Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Mixed NST. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmixedNST.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Mixture of ductal carcinoma NOS and lobular carcinoma
Terminology
- Not part of WHO breast classification
Clinical features
- Age of onset similar to infiltrating ductal carcinoma
- Survival similar to pure ductal or lobular types
- Compared to pure ductal carcinomas, have higher rate of second primary breast cancers (World J Surg Oncol 2010;8:51, Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;114:243)
- Compared to pure lobular carcinomas, have lower rate of synchronous contralateral breast cancer
- 4% of breast carcinomas
- 89% have DCIS, 31% have LCIS
- 41% have positive lymph nodes at diagnosis
- May have higher plasma levels of Soluble human leukocyte antigen s(HLA)-G (Anticancer Res 2012;32:1021)
Microscopic (histologic) description
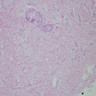
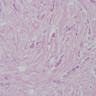
- Definite features of invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma in same tumor
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- E-cadherin patterns include no staining (similar to lobular), full staining (similar to ductal) or staining of ductal areas only (Am J Clin Pathol 2001;115:85)
Differential diagnosis
- Tubulolobular carcinoma: typical areas of invasive lobular carcinoma with cords of single file cells, which merge with small round to angulated tubules with minute or undetectable lumina
- Collision of two separate neoplasms