Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Agarwal I, Blanco L. Hamartoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breasthamartoma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Well circumscribed, often encapsulated mass composed of normal but disorganized components of breast tissue
Essential features
- Uncommon breast mass lesion that contains normal breast elements in varying proportions
- Clinically presents as painless lump or detected via breast imaging
- Microscopy shows well circumscribed mass with normal breast components (e.g., mammary glands, adipose tissue and fibrous stroma)
- Definitive diagnosis on core needle biopsy requires correlation with imaging
Terminology
- First described by Hogeman and Ostberg in 1968; term first used by Arrigoni in 1971 (Sem Hop 1976;52:1405)
- Acceptable by WHO: adenolipoma, chondrolipoma, myoid hamartoma
- Not recommended by WHO: fibroadenolipoma, adenolipofibroma
Epidemiology
- Uncommon; < 5% of all benign breast masses (Histopathology 2022;80:304)
- Predominantly women in fifth decade but can be seen at any age
Sites
- No specific location in the breast
Etiology
- Largely unknown; unclear whether a malformation or neoplasm
- Mostly sporadic; rarely associated with Cowden syndrome (multiple hamartomas)
Clinical features
- Presents as painless breast mass or detected by screening mammography or other breast imaging modalities
Diagnosis
- Mammographic or sonographic abnormality
- Often cannot be definitively diagnosed on core needle biopsy; excisional biopsy is more definitive
