Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Welter SM, Racila E. Medullary. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantmedullary.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Medullary pattern is a histological pattern that can be applied to an invasive breast carcinoma of no special type that contains pushing borders, syncytial growth, high grade nuclei and prominent lymphoid infiltrate
- Represents one end of the spectrum of tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) rich invasive breast carcinomas of no special type rather than a distinct morphological subtype
Essential features
- Medullary pattern of invasive breast carcinoma no special type has 4 characteristic histological features (ideally, all 4 should be present for the diagnosis):
- Pushing border
- Syncytial growth pattern
- High grade nuclei
- Prominent lymphoid infiltrate
Terminology
- Preferred term according to WHO: invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern
- Historically described as medullary carcinoma, atypical medullary carcinoma, medullary features
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8500/3 - infiltrating duct carcinoma, NOS
- ICD-11: 2C61.0 & XH7KH3 - invasive carcinoma of breast, NOS & infiltrating duct carcinoma, NOS
Epidemiology
- Often present earlier in life, median age of 53 (45 - 62) years (JAMA Netw Open 2021;4:e214123)
- Rare: less than 5% of all invasive breast cancers
Sites
- Breast
Pathophysiology
- Basal-like molecular subtype
- Same as molecular subtype matched invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013;142:257)
Etiology
Clinical features
- Younger age
- Soft, palpable, circumscribed mass
- May have lymphadenopathy (due to hyperplasia rather than metastasis, which is uncommon)
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic steps are identical to invasive breast carcinoma (screening mammogram, diagnostic mammogram, ultrasound, core biopsy, etc.)
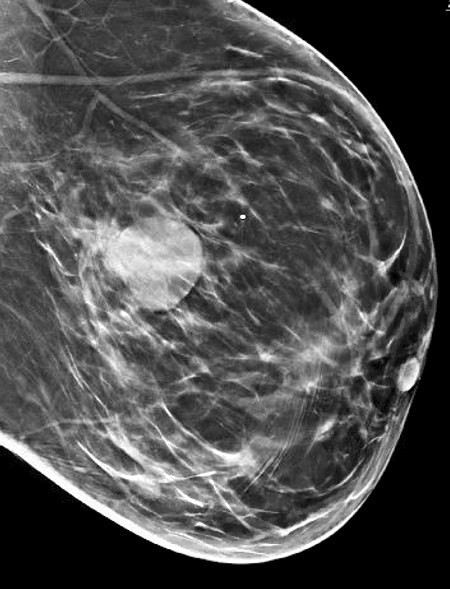
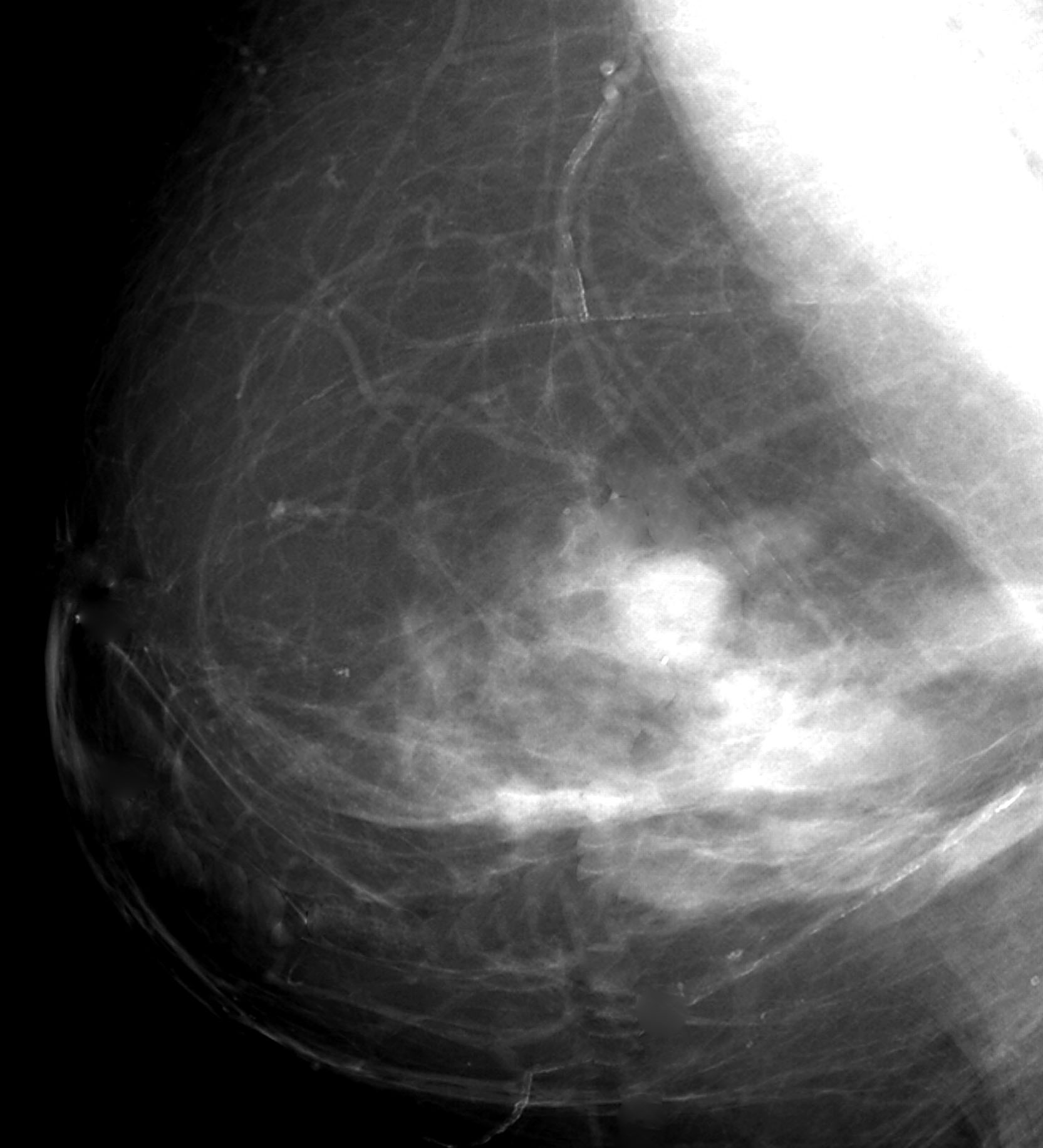
Radiology description
- Round, oval or lobulated mass on mammography
- Hypoechoic mass on ultrasound with thick echogenic halo
Prognostic factors
- Prognostic factors identical to invasive breast carcinoma of no special type: patient age, tumor histological grade, tumor stage, lymphovascular invasion, ER, PR and HER2 status, molecular subtype
- Additional prognostic factors:
- Triple negative breast cancers have more unfavorable prognosis then nontriple negative breast cancer (JAMA Netw Open 2021;4:e214123)
- Similar prognosis to stage matched grade 3 ductal carcinoma with prominent inflammation
- Better prognosis than grade 3 ductal carcinoma without prominent inflammation (Eur J Cancer 2009;45:1780)
- Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes have been shown to be of prognostic value (Ann Oncol 2015;26:259)
Case reports
- 38 year old woman who presented with a lump in both breasts for 3 months (J Cancer Res Ther 2012;8:129)
- 72 year old woman with invasive breast carcinoma with medullary pattern that had spontaneous pathological complete regression (Pol J Pathol 2019;70:139)
Treatment
- Identical to treatment options for invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with considerations for targeted therapy based on ER, PR, HER2 status
- Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes do not alter therapy currently
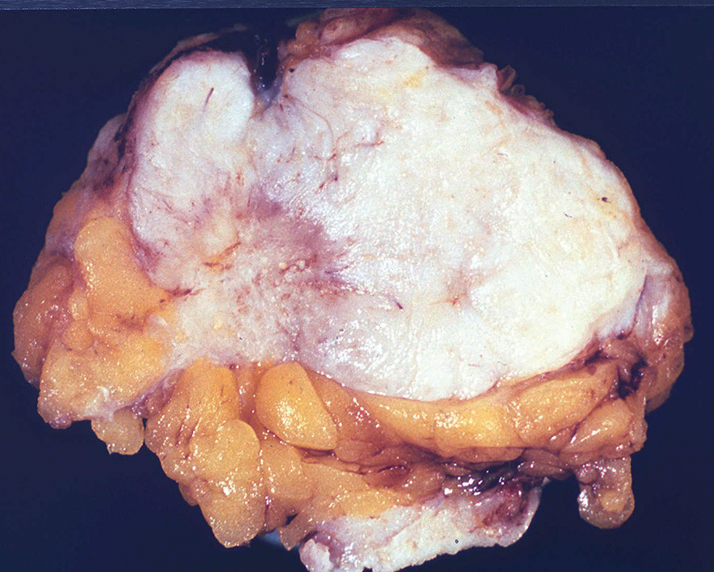
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, 2 - 3 cm in size, soft and fleshy (may resemble fibroadenoma)
- Homogenous with white to gray appearance
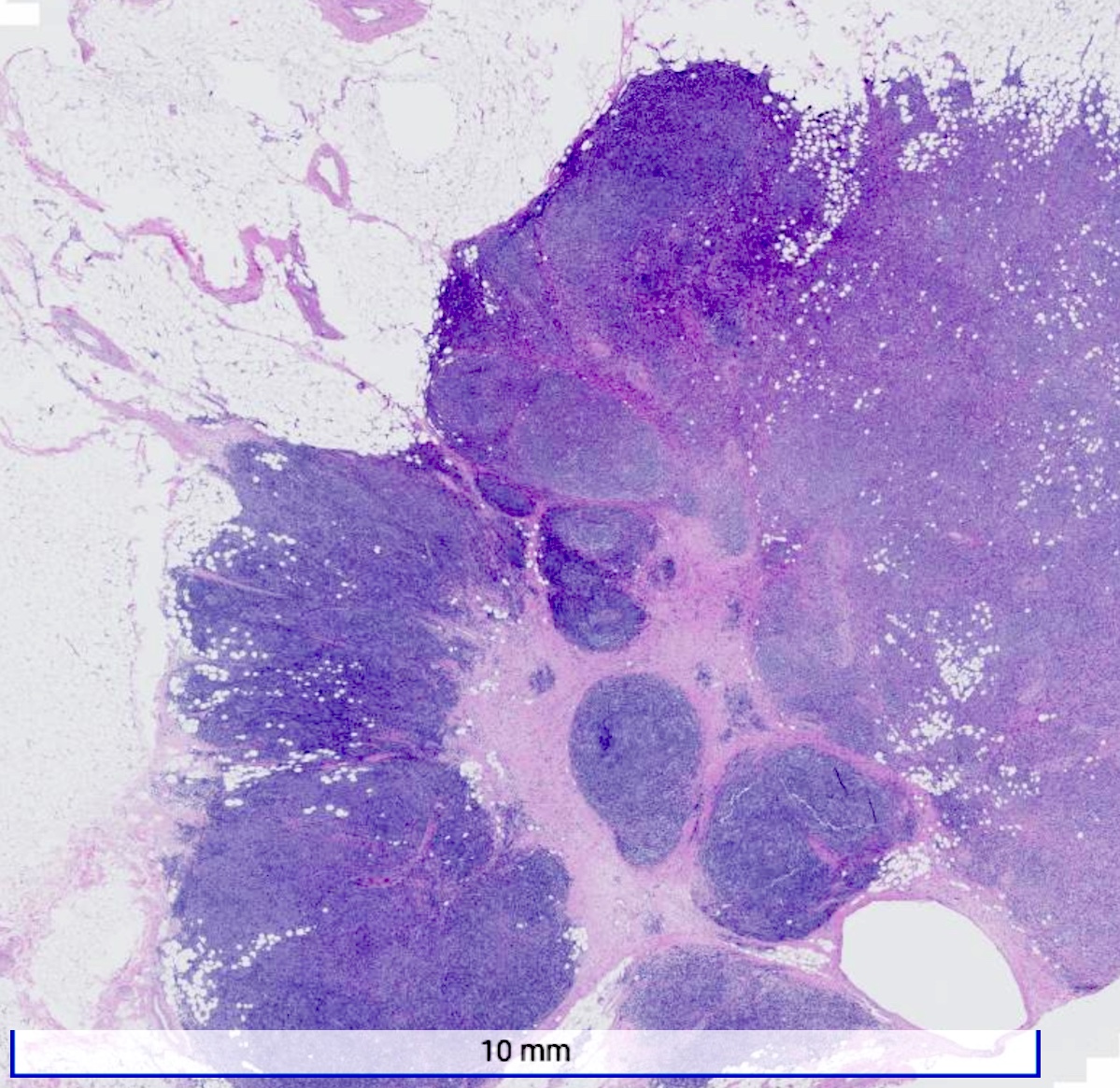
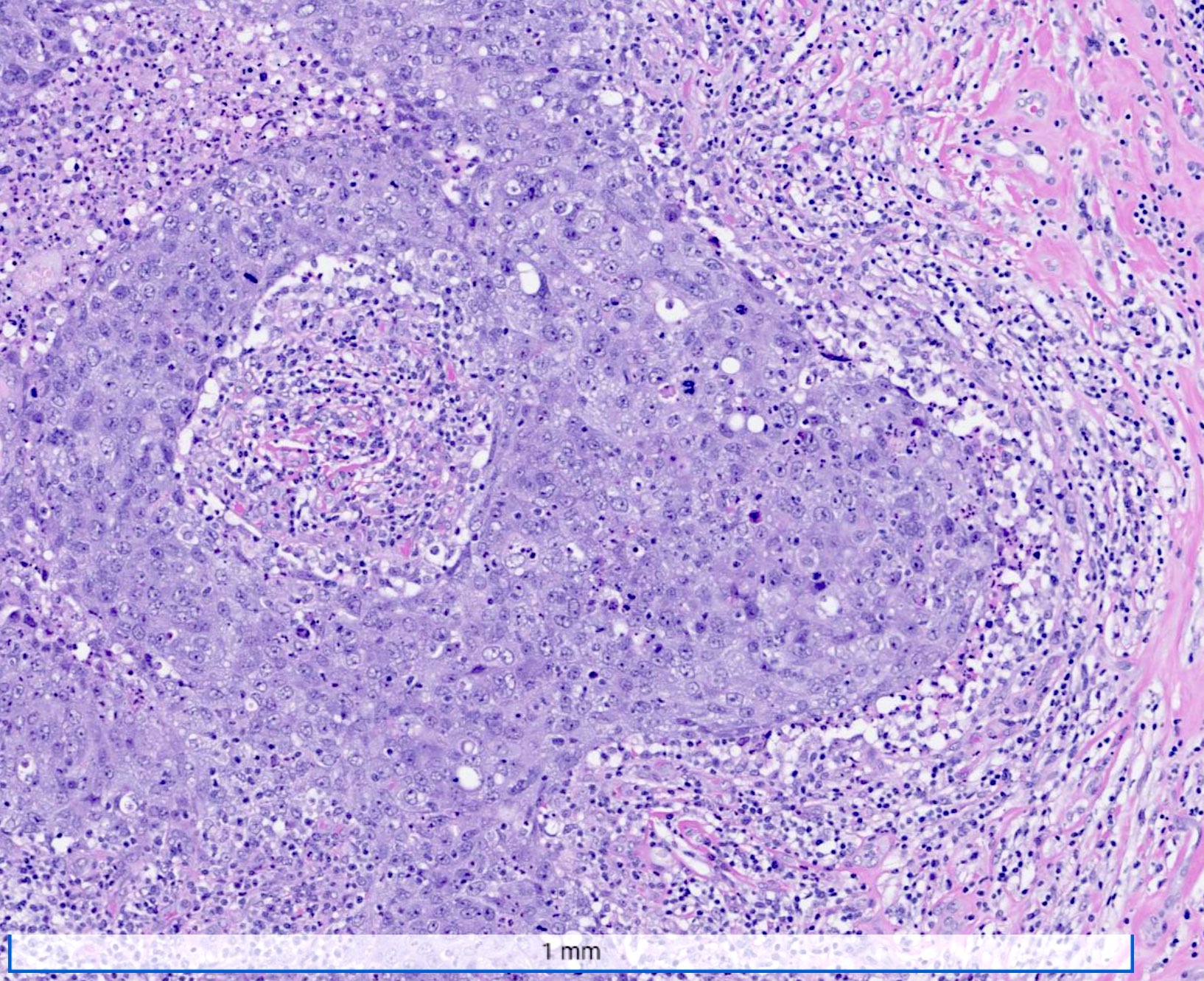
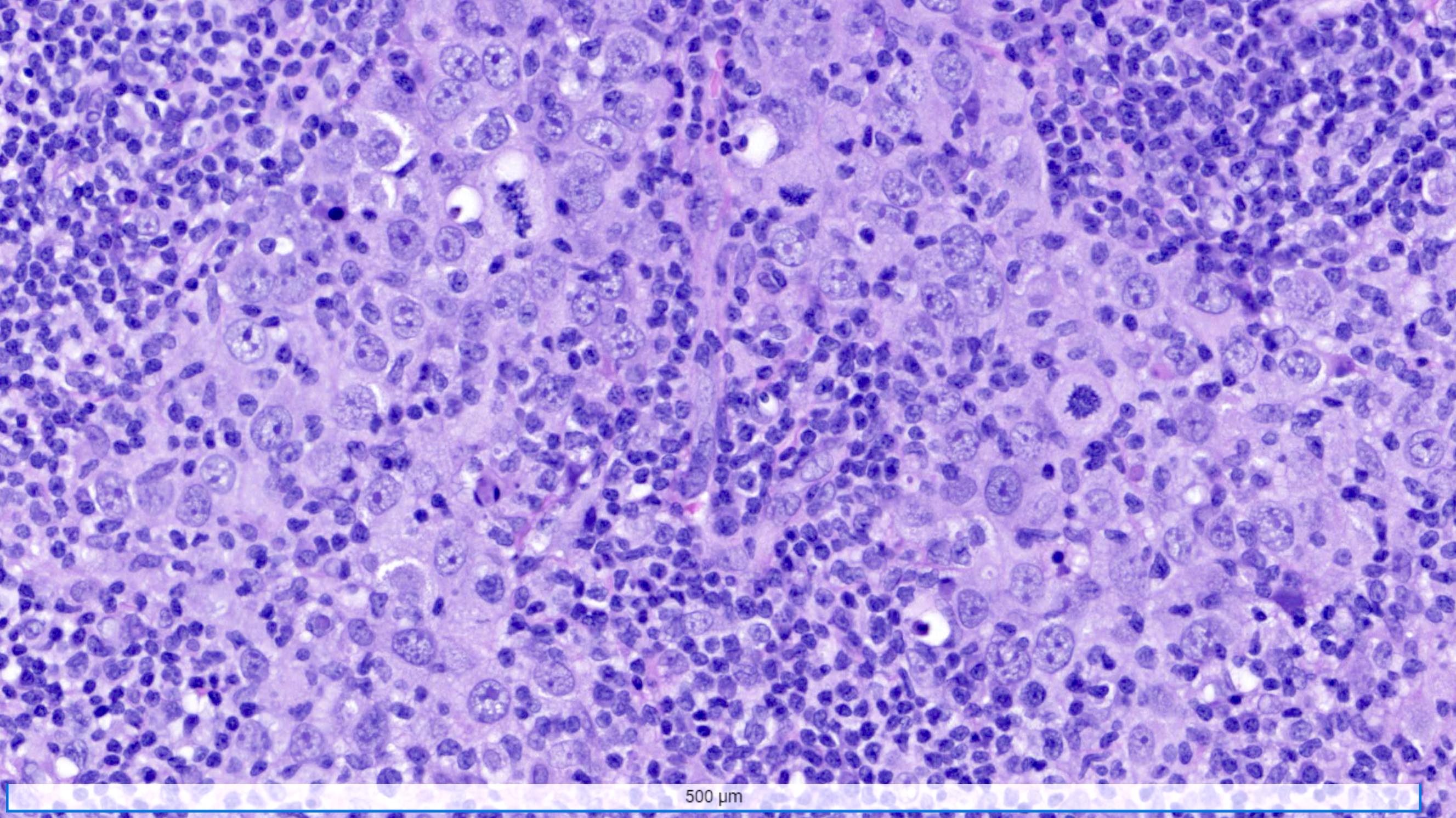
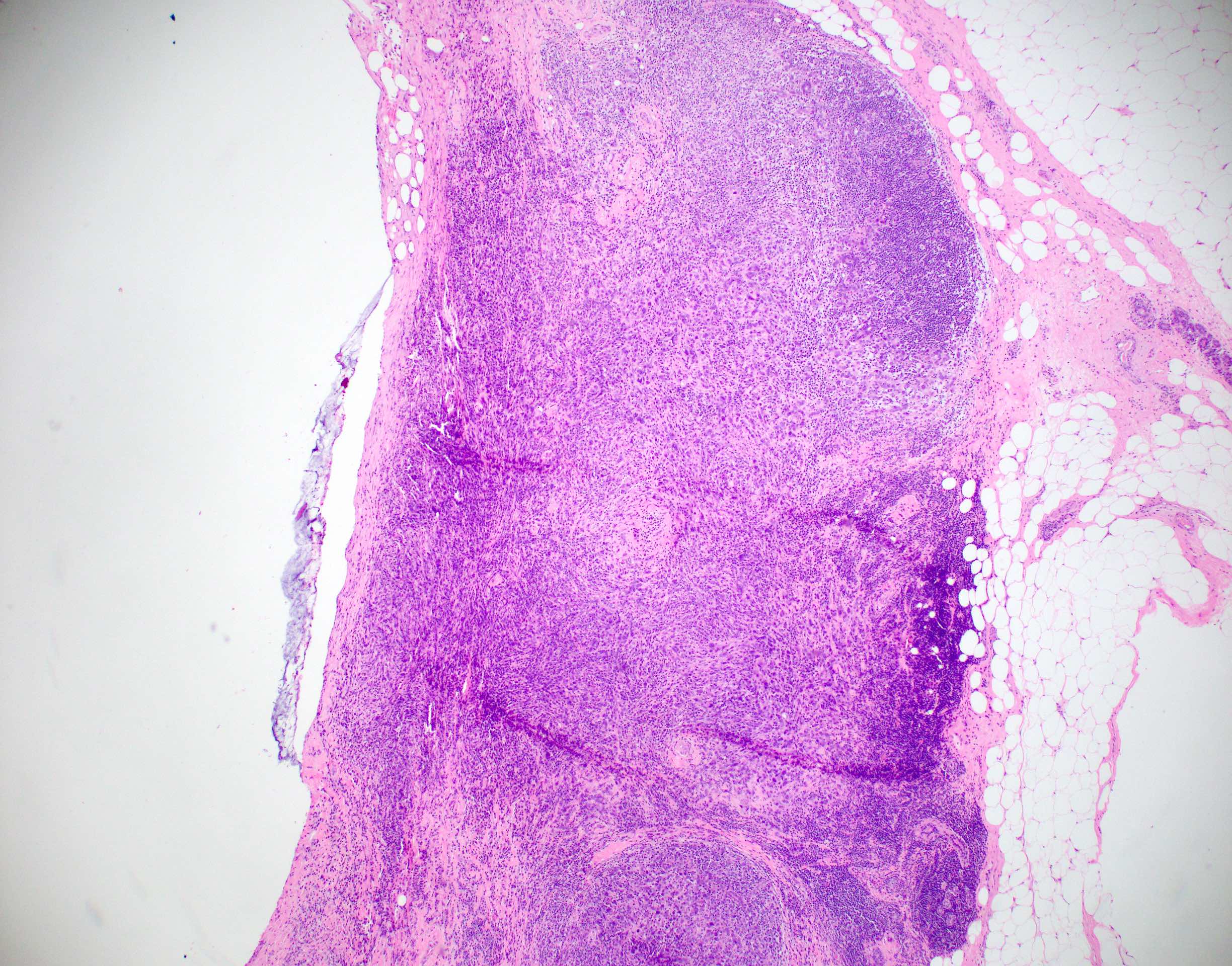
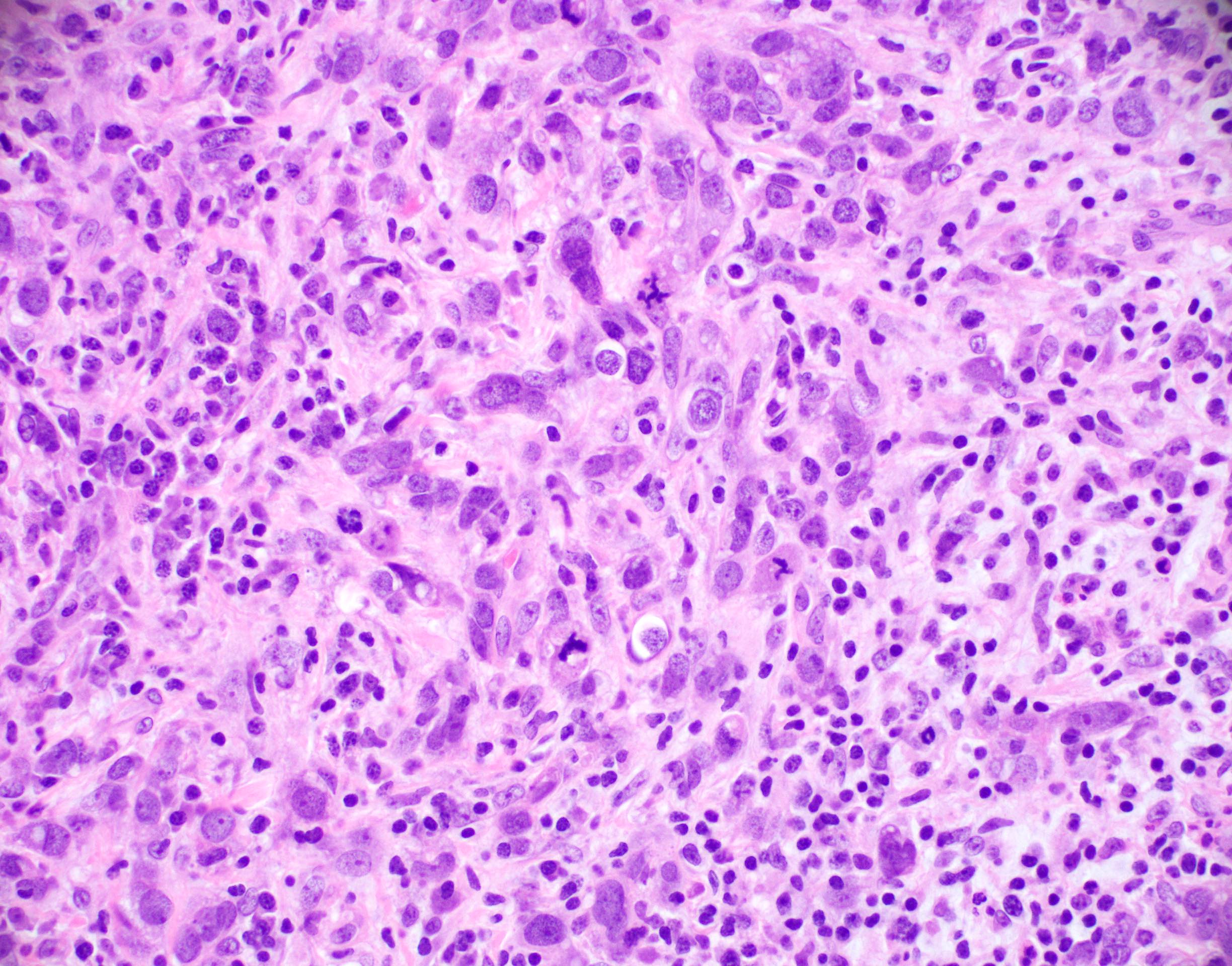
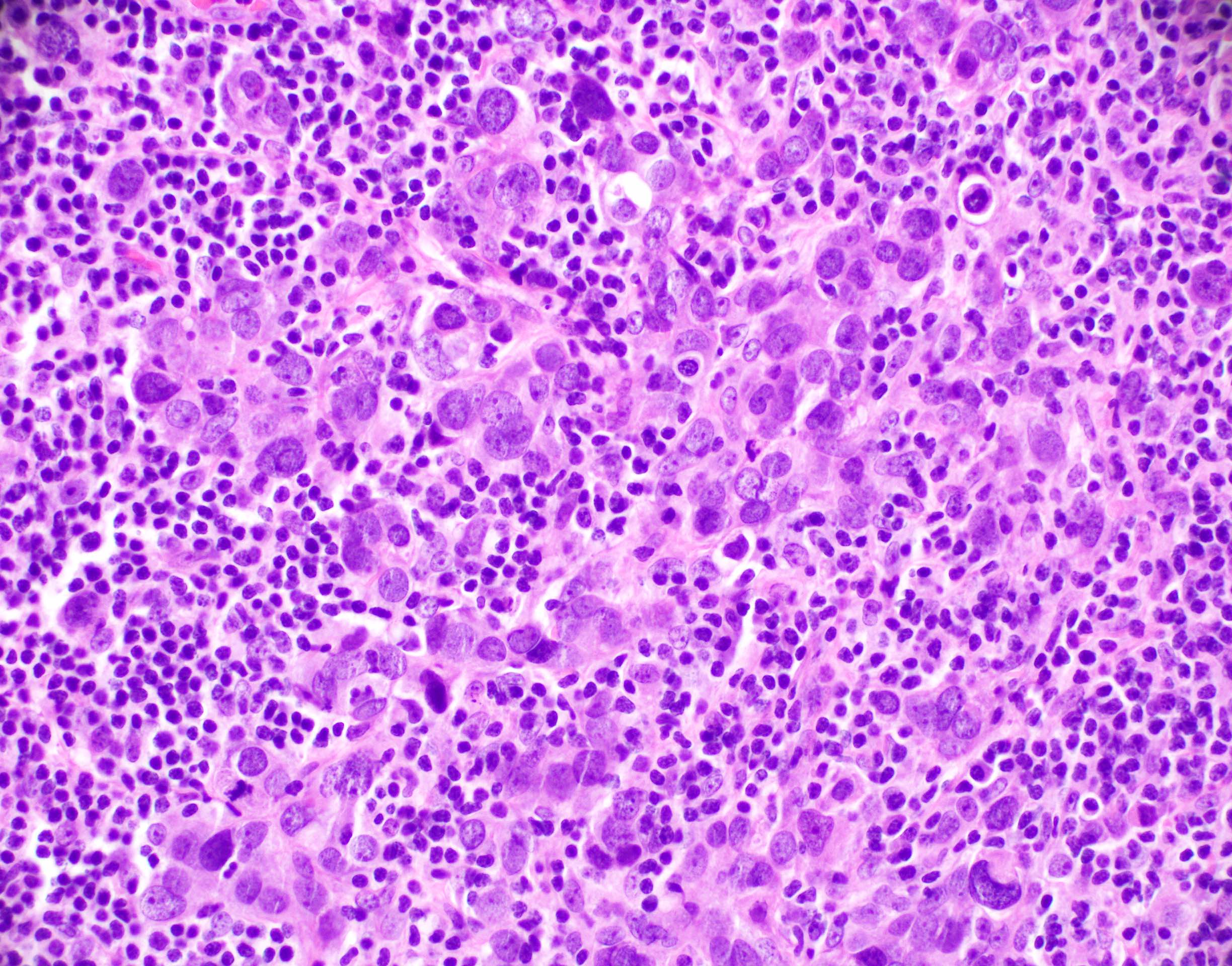
Microscopic (histologic) description
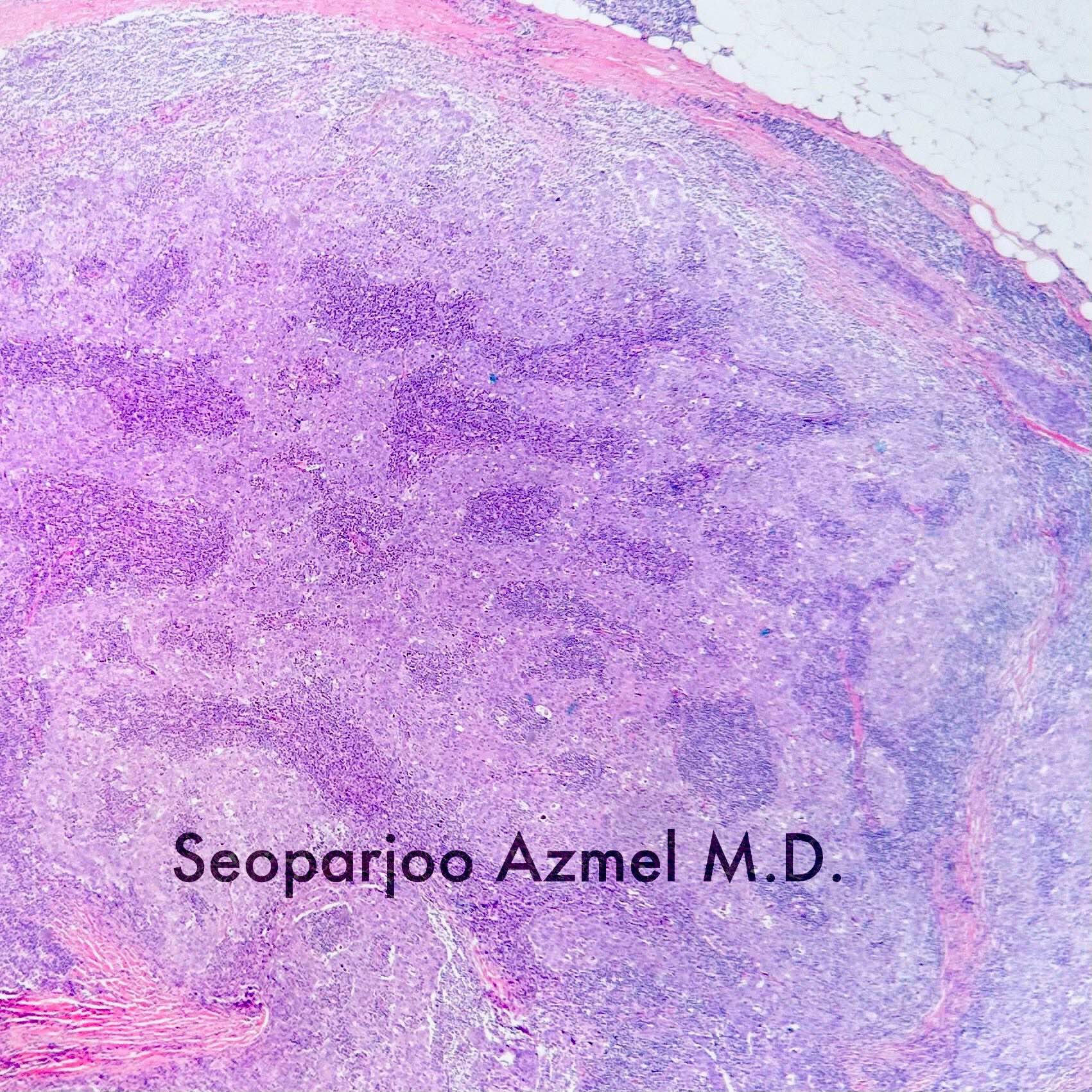
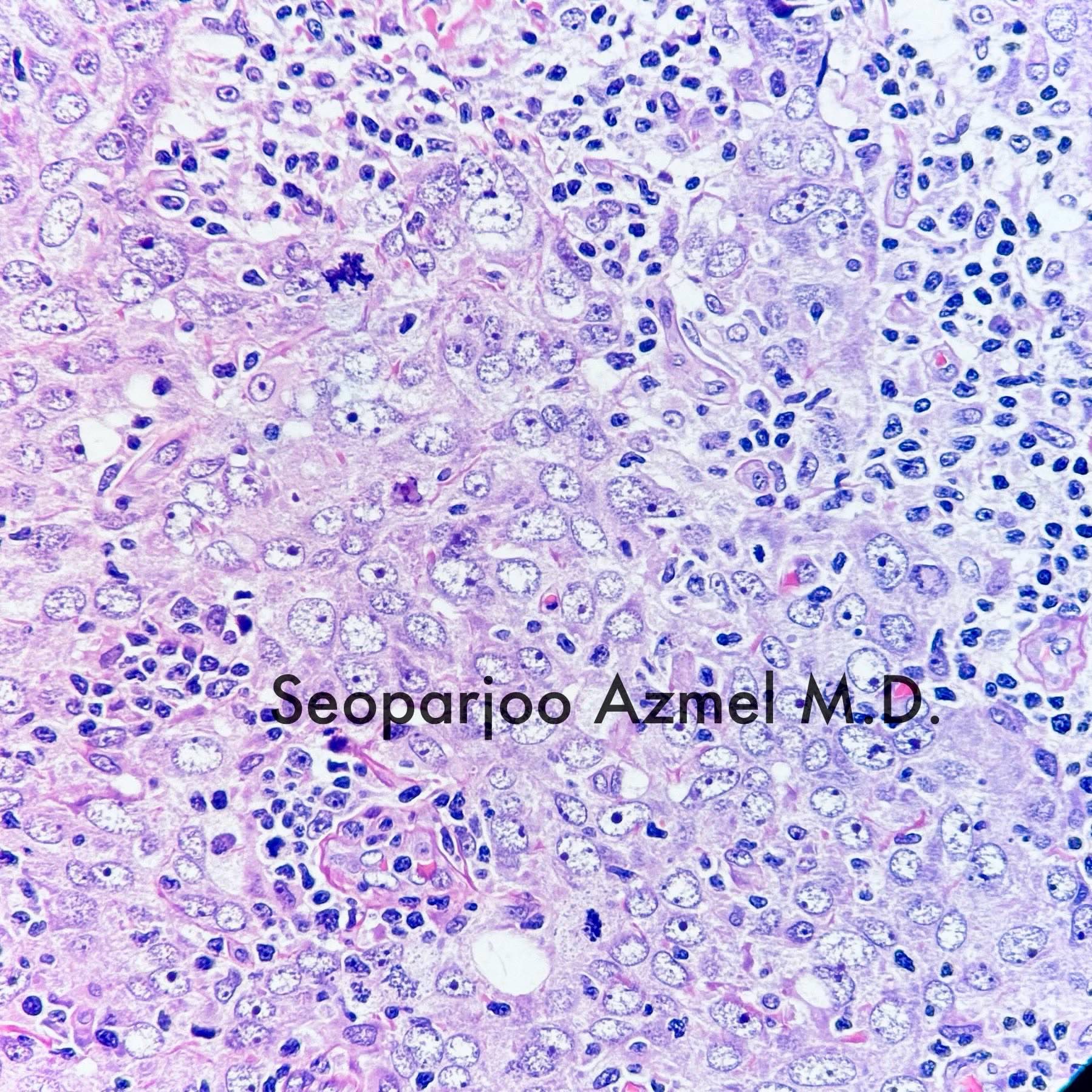
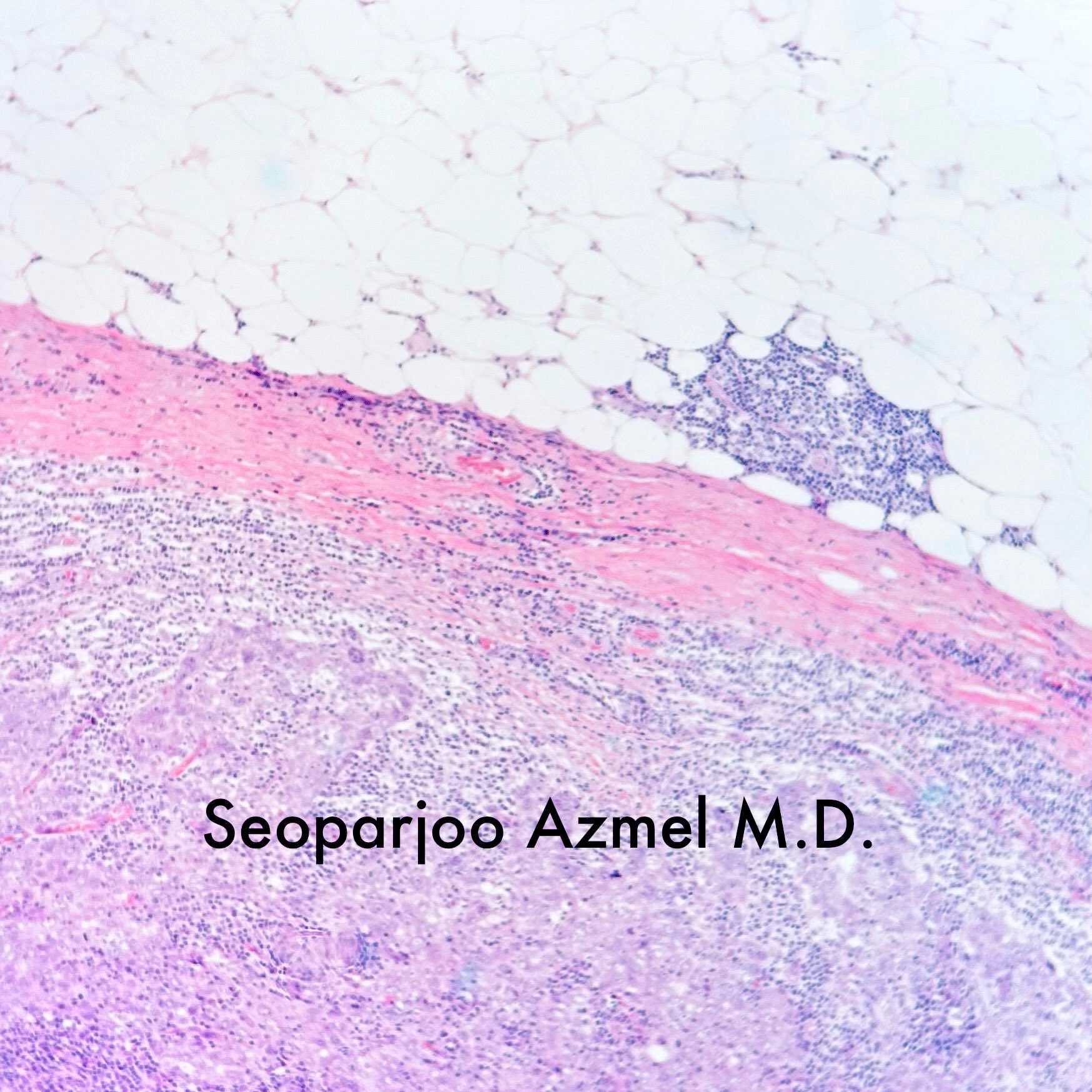
- Well circumscribed pushing border
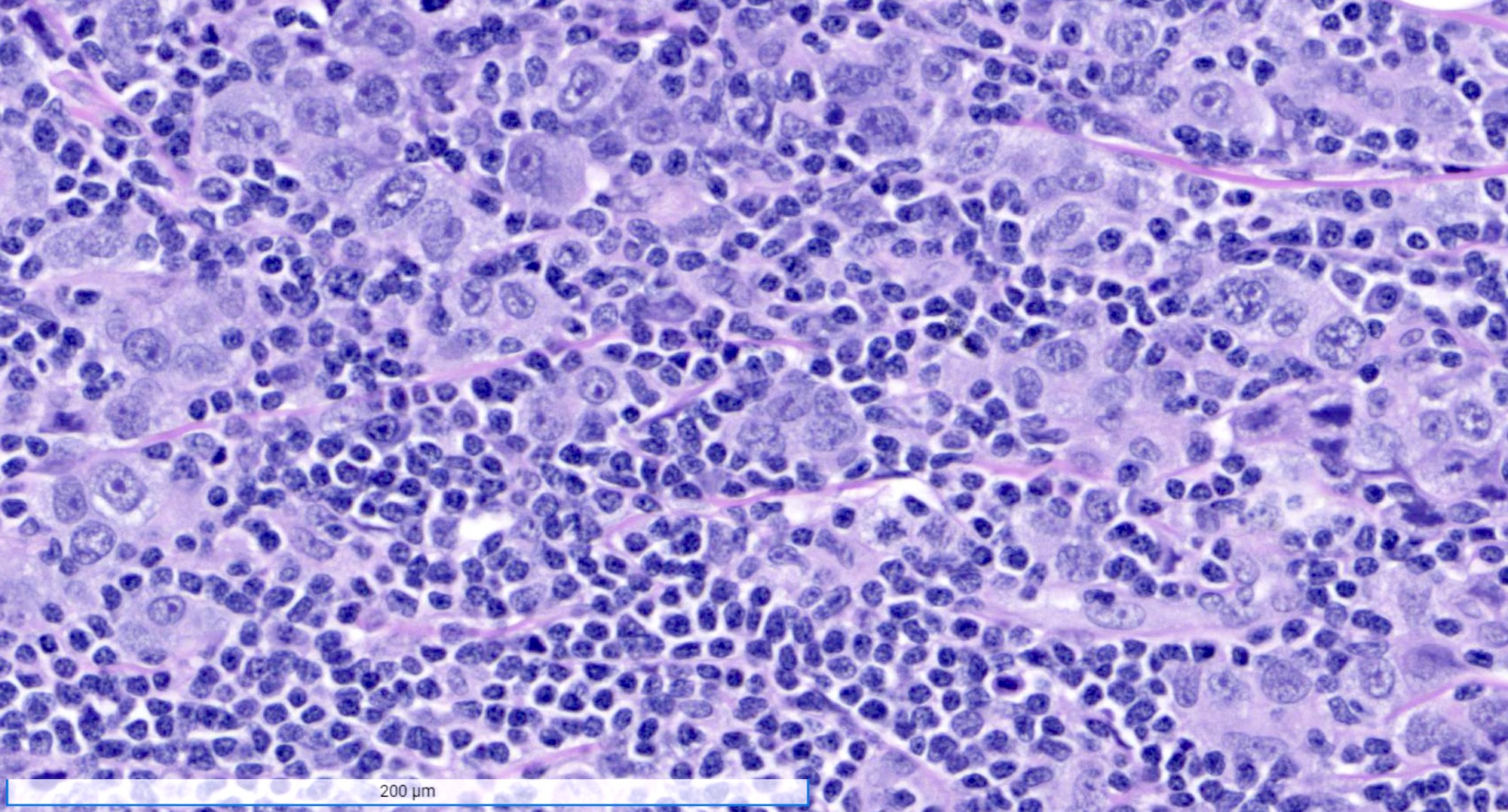
- Cells in syncytial growth pattern with no glandular structures
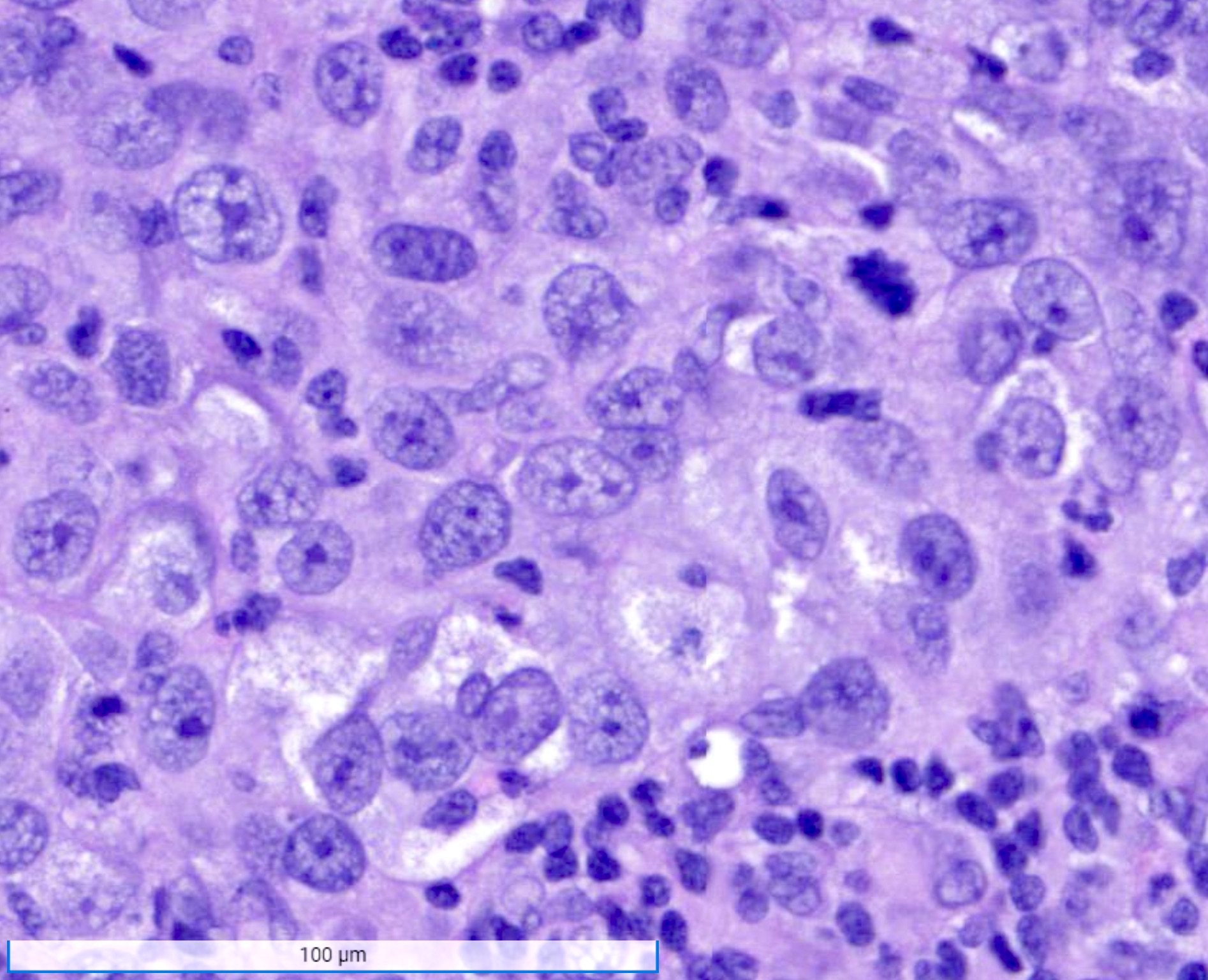
- High histologic grade, high grade nuclei with prominent nucleoli
- Prominent tumor infiltrating lymphocyte infiltrate
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Hypercellular specimen
- Numerous isolated cells and loose clusters
- Markedly enlarged, vesicular nuclei
- Prominent, often irregular macronucleolus
- Many lymphocytes and some plasma cells
Positive stains
- Variably expresses basal markers such as CK5/6, CK14, EGFR (HER1) and p53
- Higher rate of PDL1 expression (83.1%) as compared to other triple negative breast cancers (Eur J Breast Health 2019;15:235)
Negative stains
- Most often negative for hormone receptors (ER and PR) and HER2 (triple negative breast cancer)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Genomic instability is common
- Majority of these tumors fall within the basal-like molecular profile
- Approximately 15% of tumors in BRCA1 mutation carriers are classified as invasive breast carcinoma with medullary pattern (J Natl Cancer Inst 1998;90:1138)
Sample pathology report
- Breast, right, segmental mastectomy:
- Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern (see synoptic report)
- Carcinoma contains 90% stromal tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic high grade carcinoma to the breast from another site:
- Lacks a coexistent in situ component
- May be within a lymph node or have abundant associated angiolymphatic invasion
- Immunohistochemistry is often needed for distinction
- Lymph node:
- Contains capsule or subcapsular sinus; both may have germinal centers
- Lymphoma:
- Tumor cells will stain with lymphoid markers, cytokeratin negative
Additional references
Board review style question #1
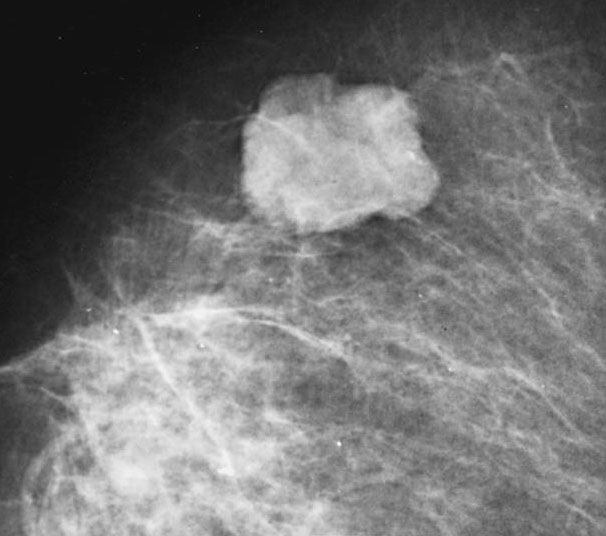
The tumor in the above image is found in the breast of a 45 year old woman. The tumor was round and soft on palpation and had pushing borders on microscopy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
- Invasive breast carcinoma with medullary pattern
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
- Secretory carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
B. Invasive breast carcinoma with medullary pattern
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is a feature of invasive breast carcinoma with medullary pattern?
- Extensive surrounding ductal carcinoma in situ
- Low histologic grade
- Present as calcifications on mammography
- Prominent lymphocytic infiltrate
Board review style answer #2
D. Prominent lymphocytic infiltrate
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern
Comment Here
Reference: Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern