Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2 | Board review style question #3 | Board review style answer #3Cite this page: Sabljic T, Mrkonjic M. Acinic cell carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastmalignantaciniccellcarcinoma.html. Accessed December 26th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant epithelial neoplasm characterized by clear and granular cells that may contain zymogen granules in the cytoplasm and shows microglandular and solid growth patterns
Essential features
- Granular eosinophilic and basophilic cytoplasm with intracytoplasmic granules that are positive for periodic acid-Schiff with diastase (PASD)
- Infiltrative microglandular and solid growth patterns
- Positive immunohistochemical staining for EMA and markers of serous acinar differentiation
Terminology
- Acinar cell carcinoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare carcinoma of the breast affecting females (20 - 80 years old); 1 case has been reported in a male, 68 cases reported in the literature (2022) (Breast Cancer 1998;5:77, Breast 2022;66:208)
Sites
- Breast, with no site predilection (Pathology 2017;49:215)
Pathophysiology
- Breast glands may show acinic differentiation that could possibly give rise to acinic cell carcinoma (Histopathology 2009;54:262)
- Acinic cell carcinoma shows similar mutations and DNA copy numbers to conventional triple negative breast carcinomas or those associated with microglandular adenosis (J Pathol 2015;237:166, Mod Pathol 2017;30:69)
- Morphologic and genetic relationship with microglandular adenosis has been reported and discussed (Mod Pathol 2017;30:1504, Mod Pathol 2017;30:1505)
- Breast acinic cell carcinomas have different mutation profiles from salivary gland acinic cell carcinomas, suggesting the entities are unrelated (Histopathology 2015;67:529)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Presentation is similar to invasive breast carcinoma of no special type, palpable mass (Pathology 2017;49:215)
Diagnosis
- Histologic and immunohistochemical examination of lesional tissue (Pathology 2017;49:215)
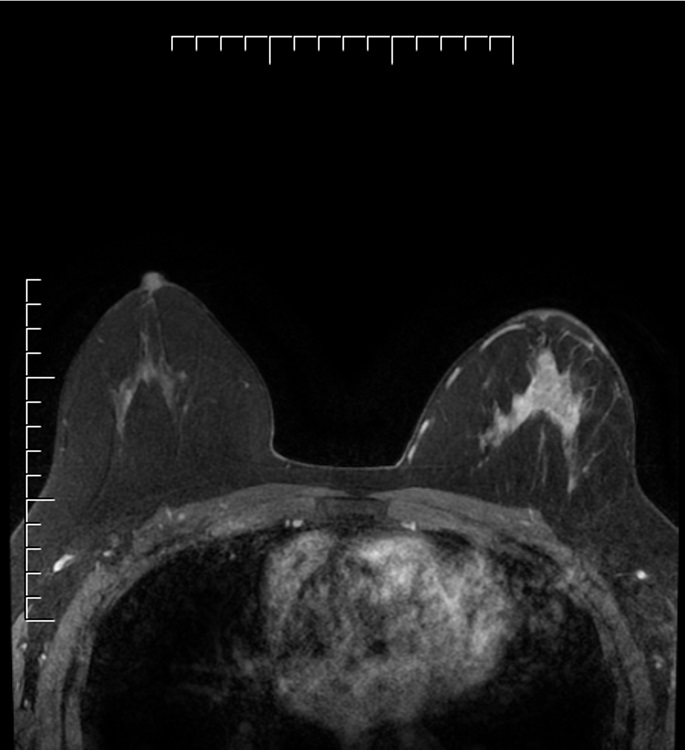
Radiology description
- Poorly defined lump / mass with microcalcifications, although may vary in clinical and radiological appearance (Breast 2022;66:208)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Knowledge about prognosis is limited, thought to be a triple negative tumor with intermediate aggressive potential
- Molecular evidence suggests that it could be the precursor of more aggressive forms of triple negative breast carcinoma (J Pathol 2015;237:166)
- Axillary lymph node metastases are rare, reported in 11 of 68 reports (Breast 2022;66:208)
- Potential for distant metastases to liver, bone and lung (Histopathology 2004;45:645, J Clin Pathol 2002;55:545, Ann Diagn Pathol 2011;15:84)
