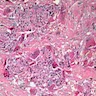
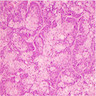
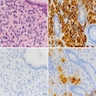
Table of Contents
Choriocarcinomatous / pleomorphic patterns (pending) | Clear cell (pending) | Glycogen rich | Lipid rich | Oncocytic (pending) | Osteoclast | Sebaceous | Signet ring cellCite this page: Roychowdhury M. NST, rare variants. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastNSTrare.html. Accessed January 9th, 2025.
Choriocarcinomatous / pleomorphic patterns (pending)
Clear cell (pending)
Glycogen rich
Definition / general
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Prognostic factors
Case reports
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
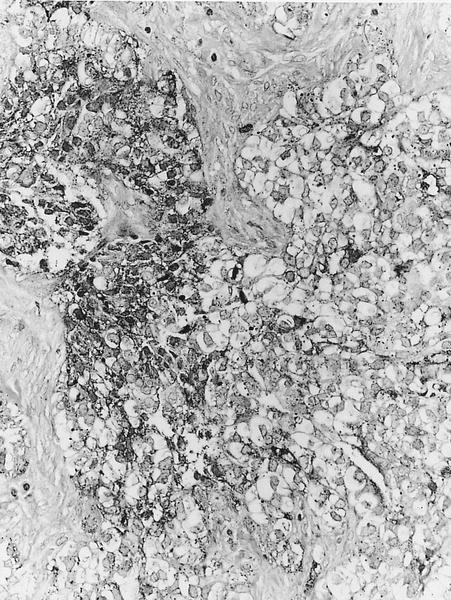
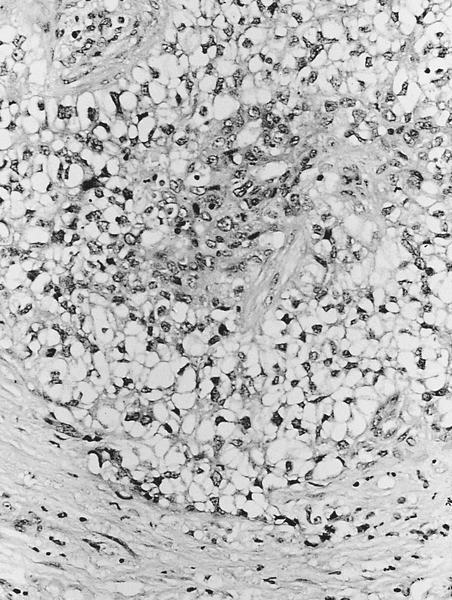
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
Positive stains
Negative stains
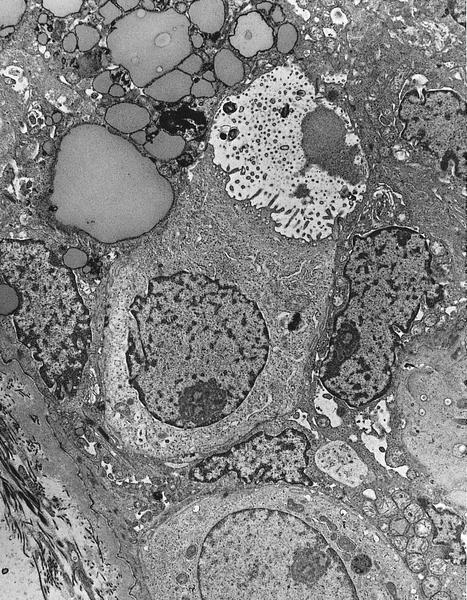
Electron microscopy description
Differential diagnosis
Additional references
- Breast carcinoma in which at least 90% of the neoplastic cells have abundant clear cytoplasm due to glycogen
- First described in 1981 (Cancer 1981;48:2003)
- Rare, 1% - 3% of breast carcinomas
- May be a variant of apocrine carcinoma
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers:
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis similar to invasive ductal carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:904)
Case reports
- 33 year old woman whose tumor had neuroendocrine features (Pathologica 2001;93:676)
- 45 year old woman with solid papillary tumor (J Clin Pathol 2003;56:552)
- 55 year old woman (Case Rep Oncol 2011;4:452)
- 59 year old woman (World J Surg Oncol 2008;6:44)
- 61 year old woman (Arch Med Lab Pathol 2003;127:1629)
- Intraductal lipid rich carcinoma with component of glycogen rich carcinoma (J Breast Cancer 2012;15:135)
Gross images
Images hosted on other servers:
Microscopic (histologic) description
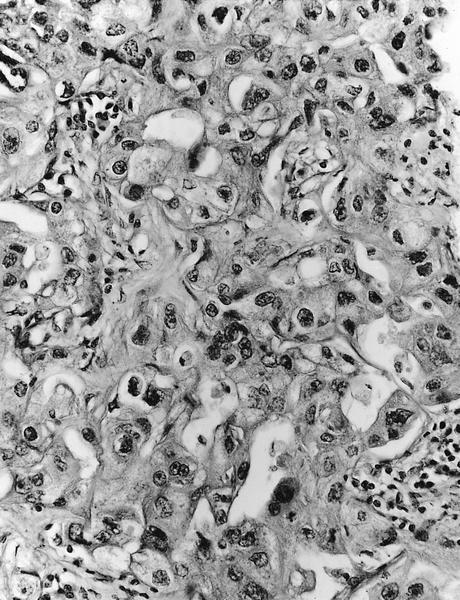
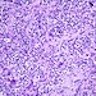
- Solid or solid / papillary patterns of large clear cells with distinct cell borders containing glycogen in 90% or more cells
- Often associated with intraductal component of varied type
- Often has apocrine features
- Cells have clear to granular cytoplasm
- May have scant intracellular mucin (Histopathology 1987;11:857)
- No cytoplasmic vacuoles
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Hypercellular with tumor cells in loosely cohesive syncytial groups and some single cells
- Most tumor cells have abundant, finely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm or foamy to clear cytoplasm with well defined cytoplasmic membranes and moderate / marked nuclear pleomorphism with central round/oval nuclei containing prominent nucleoli (Acta Cytol 2008;52:65)
- PAS staining may be helpful (J Med Invest 2002;49:193)
Positive stains
- PAS diastase sensitive (glycogen)
Negative stains
- CK20, lipid stains (done on fresh / frozen tissue)
Electron microscopy description
- Non membrane bound glycogen and empty glycogen lakes
- Tight junctions between tumor cells, immature desmosomes, occasional short microvilli (Am J Surg Pathol 1986;10:553)
Differential diagnosis
- Apocrine carcinoma
- Clear cell sugar tumor:
- Positive for melanocytic markers (Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:670)
- Lipid rich carcinoma:
- Positive for lipid stains, negative for glycogen
- Myoepithelial lesions
- Secretory carcinoma:
- Younger patients, low grade histology
Additional references
Lipid rich
Definition / general
Clinical features
Prognostic factors
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Electron microscopy images
AFIP images
Differential diagnosis