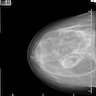
Radiology description
- Mammography: well circumscribed mass, described as "breast within breast" (Eur J Breast Health 2021;17:328, Med J Armed Forces India 2015;71:377)
- Ultrasound: mass with heterogeneous internal echogenicity
Prognostic factors
- Rarely recurs; reported recurrences represent incomplete excisions (Aust J Gen Pract 2019;48:275)
- No increase in malignancy (same malignant potential as normal breast tissue)
Case reports
- 30 year old man with a 1 month history of a painless mass in his right breast (Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e18372)
- 40 year old woman with huge myoid hamartoma of the breast treated with reduction mammaplasty (Surg Today 2014;44:2369)
- 41 year old woman with giant breast hamartoma (Oncol Lett 2015;10:3719)
Treatment
- Surgical excision is curative but not necessary
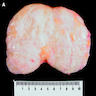
Gross description
- Well circumscribed, round to oval, range 1 - 14 cm; may resemble normal breast tissue, lipoma or fibroadenoma
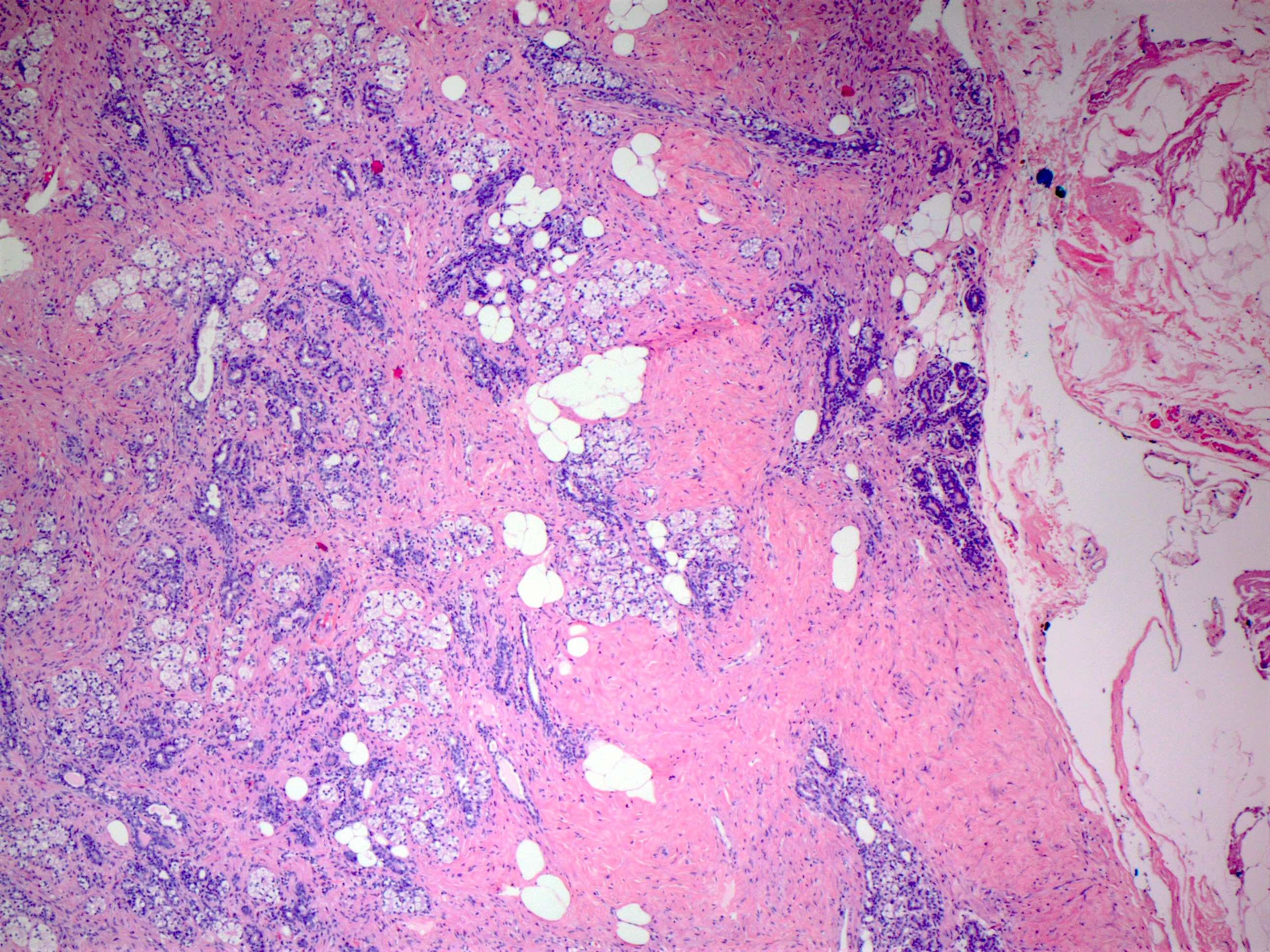
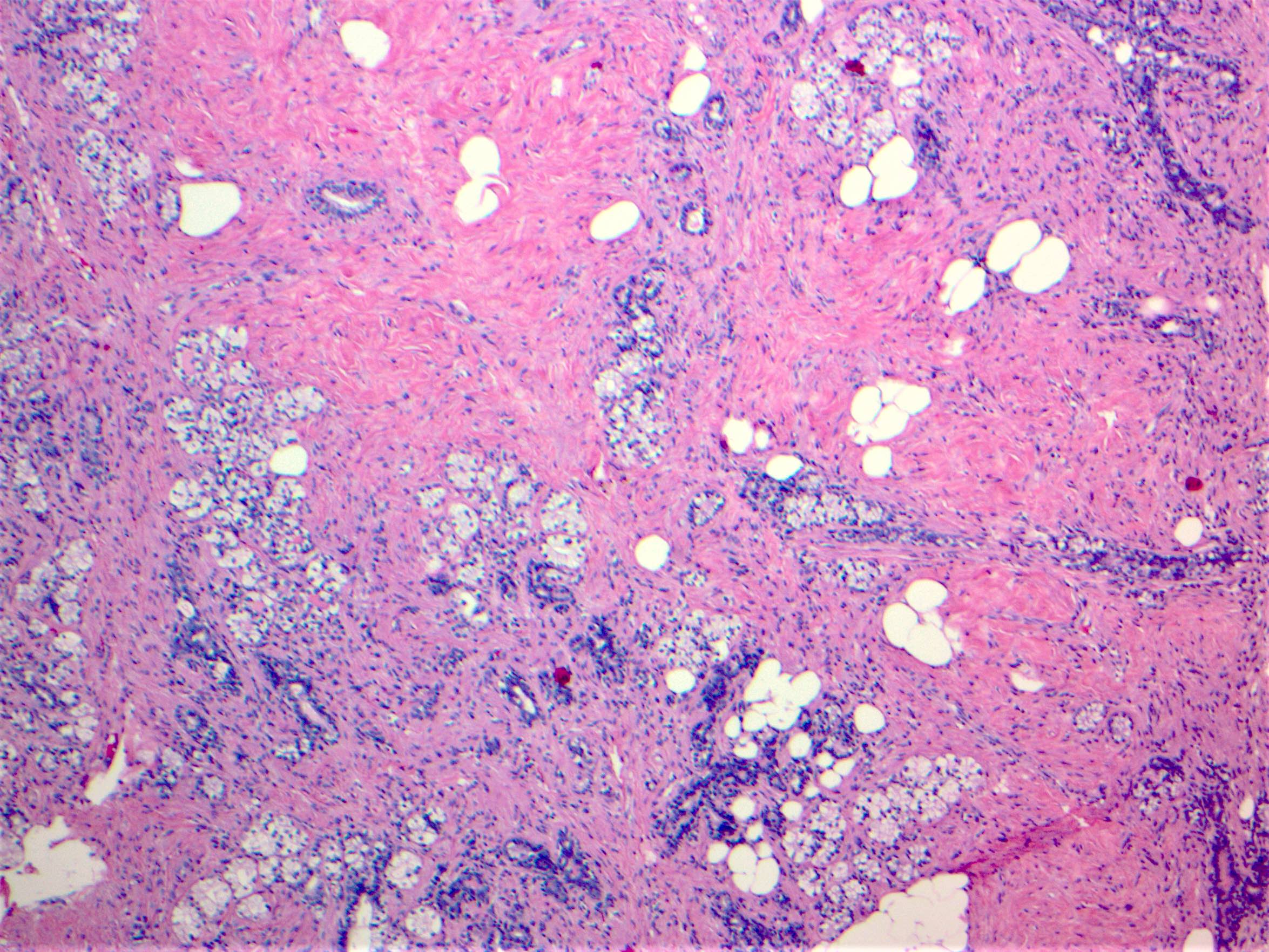
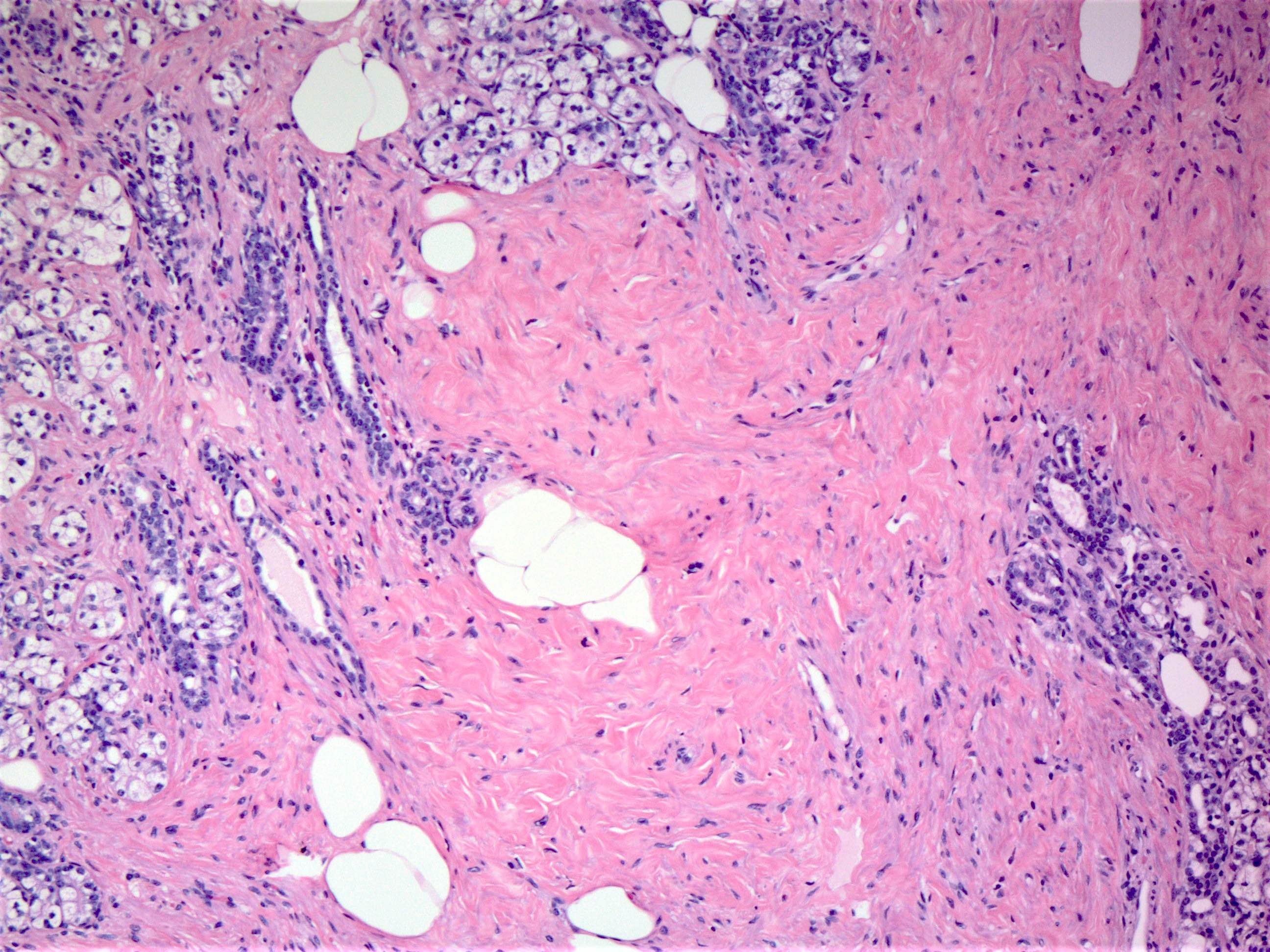
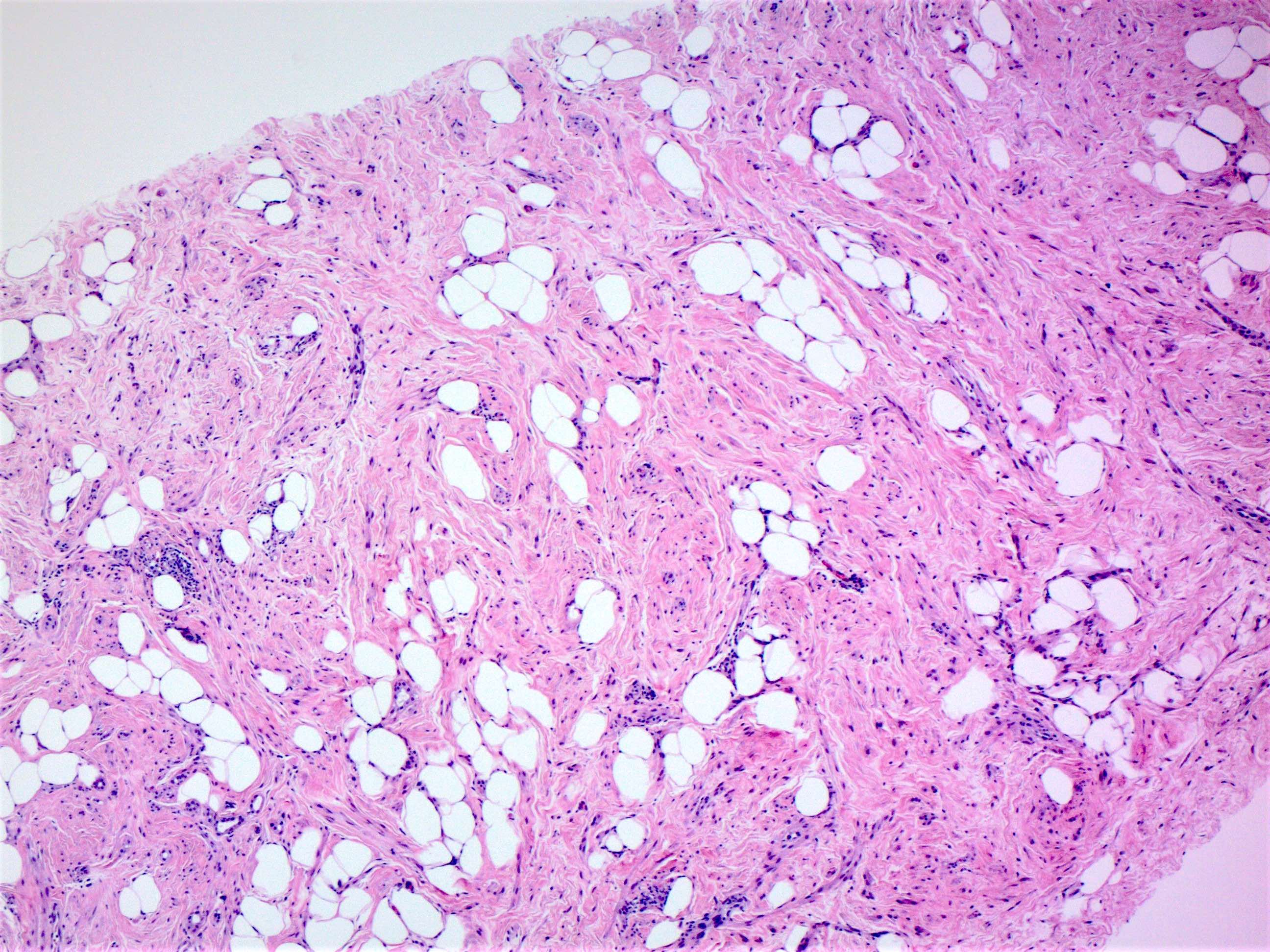
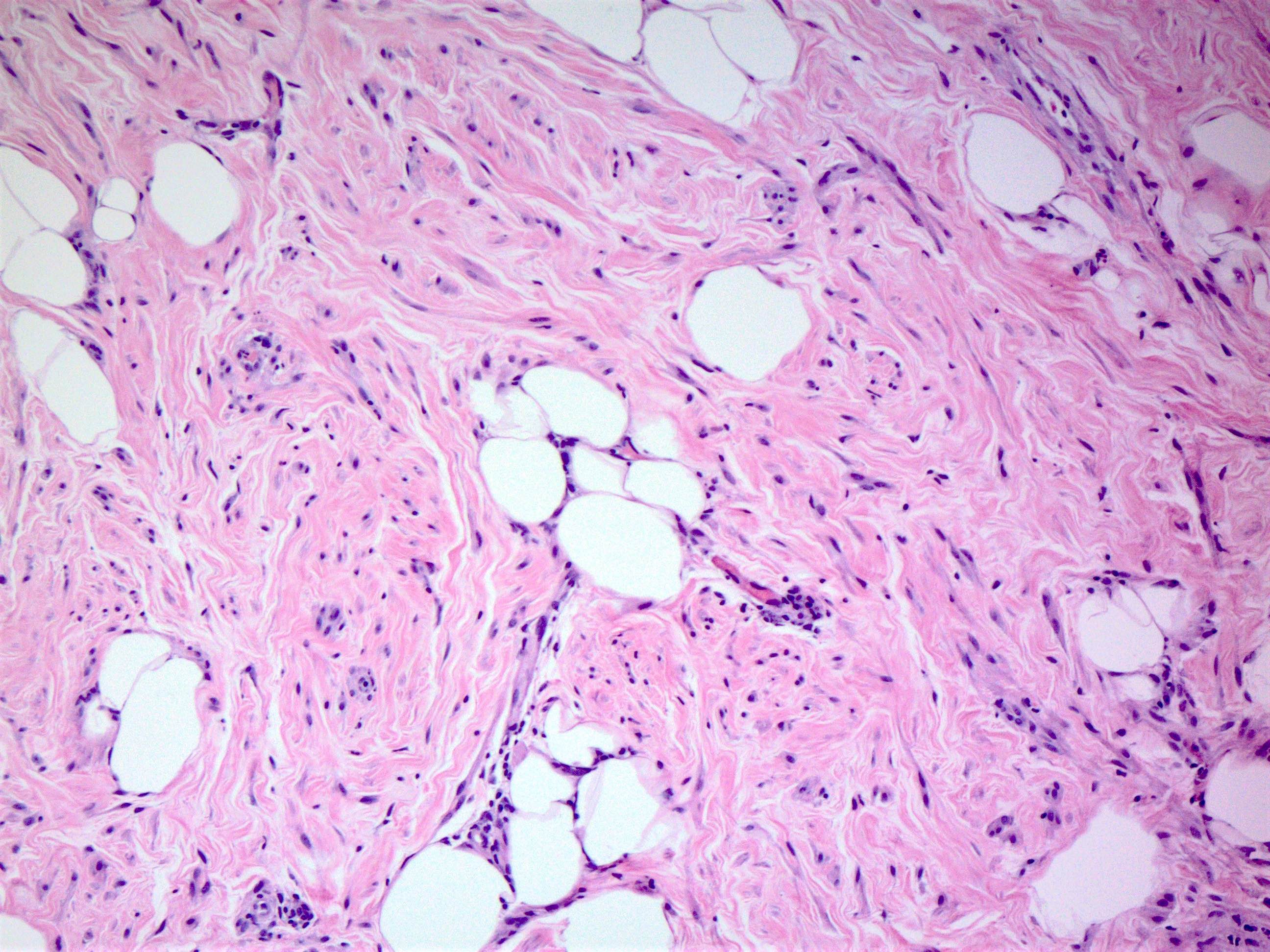
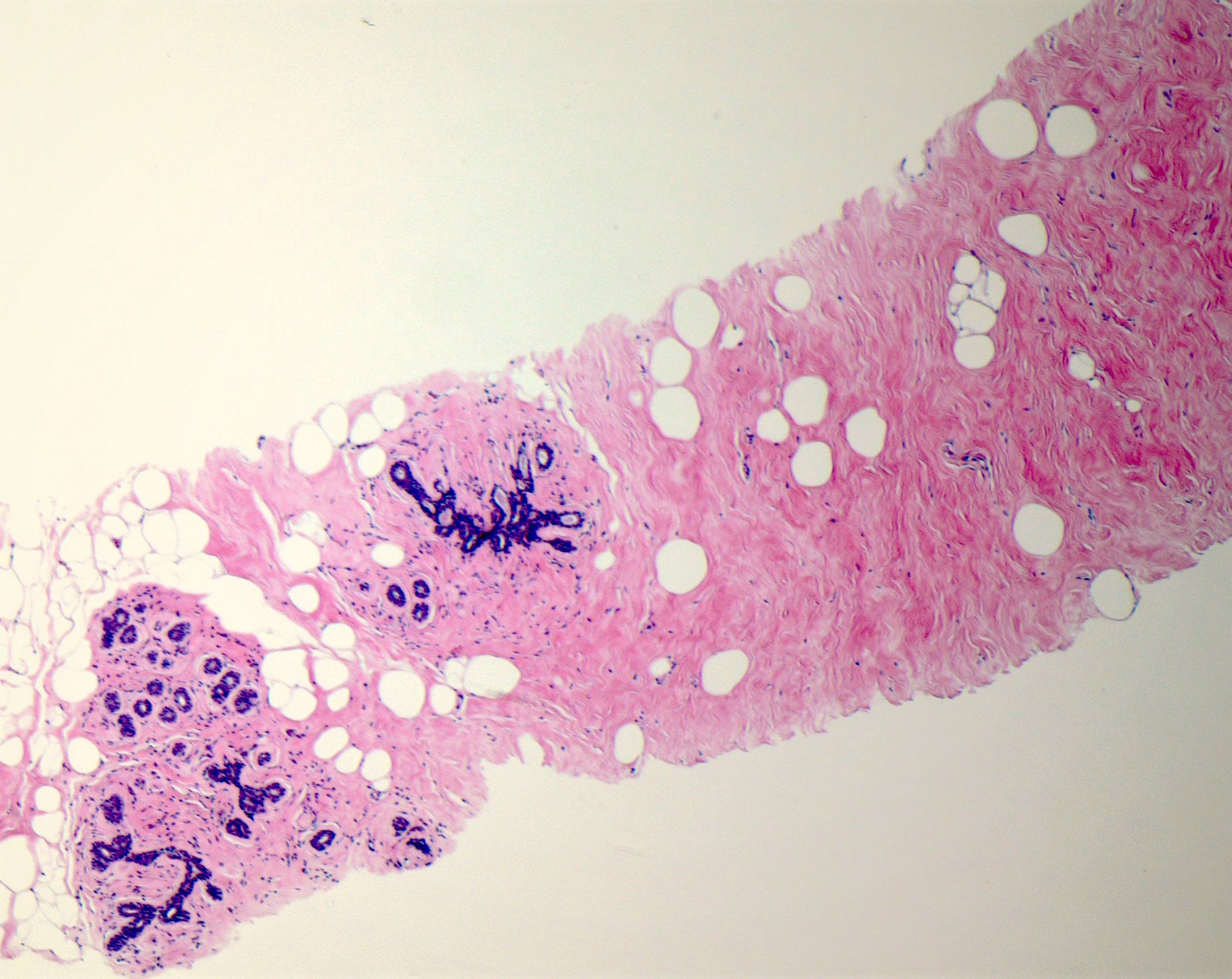
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Circumscribed mass comprised of ducts, lobules, fibrous stroma, adipose tissue in varying proportions with disorganized architecture