- Peritoneal metastases have also been reported (Mol Clin Oncol 2022;16:43)
Case reports
- 26 year old woman diagnosed with acinic cell carcinoma of the breast within a fibroadenoma (Int J Surg 2014;12:S232)
- 41 year old woman with palpable right breast lump (Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2018;35:137)
- 44 year old woman diagnosed with acinic cell carcinoma of the breast and carrying a BRCA1 mutation (BMC Cancer 2013;13:46)
- 52 year old woman with palpable lump in the outer quadrant of her right breast (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8866)
- 59 year old woman with a lump in her right breast (Mol Clin Oncol 2022;16:43)
Treatment
- Breast conserving surgery or mastectomy, generally with sentinel lymph node excision or axillary lymph node dissection; with or without neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy, hormonal therapy (if ER positive) (Breast 2022;66:208)
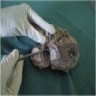
Gross description
- Poorly defined, gray-brown, rubbery, slightly lobulated appearance (J Breast Cancer 2011;14:160)
Gross images
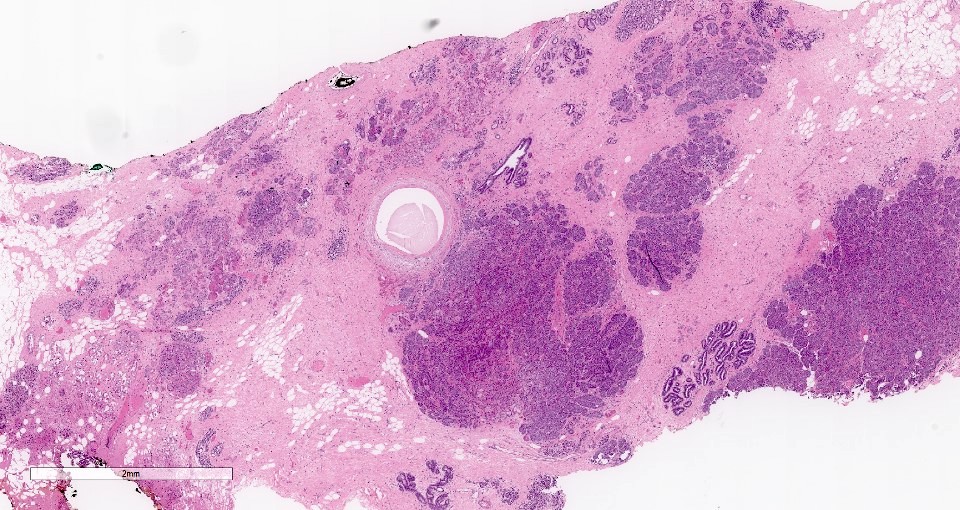
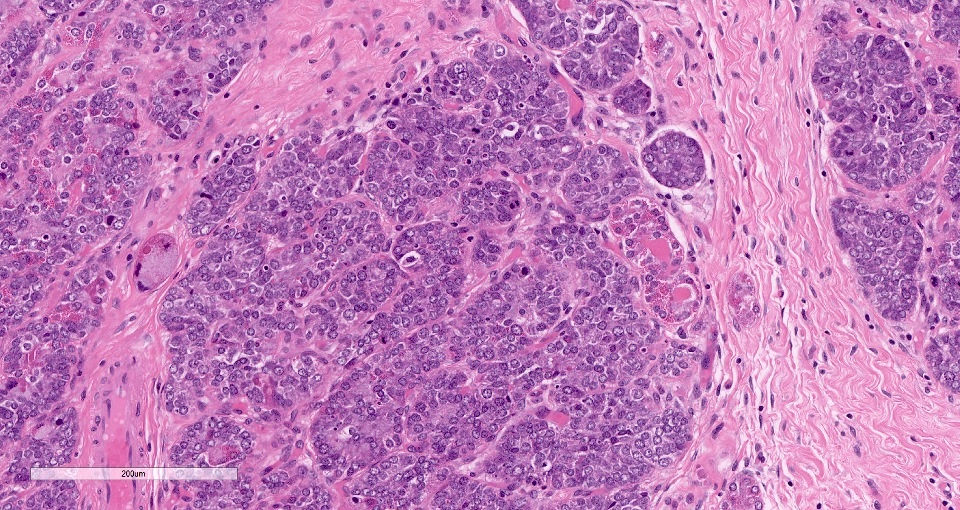
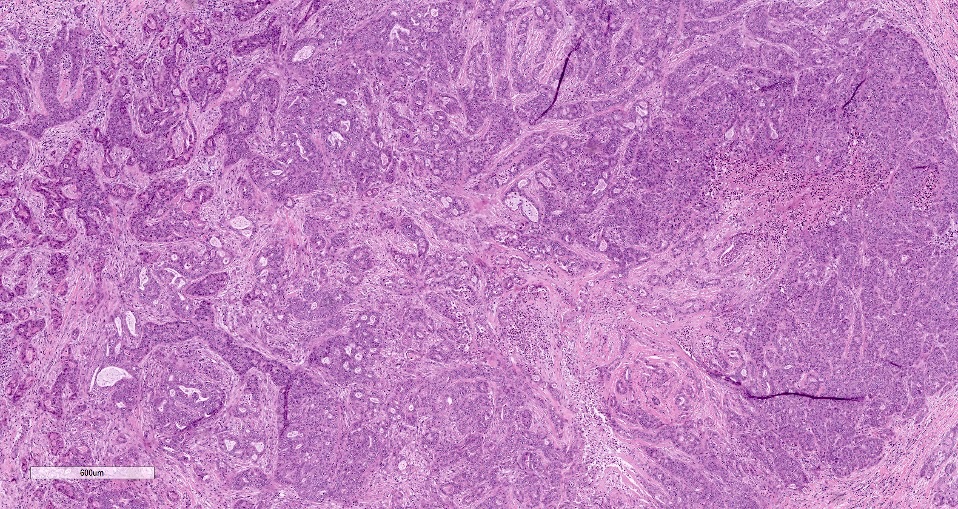
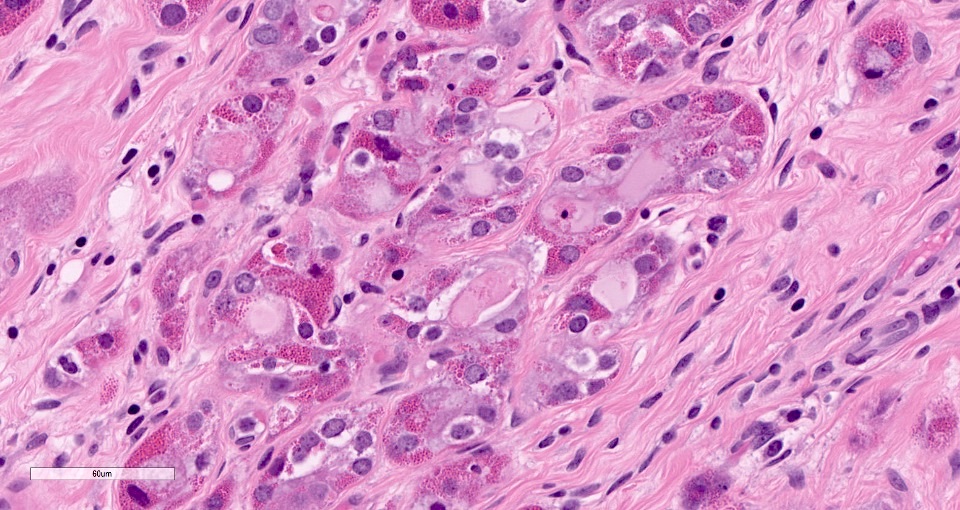
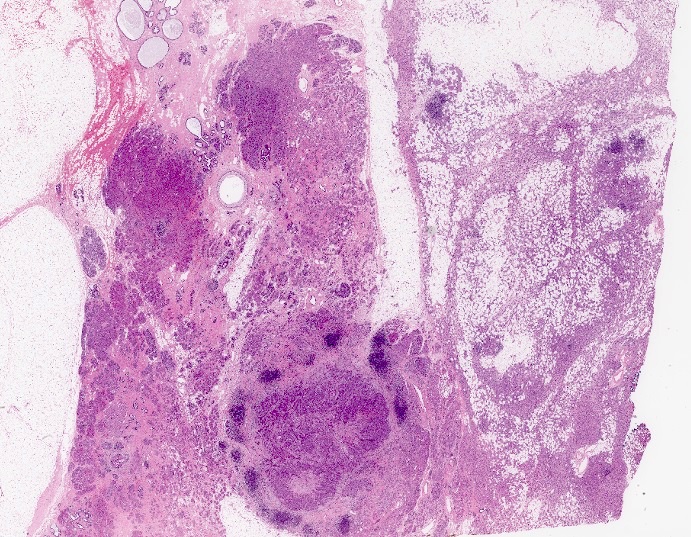
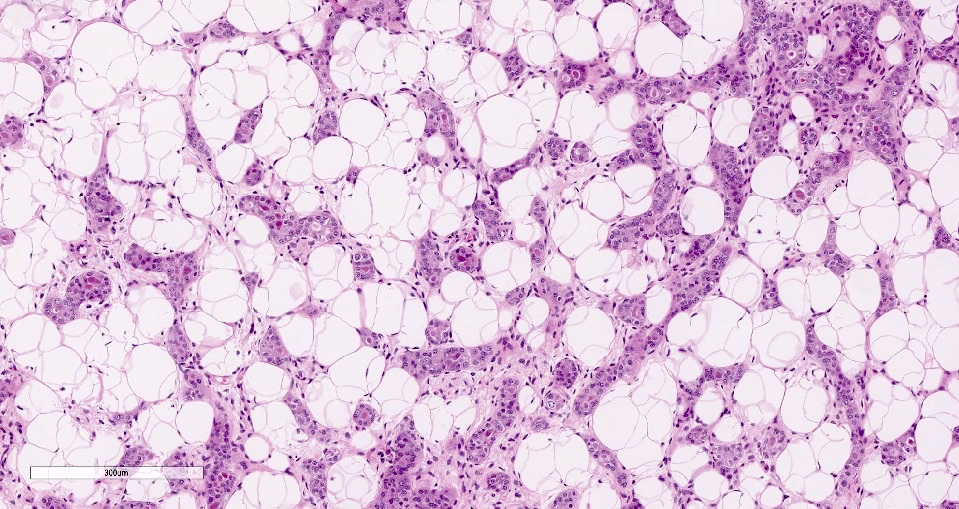
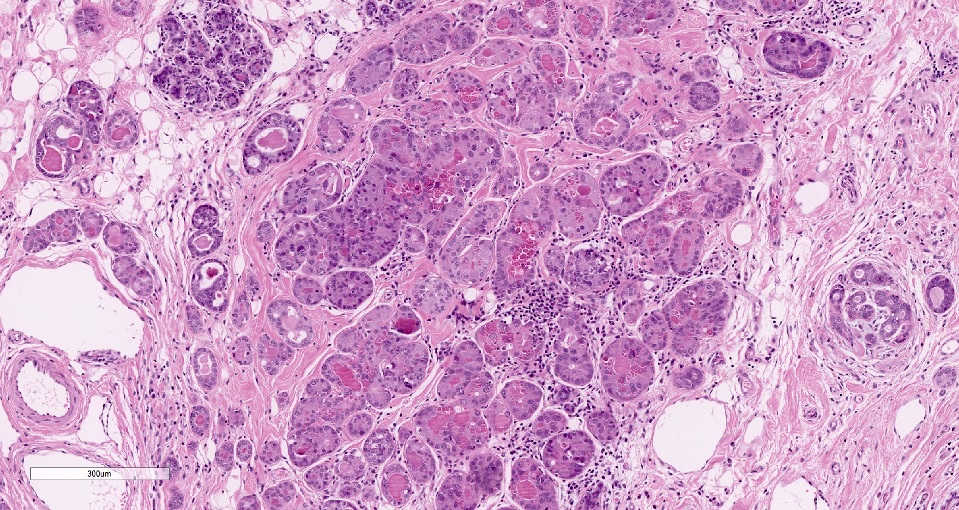
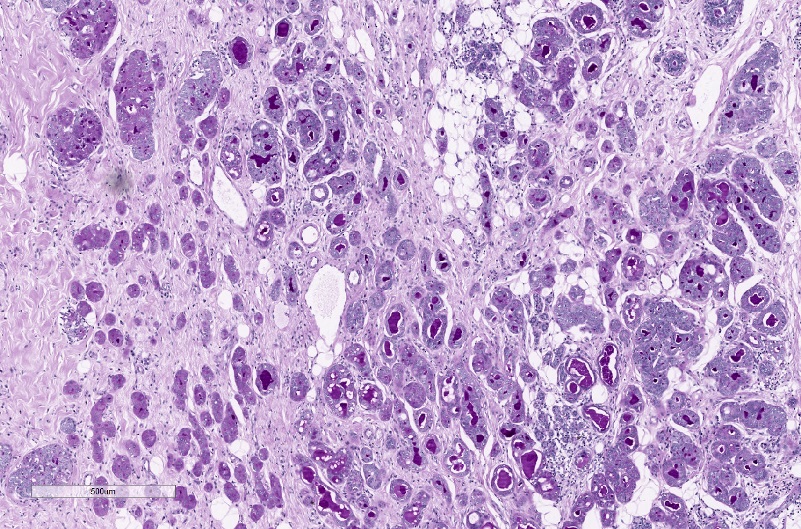
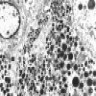
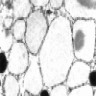
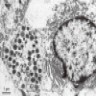
Microscopic (histologic) description
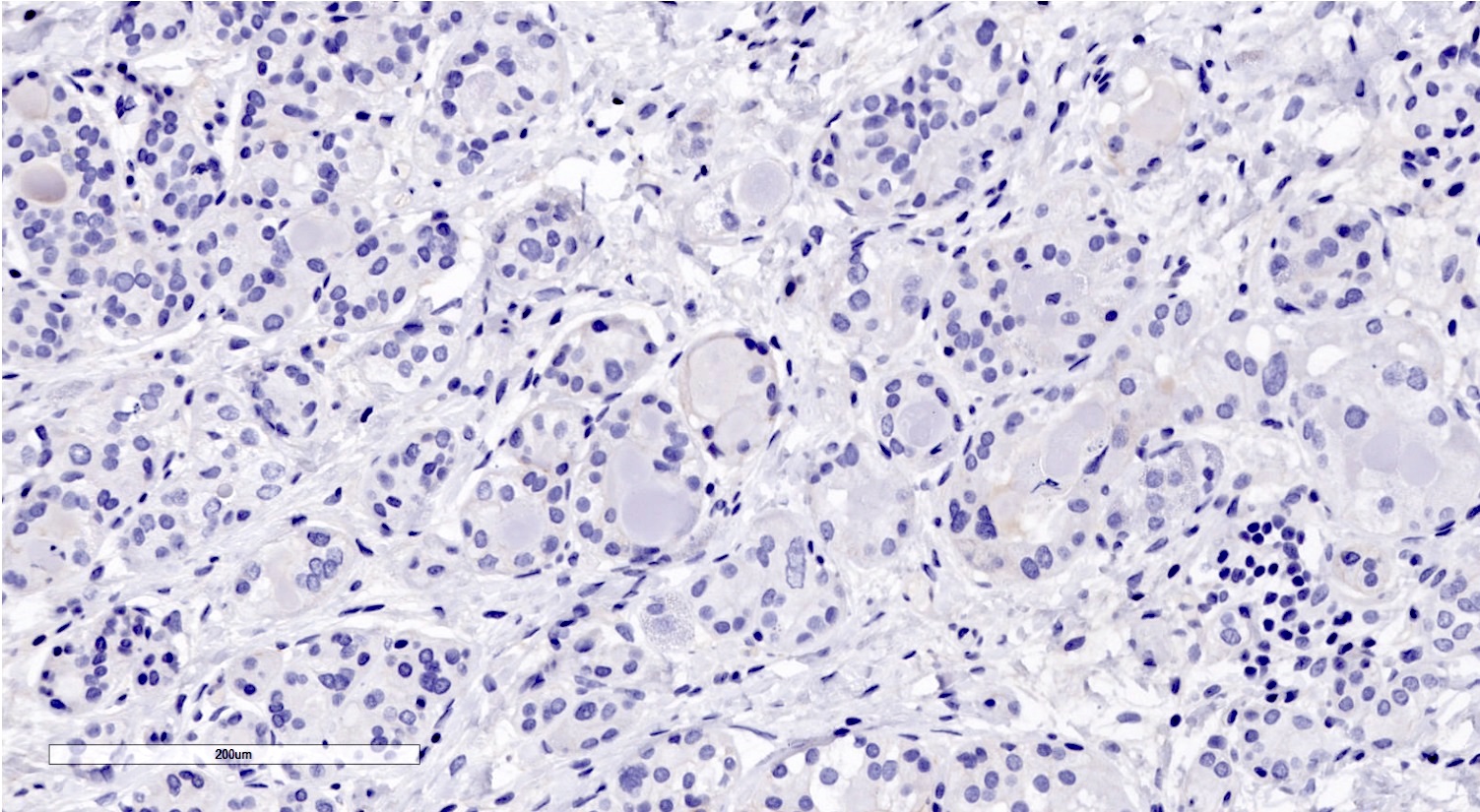
- Cells with serous differentiation containing zymogen granules in the cytoplasm that stain with PASD
- Predominantly solid or microglandular growth but may be cystic, trabecular or show other growth patterns (Breast 2022;66:208)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Miralem Mrkonjic, M.D., Ph.D.
Cytology description
- Fine needle aspiration: hypercellular, atypical cells in sheets, round to oval nuclei, single nucleoli, mild pleomorphism in size, moderately increased N:C ratio, intercellular cystic spaces, acinic pattern, cytoplasmic vacuoles and granules visible on Papanicolaou and Giemsa stains (Cytopathology 2013;24:403)
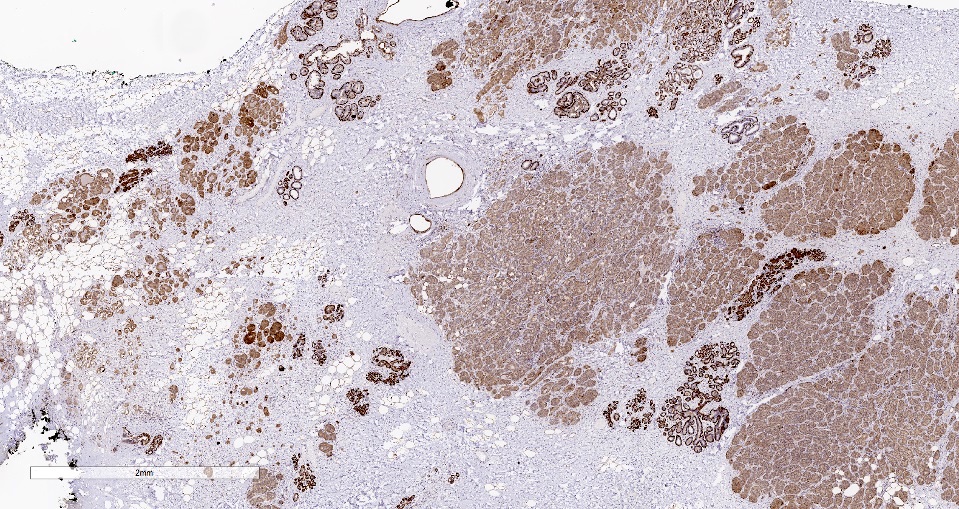
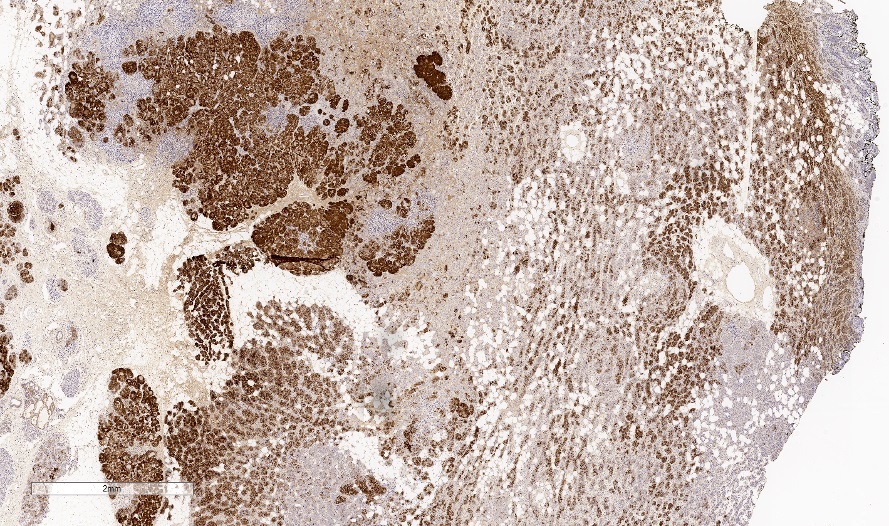
Positive stains
- PASD
- EMA (100% positive, 29/29 cases)
- S100 (93% positive, 50/54 cases)
- Lysozyme (95% positive, 39/41 cases)
- Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin / trypsin (96% positive, 25/26 cases)
- Amylase (94% positive, 17/18 cases)
- E-cadherin (100% positive, 7/7 cases)
- CK7 (100% positive, 9/9 cases)
- Ki67 (range 5 - 30% most commonly reported)
- GCDFP-15 (56% positive, 14/25 cases)
- Reference: Breast 2022;66:208
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cells with vacuolated cytoplasm containing many electron dense granules of varying size and a prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) (J Breast Cancer 2011;14:160)
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No pathognomonic genomic alterations have been described
- Has a similar molecular profile to triple negative breast carcinoma and does not share the genomic rearrangement seen in salivary gland acinic cell carcinoma (Histopathology 2019;75:931)
- TP53 mutations are the most consistent molecular event (Breast 2022;66:208)
- PIK3CA and other mutations have been described in a subset of cases (Mod Pathol 2017;30:69)
- BRCA1 gene alterations have also been described (BMC Cancer 2013;13:46, Histol Histopathol 2023;38:91)
Sample pathology report
- Breast (right), lumpectomy:
- Acinic cell carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: Sections show breast tissue involved by acinic cell carcinoma in solid nests and acini of polygonal cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm. These tumor cells display round, uniform nuclei with prominent nucleoli. Periodic acid-Schiff with diastase (PASD) staining demonstrates the presence of zymogen-like granules in the cytoplasm, confirming the acinar differentiation characteristic of this tumor.
Differential diagnosis
- Lactational changes:
- Cytoplasmic vacuolization and secretory material
- Microglandular adenosis:
- Intact basal lamina
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Dual cell population showing positivity for myoepithelial markers like SMA
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma:
- Presence of intracellular and extracellular mucin
- Mucicarmine positive
Board review style question #1
A premenopausal woman presents with a painless, palpable, slow growing mass in her left breast. Histological examination reveals cells with abundant eosinophilic and basophilic cytoplasm with large coarse PASD+ intracytoplasmic granules and centrally located nuclei with prominent nucleoli, showing an infiltrative microglandular growth pattern. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Acinic cell carcinoma
- Angiolipoma
- Burkitt lymphoma
- Fibroadenoma
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
A. Acinic cell carcinoma. These are the features of acinic cell carcinoma (see microscopic image).
Answer D is incorrect because fibroadenoma is a fibroepithelial lesion, which is not infiltrative and the epithelial component does not have diffuse acinar morphology.
Answer B is incorrect because angiolipoma is a mesenchymal neoplasm comprised of mature adipocytes and blood vessels.
Answer E is incorrect because invasive lobular carcinoma lacks cytoplasmic granules and microglandular growth pattern.
Answer C is incorrect because Burkitt lymphoma is a non-Hodgkin lymphoma growing in solid sheets with starry sky appearance.
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. Lysozyme+. Acinic cell carcinoma is positive for EMA and lysozyme.
Answer E is incorrect because S100 is positive in acinic cell carcinoma and angiolipoma, so it would not help in differentiating between these entities.
Answer D is incorrect because Burkitt lymphomas and not acinic cell carcinomas have a Ki67 index close to 100%.
Answer A is incorrect because E-cadherin positivity is not specific to acinic cell carcinoma.
Answer B is incorrect because acinic cell carcinomas are not HER2 amplified.
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma
Board review style question #3
Which biomarker profile is typical of acinic cell carcinoma?
- ER+, PR+, HER2+
- ER+, PR+, HER2-
- ER+, PR-, HER2-
- ER-, PR-, HER2+
- ER-, PR-, HER2-
Board review style answer #3
E. ER-, PR-, HER2-. Acinic cell carcinomas are predominantly triple negative with rare cases showing weak ER positivity.
Answer C is incorrect because only rare cases of acinic cell carcinoma have been reported to have weak ER positivity. Answers A, B and D are incorrect because acinic cell carcinoma does not share luminal, HER2 amplified or triple positive biomarker profile.
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Acinic cell carcinoma