- 90%+ cells have prominent intracytoplasmic neutral lipid
Clinical features
- 1% - 2% of breast carcinomas
- Axillary metastases may resemble histiocytes
Prognostic factors
- Poor prognosis due to frequent (70%) nodal metastases at presentation
Case reports
- 53 year old woman (Acta Chir Belg 2008;108:115)
- 55 year old man (Pathology 1995;27:280)
- 56 year old woman with focal chondroid metaplasia in tumor (Pathol Int 1998;48:912)
- 62 year old woman (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e396)
- 78 year old woman with solid alveolar pattern in tumor (Breast Cancer 1998;5:171)
Gross description
- Lobulated, variable circumscription, firm
- 1 to 15 cm
Microscopic (histologic) description
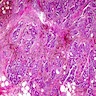
- Nests, cords and sheets of large polygonal cells with foamy or vacuolated cytoplasm containing lipid
- May resemble clear cells or lipoblasts
- Irregular nuclei with coarse chromatin, moderate atypia, prominent nucleoli
- Other patterns are large pleomorphic cells in alveolar pattern with hobnail appearance, oncocytic or apocrine type change
Microscopic (histologic) images
AFIP images
Positive stains
- Lipid stains (Sudan black, Oil red O on fresh tissue)
- HER2 (71%+) (Tumori 2008;94:342, Ann Diagn Pathol 2011;15:225)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Numerous intracytoplasmic non membrane bound lipid droplets, often within autophagocytic vacuoles
- No evidence of lipid synthesis by rough ER or Golgi complexes (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1988;413:381)
Electron microscopy images
AFIP images
Differential diagnosis
- Apocrine carcinoma:
- Uniformly granular and eosinophilic cytoplasm, GCDFP-15+, no lipid
- Glycogen rich carcinoma:
- Clear cytoplasm, secretions are glycogen (PAS+), not lipid
- Oncocytic carcinoma:
- Granular and markedly eosinophilic cytoplasm, no lipid
- Secretory carcinoma:
- Low grade, PASd+ secretions, no lipid
- Xanthogranulomatous mastitis (on core biopsy):
- Not invasive, cells are CD68+, alpha-1-antitrypsin+ histiocytes (Pathol Int 2009;59:234)
Oncocytic (pending)
Osteoclast
Definition / general
Case reports
Gross description
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Additional references
- Part of WHO classification
- Osteoclastic giant cells are present in stroma
- Presence of giant cells does not alter prognosis
Case reports
- 44 year old and 83 year old women (Diagn Pathol 2010;23:55)
- 46 year old woman (Radiographics 2002;22:691)
- 51 year old woman with pleomorphic carcinoma and prominent osteoclastic giant cells (Pathol Int 2009;59:91)
- Cases with neuroendocrine carcinoma (Pathologica 2008;100:176)
Gross description
- Often brown due to vascular stroma with hemosiderin
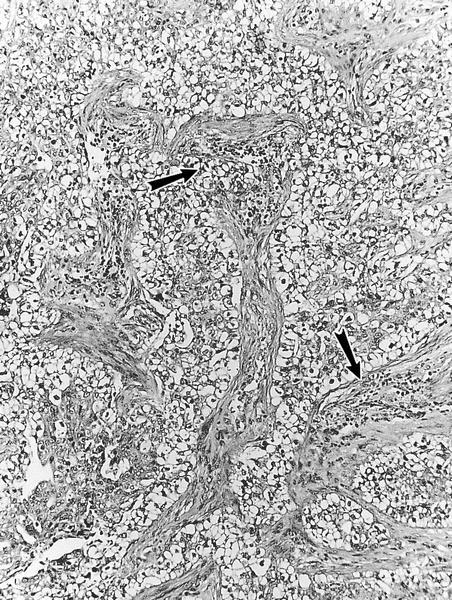
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Giant cells are associated with vascular stroma with extravasated red blood cells and hemosiderin, also chronic inflammatory cells and fibroblasts
- Giant cells have variable size and variable numbers of nuclei
- Similar histologic features in nodal metastases and recurrences (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:636)
- Carcinoma component may be any type
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Abundant giant cells and mononucleated stromal cells associated with carcinoma cells (Diagn Cytopathol 2005;33:246)
Positive stains
- Osteoclastic giant cells: CD68; also acid phosphatase, lysosome, nonspecific esterase; also MMP9, TRAP, cathepsin K
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Osteoclasts are histiocytes
Additional references
Sebaceous
Definition / general
Clinical features
Case reports
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
Differential diagnosis
- Very rare primary breast carcinoma resembling skin adnexal tumor with sebaceous differentiation, but no evidence of cutaneous derivation (see J Med Case Rep 2008;2:276 for cutaneous tumor of breast)
Clinical features
- Associated with Muir-Torre syndrome (Cancer 2005;103:1018)
Case reports
- 45 year old woman with extensive metastatic disease (Pathol Int 2000;50:63)
- 46 year old woman with Muir-Torre syndrome (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:541)
- 50 year old woman (Pathol Int 2009;59:188)
- 63 year old woman (Virchows Arch 2006;449:484)
- 83 year old woman with tumor of nipple (J Cutan Pathol 2008;35:608)
Microscopic (histologic) description
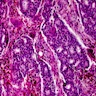
- Well defined solid sheets or lobules of atypical epithelial cells, including large, pale or clear cells with coarsely vacuolated cytoplasm, containing Oil red O staining lipid and often scalloped nuclei
- Often focal squamous morules
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Positive stains
- Cytokeratin, including 35betaH11, EMA (Pathol Res Pract 1993;189:888)
- ER, PR, Oil Red O
- Mismatch repair genes: MLH1, PMS2, MSH2, MSH6 (Ceska Gynekol 2010;75:50)
- Some cells may express neuroendocrine markers
Negative stains
- GCDFP-15, CEA, S100 and vimentin
- Alpha smooth muscle actin, p63, androgen receptor (usually), mucins, HER2 and CK15
Electron microscopy description
- Empty appearing, non membrane bound vacuoles
Differential diagnosis
- Apocrine carcinoma:
- > 90% of tumor cells have cytologic or immunohistochemical features of apocrine cells
- Lipid rich carcinoma:
Signet ring cell
Definition / general
Case reports
Microscopic (histologic) description
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
Differential diagnosis
- Ductal carcinoma with cells resembling gastric carcinoma due to acidic mucin that fills cytoplasm and displaces nucleus
- Excludes cases with lobular features (signet ring cell variant of lobular carcinoma)
Case reports
- 40 year old woman with signet ring cell carcinoma of the breast as a source of pelvic floor metastatic mass (Acta Chir Belg 2005;105:224)
- 52 year old woman with signet ring cell carcinoma associated with invasive ductal carcinoma (Breast Cancer 1999;6:223)
- 54 year old woman with signet ring cell carcinoma of the breast with uterine metastasis (J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2012;38:948)
- 68 year old woman with signet ring cell carcinoma of the breast (Pathol Int 2000;50:67)
- 73 year old woman with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with signet ring cell and mucinous carcinoma components (Diagn Cytopathol 2007;35:171)
- 74 year old woman with metastatic breast cancer to the stomach (Case Rep Oncol 2010;3:142)
- Ductal type signet ring cell carcinoma of breast (Pathology 2011;43:282)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Mucin fills cytoplasm and displaces nucleus
- Usually coexists with invasive ductal NOS
- High nuclear grade; DCIS may be present, but no lobular features (by definition)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Images hosted on other servers:
Cytology description
- Look for signet ring cells if plasmacytoid cells are identified
- Favor ductal carcinoma if hypercellular, single signet ring cells, high nuclear grade and tubule formation
- Favor lobular carcinoma if hypocellular, single signet ring cells and mild / moderate nuclear grade (Cytopathology 2009;20:321)
Differential diagnosis
- Metastatic GI signet ring cell carcinoma:
- History, no DCIS, CDX2+ and ER- (Am J Clin Pathol 2004;121:884, ISRN Obstet Gynecol 2011;2011:426150)
- Signet ring cell variant of lobular carcinoma:
- Usually classic lobular component present, no DCIS, ER+ and E-cadherin negative