- May have smooth muscle, cartilage or pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH) (Histopathology 2022;80:304)
- Lesions with prominent myoid changes called myoid hamartomas (Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2012;72:412)
- 2 variants:
- Adenolipoma: mature fat and mammary parenchyma in varying proportions, glands appear structurally normal with little proliferation
- Chondrolipoma: contains hyaline cartilage / cartilaginous metaplasia and fat, glandular elements are often scanty (Virchows Arch 2017;471:531)
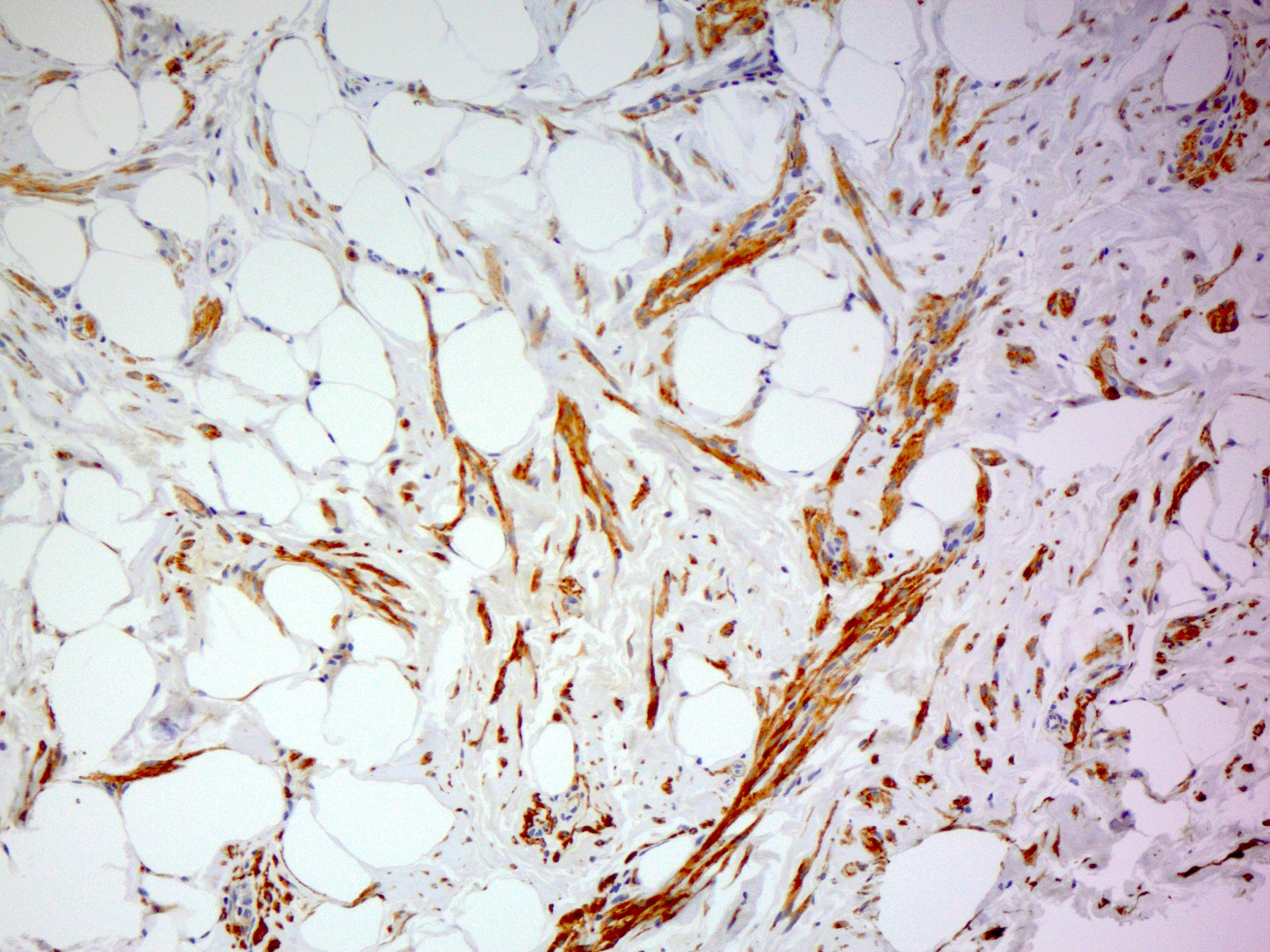
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Moderately cellular, bland epithelial and stromal components
- Diagnosis limited as findings are not specific (J Clin Pathol 2002;55:951)
Positive stains
