Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Molecular / cytogenetics images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Rana C. BRCA associated carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantbrca1.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Group of inherited breast cancers attributed to mutations in the breast cancer associated genes: BRCA1 and BRCA2
- Associated with increased risk of breast and ovarian cancers in women with BRCA germline mutations
Essential features
- Presence of BRCA1 / 2 genes germline mutation
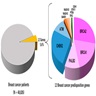
- Responsible for 25 - 30% of familial breast cancers and ~2% of all breast cancers
- Differs from sporadic breast carcinoma genotypically and phenotypically
- Occurs at a younger age (< 50 years) with high predilection for contralateral breast involvement
- Often well demarcated with pushing margins and medullary-like features
- Usually high grade (poorly differentiated) and triple negative
Terminology
- BRCA1 related breast cancer or BRCA1 germline mutation related breast cancer
- BRCA1 / 2 associated hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome
Epidemiology
- Familial breast cancer was first described by Paul Broca in 1866 (Broca: Traite Des Tumeurs, 2018)
- Constitutes 5 - 10% of all breast cancers (Breast Cancer 2021;28:1167)
- BRCA1 / 2 genes germline mutation is responsible for 25 - 30% of familial breast cancers and ~2% of all breast cancers (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Sci Rep 2020;10:7073)
- Prevalence varies among ethnic groups and countries (Clin Epidemiol 2019;11:543)
- Majority of studies are from White populations in Europe and North America (Clin Epidemiol 2019;11:543)
- Founder mutations have been documented in Ashkenazi Jewish, Icelandic, Polish, Slovenian and other populations (Am J Hum Genet 1997;60:1059, Am J Hum Genet 1997;60:1079, Int J Cancer 2004;110:683, BMC Med Genet 2008;9:83)
- Prevalence of pathogenic BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants is estimated to be between 1 in 300 and 1 in 800 in the general population (Sci Rep 2020;10:7669)
- ~1 in 40 Ashkenazi Jewish women are known to have a BRCA gene mutation (Sci Rep 2020;10:7669)
Sites
- Breast, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate and possibly other cancers can be associated with BRCA1 / 2 associated hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome
Pathophysiology
- BRCA stands for BReast CAncer gene (Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 are 2 distinct tumor suppressor genes located on chromosome 17p2.1 and chromosome 13q12.3, respectively (Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- BRCA1 / BRCA2 play crucial roles in chromatin remodeling, transcription control, cell cycle regulation and DNA repair processes (Mol Pathol 2003;56:191, Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- Cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair management have been attributed to tumor suppressive effects (Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- > 1,600 and 1,800 known variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2, respectively (Genet Med 2010;12:245)
- Majority induce frameshifts, leading to missense or nonfunctional proteins (Genet Med 2010;12:245)
