Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology imagesCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Juvenile papillomatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastjuvenilepapillomatosis.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
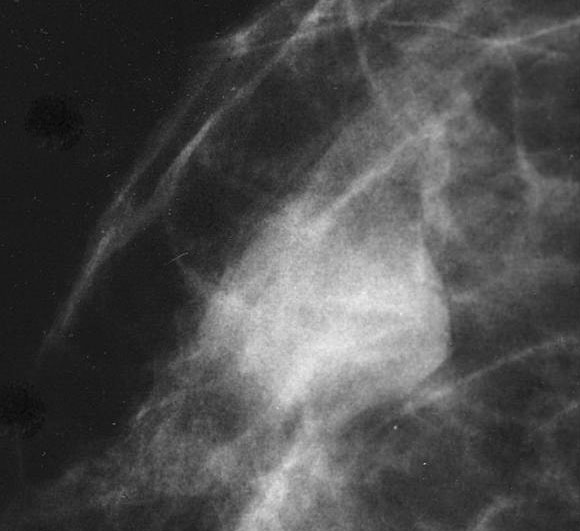
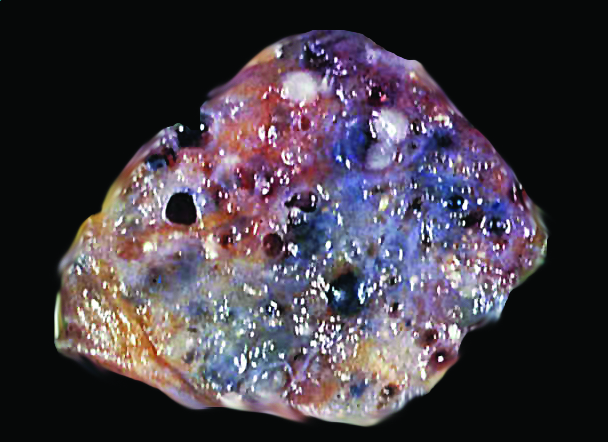
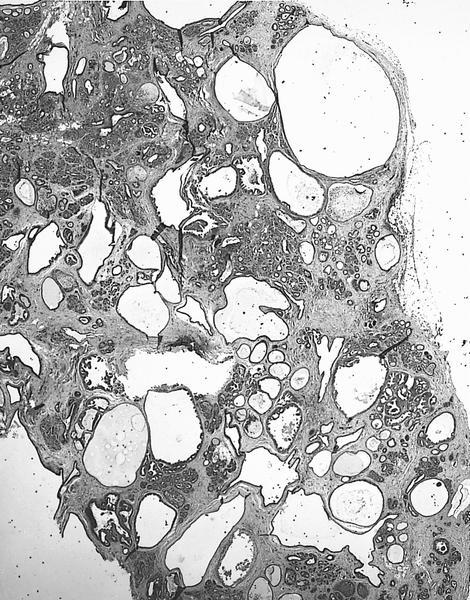
- Grossly distinct multinodular mass with clustering of cystic formations resembling swiss cheese, composed of epithelial proliferation and clustered cysts
- First described by Rosen in 1980 (Am J Surg Pathol 1980;4:3)
Terminology
- Not part of WHO breast classification
Epidemiology
- Mean age 19 years
- 2 / 3 are less than age 20 years
Clinical features
- Resembles fibroadenoma clinically
- 10% develop breast carcinoma, higher risk if recurrent, bilateral disease and family history of breast cancer (Am J Clin Pathol 1990;93:599)
- 26 - 58% have positive family history of breast cancer (Cancer 1982;49:2591, Am J Clin Pathol 1986;86:745), 15% have bilateral disease
- May be associated with secretory carcinoma (Jpn J Clin Oncol 1985;15:457)
