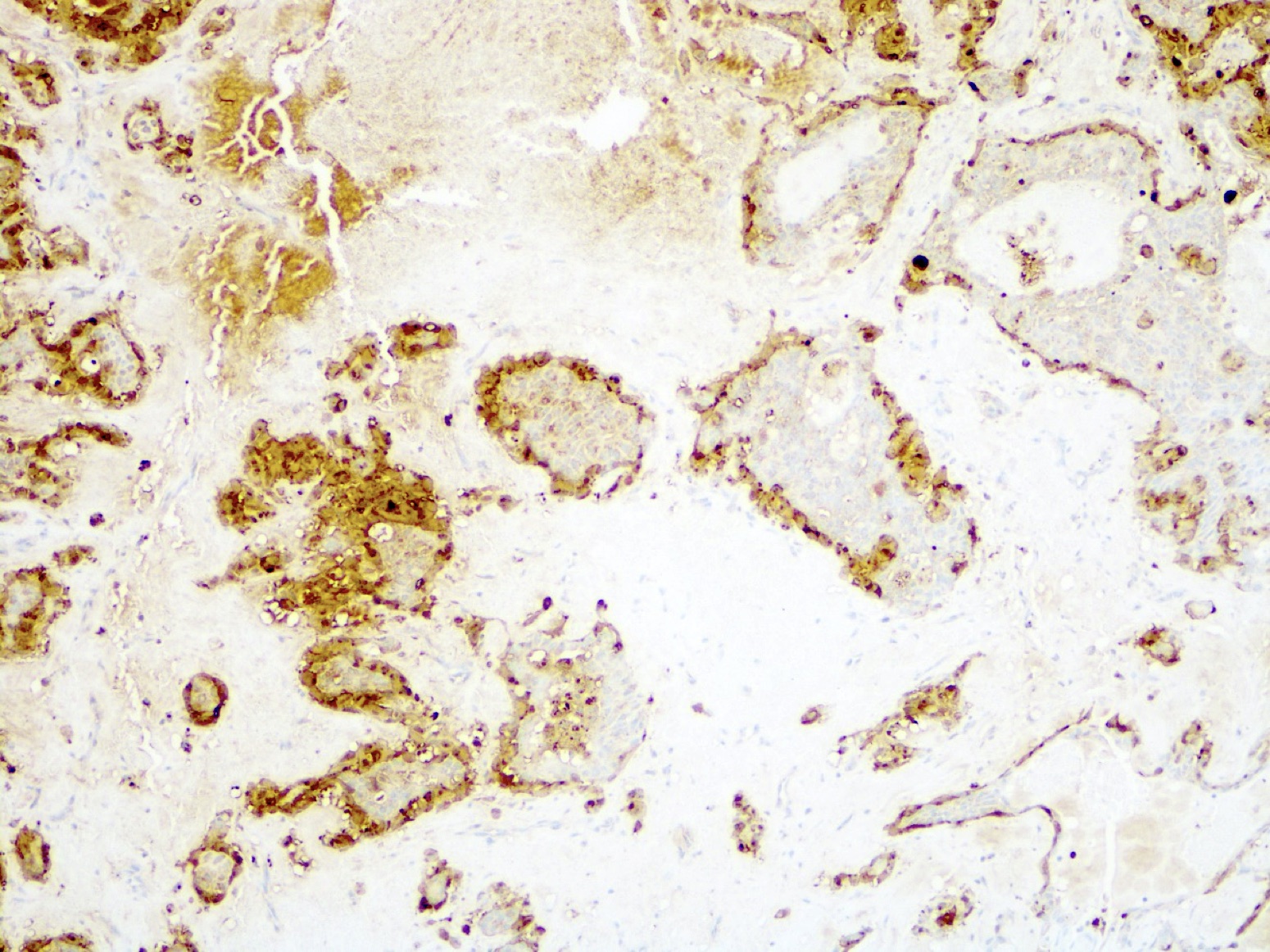
Positive stains
Electron microscopy description
- Biphasic tumor (Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93:795)
- Epithelial: microvilli and lumina
- Myoepithelial: spindled stromal cells with intermediate filaments, dense bodies and intercellular junctions
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Diploid
- Deletion of PLAG1 by FISH
- HMGIC and HGMIY not rearranged by FISH (Pathol Res Pract 2005;201:333)
- Similar to ear, nose and throat sites, HMGA2-WIFI and CTNNB1-PLAG1 have been identified in case reports (NPJ Breast Cancer 2020;6:20)
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, mass, lumpectomy:
- Pleomorphic adenoma, 3.2 cm (see comment)
- Surgical margins, negative for tumor
- Comment: The lesion is a circumscribed benign biphasic tumor by morphology and immunohistochemistry. AE1/3 and p63 are expressed. There is associated myxoid stroma. These findings are consistent with pleomorphic adenoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Intraductal papilloma with chondromyxoid stroma:
- Chondromyxoid stroma is focal, has uniform composition and is a minor component
- Metaplastic carcinoma, matrix producing:
- May be difficult to differentiate on a core needle biopsy
- Infiltrative tumor, has atypia, mitoses, necrosis
- Ductal adenoma:
- Lacks myxoid stroma
- Intraductal / within duct lumen
- May be a variant of intraductal papilloma
- Mucinous carcinoma:
- Infiltrative tumor, has atypia, mitoses, mucin
- With or without ductal carcinoma in situ
- Alcian blue hyaluronidase resistant (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:474)
- Adenomyoepithelioma:
- Lacks chondromyxoid stroma
- Phyllodes tumor with chondromyxoid differentiation:
- Leafy architecture with cellular stroma
- Stroma with mitotic figures
- Chondromyxoid areas with atypia
Additional references