Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Muller KE. Fibromatosis-like. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantmetaplasticfibro.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Variant of metaplastic carcinoma with low grade, bland spindle cells histologically resembling fibromatosis
- May arise de novo or in association with papillary or sclerosing lesions
- High propensity for local recurrence but lymph node and distant metastases are rare
- May represent a distinct subtype as these tumors do not share similar genomic alterations with other types of metaplastic carcinomas
Essential features
- Variant of metaplastic carcinoma composed of cytologically bland spindle cells resembling fibromatosis within abundant stromal collagen
- Immunohistochemical stains needed to establish epithelial differentiation (cytokeratins, p63) since in situ and conventional type invasive breast carcinoma are typically absent
Terminology
- Low grade fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma
- Fibromatosis-like spindle cell metaplastic carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8575/3 - metaplastic carcinoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2C6Y & XH0RD4 - metaplastic carcinoma of breast & metaplastic carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Rare; 70 reported cases in the literature (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
- Women > 50 years old (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
Sites
- Breast, unilateral
Pathophysiology
- Unknown; may arise in association with papillary or sclerosing lesions
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Detected as solitary palpable mass; increasingly detected by imaging (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
Diagnosis
- Core needle biopsy or surgical excision
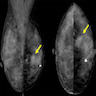
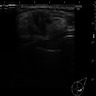
Radiology description
- Variable appearance: round, oval, lobular or irregularly shaped; densely solid, heterogeneous or cystic parenchyma; well circumscribed or irregular / spiculated shaped (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552)
- Calcifications uncommon
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Low grade variant of spindle cell carcinoma of the breast, with a favorable prognosis compared to other metaplastic carcinoma variants (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552)
- High risk of local recurrence (Cancer 1999;85:2170, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1009)
