Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Nebbache H, Bachert SE. Tubulolobular carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignanttubulolobular.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Carcinoma with mixed histologic features of both tubular carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma (Virchows Arch 2006;448:500)
Essential features
- Carcinoma with areas of tubular carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma
- Most are estrogen receptor (ER) positive and HER2 negative
- Not synonymous with invasive carcinoma with ductal and lobular features
Terminology
- In the 5th edition of the WHO Classification of Breast Tumours, tubulolobular carcinoma is considered a histologic variant of invasive lobular carcinoma; however, many authors consider this histological pattern a variant of invasive breast carcinoma of NST (Diagnostics (Basel) 2022;12:2658)
ICD coding
- ICD-11: XH3RK9 - tubulolobular carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Rare; 1 - 2% of all invasive breast carcinomas
- Predominantly in women; has been reported in men
- Mean age is 59 - 60 years (range: 43 - 79) (Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2012;41:681, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587)
Sites
- Breast
- Single case report in the anogenital region (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1193)
Etiology
- Etiology is multifactorial: genetics, hormones, diet, age and reproductive factors are risk factors (WHO 5th edition)
- ER positive pathway of breast cancer development characterized by gains of 1q and losses of 16q (WHO 5th edition)
- See etiologies associated with low grade, ER positive invasive breast cancer of no special type (NST)
- Expression of E-cadherin supports ductal differentiation, despite a dominant lobular growth pattern (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587)
Clinical features
- Can be multifocal (~20%) (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:653)
- Presence of palpable mass (85%) (Eur J Radiol 2006;60:418)
- Usually presents at early pathologic stage, pT1 and N0 disease (75%) (Mod Pathol 2007;20:130)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis can be made on core needle biopsy or resection specimens