- ER and PR expression similar to normal breast epithelium
- ER, PR and HMGA expression in stromal cells (Histopathology 2022;80:304)
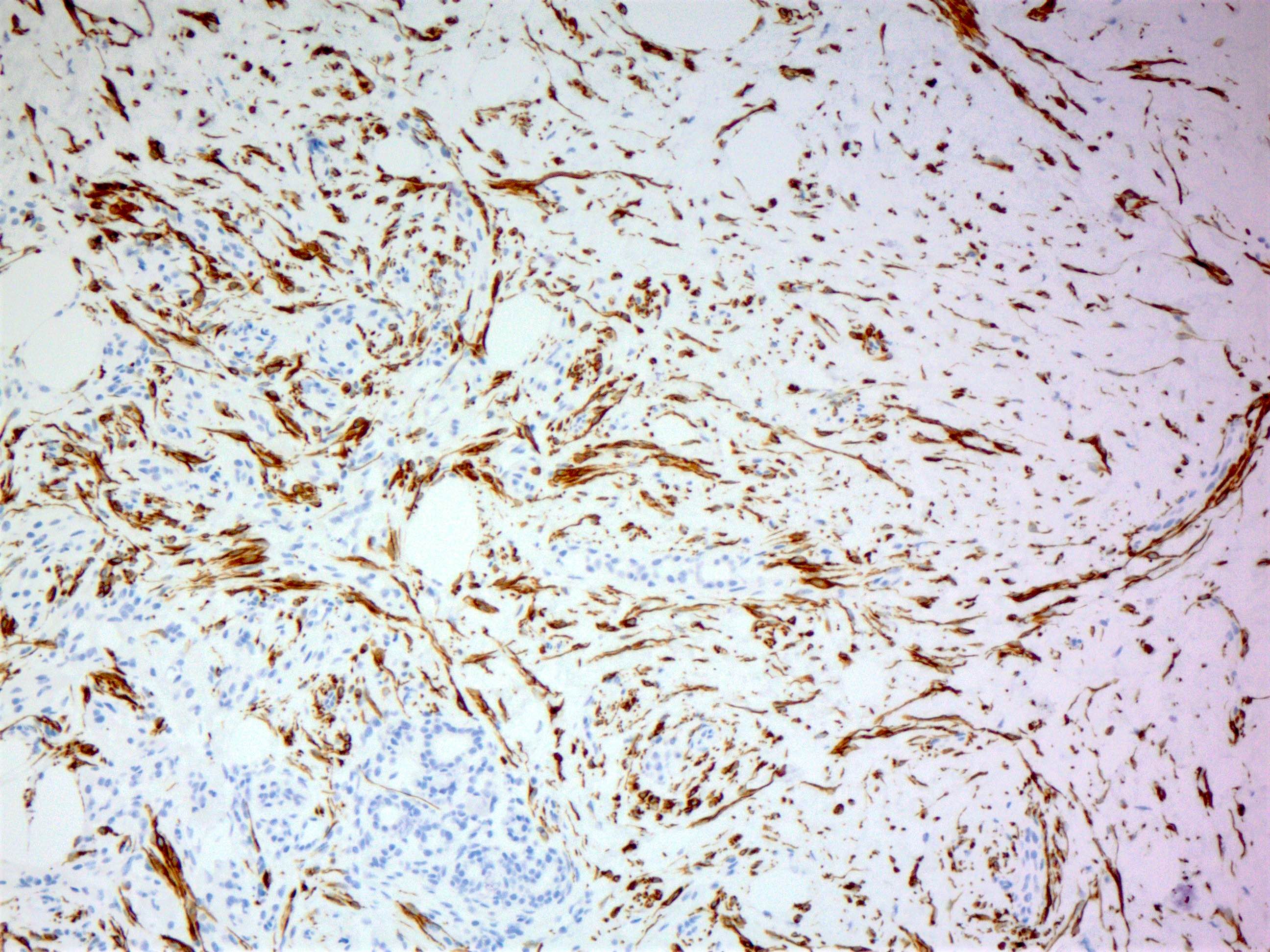
- CD34 in intralobular, perilobular and interlobular distribution (Histopathology 2022;80:304)
- p63, CK5/6, calponin, smooth muscle myosin positive in myoepithelial cells
- Smooth muscle actin, desmin positive if smooth muscle elements present (Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2014;69:515)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Translocation in HMGA2 and germline mutations in tumor suppressor gene PTEN have been described (Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2019;16:563)
- Data is limited
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, mass at 11 o'clock, ultrasound guided core needle biopsy:
- Consistent with mammary hamartoma (see comment)
- Comment: A well circumscribed lesion is seen comprised of benign breast elements arranged in a disorganized manner. In light of the known breast mass seen on imaging, findings are consistent with a mammary hamartoma.
Differential diagnosis
- Fibroadenomas:
- In fibroadenoma, the epithelial elements often show more proliferative changes (e.g., usual type ductal hyperplasia, apocrine metaplasia)
- Fibroadenomas only rarely include adipose tissue
- Phyllodes tumor:
- Hypercellular stromal component, stromal atypia, frond formation, may show infiltrative borders
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 45 year old woman presents for screening mammogram and a multilobulated 1.5 cm mass is detected. Ultrasound confirms the findings and a guided core needle biopsy is performed, which shows normal breast ducts, lobules, fibrous stroma and adipose tissue. The radiologist confirms that the lesion was biopsied. What is the most likely possibility?
- Angiolipoma
- Breast hamartoma
- Myofibroblastoma
- Radiologist missed the lesion
Board review style answer #1
B. Breast hamartoma. The mass lesion by imaging and the histologic finding of normal breast components with somewhat disorganized architecture support this diagnosis. Also, since the radiologist was confident that the lesion was biopsied, the possibility that the lesion was missed is excluded.
Comment here
Reference: Hamartoma
Comment here
Reference: Hamartoma