- Pathogenic variant of BRCA1 increases the risk of breast cancer by 65% (44 - 78%) and ovarian cancer by 39% (18 - 54%) by the age of 70; corresponding risks are 45% (31- 56%) and 11% (2.4 - 19%) for BRCA2 (Am J Hum Genet 2003;72:1117, Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- There is an increased risk of ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, Hodgkin disease and prostate cancer associated with BRCA1 pathogenic variants (JAMA 2017;317:2402, Prostate 2019;79:880, Hered Cancer Clin Pract 2015;13:16, Medicina (Kaunas) 2021;57:905)
- Additionally, BRCA2 pathogenic variants increase the risk of cholangiocarcinoma, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, uveal melanoma and bone cancer (Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114, Hered Cancer Clin Pract 2015;13:16, Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:5953, Medicina (Kaunas) 2021;57:905)
Etiology
- Associated with underlying BRCA1 / BRCA2 germline mutation (Am J Hum Genet 2003;72:1117, Ann Lab Med 2020;40:114)
- High penetrance mutations, inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion (Am J Hum Genet 1998;62:676)
Clinical features
- Younger age at onset (usually < 50 years) (Breast Cancer 2021;28:1167)
- Higher prevalence of bilateral breast cancer (GeneReviews: BRCA1- and BRCA2-Associated Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer [Accessed 1 November 2023])
- Risk factors for contralateral breast involvement are initial cancer at a young age, family history and BRCA1 pathogenic variant (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:378)
- Higher tumor grade at the time of presentation (Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2011;34:71, Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27)
Diagnosis
- Genetic testing to detect BRCA1 and BRCA2 sequence variants is recommended (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10)
- Selection of candidates for high risk assessments is based on guidelines set by international societies such as National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2020;18:380, Ann Oncol 2023;34:33)
- Typically, blood is used; other samples such as buccal scrapes and saliva can also be used (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10, J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2020;18:380)
- Direct (Sanger) DNA sequencing is considered the gold standard (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10)
- Next generation sequencing (NGS) is better due to its ability to detect large genomic rearrangements (LGRs) in a single workflow (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10)
- Other methods include quantitative PCR and multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA) but are more labor intensive (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10)
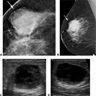
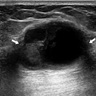
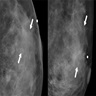
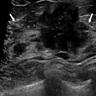
Radiology description
- Generally presents as round to oval, hypoechoic mass with a circumscribed margin (Radiology 2019;291:554)
- Not typically associated with architectural distortion and calcification (Radiology 2019;291:554)
- Mammography and ultrasound have decreased sensitivity due to (Radiology 2019;291:554, AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017;209:920)
- Masking effect of dense breast tissue in young women
- Benign appearance
- Lower incidence of ductal carcinoma in situ (especially in BRCA1 carriers)
- Dynamic contrast enhanced breast MRI is the most sensitive screening modality (sensitivity of 71 - 94%) (Radiology 2019;291:554, AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017;209:920)
- Most guidelines recommend an annual MRI screening as an adjunct to mammography (N Engl J Med 2004;351:427, AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017;209:920)
- Calcification, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), irregular / spiculated margins and architectural distortion are more commonly seen in BRCA2 associated cases (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017;209:920)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Prognostic significance of BRCA1 / 2 mutational status on breast cancer survival is still debatable (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010;119:13)
- Majority of studies have failed to demonstrate a significant overall survival difference between BRCA associated breast cancer and sporadic breast cancer (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010;119:13)
- High risk of contralateral breast cancers (10 year risk ranging from 20 to 40%) (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010;119:13)
- Metastases to the CNS occur frequently in women with BRCA1 / BRCA2 germline mutations, especially with BRCA2 mutation (Cancer 2020;126:271)
- Negative factors for overall survival may be infiltration of axillary lymph nodes, negative steroid receptor status and increased size of the primary tumor (Oncol Lett 2019;17:1986)
Case reports
- 14 year old girl with early onset breast cancer with germline pathogenic variants in both BRCA1 and TP53 genes (Front Oncol 2022;12:970641)
- 15 year old girl with BRCA positive breast cancer (Int J Surg Case Rep 2022;98:107513)
- 33 year old BRCA1 positive African American woman with locoregional recurrence (Clin Case Rep 2018;6:2457)
- 50 year old BRCA1 positive woman with brainstem metastasis under PARP inhibitors (Arch Clin Cases 2021;6:69)
- 64 year old man with a BRCA1 gene mutation associated with HER2 expression on receptor analysis (Ochsner J 2015;15:448)
Treatment
- BRCA mutation carriers
- Genetic counseling
- Regular screening as recommended by NCCN guidelines (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2021;19:77)
- As early as 18 years of age in women and 35 years of age in men, a clinical breast examination and radiological evaluation (breast MRI and mammogram) are recommended
- Ovarian cancer screening: transvaginal ultrasound and serum CA125
- Screening for prostate cancer starting 40 years of age
- Risk reduction surgeries: prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and bilateral mastectomy (nipple sparing, skin sparing) (Onco Targets Ther 2022;15:815, J Natl Cancer Inst 2009;101:80, J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2021;19:77)
- Chemoprevention: estrogen receptor modulators (i.e., tamoxifen, raloxifene) and aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal women (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2021;19:77)
- Counseling for reproductive options: prenatal diagnosis and assisted reproduction using preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) (J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2021;19:77)
- BRCA mutation associated breast cancer (Onco Targets Ther 2022;15:815)
- Total mastectomy is preferred over breast conserving surgery
- Responsive to platinum based therapy
- PARP inhibitors are effective in adjuvant, neoadjuvant and metastatic settings
Gross description
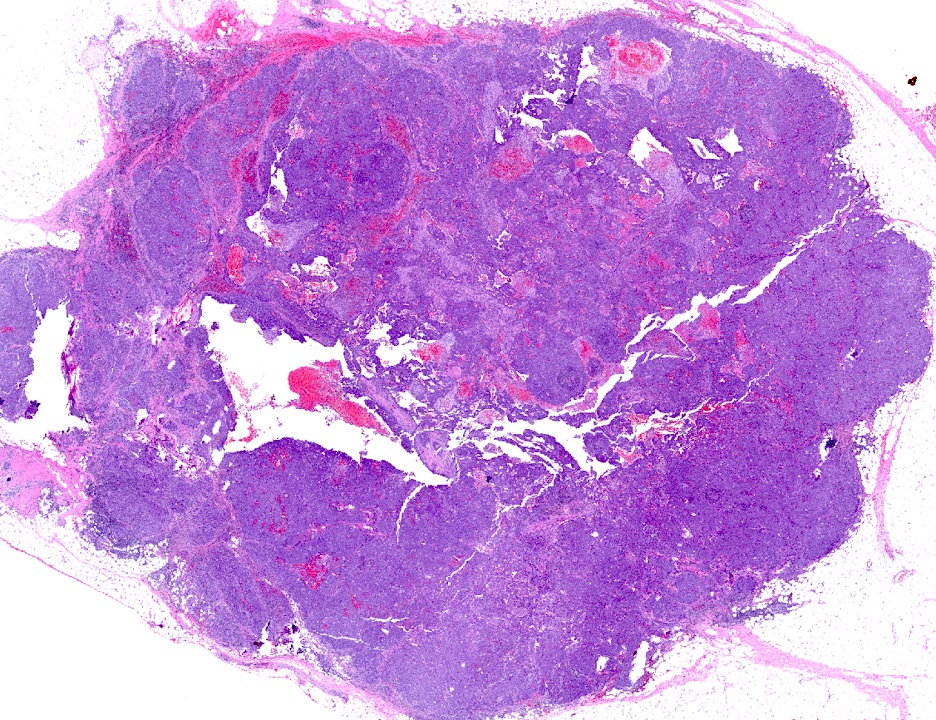
- Usually presents as well circumscribed / well demarcated fleshy mass
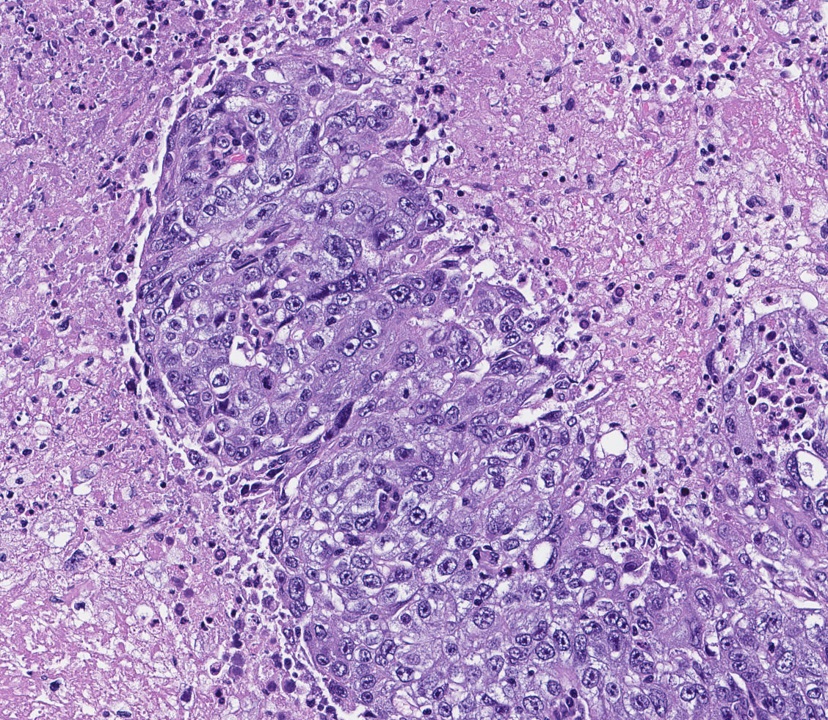
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Majority of BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancers are invasive ductal adenocarcinoma (~74%) (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27)
- Specific features of BRCA1 associated breast cancer
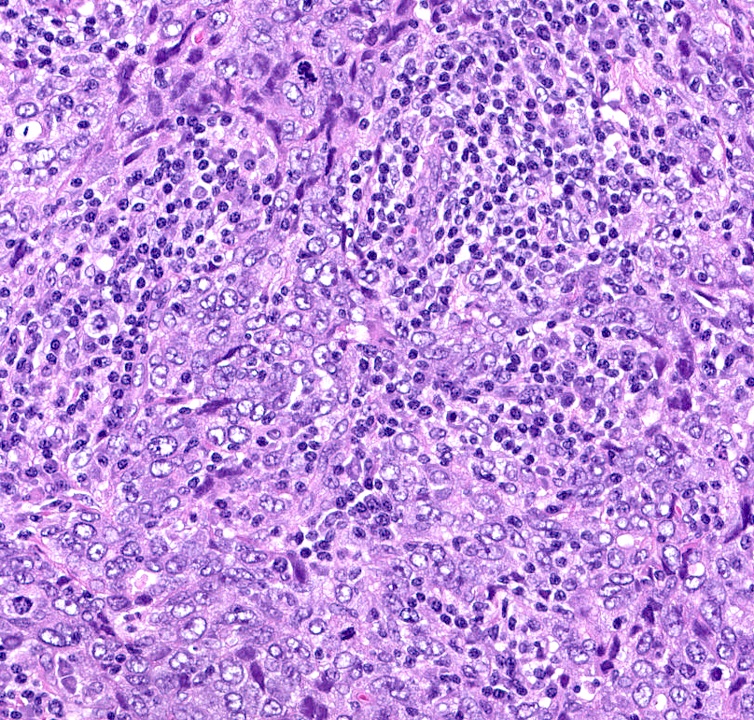
- Higher frequency of invasive breast carcinoma, NST with medullary pattern and basal-like features than sporadic breast cancer (13% versus 2%) (Lancet 1997;349:1505, Mod Pathol 2010;23:S46)
- Mostly (66 - 100%) poorly differentiated grade 3 carcinoma with syncytial appearance, large pleomorphic cells and indistinct cell membranes (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2011;34:71)
- Usually well demarcated with pushing borders, solid growth and prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Histopathology 2023;82:70)
- A high proportion (~48%) show extensive areas of necrosis (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27)
- Low grade subtypes such as tubular carcinoma are rare (J Clin Oncol 2010;28:5265)
- Specific features of BRCA2 associated breast cancer
- More heterogeneous in grade and spectrum of histological type (Mod Pathol 2010;23:S46)
- Generally low to intermediate grade compared to BRCA1 associated breast cancer (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Histopathology 2023;82:70)
- Studies have documented a higher incidence of tubular, lobular and cribriform carcinomas (Mod Pathol 2010;23:S46, Histopathology 2023;82:70)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- No specific cytology findings
- Corresponds to the histological type
Positive stains
- Basal / myoepithelial cell markers: CK5/6, CK14, EGFR (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2022;44:761)
- High Ki67 expression (Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2011;34:71, Am J Cancer Res 2015;5:2330)
- p53 overexpression (37 - 77%) (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Med Sci Monit 2016;22:1939)
- Hypoxia related proteins: HIF1a, GLUT1, CAIX (Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2011;34:71, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2020;21:629)
- Cell cycle related proteins: cyclin A, cyclin B1, cyclin E (Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:1416)
Negative stains
- Hormone receptor, usually triple negative: ER (63 - 90%), PR (60 - 80%) and HER2 neu (97 - 100%) (Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;59:27, Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet 2022;44:761)
- Cell cycle and apoptosis markers: cyclin D1, p27 (kip1), p21, p16, BCL1, BAX (Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34:1416, Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2011;34:71)
- BRCA (variable) (J Clin Pathol 2001;54:476)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Presence of heterozygous germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene (GeneReviews: BRCA1- and BRCA2-Associated Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer [Accessed 1 November 2023])
- > 1,600 and 1,800 known variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2, respectively, the majority of which lead to missense or nonfunctional proteins (Genet Med 2010;12:245)
- Sequence variant can include a single nucleotide change, a small insertion or deletion or a large genomic rearrangement (LGRs) (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10)
- Founder mutations BRCA1.185delAG, BRCA1.5382insC and BRCA2.6174delT account for 99% of the pathogenic variants in the Ashkenazi Jewish population (BJOG 2020;127:364)
- Other associated high penetrance mutations are TP53, PTEN, CDH1 and STK11 (GeneReviews: BRCA1- and BRCA2-Associated Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer [Accessed 1 November 2023])
- MYC amplification (18 - 23%), chromosome 8 polysomy, MYB amplification (~30%) are more frequently encountered in BRCA1 breast cancer as compared to sporadic (Eur J Hum Genet 2016;24:S10, Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:499, Cancer Res 2000;60:5323)
Molecular / cytogenetics images
Sample pathology report
- Right breast mass, mastectomy:
- Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary pattern (see synoptic report)
- Grade III
- Triple negative (ER / PR / HER2 neu negative)
- Comment: In view of the presence of young age, medullary pattern and triple negativity, there is a possibility of BRCA associated breast carcinoma; genetic analysis may be advised if clinically indicated.
Differential diagnosis
- Sporadic high grade invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (invasive ductal carcinoma) with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes:
- Usually elderly age group with an absence of family history
- Generally lacks circumscription and pushing margins
- Lacks BRCA mutation
- Variable hormone receptor expression
- Sporadic invasive breast carcinoma of no special type with medullary features:
- Median age is 53 years
- Lacks family history
- Genetic analysis is often needed to differentiate
- Metastatic high grade carcinoma to the breast from another site:
- Mammaglobin negative
- Radiological evidence of a primary site
- Lymphoma:
- Tumor cells will stain with lymphoid markers, cytokeratin negative, mammaglobin negative
Board review style question #1
Which statement about BRCA1 positive breast cancer, with histological features shown in the image above, is true?
- Expression of ER, PR and HER2 neu on immunohistochemistry
- High probability of the development of contralateral breast cancer in the future
- Low chance of association with ovarian cancer
- Patient is likely to be > 60 years of age
Board review style answer #1
B. High probability of the development of contralateral breast cancer in the future. BRCA associated breast cancer has high rates of contralateral breast cancer. Answer D is incorrect because BRCA associated breast cancer develops at a younger age, usually < 50 years. Answer A is incorrect because BRCA associated breast cancer is mostly triple negative. Answer C is incorrect because patients with BRCA associated breast cancers have a high chance of developing other cancers, especially ovarian cancer in women.
Comment here
Reference: BRCA1 associated breast carcinoma
Comment here
Reference: BRCA1 associated breast carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is the most sensitive radiological investigation to diagnose as well as follow up a patient with BRCA1 associated breast cancer?
- Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI
- Mammography
- Next generation sequencing
- Ultrasound
Board review style answer #2
A. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI is the most sensitive screening modality, with a sensitivity of 71 - 94%. Answers B and D are incorrect because ultrasound and mammography are limited by the masking effect of dense breast tissue in young women, demarcated nature and lower incidence of ductal carcinoma in situ BRCA associated breast cancer. Answer C is incorrect because next generation sequencing is a molecular technique.
Comment here
Reference: BRCA1 associated breast carcinoma
Comment here
Reference: BRCA1 associated breast carcinoma