Case reports
- Juvenile papillomatosis of the breast in a male infant with Noonan syndrome (Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005;45:991)
- 6 year old girl with juvenile secretory carcinoma and juvenile papillomatosis (J Pediatr Surg 1987;22:637)
- 16 year old girl with multiple juvenile papillomatosis of the breast (Breast Cancer 1998;5:187)
- 17 year old boy with juvenile papillomatosis of the breast (G Chir 2011;32:374)
Gross description
- Localized multinodular mass with clustering of cystic formations resembling swiss cheese
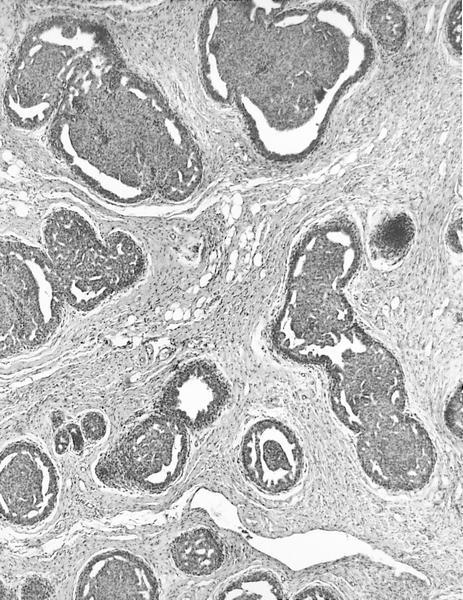
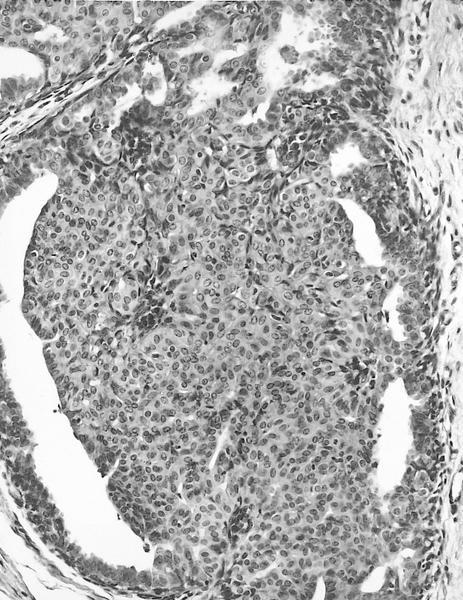
Microscopic (histologic) description
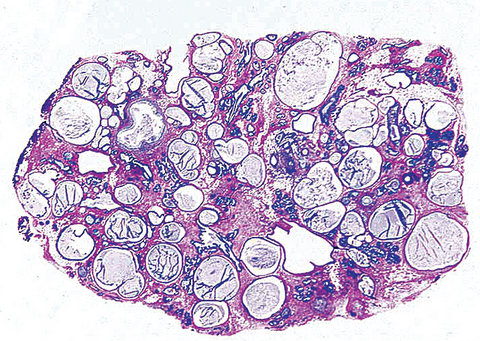
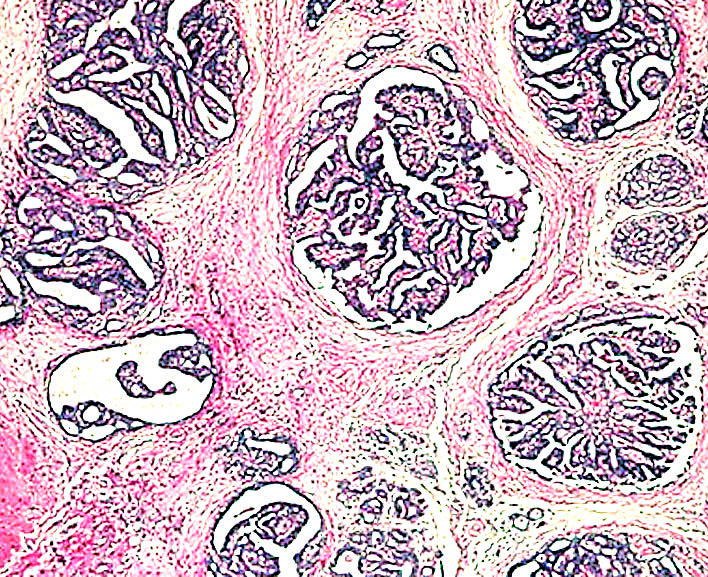
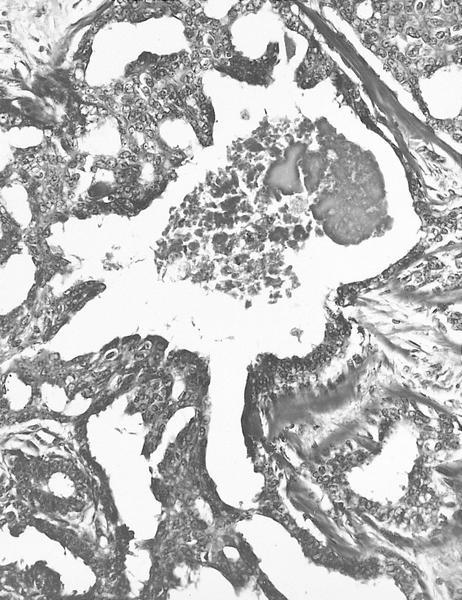
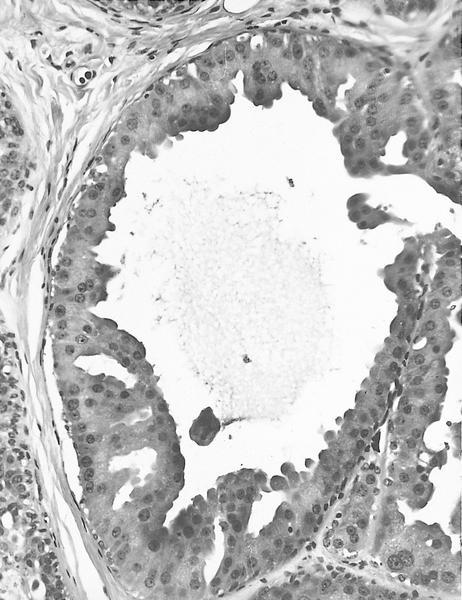
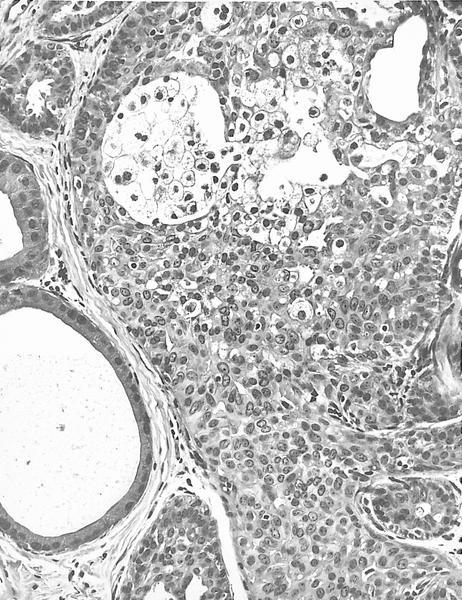
- Florid epithelial hyperplasia and papillomatosis, cysts with foamy histiocytes and sclerosing adenosis
- Variable apocrine metaplasia, atypia and necrosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Mark R. Wick, M.D.