Radiology description
- Most common finding on mammography and ultrasound is an irregular mass (Eur J Radiol 2006;60:418)
- Dense stroma may aid in the early detection of these tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587)
Prognostic factors
- Intermediate prognosis between that of classic invasive lobular carcinoma and pure tubular carcinoma (Breast Care (Basel) 2008;3:423)
- 25% of patients present with stage II disease or higher (compared with 0% for tubular carcinomas and 60% for invasive lobular carcinomas) (Mod Pathol 2007;20:130)
- Multifocal disease and positive axillary lymph nodes are more common in tubulolobular carcinoma (60%) compared with tubular carcinomas (33%) (Mod Pathol 2007;20:130, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587)
Case reports
- 60 year old woman with tubulolobular carcinoma of the breast with focal targetoid pattern (Int J Med Sci Public Health 2014;3:1018)
- 64 year old woman with mammary type tubulolobular carcinoma of the anogenital area (Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1193)
- 67 year old woman with tubulolobular carcinoma of the breast with periglandular collagen IV immunostaining (Breast Care (Basel) 2008;3:423)
- 69 year old woman with tubulolobular carcinoma of the breast with grooved and cerebriform nuclei (Diagn Cytopathol 2011;39:54)
- 70 year old woman with tubulolobular carcinoma of the breast with metastases to the colon (Onco Targets Ther 2014;7:435)
Treatment
- Localized excision / mastectomy
- Choice of treatment is based on the size and the tumor stage: localized excision, radical or modified radical mastectomy, hormone therapy and adjuvant therapy (Mod Pathol 2007;20:130)
Gross description
- Ill defined, firm, gray tumor, usually measuring < 2 cm in greatest dimension, ranging in size from 0.5 cm to 2.5 cm (median, 1.4 cm) (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587)
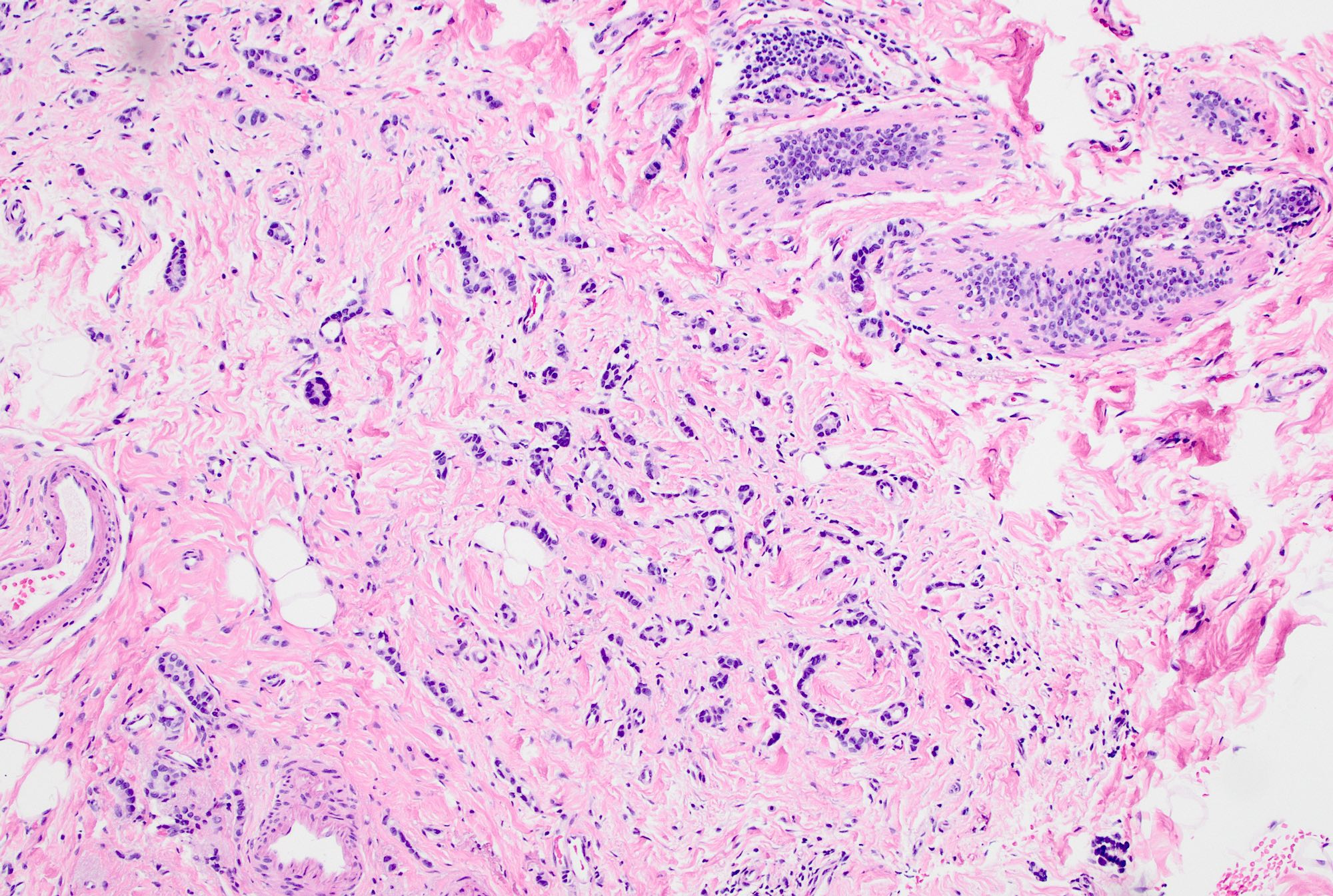
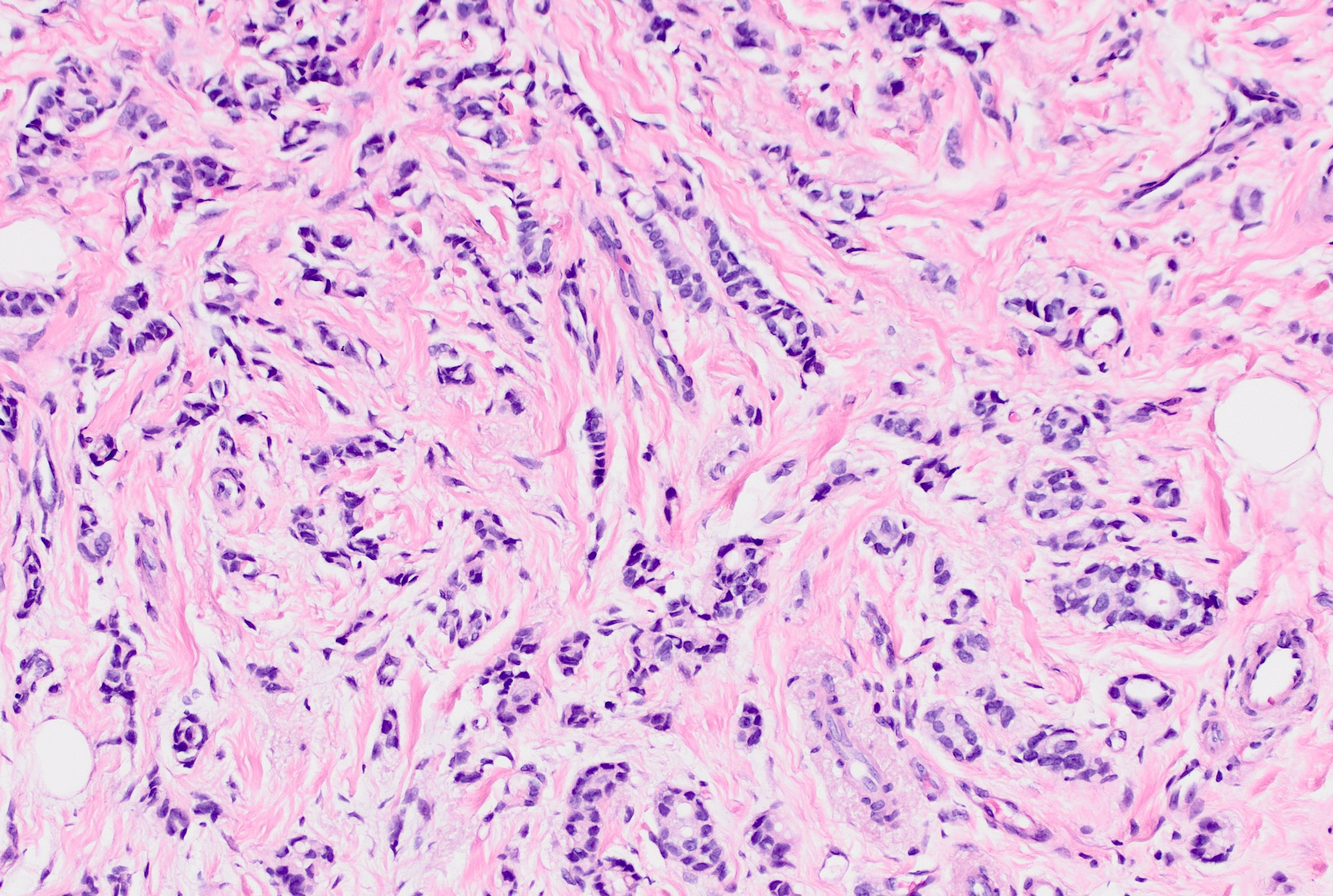
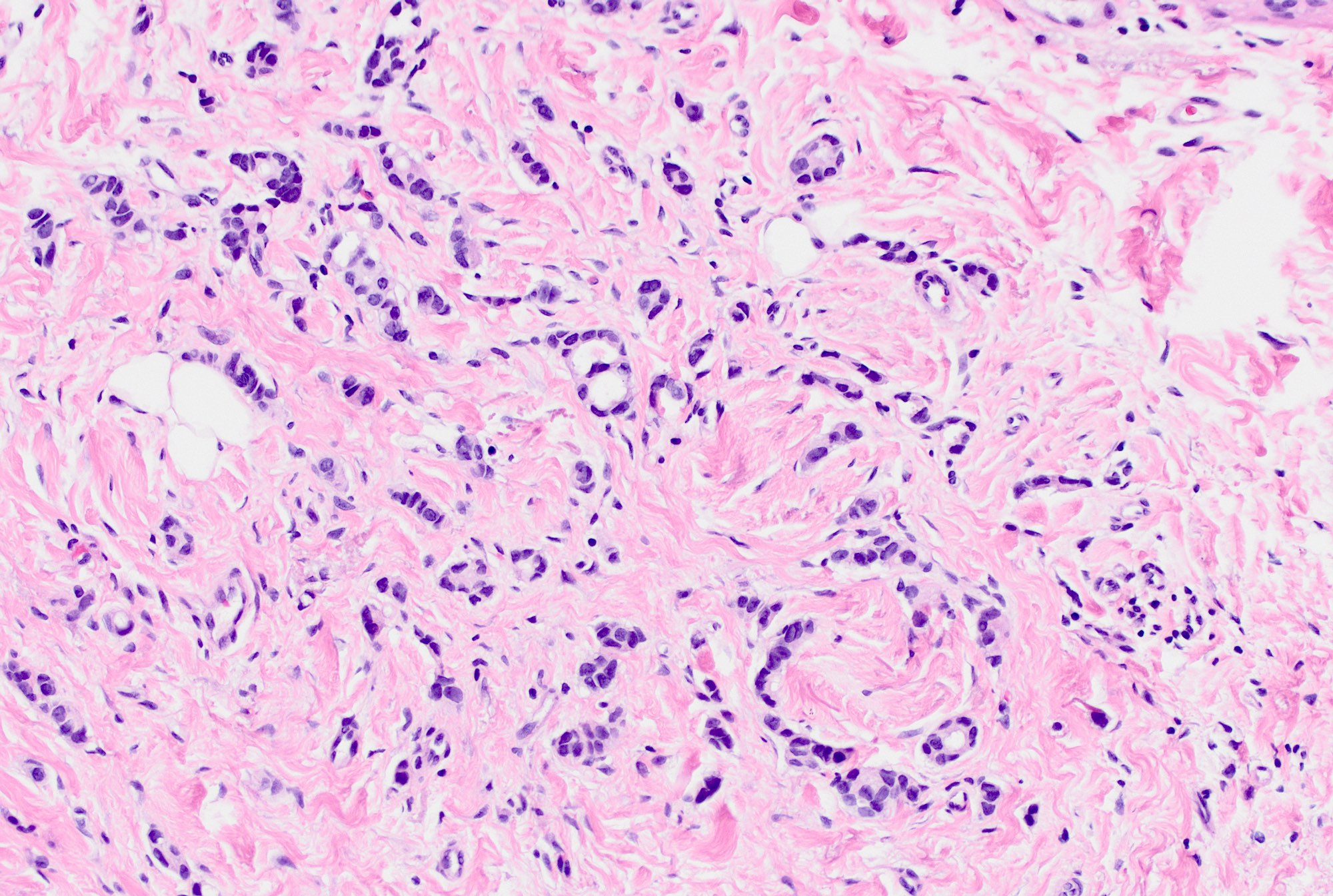
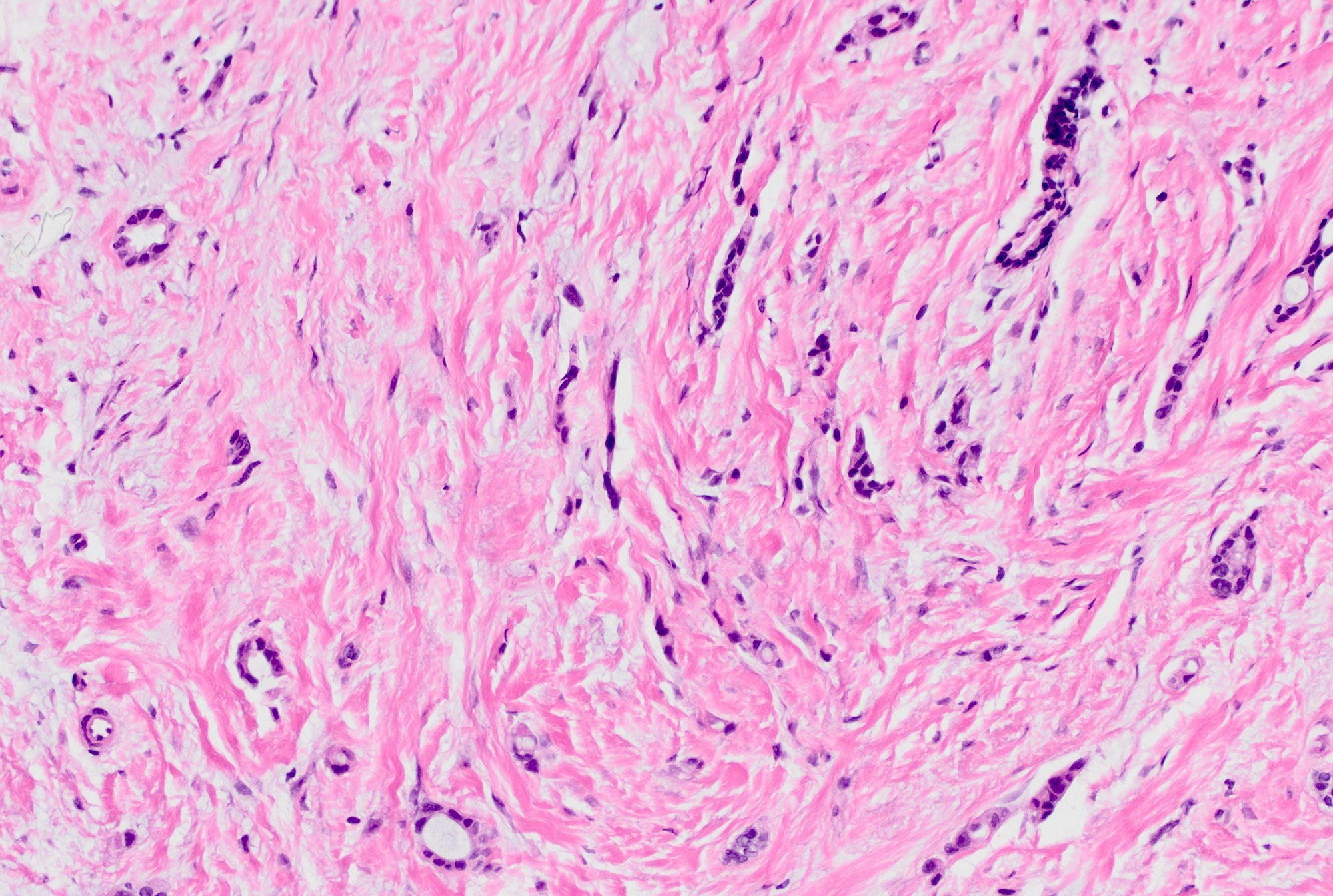
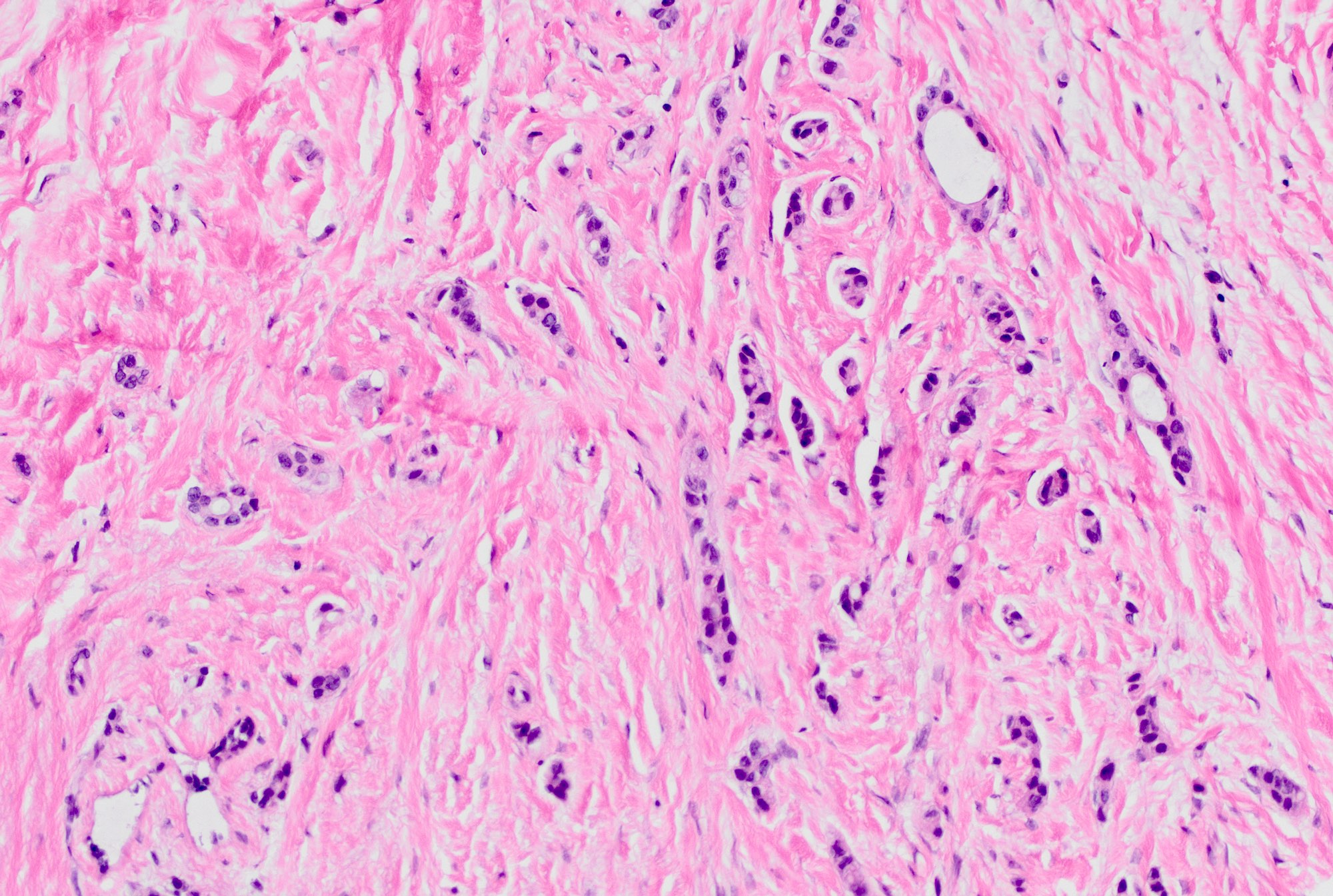
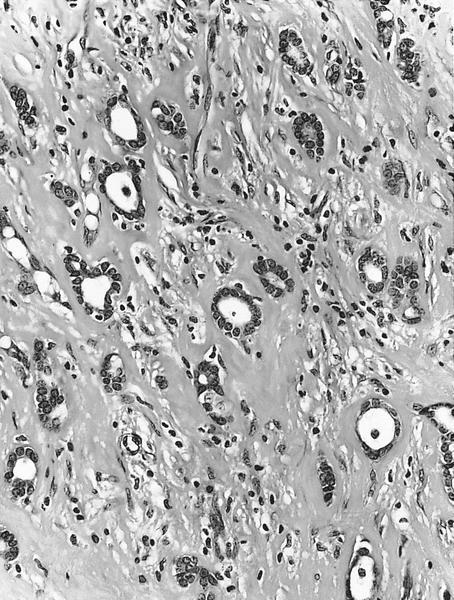
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Invasive tumor with mixed pattern of small tubules with a lobular pattern of infiltration within a dense collagenous stroma often with prominent elastosis