- Lymph node and distant metastases are rare (Cancer 1999;85:2170, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1009)
Case reports
- 56 year old woman with fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma (Surg Case Rep 2021;7:16)
- 65 year old woman with self palpated lump (Diagn Pathol 2020;15:20)
- 77 year old woman with fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma and adjacent papilloma (World J Surg Oncol 2007;5:24)
Treatment
- Surgical excision with adequately excised margins
- Axillary dissection, chemotherapy and radiation therapy likely not necessary (Cancer 1999;85:2170, Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1009)
Gross description
- White, firm, 2 - 3 cm in size (range 1 - 7 cm), well circumscribed or irregular borders, rarely cystic, never encapsulated (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552, Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
- Necrosis, hemorrhage and calcifications not typical (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552)
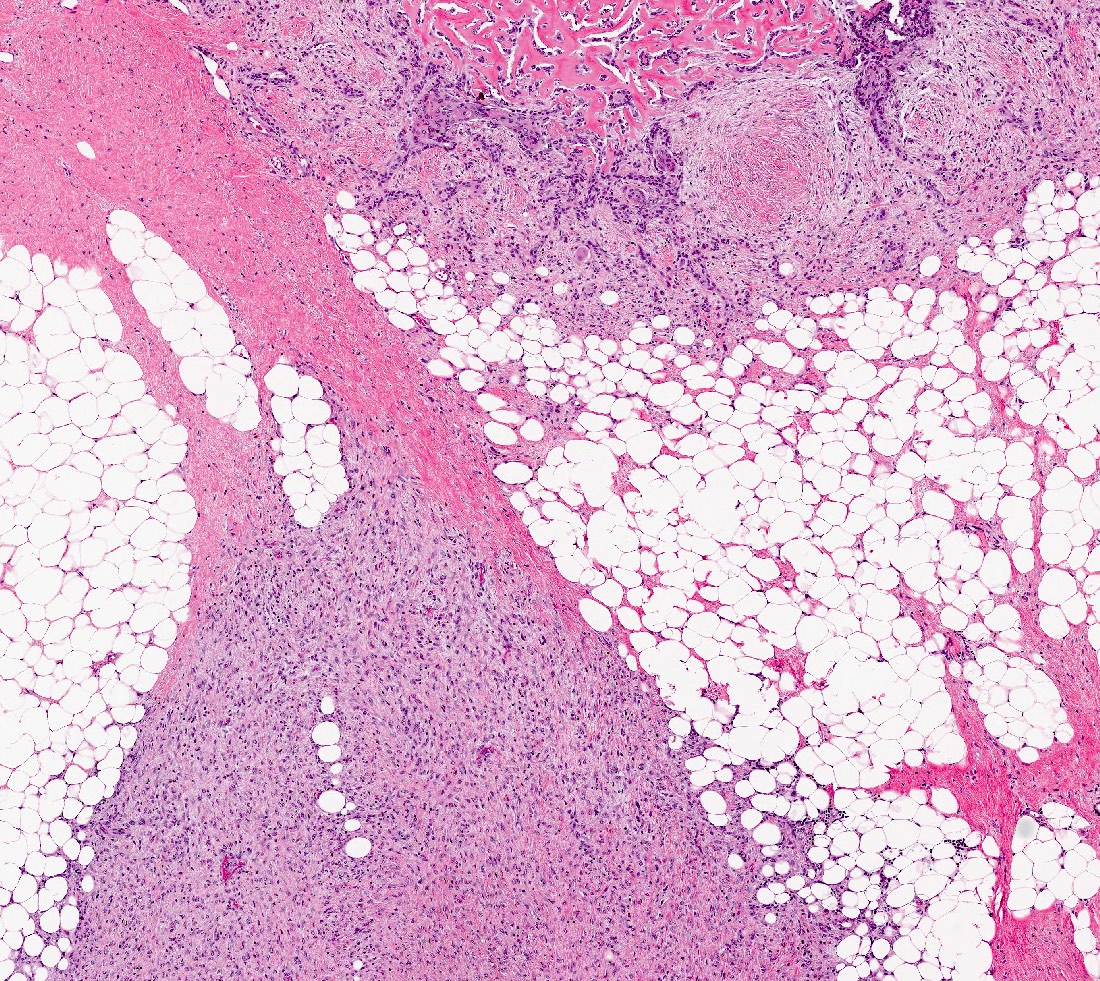
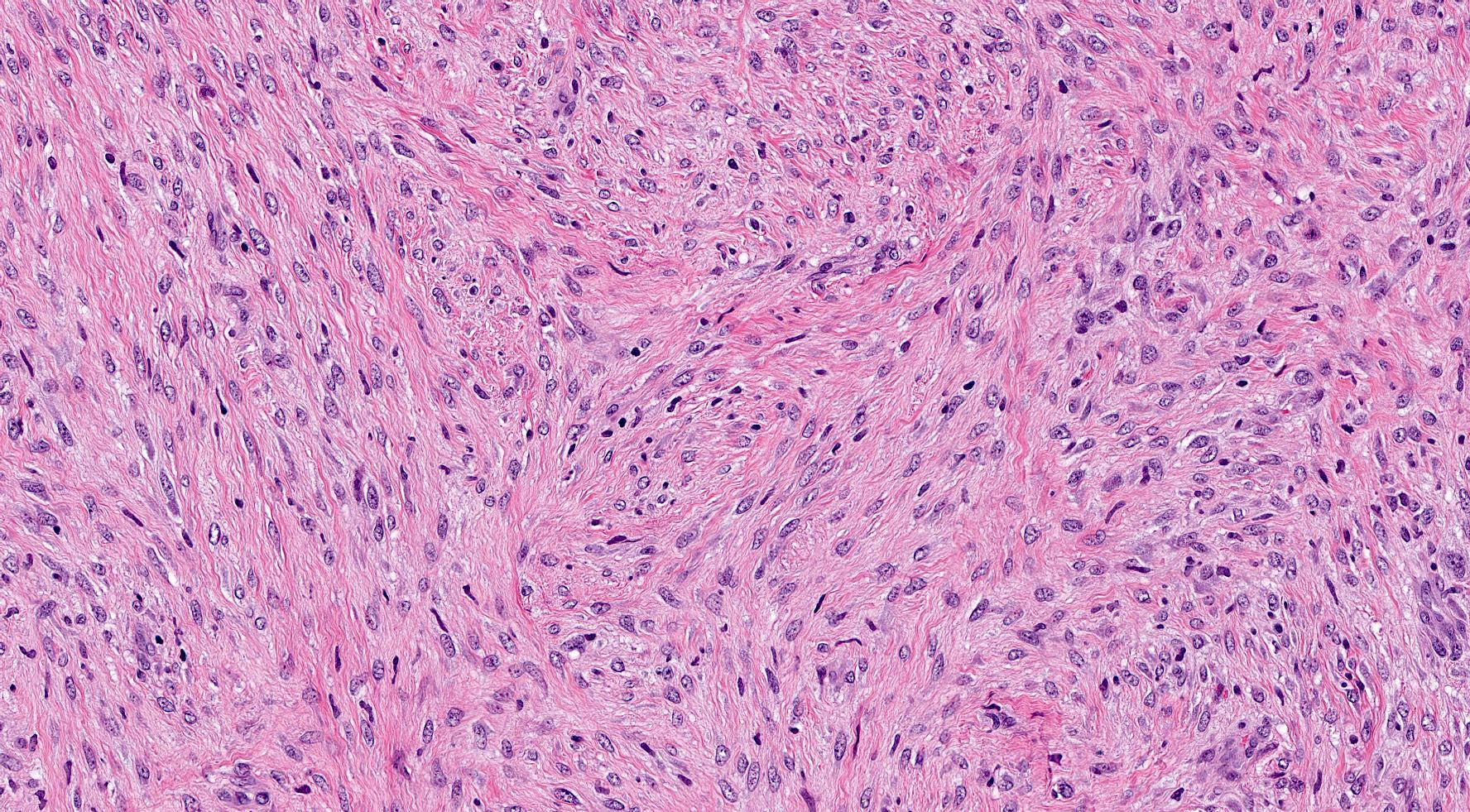
Microscopic (histologic) description
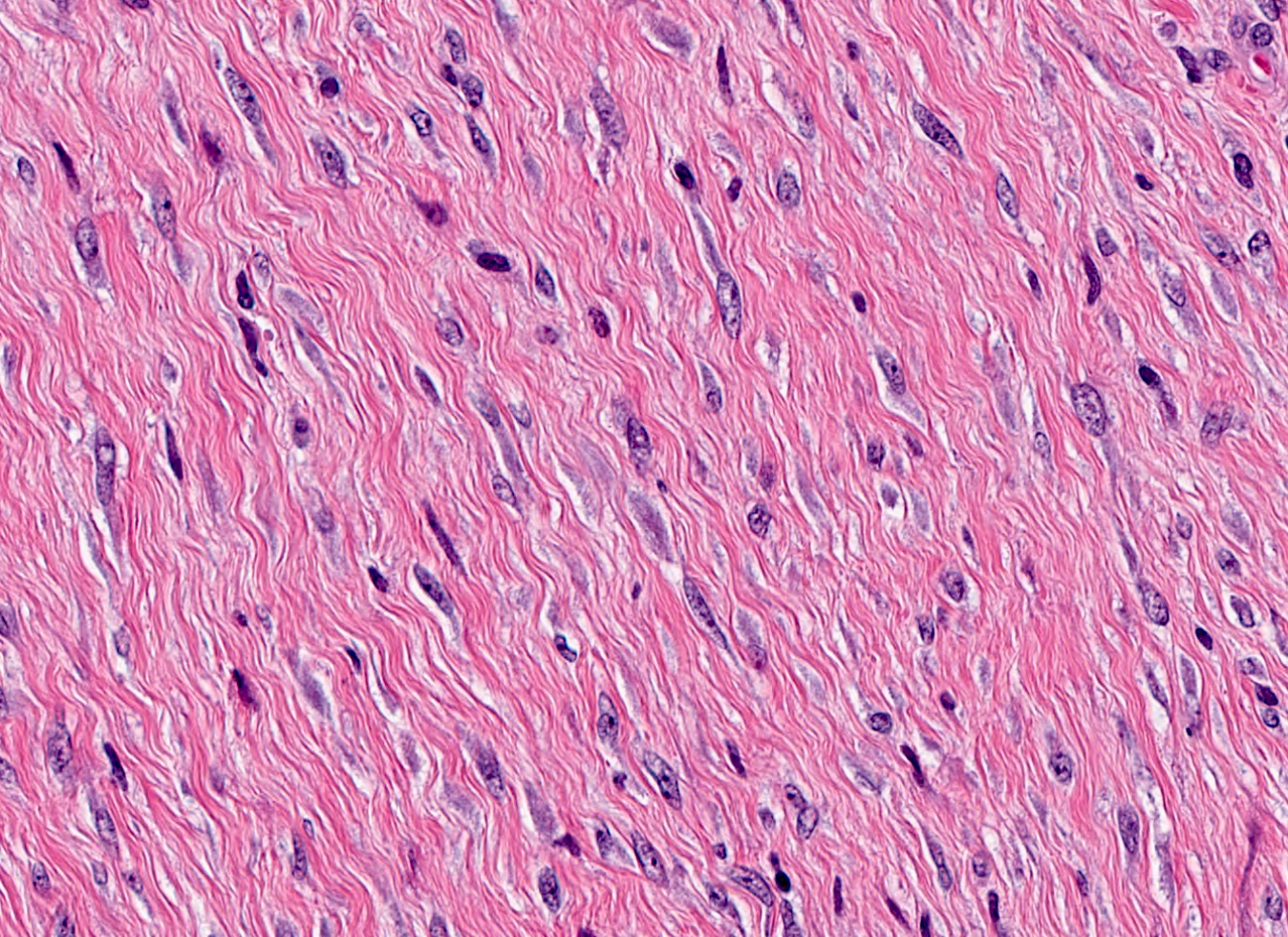
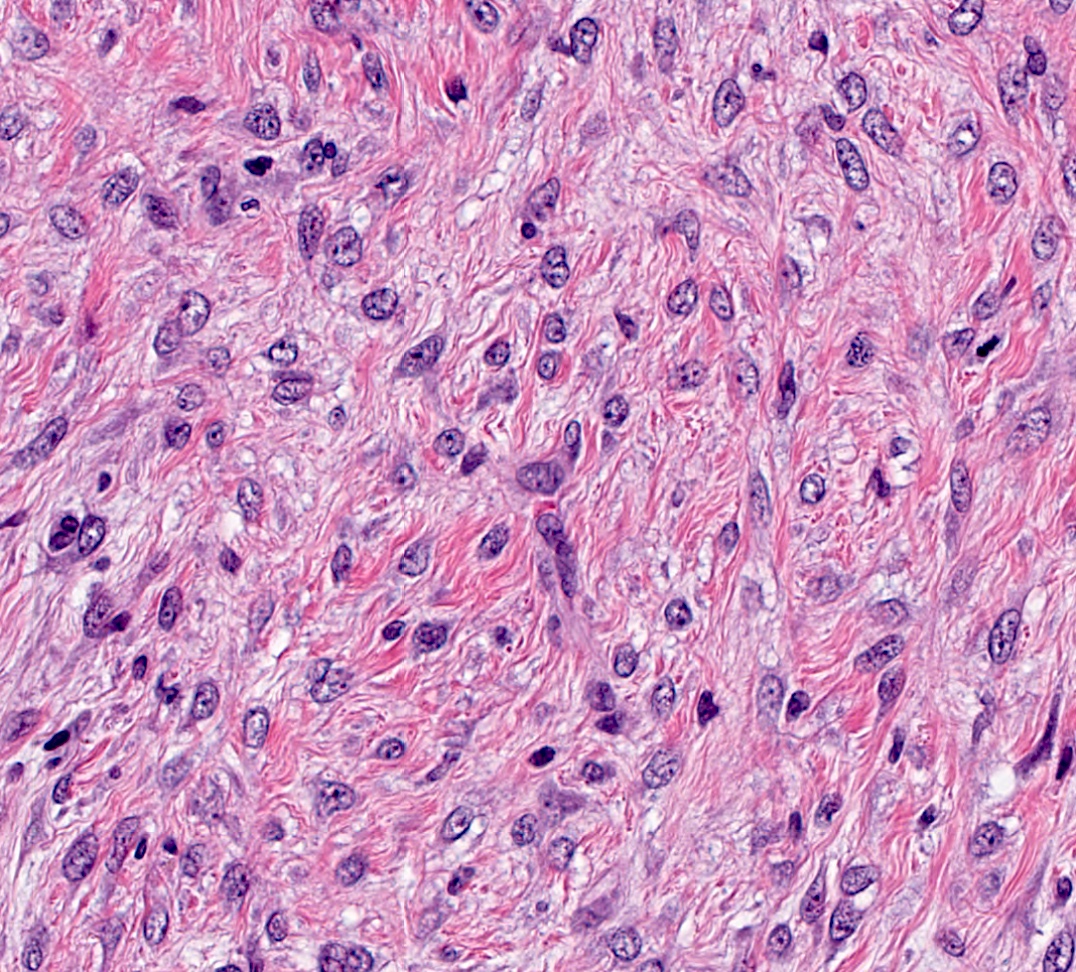
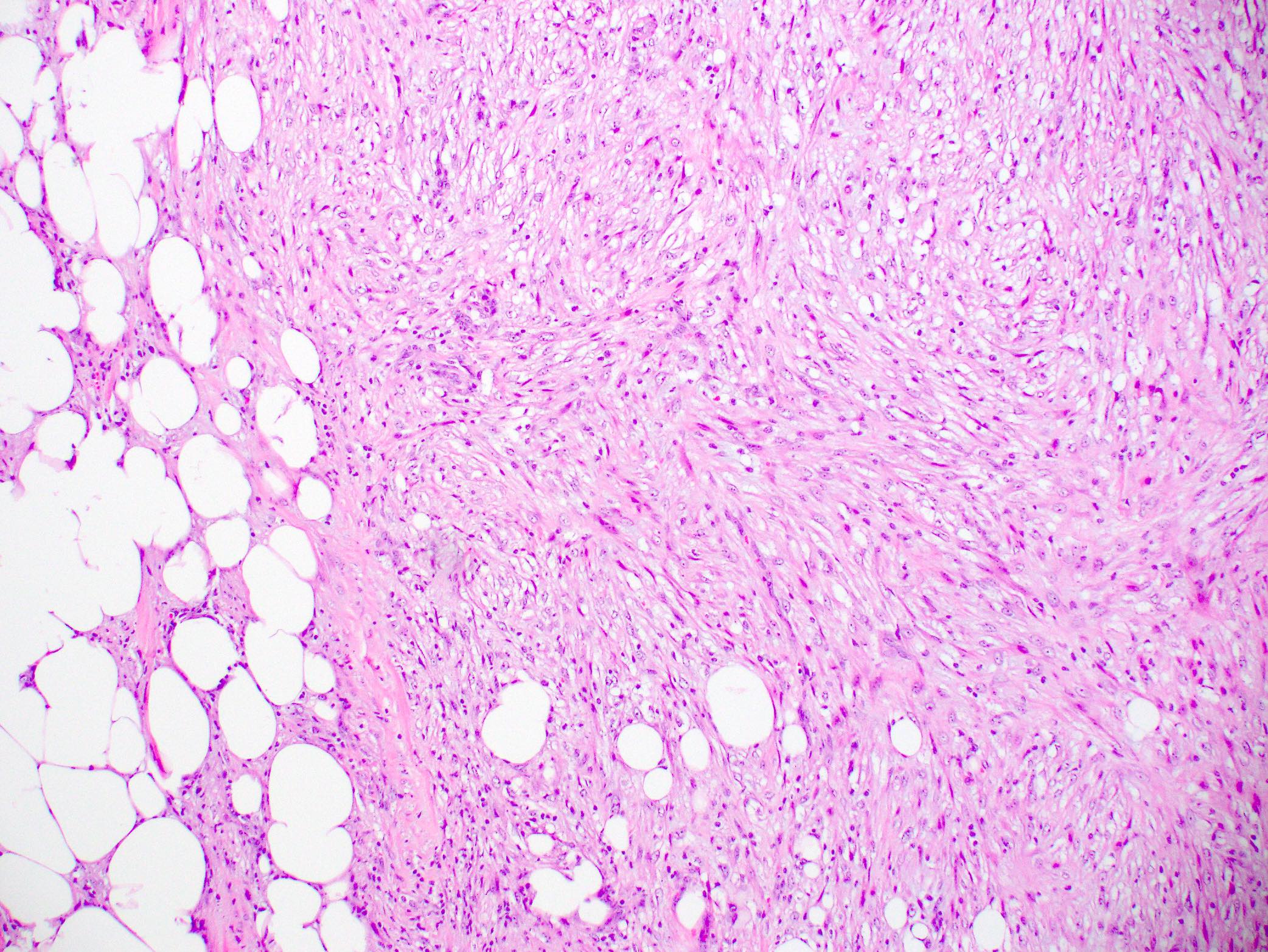
- Bland spindle cell tumor resembling desmoid type fibromatosis