AFIP images
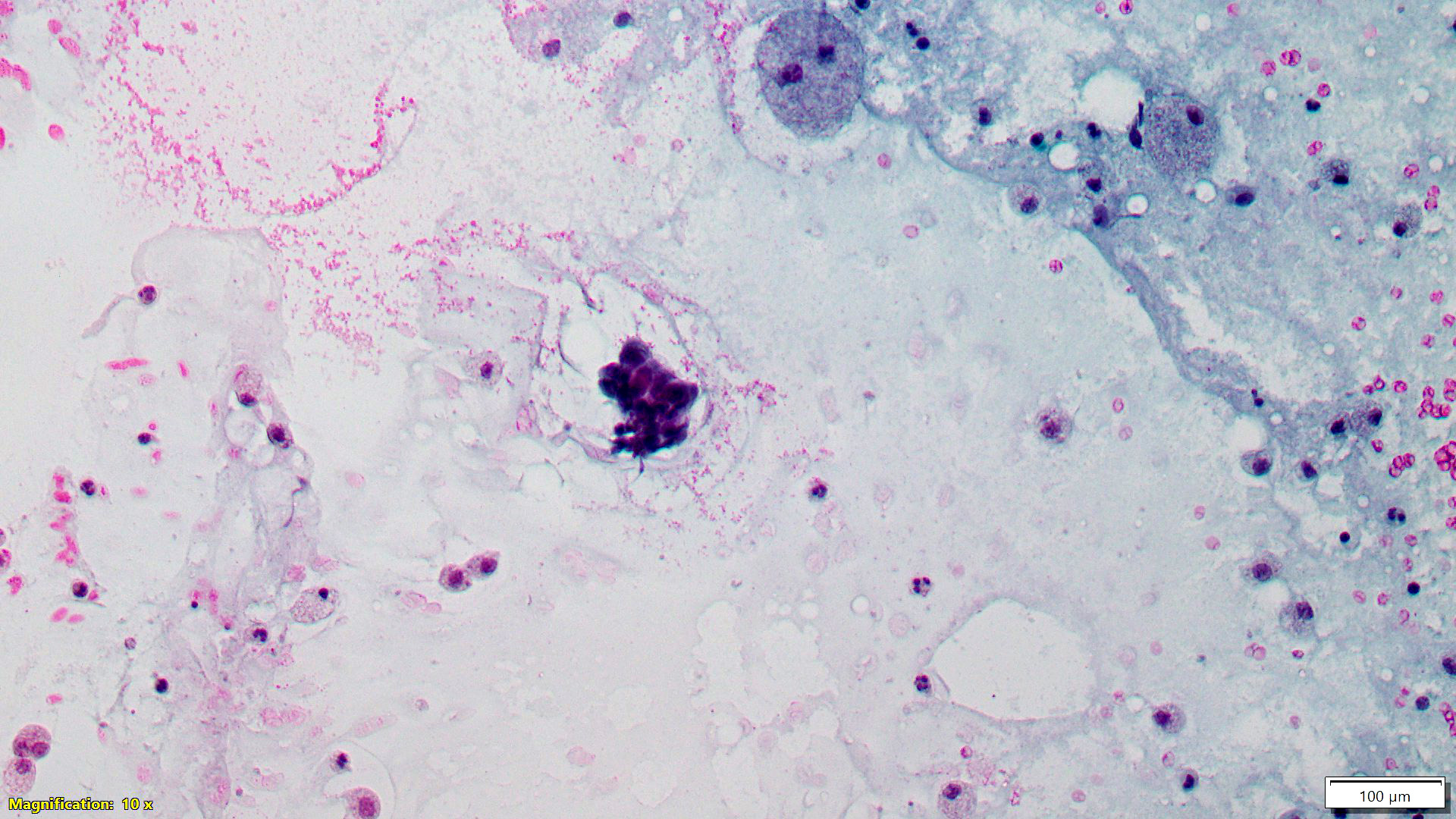
Cytology description
- Difficult to diagnose
- Cystic fluid, but mass persists after aspiration
- Sheets of hyperplastic breast epithelium with areas resembling fibroadenoma, macrophages and apocrine cells (Diagn Cytopathol 1993;9:457)