- Tubular component: small, round to angulated tubules with low grade nuclei and variable apical snouts
- Lobular component: single cells, single file cords of cells, often displaying targetoid growth around benign ducts
- Cells are uniform and display low grade nuclear atypia (nuclear grade 1 or 2) with inconspicuous nucleoli and minimal amphophilic cytoplasm
- Cells with lobular growth pattern may show occasional intracytoplasmic lumina and rare signet ring morphology
- Can have variable proportion of tubular and lobular components
- Usually well differentiated (grade 1); can be moderately differentiated
- Nuclear score can be grade 1 - 2
- May have associated ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
- Lacks surrounding myoepithelial cell layer
- References: Mod Pathol 2007;20:130, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587, Breast Care (Basel) 2008;3:423
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Diagnosis can be suggested but not definitively made on cytologic preparations
- Single filing of cells and tubular structure formation
- Low nuclear grade
- Low mitotic rate
- Intracytoplasmic vacuoles and rare nucleoli (Acta Cytol 1996;40:465)
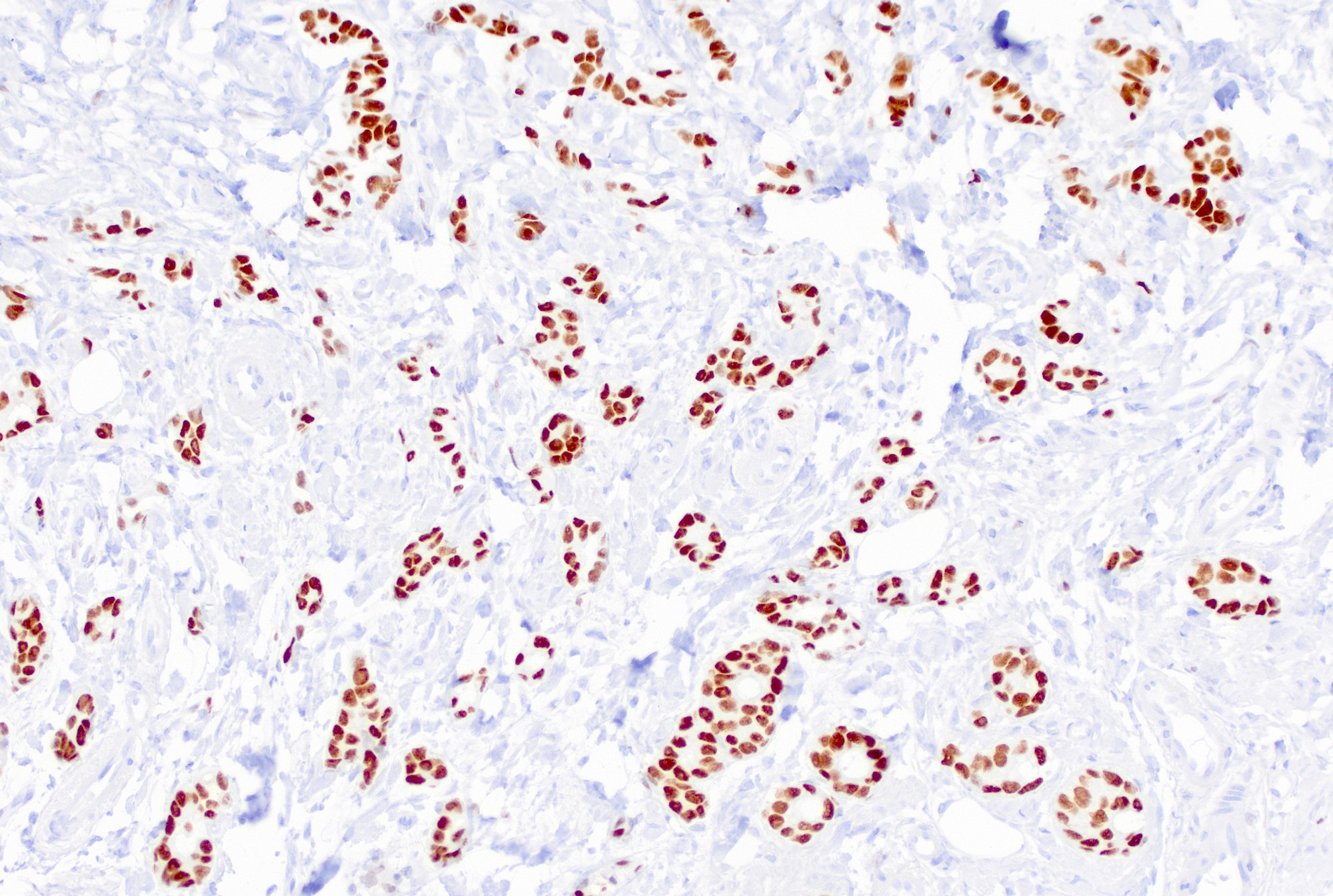
Positive stains
- Almost all are ER+ and PR+
- E-cadherin (75 - 100%), high molecular weight keratin 34 beta E12 (93%) and catenins (alpha, beta or gamma membranous staining in 100%), p120 (100%)
- GATA3, mammaglobin, GCDFP-15
- References: Mod Pathol 2007;20:130, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587
Negative stains
- SMMHC, p63, calponin (myoepithelial markers)
- S100
- HER2
- References: Mod Pathol 2007;20:130, Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1587
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, excision:
- Tubulolobular carcinoma, well differentiated, measuring 1.5 cm
- Nottingham grade I / III: tubule score = 1, nuclear score = 1, mitoses score = 1
Differential diagnosis
- Mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma:
- Lacks small, round, well formed tubules
- Invasive lobular carcinoma:
- Linear files of dyscohesive cells without tubule formation
- E-cadherin negative
- Tubular carcinoma:
- Lacks lobular component
- Microglandular adenosis:
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true regarding the histologic subtype of the breast carcinoma shown above?
- The tumor will most likely be ER negative and HER2 positive
- The tumor will most likely be ER positive and HER2 negative
- The tumor will most likely be negative for E-cadherin
- The tumor will most likely be positive for SMMHC and p63
Board review style answer #1
B. The tumor will most likely be ER positive and HER2 negative. The picture depicts an invasive carcinoma with small round tubules and single filing of cells, compatible with a tubulolobular carcinoma of the breast. Answer A is incorrect because the vast majority of these tumors are ER positive and HER2 negative. Answer C is incorrect because E-cadherin is usually positive in these tumors as they have tubule formation. Answer D is incorrect because these tumors will be negative for myoepithelial markers, compatible with invasive carcinomas.
Comment Here
Reference: Tubulolobular carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Tubulolobular carcinoma