Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Li JJX, Tse GM. Triple negative breast cancer. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignanttripleneg.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Breast cancers with absence of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) expression
Essential features
- Defined by absence of ER, PR and HER2 expression by IHC
- Overlaps with basal-like breast cancers, which are defined by gene expression profiling
- Generally associated with high stage on presentation, increased risk of recurrence and shorter survival
- Highly variable histology, including invasive ductal, metaplastic and medullary
- A small subset is low grade, comprising mostly rare salivary gland type tumors and variants of metaplastic carcinomas (fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma, low grade adenosquamous carcinoma); this subset is associated with good prognosis concordant to low grade carcinomas
Terminology
- Considerable overlap with basal-like breast cancers but not interchangeable
- Triple negative breast cancers are defined by absence of ER, PR and HER2 expression by IHC
- Basal-like breast cancers are defined by gene expression profiling
- ~80% of triple negative breast cancers belong to basal-like breast cancers (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:27)
- Triple negative staining has been advocated as IHC surrogate for molecular basal-like breast cancer in clinical practice
ICD coding
- No specific ICD code for triple negative breast cancer
Epidemiology
- Constitutes 16% of invasive breast carcinomas (Cancer 2007;109:25)
- More common in younger patients than other types of invasive breast carcinoma (Cancer 2007;109:1721)
- More common in African Americans (Cancer 2007;110:876)
Sites
- Breast parenchyma
Etiology
- Reproductive / hormonal factors may play a role
- Decreased risk of triple negative breast cancer in nulliparous women (J Natl Cancer Inst 2011;103:470)
- Breastfeeding (≥ 6 months) decreases risk of triple negative breast cancer (Cancer 2008;113:1521)
- Increased risk of triple negative breast cancer in young (≤ 40 years) with oral contraceptive use (Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009;18:1157)
- BRCA1/2 (Breast Dis 2010;32:25)
- Majority (71%) of breast cancers in BRCA1 carriers
- 25% of breast cancers in BRCA2 carriers
- Triple negative breast cancer represents 17% of breast cancers in non-BRCA1/2 carriers
- Precursor lesion
- Microglandular adenosis (MGA) or atypical MGA has been postulated to be a potential precursor lesion for some triple negative breast cancers
- Evidence that some atypical MGA shared similar genomic changes with the associated triple negative breast cancer (more commonly acinic cell carcinoma) (J Pathol 2016;238:677)
Clinical features
- Advanced stage at diagnosis (Cancer 2007;109:1721, Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429)
- Larger tumor size
- Higher rate of node positivity
- More likely to present with metastatic disease at diagnosis
- Shorter survival (Cancer 2007;109:1721)