- Characterized by proliferation of spindle shaped, fibroblast-like and myofibroblast-like cells arranged in interlacing fascicles with irregular infiltrative margins into surrounding breast parenchyma (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
- Minimal nuclear pleomorphism: nuclei may vary from thin, spindled with tapered ends to more plump, round to oval with discrete nucleoli (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print])
- Mitotic activity absent or rare (Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 29 [Epub ahead of print])
- Usually lacks in situ and conventional invasive breast carcinoma components
- Background stroma can be fibrotic, sclerotic, collagenized
- Associated stromal lymphocytic infiltrates common, often present at the periphery (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:1009)
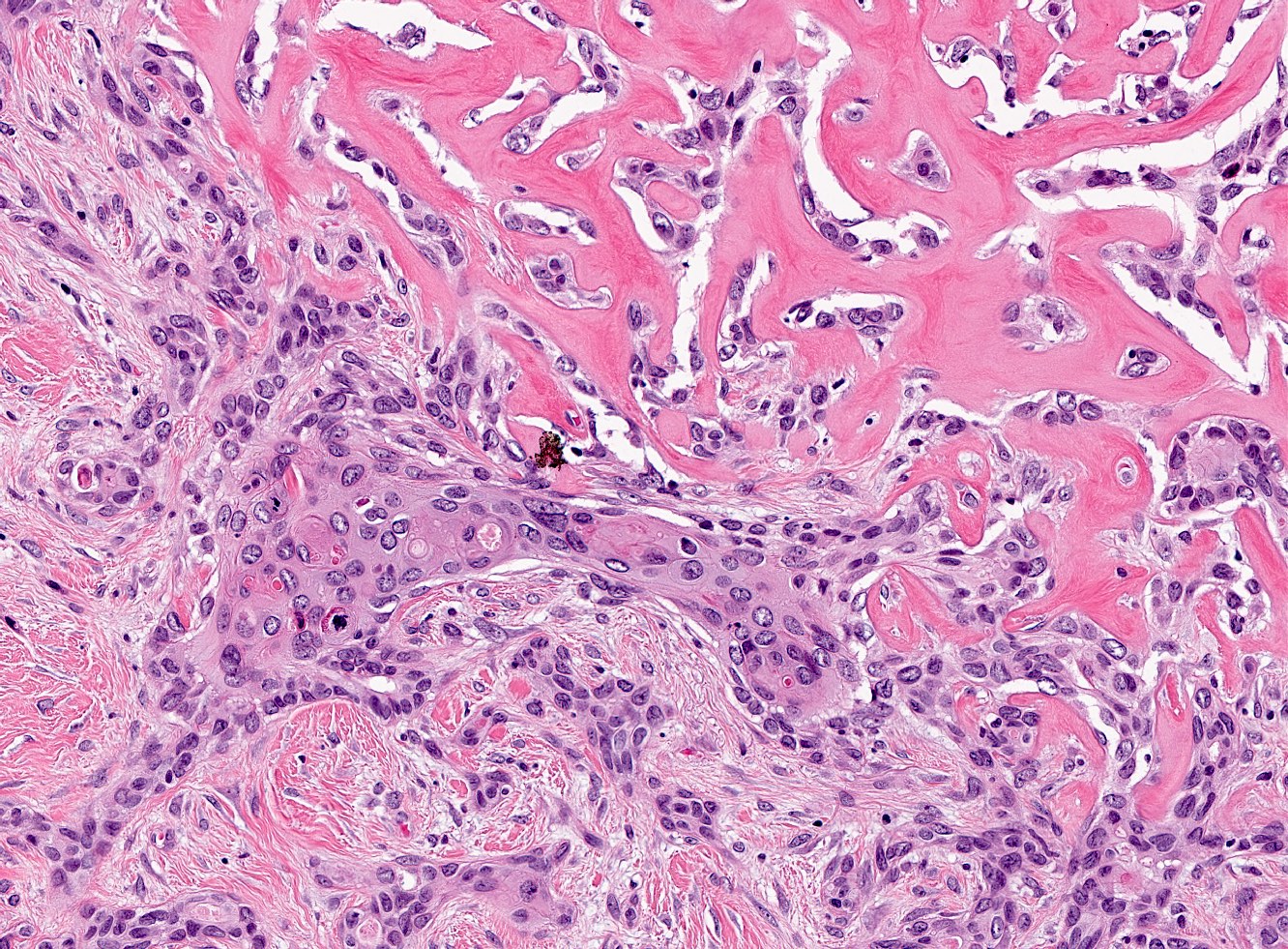
- Squamous or glandular elements may be seen but should be a minor component (< 5% tumor area) (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552)
- May be associated / arising from sclerosing lesions such as radial scars / complex sclerosing lesions and papillary lesions (Mod Pathol 2003;16:893)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Low cellularity smear with clusters of round to oval and spindle shape cells with low grade, bland nuclear features (Acta Cytol 2010;54:712)
Positive stains
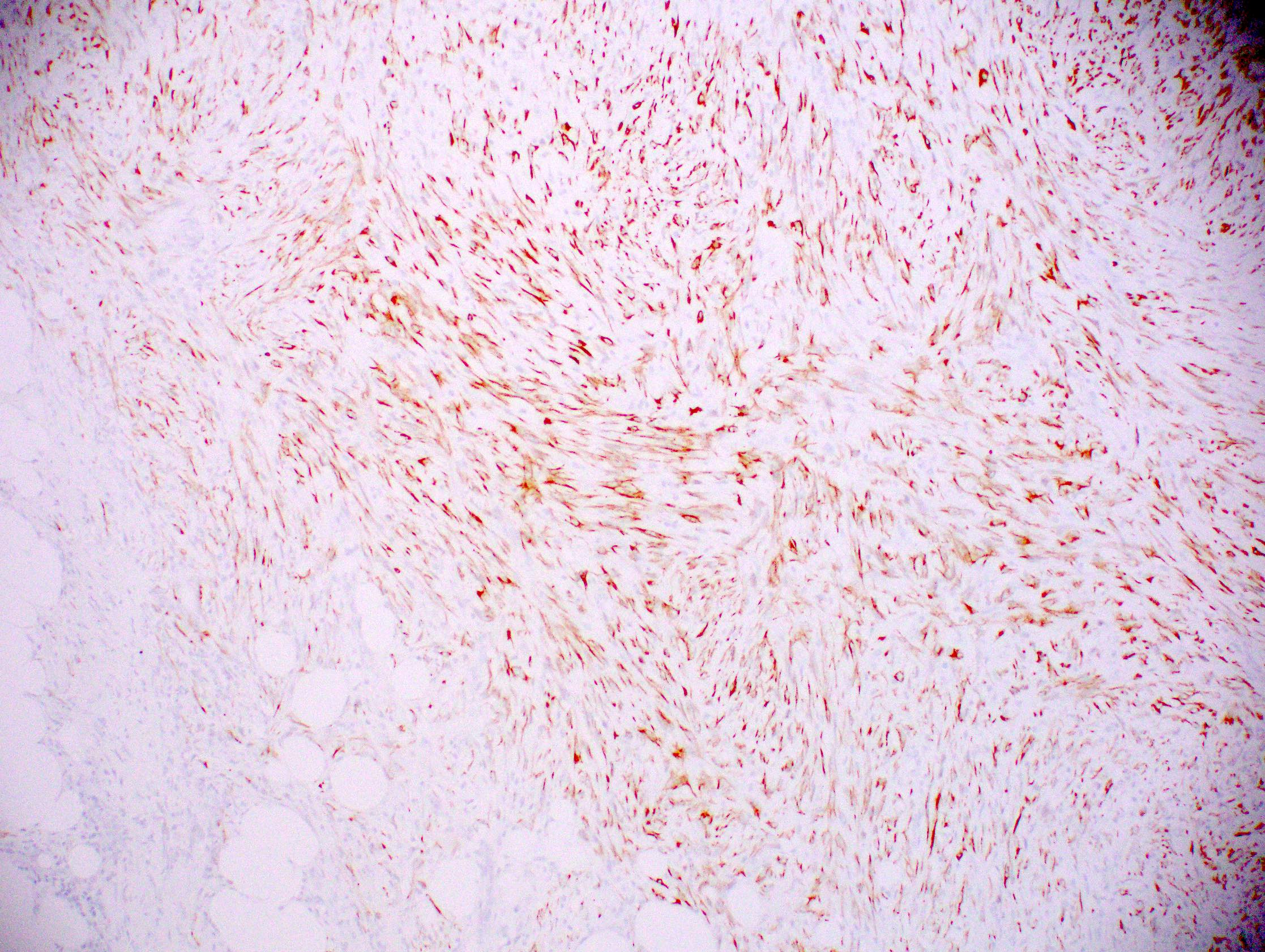
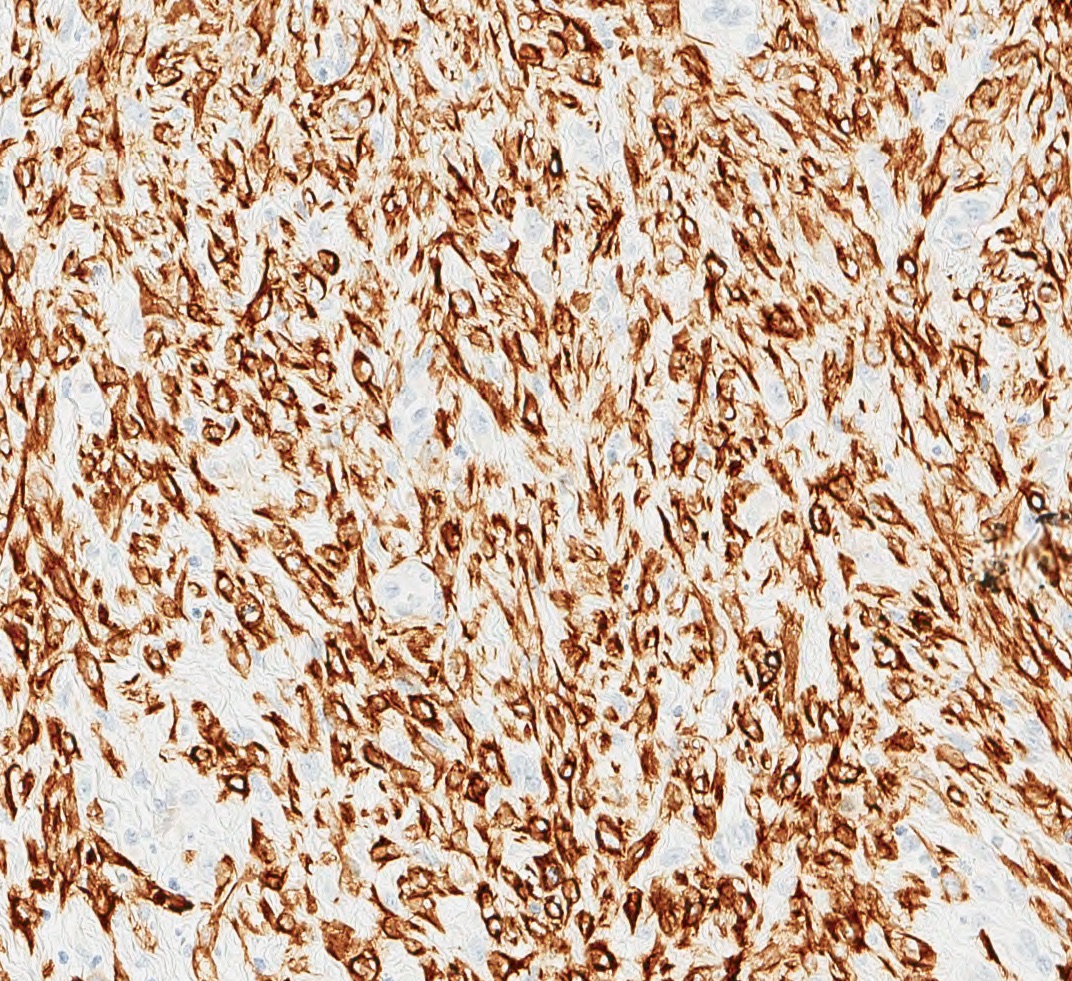
- Expression of epithelial markers; panel of cytokeratin antibodies (broad spectrum and high molecular weight keratins) suggested since tumor cells can show focal to diffuse cytokeratin expression
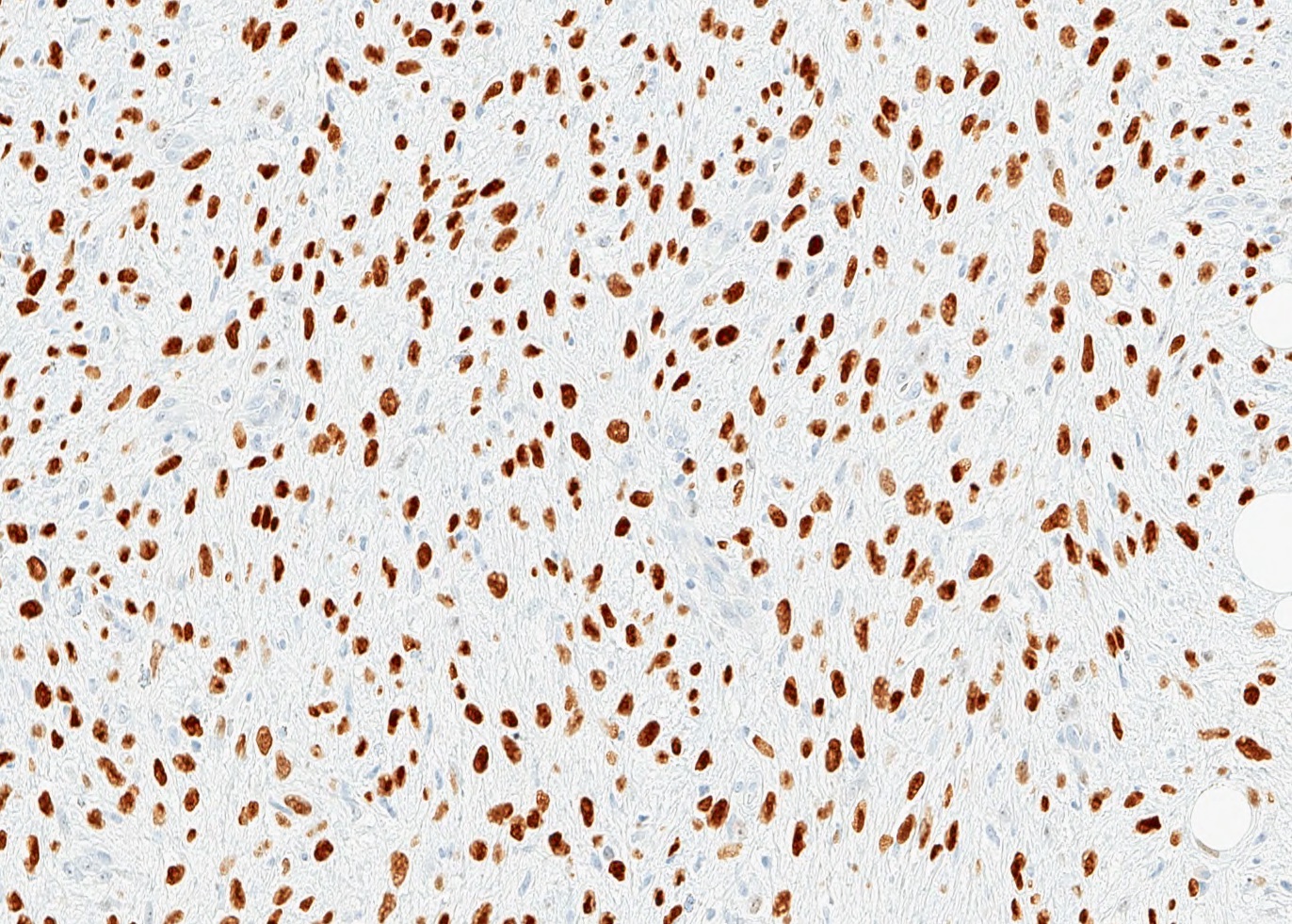
- p63
- Myoepithelial markers may show scattered expression (CD10, calponin, SMA)
- References: Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552, Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print]
Negative stains
- ER, PR, HER2
- Beta catenin (nuclear) expression
- References: Arch Pathol Lab Med 2015;139:552, Virchows Arch 2021 Jul 22 [Epub ahead of print]
Electron microscopy description
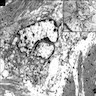
- Tumor cells show fibroblastic, myoepithelial and epithelial features with peripheral villous processes with a focal basal lamina and intercellular junctions (World J Surg Oncol 2007;5:24)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- PIK3CA and TERT promoter mutations common (J Clin Pathol 2021 May 5 [Epub ahead of print])
- Low genomic instability, common 9p21.3 loss in one study (2 of 3 tumors tested), do not share copy number alterations with other metaplastic carcinoma types (J Clin Pathol 2015;68:362)
- Claudin low phenotype (Virchows Arch 2014;465:185)
Sample pathology report
- Breast, right, partial mastectomy:
- Fibromatosis-like spindle cell metaplastic carcinoma (see comment and synoptic report for additional details and staging)
- Comment: H&E sections show an infiltrative spindle cell tumor arranged in long sweeping fascicles. The lesional cells lack significant nuclear atypia and mitotic activity is scarce. Conventional in situ (DCIS) and invasive carcinoma are not identified. Immunohistochemical staining shows that the tumor cells are positive for multiple cytokeratins (CK5, CK MNF 116, CK AE1 / AE3) and p63. The morphology and immunoprofile are consistent with fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Bland spindle cell lesions:
- Fibromatosis:
- Beta catenin nuclear staining, CTNNB1 mutations
- Lacks focal overt epithelial (glandular or squamous) components
- Negative for keratins and p63
- Myofibroblastoma:
- Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH):
- Scar:
- Fibromatosis:
Board review style question #1
The lesion depicted in the image was taken from a 67 year old woman with a 2 cm mass. Which immunohistochemical panel supports a diagnosis of fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma?
