Table of Contents
Terminology | Clinical features | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Mucoepidermoid. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantmucoepidermoid.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Terminology
- See also adenosquamous carcinoma; also called adenoacanthoma
Clinical features
- Very rare
- Grading system used for salivary gland tumors is recommended (Virchows Arch 2004;444:13)
Case reports
- 46 year old woman with high grade tumor and axillary metastases (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1981;105:612)
- 54 year old woman with mucoepidermoid carcinoma of breast (Pathol Int 2006;56:549)
- Two low grade tumors (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1979;103:196)
- High grade and low grade tumors (Neoplasma 2007;54:168)
Microscopic (histologic) description
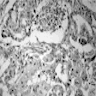
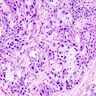
- Resembles salivary gland counterpart (Virchows Arch 2004;444:13)
- Mixture of neoplastic mucus secreting, squamous and intermediate cells
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
High grade tumors:
- Clusters of epithelial ductal cells with mixed glandular, squamous and intermediate cells
- May be scant intra- and extracellular mucin (Acta Cytol 2006;50:344)
Positive stains
- Keratin, EMA and CEA
- Mucin is PAS+
- Have basal-like phenotype: strong and diffuse expression of CK5 / 6, p-cadherin, p63, EGFR (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2013;21:283)
Negative stains
- ER, PR and HER2 (Mod Pathol 2010;23:951)
Electron microscopy description
- Intermediate cells are modified myoepithelial cells (Hum Pathol 1985;16:941)
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic salivary gland tumor (Acta Cytol 2002;46:377)