- Increased risk of recurrence (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429)
- Poor short term survival, recurrence peaks at 3 years and is not increased after 5 years (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429)
- Higher risk of visceral and central nervous system metastasis (Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2011;23:587)
- Does not benefit from hormonal therapy or trastuzumab
- Low grade subset has excellent prognosis
Diagnosis
- Microscopic examination of resected tissue that is then tested for ER, PR and HER2
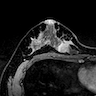
Radiology description
- Mammography (Acta Radiol 2013;54:889)
- Hyperdense, oval or lobular masses
- Indistinct or circumscribed margins
- Ultrasound (Ann Oncol 2012;23:vi23)
- Distinct masses with well circumscribed margins
- Posterior acoustic enhancement occasionally identified
- Magnetic resonance imaging (Breast J 2013;19:643)
- Rim and mass enhancement
- Areas of high intratumoral T2 signal intensity
- Highest sensitivity among all modalities (Ann Oncol 2012;23:vi23)
Prognostic factors
- Clinical favorable prognostic factors include pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Clin Breast Cancer 2013;13:40)
- Tumors with rich tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and absence of central fibrosis were associated with better survival (Breast Cancer Res 2007;9:R65)
- Unfavorable prognostic factors include large tumor size, positive nodal status, high histological grade and presence of lymphovascular invasion (Breast Cancer Res 2007;9:R65)
- Centrally necrotizing subtype of high grade invasive ductal carcinoma has poor prognosis (BMC Cancer 2015;15:282)
- Younger age (< 65 years) is an independent risk factor for recurrence (Radiol Oncol 2011;45:46)
- Immunoprofile associated with poor prognosis includes p53 expression (Cancer 2007;109:25, Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e15449, Br J Cancer 2010;103:249)
- Some authors report expression of basal cytokeratins (e.g. CK5/6) to be associated with adverse outcome (Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:2302)
Case reports
- 48 year old woman with triple negative breast cancer, BRCA2 mutation and subsequent glioblastoma (J Breast Cancer 2017;20:108)
- 52 year old woman with triple negative breast cancer with medullary features, BRCA2 mutation and synchronous ovarian cancer (Case Rep Oncol Med 2019;2019:6958952)
- 55 year old woman with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (Cureus 2019;11:e4278)
Treatment
- Complete surgical excision remains mainstay of curative treatment
- Neoadjuvant treatment is given for locally advanced disease but also recommended for early (up to pT1cN0M0) disease in triple negative breast cancer (Ann Oncol 2015;26:v8, Eur J Cancer 2020;135:66)
- Metastatic / advanced / recurrent disease
- PDL1 inhibitor in combination with chemotherapy for PDL1 positive tumors (N Engl J Med 2018;379:2108)
- PARP inhibitor in combination with chemotherapy (N Engl J Med 2011;364:205)
Gross description
- Similar gross features to nontriple negative breast cancer
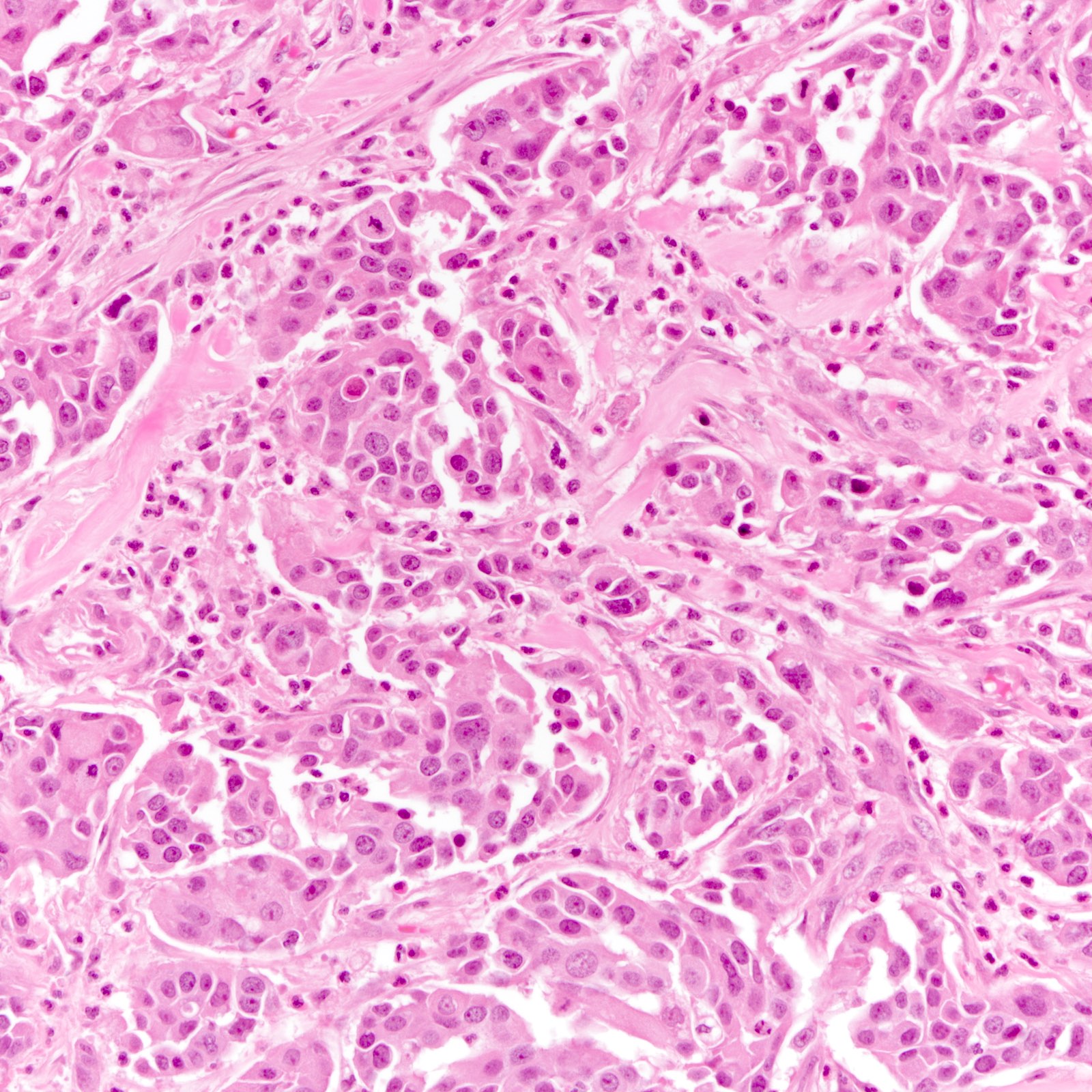
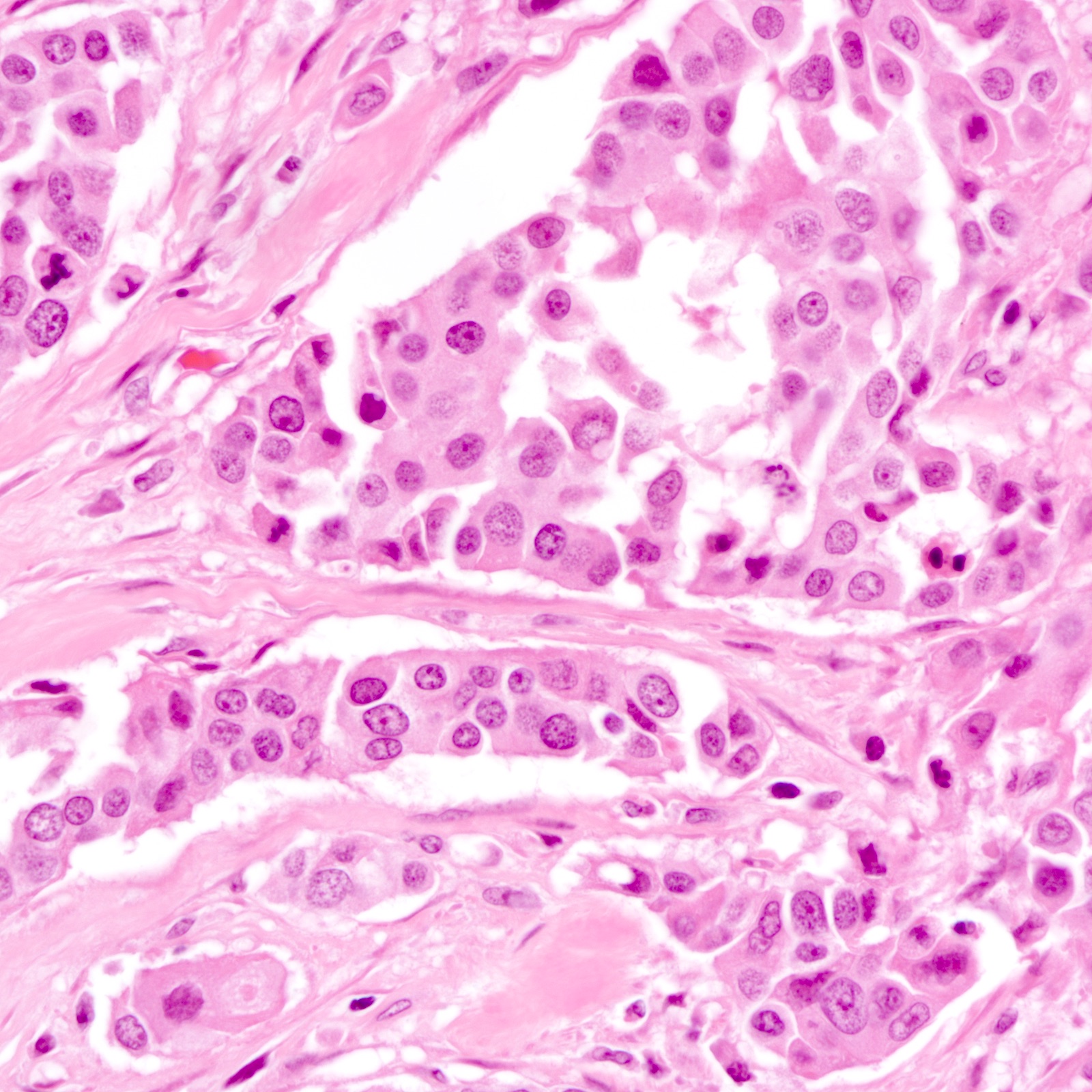
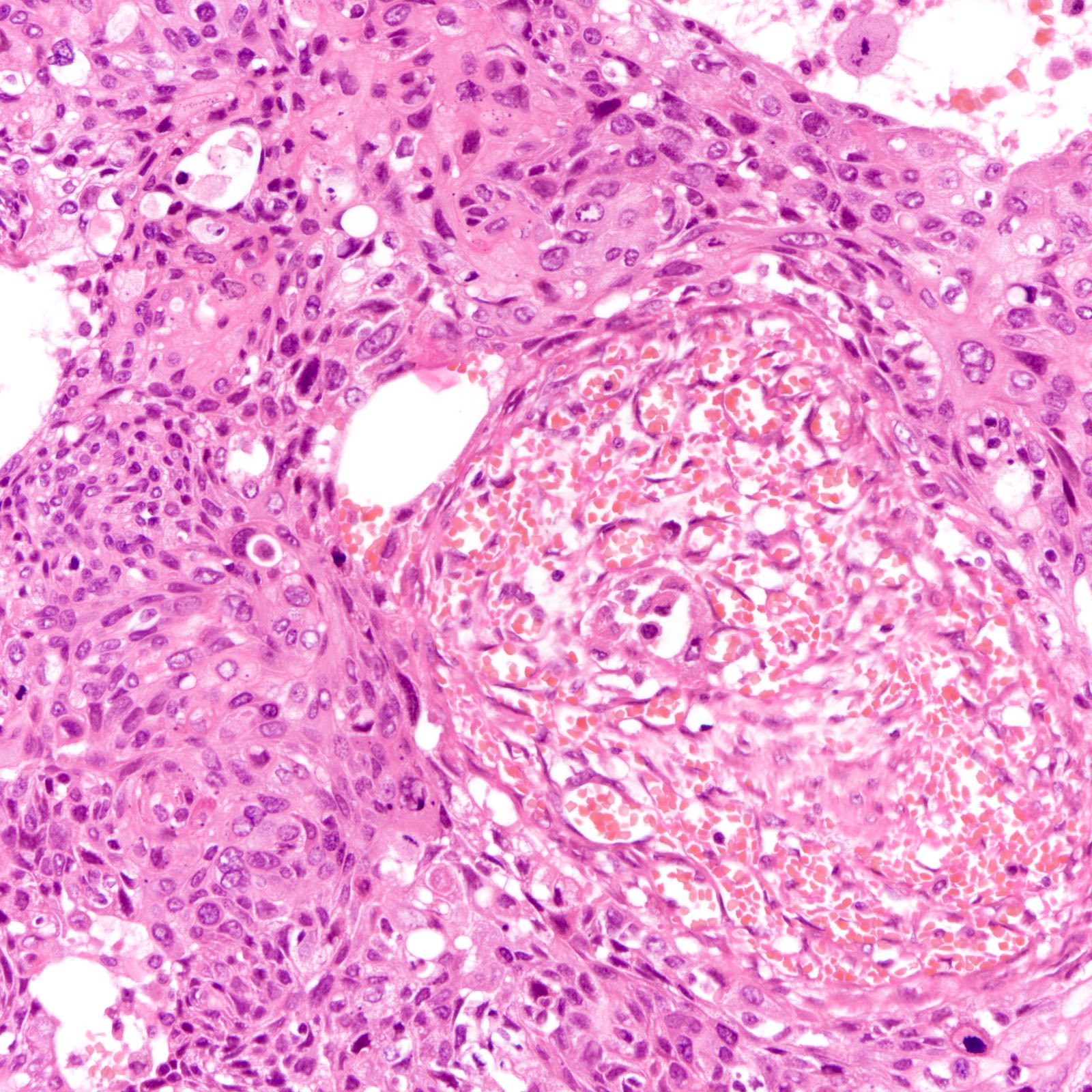
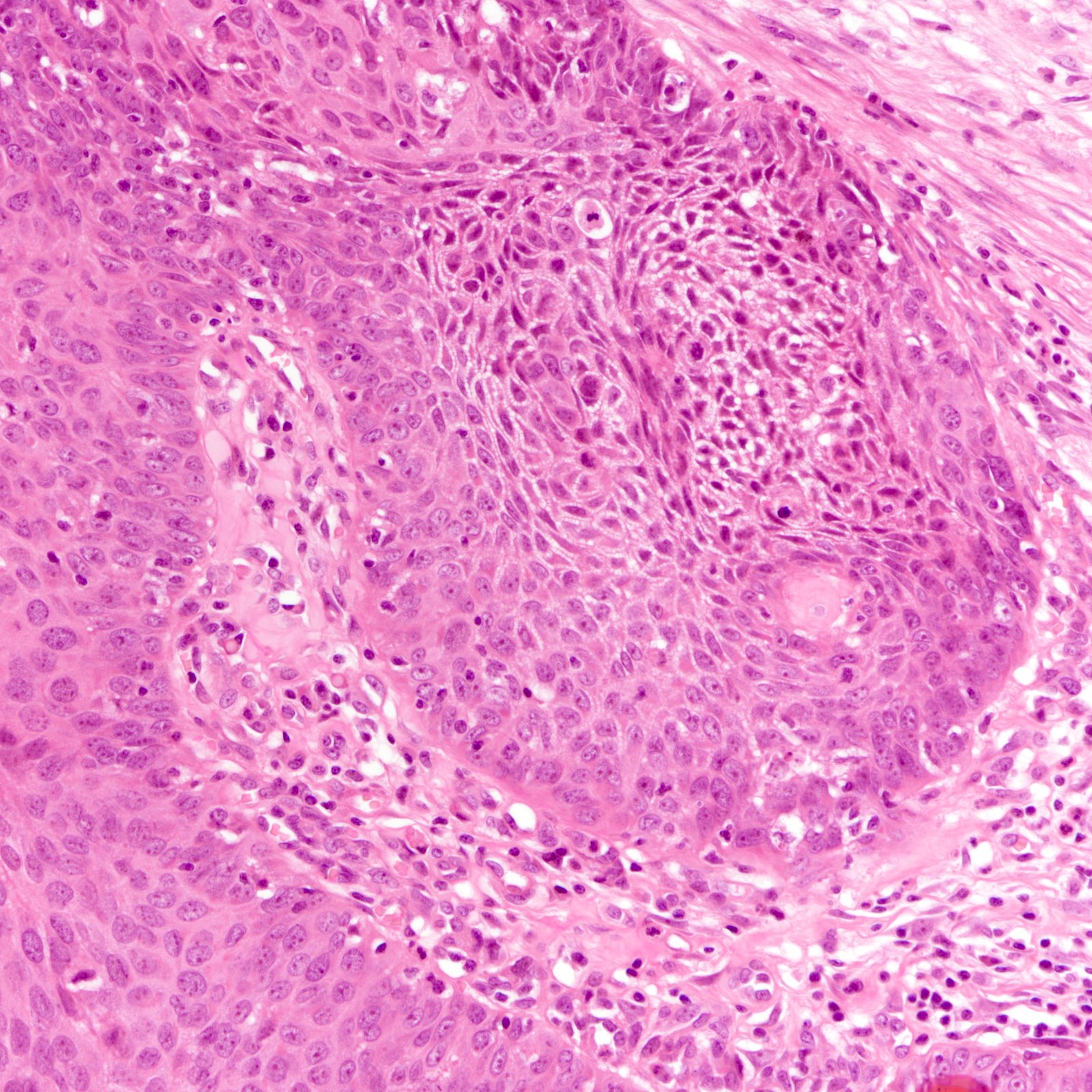
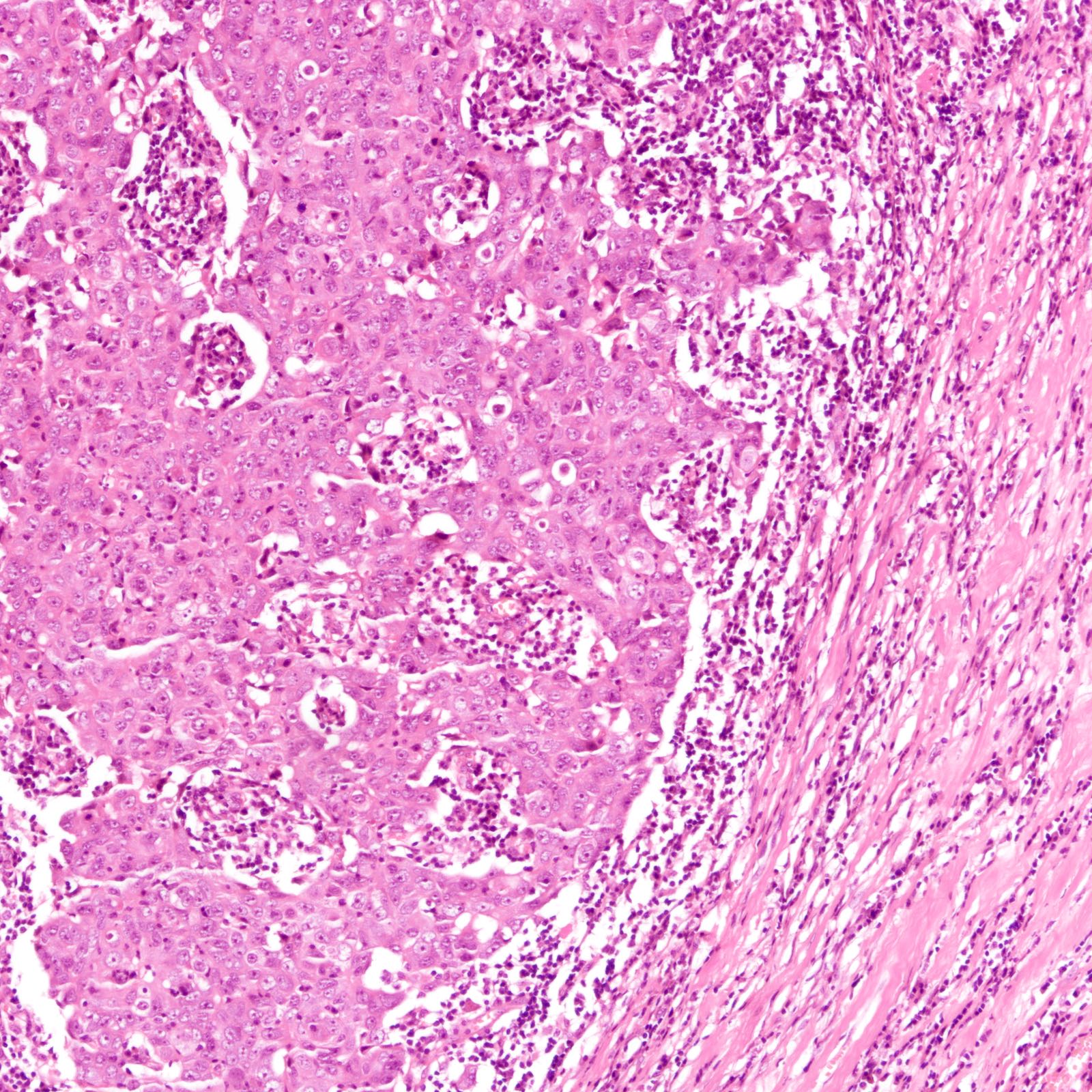
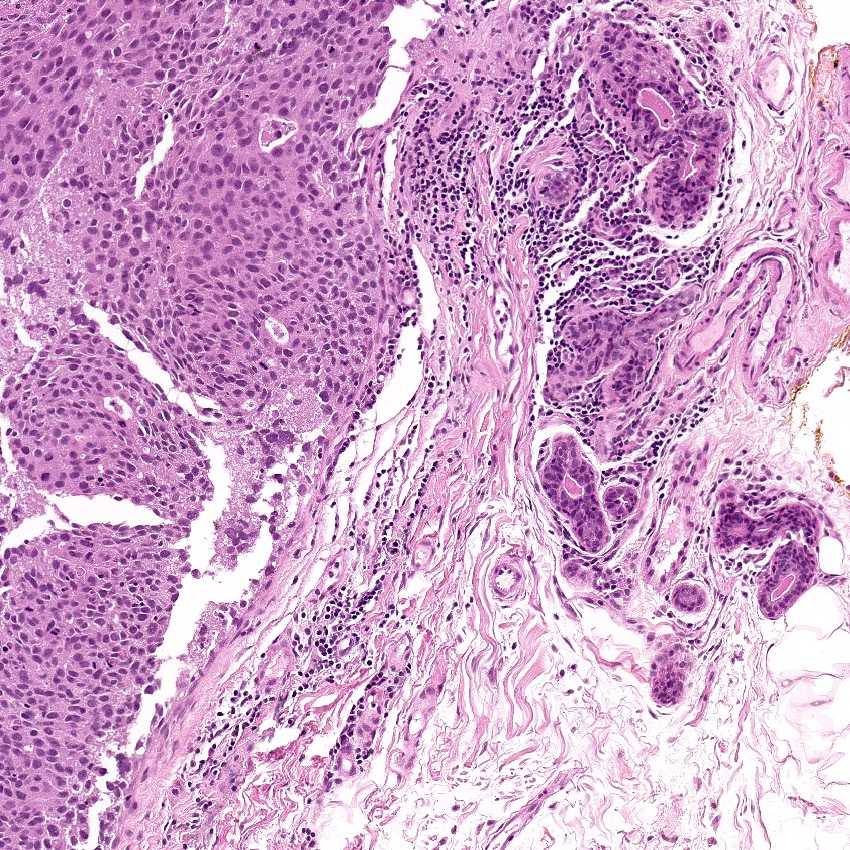
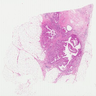
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Diverse spectrum of high grade and low grade morphology (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:27)
- Low grade: adenoid cystic carcinoma, secretory carcinoma, fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma, low grade adenosquamous carcinoma, tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity
- High grade: infiltrating duct carcinoma, no special type, squamous cell carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, carcinoma with heterologous elements, carcinoma with medullary features
- Majority (88%) are invasive ductal carcinoma, no special type (Ann Diagn Pathol 2020;46:151490)
- Most commonly poorly differentiated / high grade (grade 3) (Cancer 2007;109:1721, Cancer 2007;110:876)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Virtual slides
Cytology description
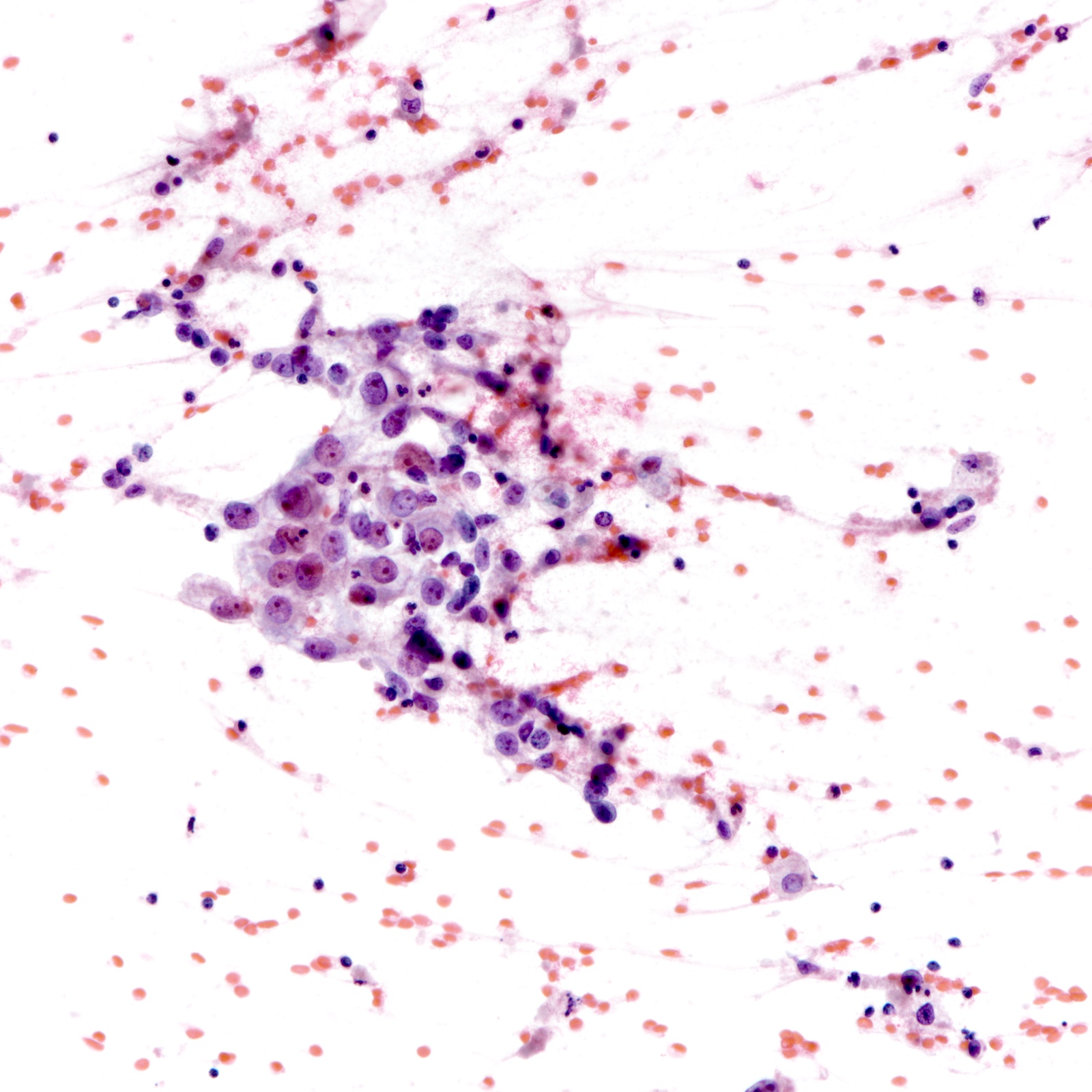
- Features more likely seen in triple negative breast cancers (Cancer Cytopathol 2012;120:401)
- Necrotic background, lymphocytes
- Syncytial clusters
- Ill defined cell borders
Cytology images
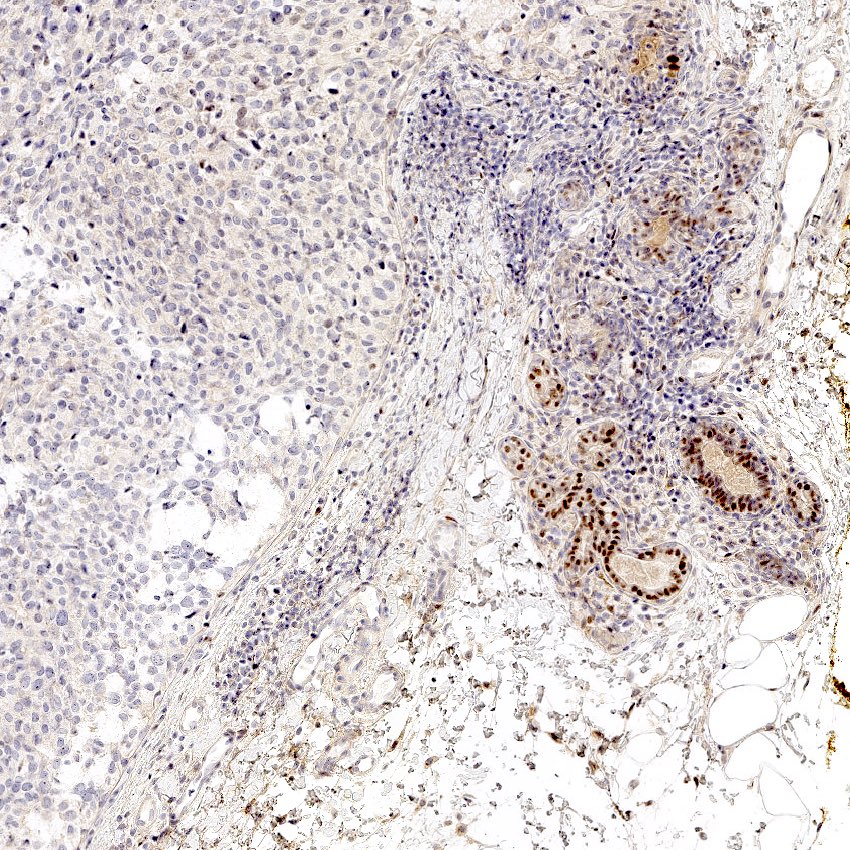
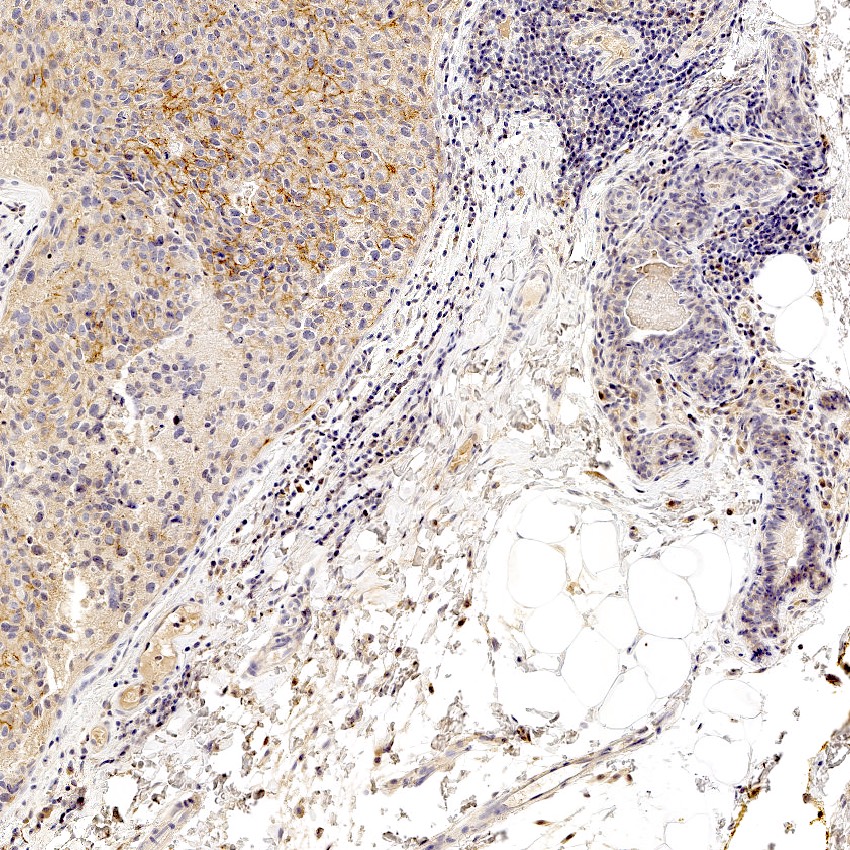
Positive stains
- High molecular weight / basal cytokeratins: CK5/6, CK14, CK17 (Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:4429)
- EGFR (89%) (J Lab Physicians 2015;7:79)
Negative stains
- ER, PR, HER2
- AR (41%) (PLoS One 2018;13:e0197827)
- SOX10 (31%), GATA3 (35%), mammaglobin (28%), GCDFP-15 (25%) (Histopathology 2020;77:936)
- More sensitive when SOX10 and GATA3 used in combination (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2020;184:11)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Gene expression (mRNA) profiling (Vanderbilt)
- Basal-like 1, basal-like 2, immunomodulatory, mesenchymal, mesenchymal stem-like and luminal androgen receptor subtypes (J Clin Invest 2011;121:2750)
- Immunomodulatory and mesenchymal stem-like subtypes removed from revision as they are shown to be derived from tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and peritumoral stroma cells (PLoS One 2016;11:e0157368)
- RNA and DNA profiling (Baylor)
- Basal-like immune suppressed, basal-like immune activated, mesenchymal and luminal androgen receptor subtypes (Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:1688)
- Basal-like 1 and basal-like 2 distributed across basal-like immune suppressed and activated (J Breast Cancer 2016;19:223)
- Basal-like subtypes
- Basal-like 1 and 2 preferentially responds to cisplatin in in vitro studies (J Clin Invest 2011;121:2750)
- Basal-like 1 cancers have the highest response rate to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:5533)
- Basal-like 1 cancers show high copy number losses for TP53, BRCA1/2 and RB1 gene (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:27)
- High copy number gain in basal-like 1 cancers for PPAR1 gene suggests response to PARP inhibitors (Adv Anat Pathol 2020;27:27)
- Mesenchymal subtype
- Associated with PI3K pathway aberrations
- mTOR inhibitors under investigation (JAMA Oncol 2017;3:509)
- Luminal androgen receptor subtype
- Associated with AR expression
- May benefit from antiandrogen therapies (Cancer Treat Rev 2018;68:102)
- Specific translocations for adenoid cystic carcinoma and secretory carcinoma
- IDH2 R172 hotspot mutation in tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, 3 o’clock, needle core biopsy:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, grade 3 (glandular differentiation 3, nuclear pleomorphism 3, mitotic rate 3)
- ER negative (0%), PR negative (0%), HER2 negative (1+) for expression
Differential diagnosis
- Adnexal carcinomas arising from mammary skin:
- More superficial location
- May not be differentiable from their mammary counterparts
- Prognosis and treatment may not be significantly different in low grade lesions
- Phyllodes tumor with extensive stromal overgrowth:
- Morphological overlap with spindle cell carcinoma
- Cytokeratins, p63 negative
- Lung adenocarcinoma:
- Malignant melanoma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Presence of central necrosis. Tumors rich in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are associated with better survival. Complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and lower tumor / node stage are all favorable prognostic factors. Centrally necrotizing breast carcinomas have poor prognosis (BMC Cancer 2015;15:282).
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer
Board review style question #2
Which of the following types of invasive breast carcinoma most likely displays a triple negative immunophenotype?
- Encapsulated papillary carcinoma
- Invasive cribriform carcinoma
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
- Invasive papillary carcinoma
- Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
E. Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma. Encapsulated papillary, invasive cribriform and invasive lobular carcinoma commonly and invasive micropapillary carcinoma less commonly show hormone receptor expression. Low grade adenosquamous carcinomas are invariably triple negative.
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer
Board review style question #3
Which of the following type of triple negative breast cancer is associated with a more aggressive course of disease?
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma
- Low grade adenosquamous carcinoma
- Secretory carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #3
E. Squamous cell carcinoma. Adenoid cystic carcinoma, secretory carcinoma, fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma and low grade adenosquamous carcinoma are considered low grade triple negative breast cancers. Squamous cell carcinoma of the breast is morphologically of a higher grade and associated with a worse prognosis (Hum Pathol 2010;41:679).
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer
Comment Here
Reference: Triple negative breast cancer