- ER positive, CD34 negative, beta catenin cytoplasmic expression
- ER positive, CD34 negative, beta catenin nuclear expression
- ER negative, CK AE1 / AE3 negative, beta catenin cytoplasmic expression
- ER negative, CK AE1 / AE3 positive, beta catenin cytoplasmic expression
Board review style answer #1
D. ER negative, CK AE1 / AE3 positive, beta catenin cytoplasmic expression. Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma shows the following immunoprofile: cytokeratin positive (typically high molecular weight and broad spectrum keratins), p63 positive, ER, PR and HER2 negative and are CD34 negative. A distinguishing factor in differentiating this lesion with desmoid type fibromatosis is the lack of nuclear beta catenin expression that is characteristic of fibromatosis.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma
Board review style question #2
The lesion depicted in the image was taken from a 72 year old woman with a 3 cm mass. The lesional cells showed scattered expression of CK5/6 and p63. Focal squamous differentiation was seen, which comprised approximately 2% of the tumor. Which statement is true regarding this lesion?
- These tumors typically lack cytologic atypia and conspicuous mitoses
- This variant is an unfavorable pattern of metaplastic breast carcinoma with frequent lymph node metastases
- This variant is commonly associated with conventional invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal carcinoma in situ
- This variant shares similar molecular alterations with other variants of metaplastic breast carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
A. These tumors typically lack cytologic atypia and conspicuous mitoses. The photo and vignette describe a fibromatosis-like metaplastic breast carcinoma. These tumors can histologically mimic desmoid type fibromatosis and are composed of bland spindle cells arranged in long sweeping fascicles with infrequent mitotic activity. Focal glandular and squamous elements can be present; however, conventional invasive carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ are rarely present. Compared to other variants of metaplastic breast carcinomas, fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma portends a more favorable prognosis with infrequent lymph node and distant metastases. These tumors show low genomic instability and do not share copy number alterations with other metaplastic carcinoma types.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma